36 diagram of the krebs cycle
1 answerKrebs cycle explains the aerobic phase of respiration. There are a series of cyclic reactions involved in converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and ... Krebs cycle Definition. The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the mitochondria resulting in oxidation of acetyl CoA to release carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms that later lead to the formation of water.
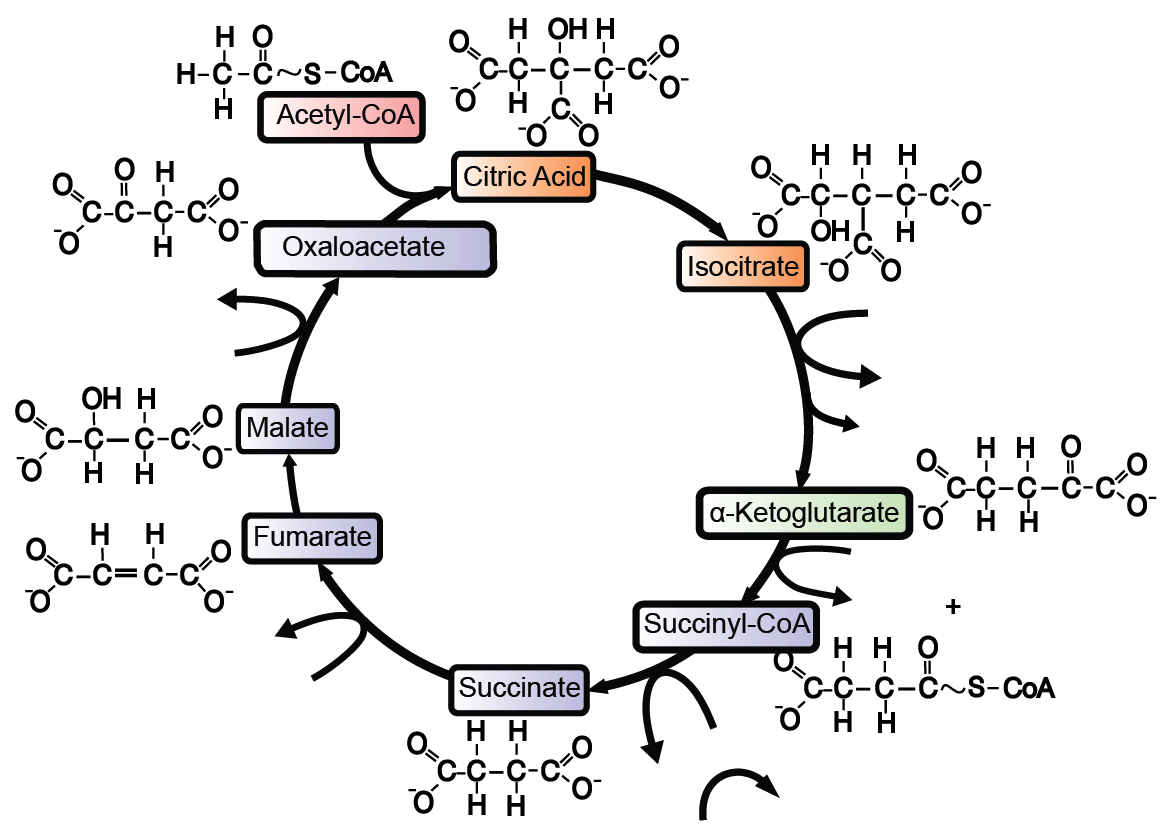
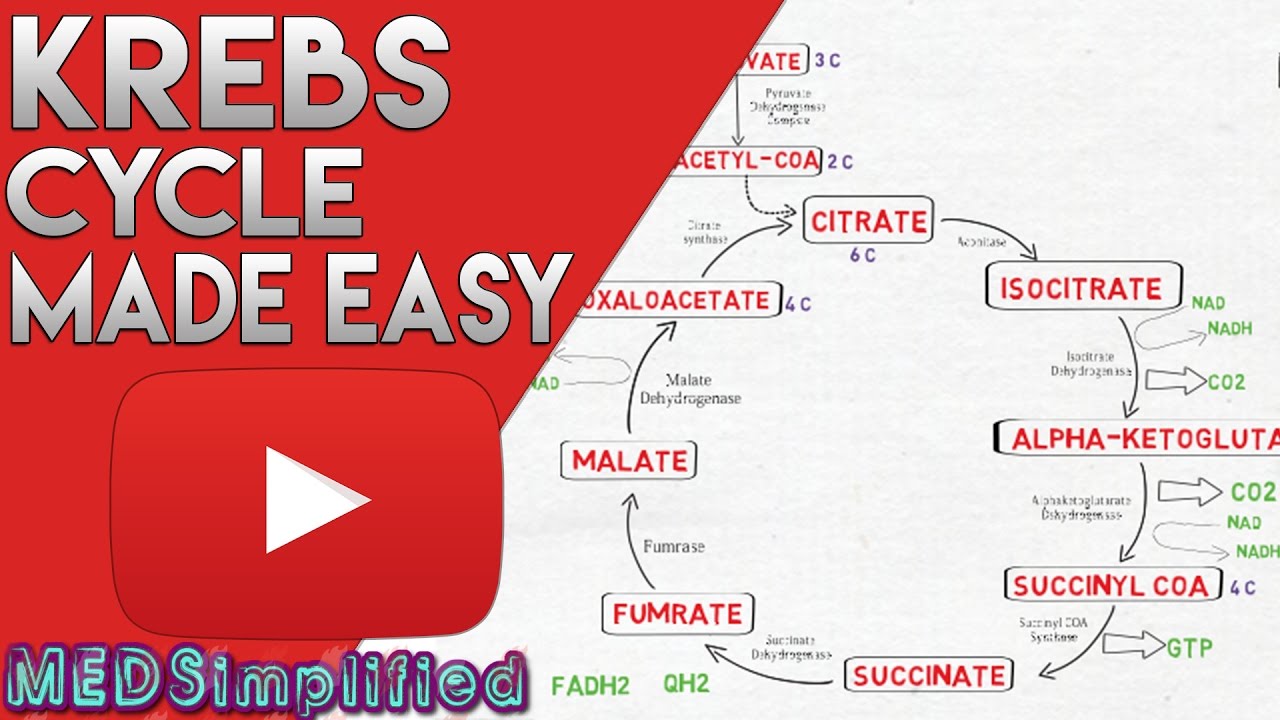
Krebs Cycle Steps. It is an eight-step process. Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic condition. Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalysed by citrate synthase.

Diagram of the krebs cycle
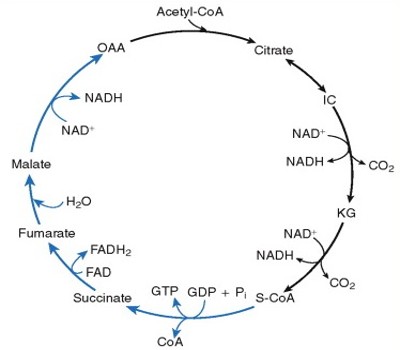
Krebs cycle steps · The TCA cycle begins with an enzymatic aldol addition reaction of acetyl CoA to oxaloacetate, forming citrate. · The citrate is isomerized by ... The TCA cycle or Krebs' cycle (after H. A. Krebs) is a cyclic sequence of reactions through which pyruvic acid produced in the EMP and EDP is oxidized. The cycle operates in aerobic organisms including animals, plants and microorganisms. The main function of the cycle is to generate energy by oxidation of acetic acid which is produced by ... The Krebs Cycle LSM 2.2-3 Krebs Cycle enters the cycle and then combines with to make the six-carbon compound . During the eight steps of the Krebs cycle, undergoes a number of reactions, releasing and in a number of steps. is eventually converted into so it can be used again during the Krebs cycle. Pyruvate Oxidation
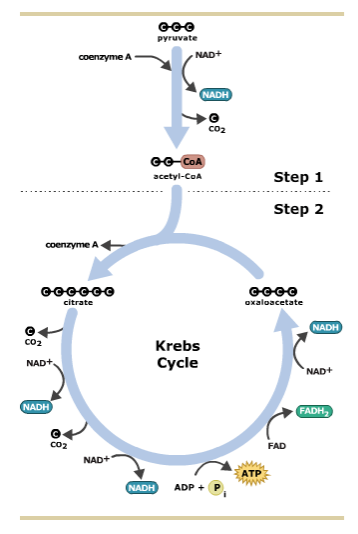
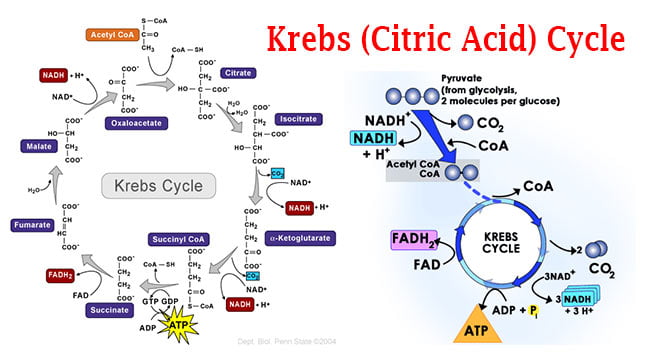
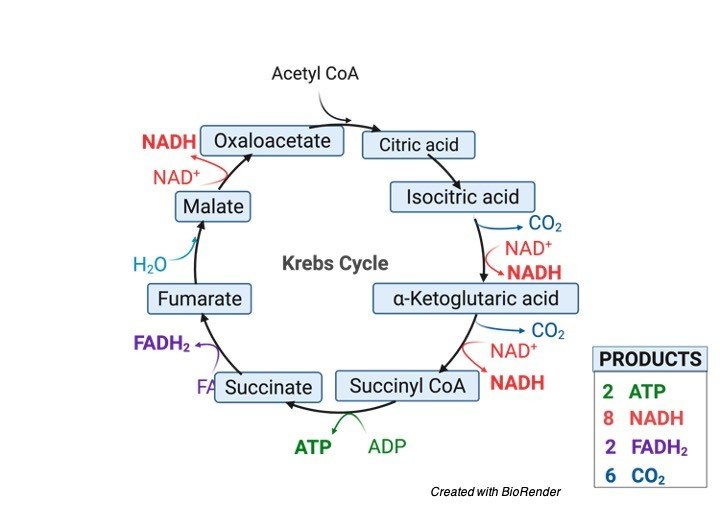
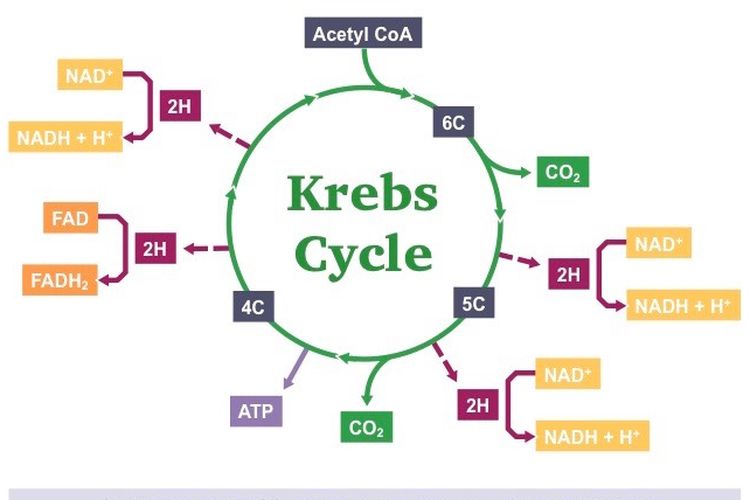
Diagram of the krebs cycle. The diagram below is a very simple outline of the Krebs Cycle showing the removal of CO2, and the making of 3. It is also known as TriCarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle. In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells, the citric. Krebs Cycle Definition. The Krebs Cycle, also called the citric acid cycle, is the second major step in oxidative phosphorylation.After glycolysis breaks glucose into smaller 3-carbon molecules, the Krebs cycle transfers the energy from these molecules to electron carriers, which will be used in the electron transport chain to produce ATP.. Krebs Cycle Overview Steps of the Krebs Cycle. The Krebs cycle itself actually begins when acetyl-CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule called OAA (oxaloacetate) (see Figure above).This produces citric acid, which has six carbonatoms.This is why the Krebs cycle is also called the citric acid cycle.. After citric acid forms, it goes through a series of reactions that release energy. The Krebs Cycle Class Date If oxygen is present, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis moves into the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle converts pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide. As carbon dioxide is formed, high energy electrons are accepted by NAD + and FAD. This results in the formation of NADH and FADH . NADH and FADH will be
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs or citric acid cycle, is the main source of energy for cells and an important part of aerobic respiration. The cycle harnesses the available chemical energy of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) into the reducing power of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). The Krebs cycle (named after Hans Krebs) is a part of cellular respiration. The diagram below shows how this part of respiration is an ever-repeating cycle. a) Krebs cycle ccurs in matrix of mitochondria. The diagram below is a very simple outline of the Krebs Cycle showing the removal of CO2, and the making of 3. The Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle) is just one part of ATP synthesis. The cycle is a set of reactions which produce a few ATP (or ... Krebs Cycle · Two carbon atoms are released via decarboxylation to form two molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) · Multiple oxidation reactions result in the ...
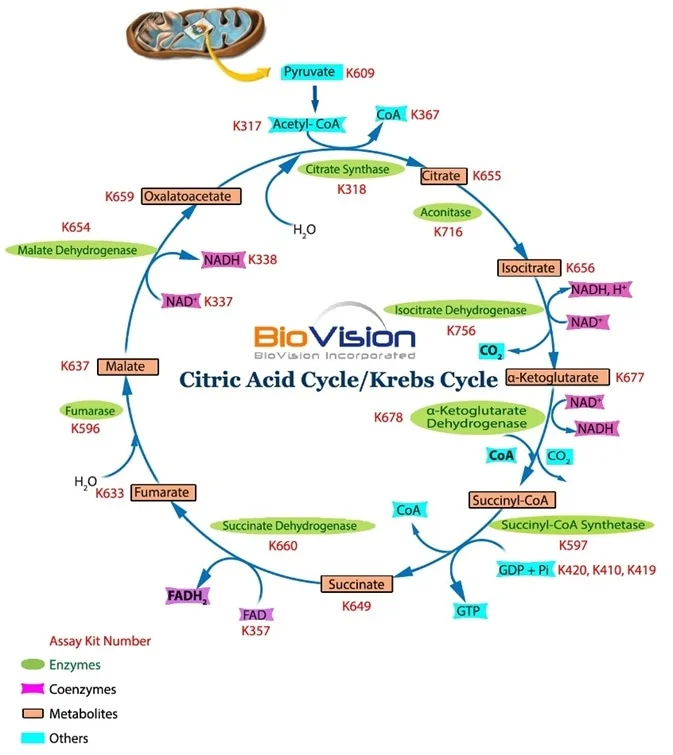
Schematic diagram of the Krebs cycle illustrating major components and enzymes. Citrate synthase is the primary enzyme converting oxaloacetate to citrate in the initial step of ATP synthesis. Krebs Cycle Diagram Easy. The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would. Glycolysis- 10 steps explained steps by steps with diagram. This step involves a simple rearrangement of the position of the phosphate group of oxygen will continue on to ... Kreb Cycle Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle. It was discovered by H.A.Kreb in 1953. This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. The whole cycle of Kreb is described in the following figure. In this article we will discuss about the functions of the Krebs cycle, explained with the help of diagrams. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle, owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids, including citric acid.
Biology: Flow Chart for Cellular Respiration Complete respiration flow-chart Cellular respiration from glycolysis to the Krebs cycle, including co-enzymes and ATP production. Steps of cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
The citric acid cycle (CAC) - also known as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or the Krebs cycle - is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.The TCA cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or ...
Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps Explanation. It is also known as TriCarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle. In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The cycle was first elucidated by scientist "Sir Hans Adolf Krebs" (1900 to ...
In aerobic respiration both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are involved whereas in anaerobic respiration only glycolysis takes place. The flow diagram shows that every time a stage produces two hydrogen atoms, in the presence of oxygen, three ATP molecules are produced. The role of these hydrogen atoms is shown in the electron carrier system.
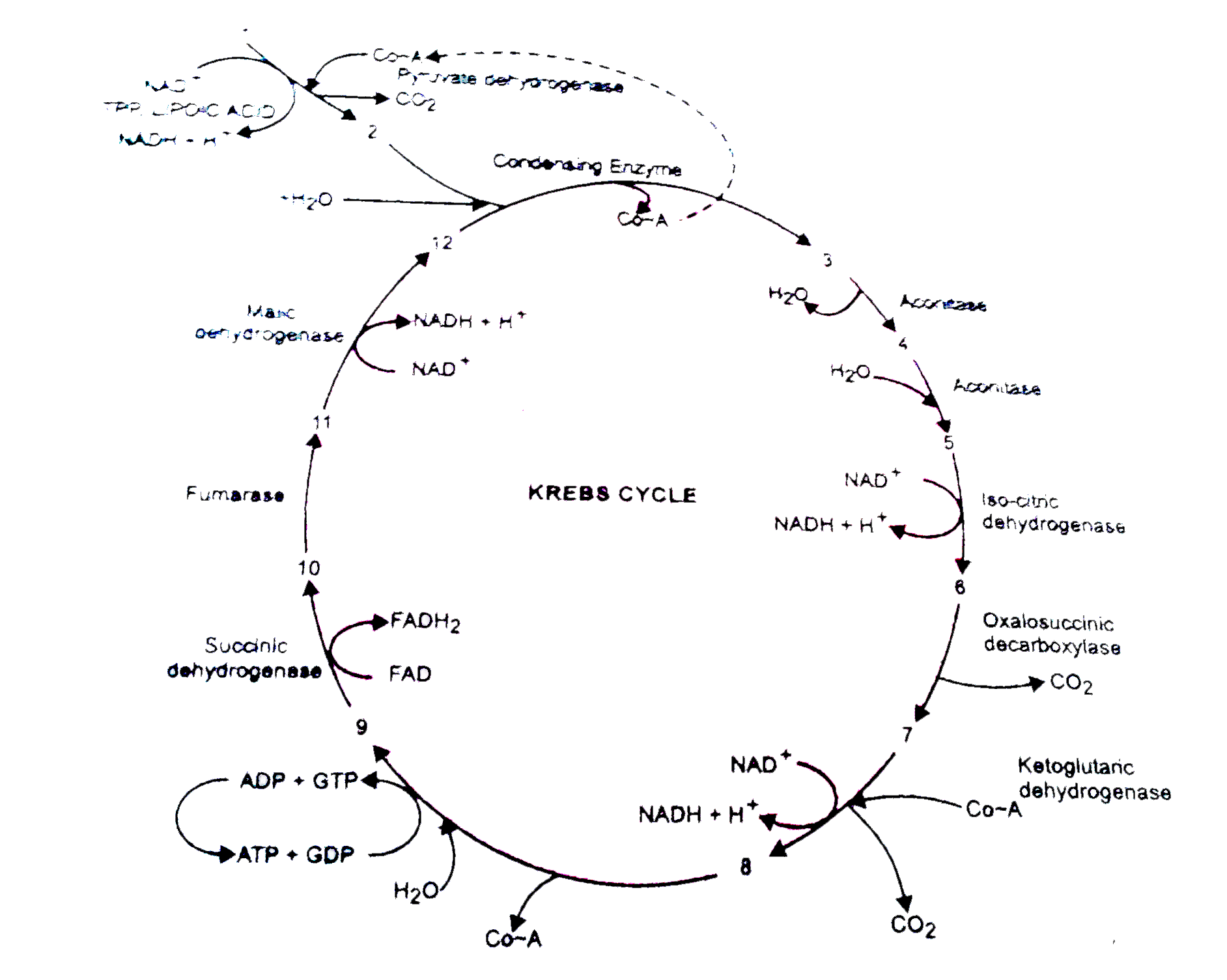
An Outline Diagram Of Krebs Cycle Is Given Below Label 1 12 And Also Mention The Number Of Carbon Atoms In Each Molecule Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Pr Bio Xi V01 C15 E05 008 Q01 Png Width 80
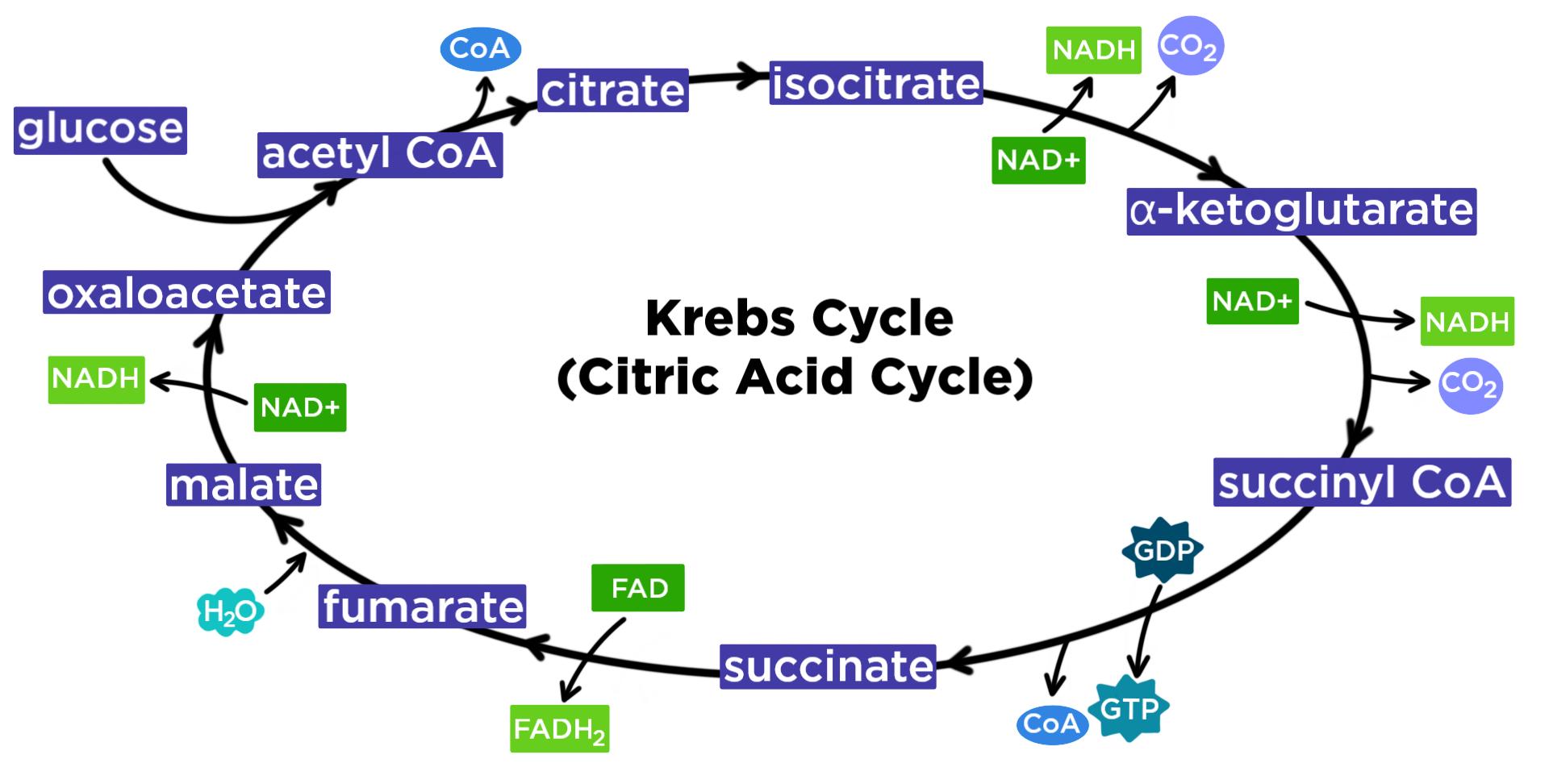
Overview of the Krebs or citric acid cycle, which is a series of reactions that takes in acetyl CoA.The Krebs Cycle, Solution LSM Krebs Cycle Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle and then combines with oxaloacetate to make the six-carbon compound citrate. During the eight steps of the Krebs cycle, citrate undergoes a number of reactions, releasing CO 2 ...
Krebs Cycle (TCA or Citric Acid Cycle): It is the common pathway for complete oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids as they are metabolised to acetyl coenzyme A or other intermediates of the cycle.The Acetyl CoA produced enters the Tricarboxylic acid cycle or Citric acid cycle. Glucose is fully oxidised in this process. The acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate (4C) to form citrate (6C).

An Outline Diagram Of Krebs Cycle Is Given Below Label 1 12 And Also Mention The Number Of Carbon Atoms In Each Molecule Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Pr Bio Xi V01 C15 E05 008 Q01 Png Width 80
The Krebs cycle, named after 1953 Nobel Prize winner and physiologist Hans Krebs, is a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.Put more simply, this means that bacteria do not have the cellular machinery for the Krebs cycle, so it limited to plants, animals and fungi.
The Krebs Cycle Step 1: In the first step of the Krebs cycle, acetyl CoA is added to oxaloacetate to form citrate. Note that coenzyme A (CoA-SH) is removed in the process. Step 2: Citrate is isomerized forming isocitrate, which is less stable than citrate. During this step, one water molecule is
Match. Gravity. Total energy production per glucose of ONLY the Krebs cycle (before electron transport chain) Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 8 NADH, 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 2 FADH2. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Describe the Pre-Krebs Cycle.
Krebs Cycle and Link Reaction: Interactive Tutorial. 1. Introduction. If oxygen is present in a cell where respiration is occurring, then glycolysis is followed by a series of reactions that completely oxidize pyruvate (pyruvic acid) and the molecules it gets broken down into. You can see this in steps "2" and "3" in the diagram below.
Krebs cycle The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, is one of the most important reaction sequences in biochemistry. Not only is this series of reactions responsible for most of the energy needs in complex organisms, the molecules that are produced in these reactions can be used as building blocks for a large number of important processes ...
These cycle diagrams are designed to guide you in studying the acid cycle. This Krebs cycle is the oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO 2 and water. This cycle is also called citric acid cycle because the cycle begins with the formation of citric acid. Citric acid is a carboxylic acid containing 3 COOH groups. Hence this cycle is also called as ...
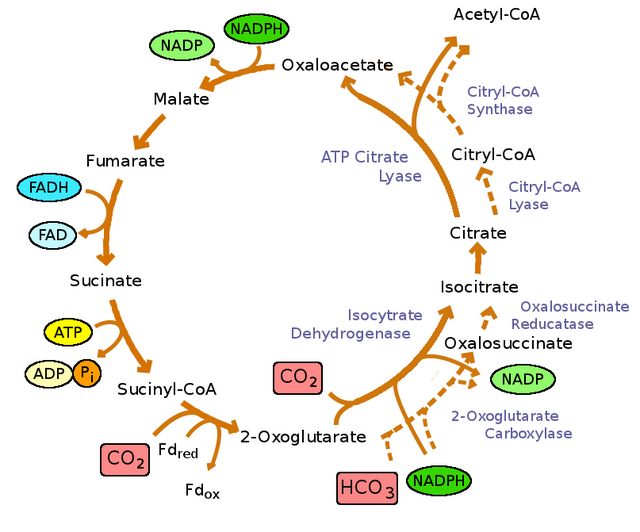
The acetyl CoA then enters the Krebs cycle. Within the cell, the Krebs cycle organic acids are not arranged in a circle nor is there any circular arrangement of the enzymes. This pathway is termed a "cycle" (and diagrammed as a circle) because the end product becomes the first product after reacting with acetyl CoA.
Step 1. In the first step of the citric acid cycle, acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Step 2. In the second step, citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate.
Krebs Cycle. Identify the phase of cellular respiration where the pyruvate molecules would enter the cellular respiration process. Link Reaction. Glucose has six carbons. A fat molecule could have ten times that many carbons. Predict how the number of ATP molecules produced would differ between a glucose molecule and a fat molecule.
The Krebs Cycle LSM 2.2-3 Krebs Cycle enters the cycle and then combines with to make the six-carbon compound . During the eight steps of the Krebs cycle, undergoes a number of reactions, releasing and in a number of steps. is eventually converted into so it can be used again during the Krebs cycle. Pyruvate Oxidation
The TCA cycle or Krebs' cycle (after H. A. Krebs) is a cyclic sequence of reactions through which pyruvic acid produced in the EMP and EDP is oxidized. The cycle operates in aerobic organisms including animals, plants and microorganisms. The main function of the cycle is to generate energy by oxidation of acetic acid which is produced by ...
Krebs cycle steps · The TCA cycle begins with an enzymatic aldol addition reaction of acetyl CoA to oxaloacetate, forming citrate. · The citrate is isomerized by ...









.png--diagram-flowchart-example.png)












0 Response to "36 diagram of the krebs cycle"
Post a Comment