36 the diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for two countries
19 The diagram shows production possibility curves for two countries, X and Y. O good A good B country Y country X What can be deduced from the diagram? A Both countries can benefit by specialisation. B Country X has a higher opportunity cost than Y in producing good B. C Country Y has a comparative advantage in both goods. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for the production of peaches and apples in Fruitland. The production possibilities curve illustrates which of the following relationships? A) The production of peaches decreases as apple production decreases.
on the basis of the diagram above showing an economy's production possibilities curve for two goods, which of the following statements must be true? 1. the opportunity cost of moving from point p to point r is 10 units of y 2. the opportunity cost of moving from point r to point p is 8 units of x

The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for two countries
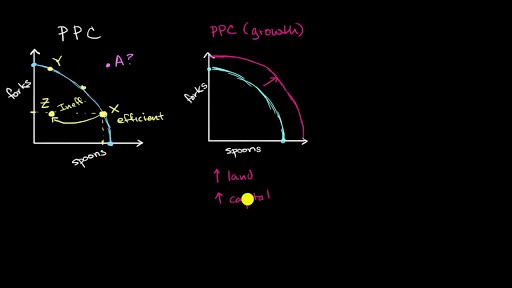
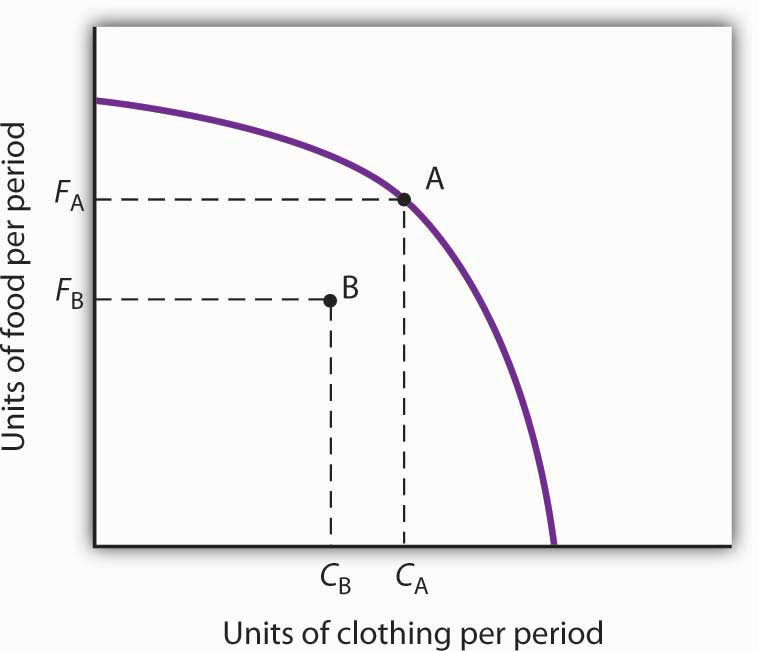
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for Country Y. Which of the following statements is true? A If Country Y is producing at point C, it is using all its resources efficiently. B The opportunity cost of producing more machines is constant. the production possibilities frontier shows the maximum amount of ... is 5 cakes of soap. As you can see, the production possibility curve is a straight line, so opportunity cost is constant and independent ... C-D in the diagram above.The PPF is thus concave whe viewed from below. A en n . linear. PPF will exhibit . In this video, Sal explains how the production possibilities curve model can be used to illustrate changes in a country's actual and potential level of output. Concepts covered include efficiency, inefficiency, economic growth and contraction, and recession. When an economy is in a recession, it is operating inside the PPC. When it is at full employment, it operates on the PPC.
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for two countries. 20 The diagram shows the production possibility curves for two countries, X and Y. A decrease in productivity moves country X's production possibility curve from X 1 to X 2. 40 30 0 50 90 120 manufactured goods raw materials X 2 Y X 1 Which statement is correct? A After the change X would export raw materials and import manufactured goods. 19 The diagram shows production possibility curves for two countries, X and Y. O good L good M country Y country X What can be deduced from the diagram? A Both countries can benefit from specialisation. B Country X has a higher opportunity cost than Y in producing good M. C Country Y has a comparative advantage in both goods. 16. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries, Country X and Country Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of resources in production. If the two countries engage in trade, both would be better off under which of the following conditions? 1. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost of one bicycle in Artland and in Rayland
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for two countries A production possibilities frontier (PPF) is a diagram that illustrates the possible production points for an economy based on its resources and technology. Q. The diagram shows the production possibilities curve for Country Y. Which of the following statements is true? A point above the curve indicates the unattainable with the available resources. A point below the curve means that the production is not utilising 100 percent of the business' resources. ... The production possibility curve also shows the choice of society between two different products. ... Production Possibilities Curve Diagram . Shape of PPC 2 9708/1/M/J/02 1 The diagram shows an economy's production possibility curve. What will cause a movement from point X on the production possibility curve to point Y within the curve? A an increase in unemployment B a fall in the size of the labour force C a reduction in the availability of land for industrial production D an improvement in technology in consumer good production
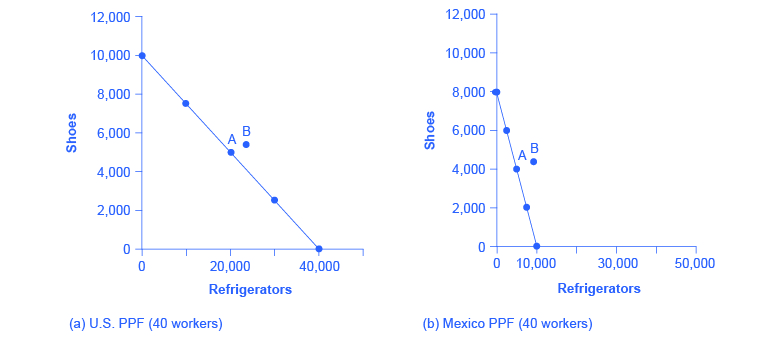
A production possibilities curve shows the combinations of two goods an economy is capable of producing. The downward slope of the production possibilities curve is an implication of scarcity. The bowed-out shape of the production possibilities curve results from allocating resources based on comparative advantage. The diagram below shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost of a bicycle in Artland. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries, Country X and Country Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of ... The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. a. Calculate the opportunity cost of a bicycle in Artland. b.
1. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost of a bicycle in Rayland.
possibility curve and then use the calculated opportunity cost to identify which ... that Rayland has a comparative advantage in the production of bicycles.6 pages
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost of a bicycle in Artland.
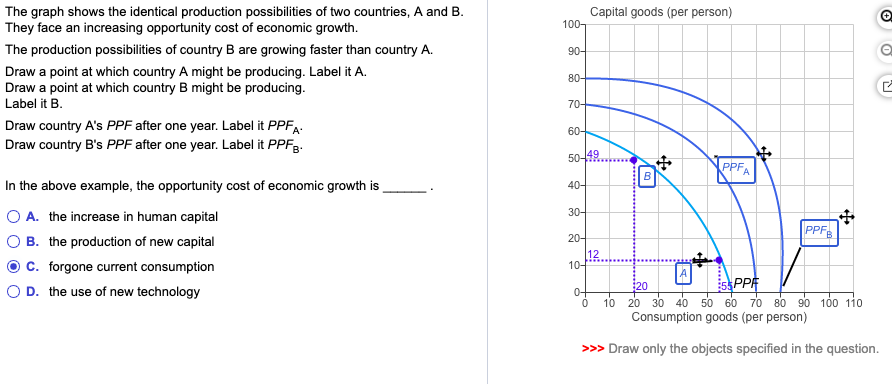
2. Assume that the country of Fischerland produces only consumer goods and capital goods. (a) The graph above shows the production possibilities curve for Fischerland. The production of which of the following exhibits increasing opportunity costs: consumer goods only, capital goods only, both ...
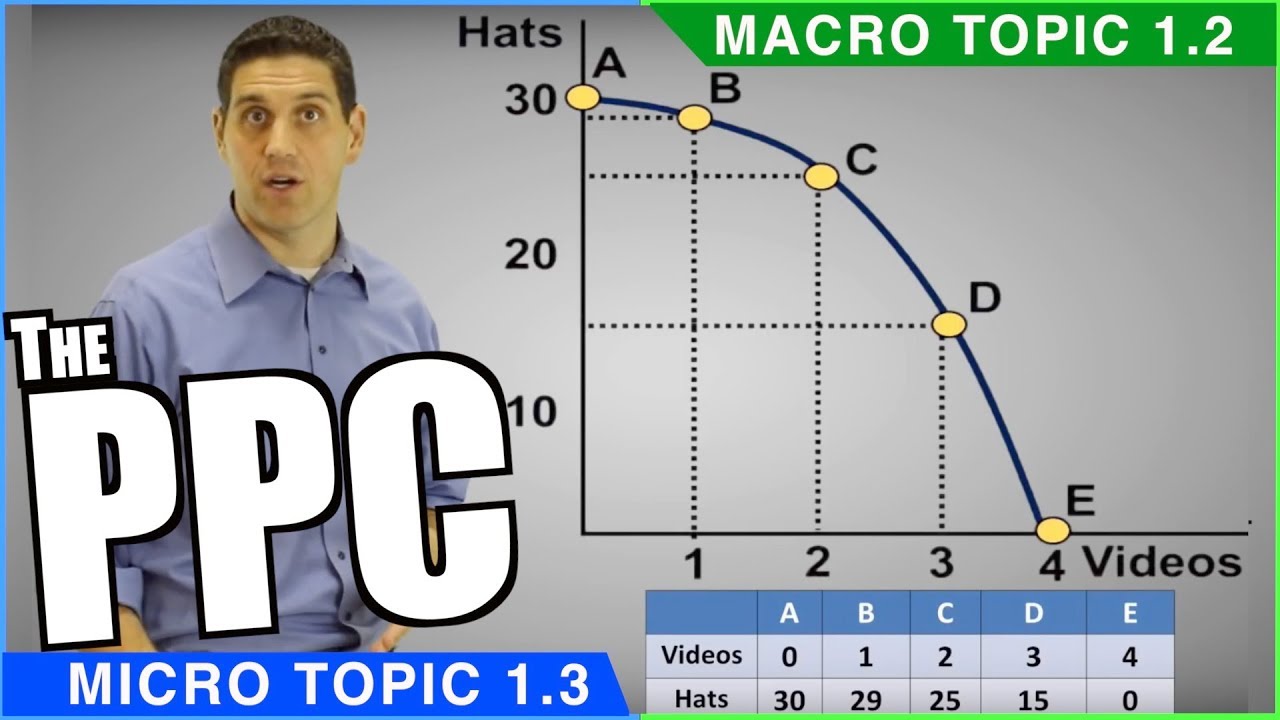
A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. 1 The diagram shows the production possibility curve for a country that produces just two goods: X, a consumer ...20 pages
Question 24 NUMBER OF HATS 1.200 Rayland 600 Artland 300 NUMBER OF BICYCLES The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats ...
3. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts Of resources, Artland can produce hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost af a bicycle in Artland.
The diagram shows the production possibilities curve, indifference curves and the pretrade equilibrium for Slobovia. Suppose that the world price of X in terms of Y is lower than the pre trade price in Slobovia. a) With trade, which product will Slobovia export? b) Indicate on the diagram below ...
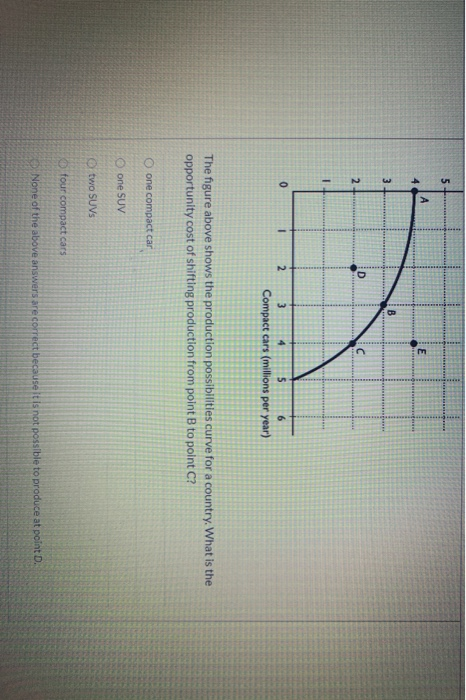
On the basis of the diagram above showing an economy's production possibilities curve for two goods, which of the following statements must be true. 1, 11, and 111. If the countries currently producing at point C, it can produce more capital goods by moving in the direction of. Point D.
Question 1 is based on the diagram below, which shows the production possibilities curve for an economy that produces only two goods: X and Y. 1. The opportunity cost of moving production from point R to point T is (A) one unit of Good Y (B) five units of Good Y (C) six units of Good Y (D) three units of Good X (E) seven units of Good X 2.
The following diagram shows the production possibilities curves for two countries, Country X and Country Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of resources in production. If the two countries engage in trade, both would be better off under which of the following conditions?
200 Rayland 600 Artland 300 NUMBER OF BICYCLES 2) The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost of a bicycle in Artland.
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries, Country X and Country Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of resources in production. If the two countries engage in trade, both would be better off under which of the following conditions?
An outward shift in the production possibilities curve of an economy can be caused by an increase in (A) unemployment (B) the labor force (C) inflation (D) output (E) demand 17 0 E FD UNITS OF GOOD X The graph above shows an economy's production possibilities frontier for the production of two goods, X and Y. Assume that the economy is
Solved Two Countries A And B Have Identical Production Possibilities The Graph Shows Capital Goods Per Person The Ppf Of These Economies 100 Course Hero
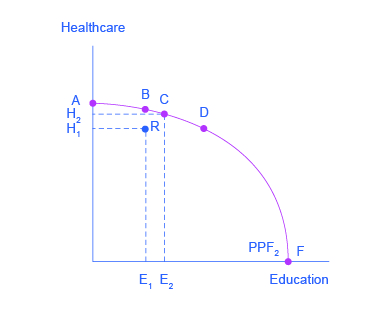
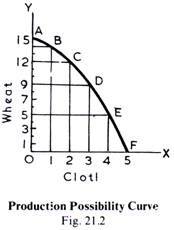
The following diagram (21.2) illustrates the production possibilities set out in the above table. In this diagram AF is the production possibility curve, also called or the production possibility frontier, which shows the various combinations of the two goods which the economy can produce with a given amount of resources.
3 The diagram shows the production possibility curve of an economy. O consumer goods capital goods ... 8 The diagram shows the demand curve for a product. price quantity D O ... 22 The table shows how much rice and wheat two countries, X and Y, can grow when each country ...
As nations specialize in production and trade in international markets, ... diagram above showing an economy's production possibilities curve for two goods, ...
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce ...4 pages
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts of resources, Artland can produce 600 hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 biCycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost of a bicycle in Artland.
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for an economy that produces only consumption and capital goods. All of the following statements about this economy are true EXCEPT: Point X represents the most efficient combination of the two goods that can be produced by this economy.
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries: Artland and Rayland. Using equal amounts Of resources, Artland can produce hats or 300 bicycles, whereas Rayland can produce 1,200 hats or 300 bicycles. (a) Calculate the opportunity cost af a bicycle in Artland.
Suppose two countries are each capable of individually producing two given ... The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for the production ...
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for the production of peaches and apples in Fruitland. Between points X and Y on the PPC, the opportunity cost of one unit of peaches is which of the following?
16. The diagram above shows the production possibilities curves for two countries, Country X and Country Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of resources in production. If the two countries engage in trade, both would be better off under which of the following conditions?
A production possibilities curve shows: A) that resources are unlimited. B) that people prefer one of the goods more than the other. C) the maximum amounts of two goods that can be produced assuming the full and efficient use of available resources. D) combinations of capital and labor necessary ...
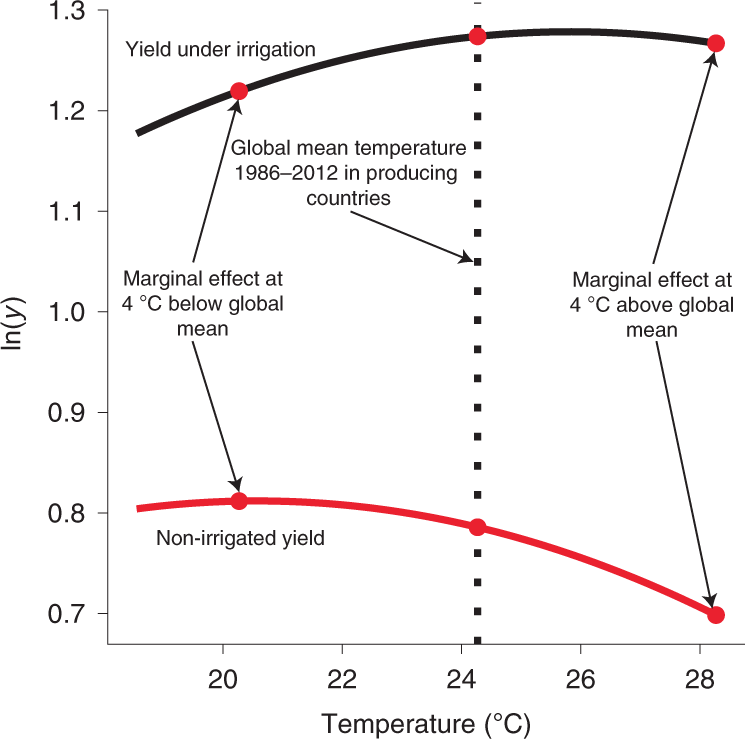
Impacts Of Rising Temperatures And Farm Management Practices On Global Yields Of 18 Crops Nature Food
20 The diagram shows the production possibility curves for two countries, X and Y. A decrease in productivity moves country X's production possibility curve from X 1 to X 2. 40 30 0 50 90 120 manufactured goods raw materials X 2 Y X 1 Which statement is correct? A After the change X would export raw materials and import manufactured goods.
On the basis of the diagram above showing an economy's production possibilities curve for two goods, which of the following statements must be true? I. The opportunity cost of moving from point P to point R is 10 units of Y II. The opportunity cost of moving from point R to point P is 8 units of X III. The opportunity cost of moving from point ...
In this video, Sal explains how the production possibilities curve model can be used to illustrate changes in a country's actual and potential level of output. Concepts covered include efficiency, inefficiency, economic growth and contraction, and recession. When an economy is in a recession, it is operating inside the PPC. When it is at full employment, it operates on the PPC.
the production possibilities frontier shows the maximum amount of ... is 5 cakes of soap. As you can see, the production possibility curve is a straight line, so opportunity cost is constant and independent ... C-D in the diagram above.The PPF is thus concave whe viewed from below. A en n . linear. PPF will exhibit .
The diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for Country Y. Which of the following statements is true? A If Country Y is producing at point C, it is using all its resources efficiently. B The opportunity cost of producing more machines is constant.



/production-possibilities-curve-definition-explanation-examples-4169680_FINAL-1312d1267f804e0db9f7d4bf70c8d839.png)
/dotdash_Final_Production_Possibility_Frontier_PPF_Apr_2020-01-b1778ce20e204b20bf6b9cf2a437c42e.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Production_Possibility_Frontier_PPF_Apr_2020-01-b1778ce20e204b20bf6b9cf2a437c42e.jpg)
/production-possibilities-curve-definition-explanation-examples-4169680_FINAL-1312d1267f804e0db9f7d4bf70c8d839.png)



0 Response to "36 the diagram above shows the production possibilities curve for two countries"
Post a Comment