37 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
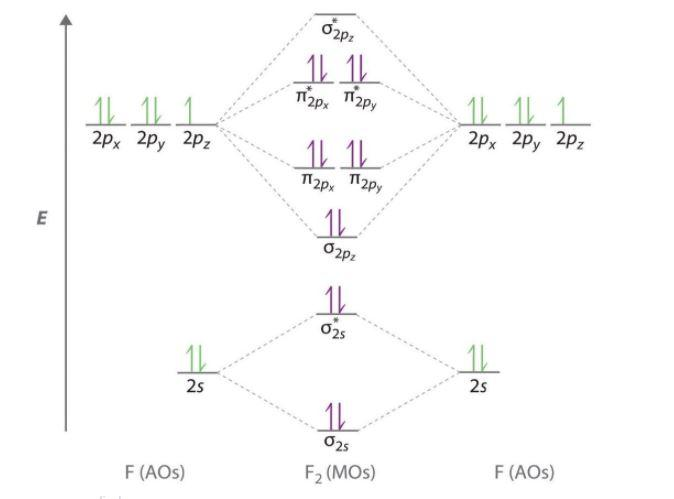
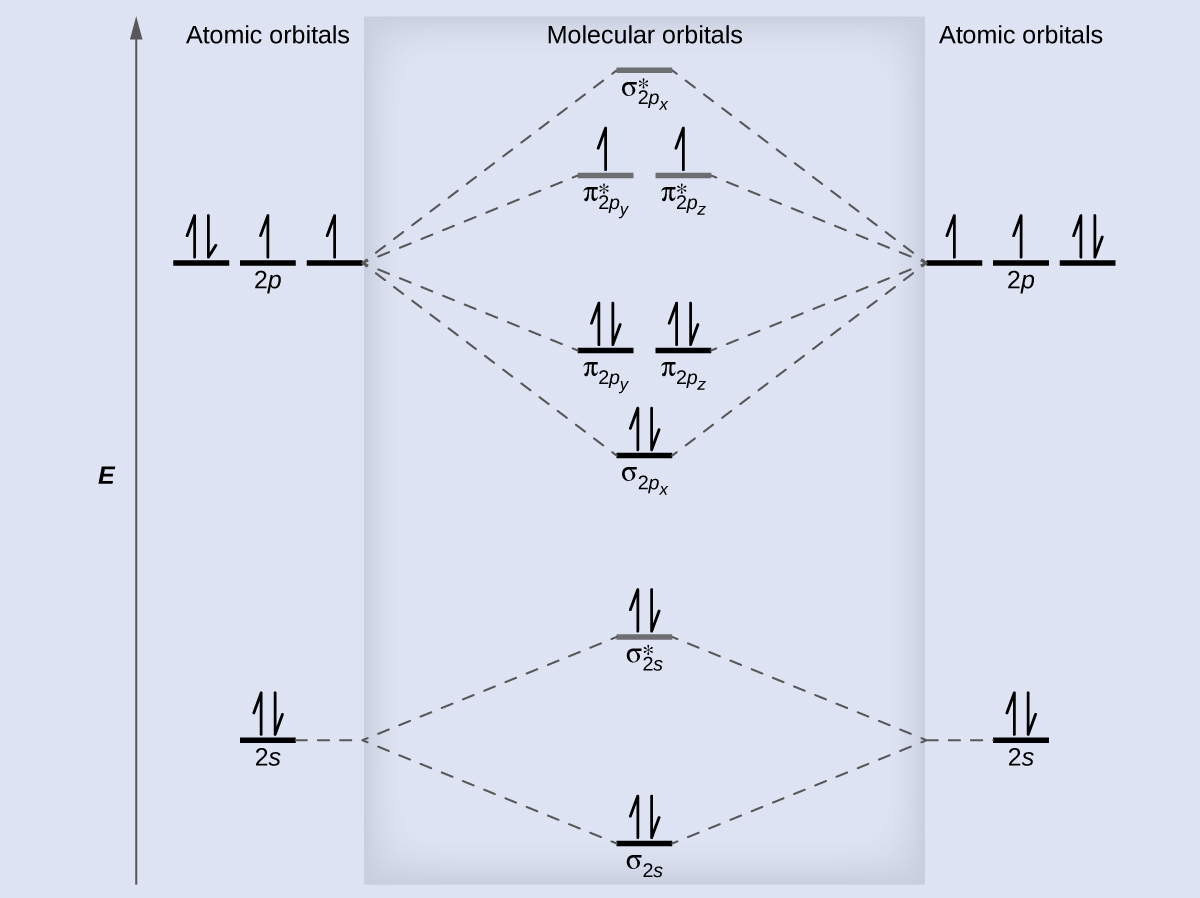
Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b – Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero. 3) Relative stability of molecule in terms of ... Originally Answered: What is the bond order of F2?In simple terms, since F has 7 valence electrons thus by sharing of electrons with another F it forms a bond to fullfil its octate. You can also find its bond order using advance Molecular orbital theory (MoT). Therefore Bond order of F2 is 1. Mar 26, 2021
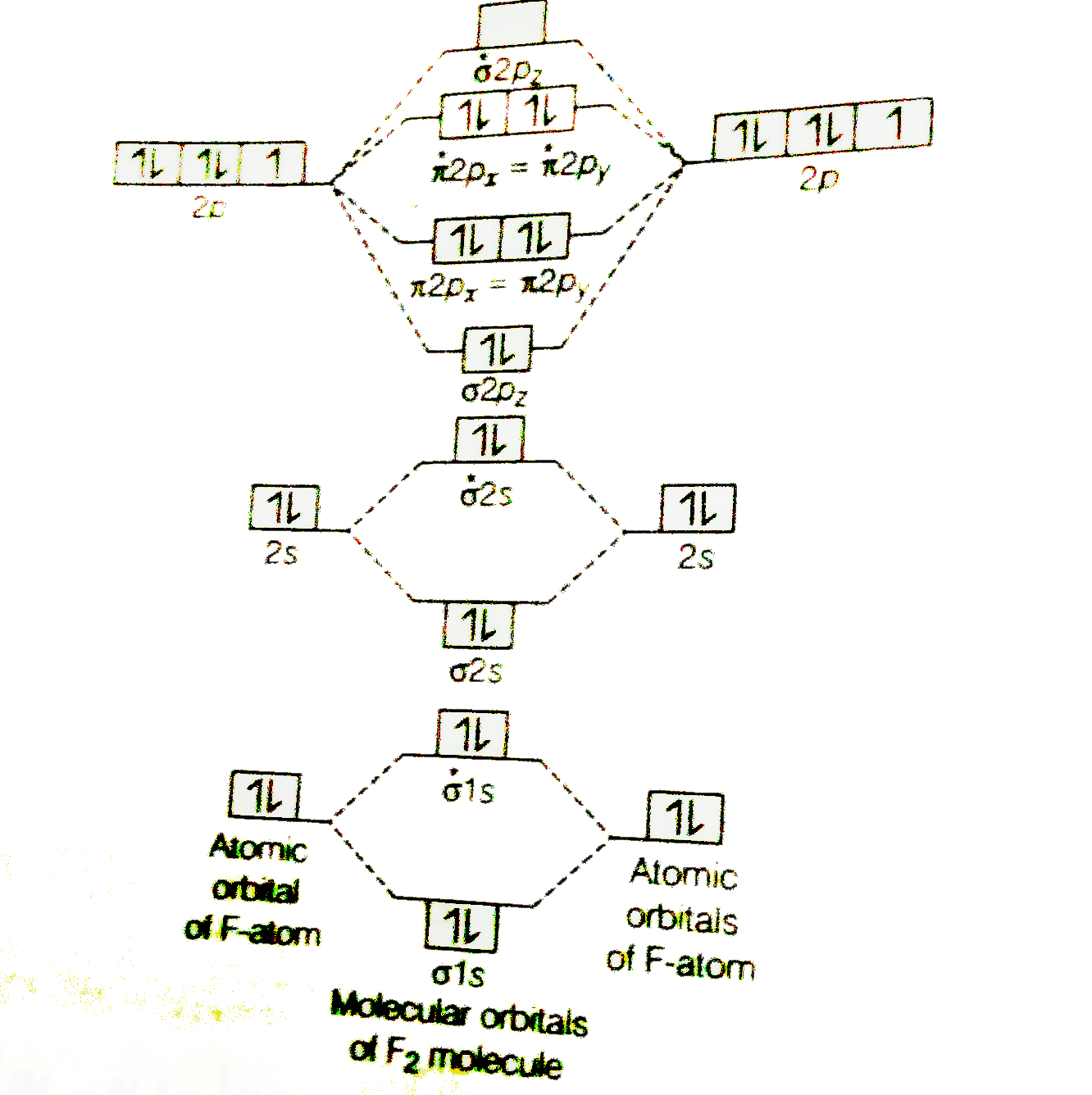
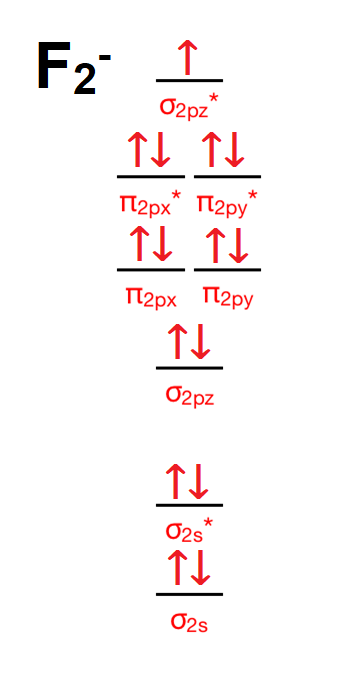
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...

F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
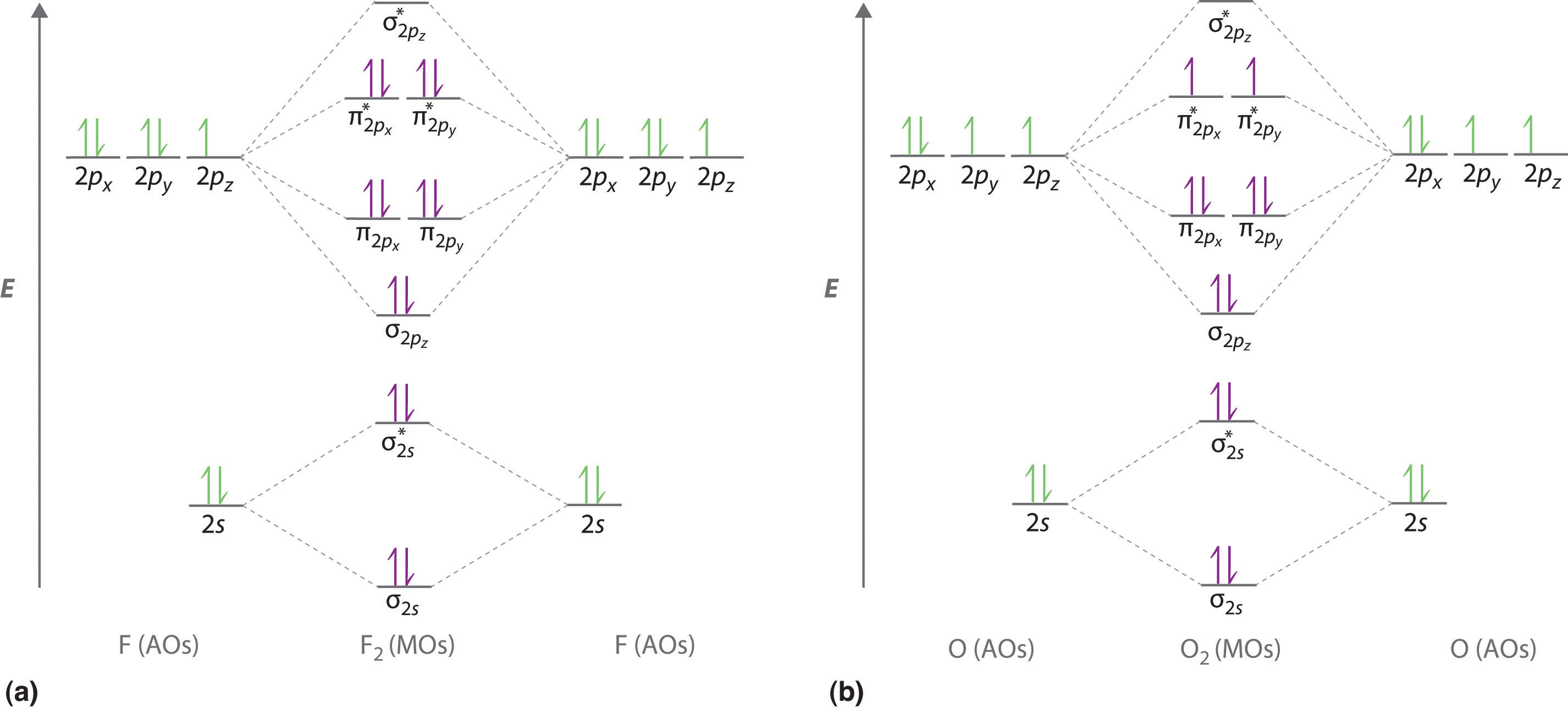
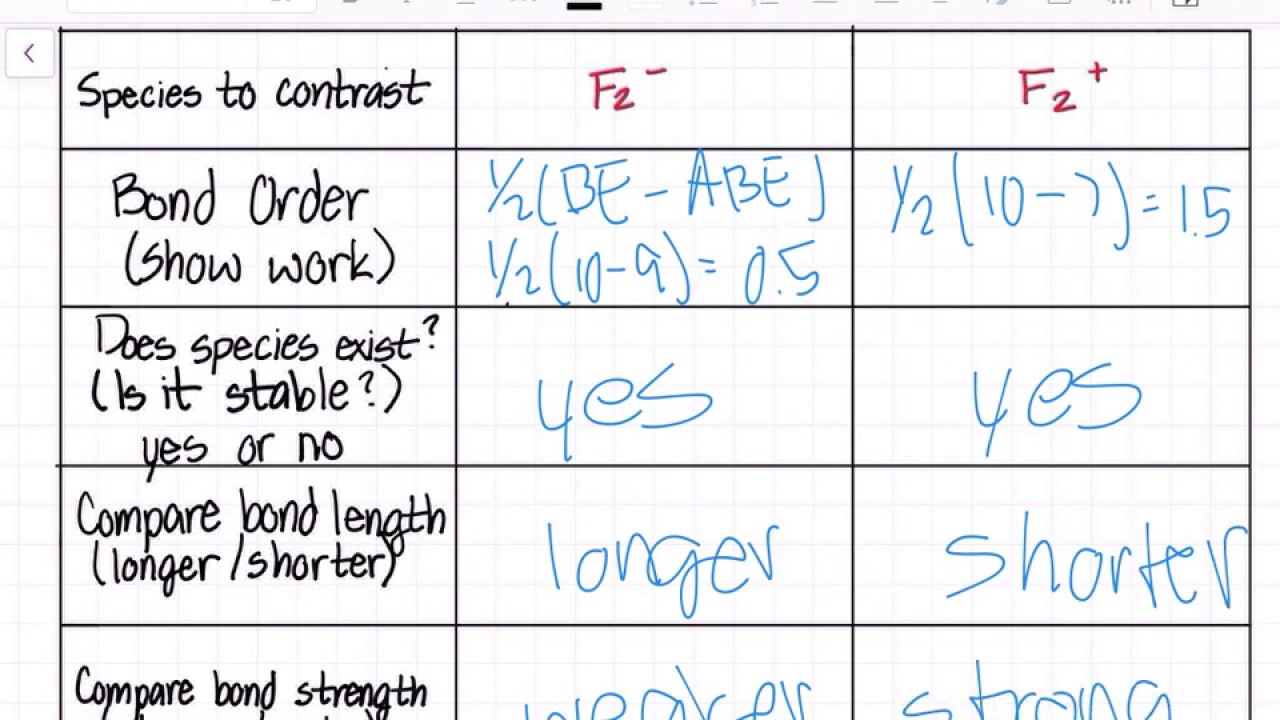
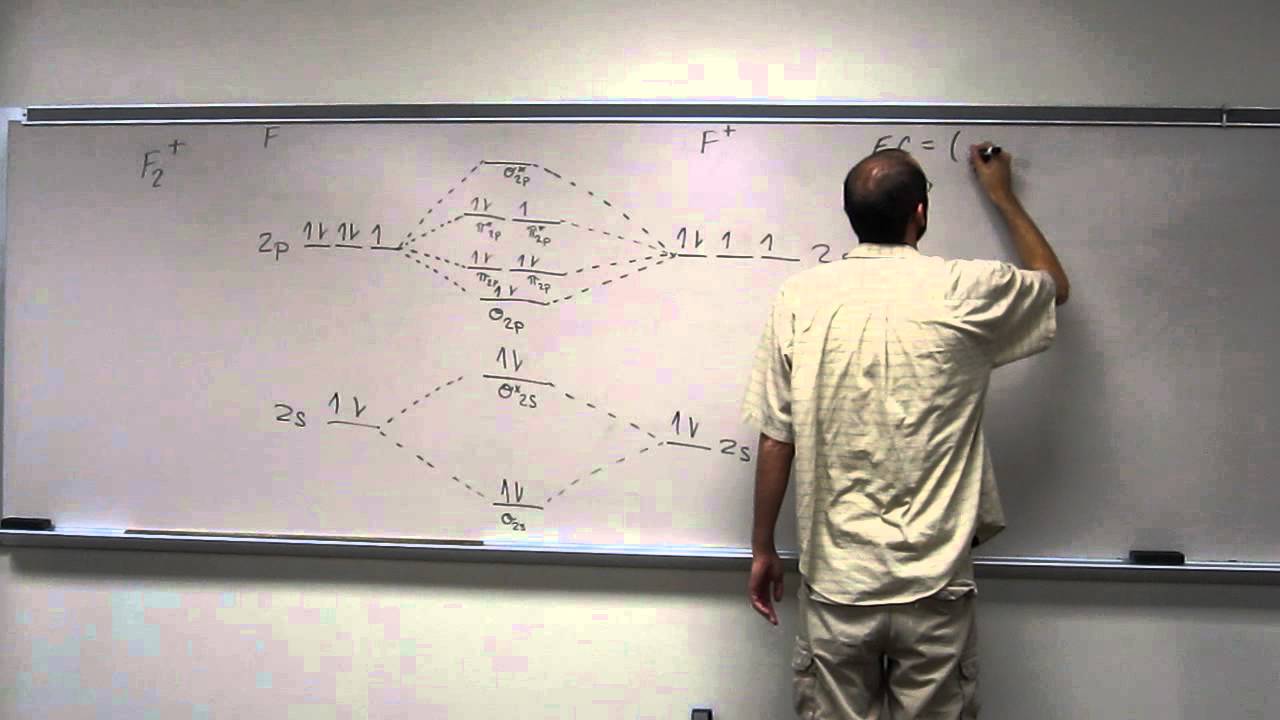
#sigma# molecular orbitals are singly-degenerate, and #pi# molecular orbitals are doubly-degenerate. #sigma# molecular orbitals, in principle, get more stabilized upon overlap than #pi# molecular orbitals do. For example, an #ns//ns# overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this: If we draw the bond structure of the f2 molecule and distribute the bonding and antibonding electrons using the molecular orbital theory, then we can calculate the bond order of the molecule. In the case of a fluorine molecule has a total of 18 electrons and out of which 14 electrons are valence electrons. For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————...
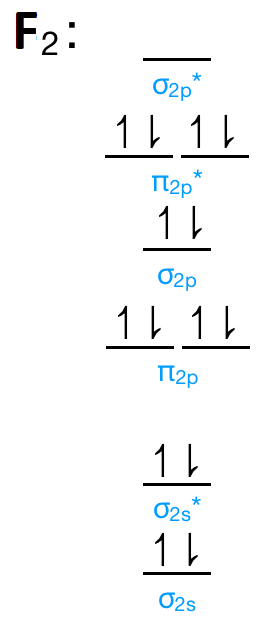
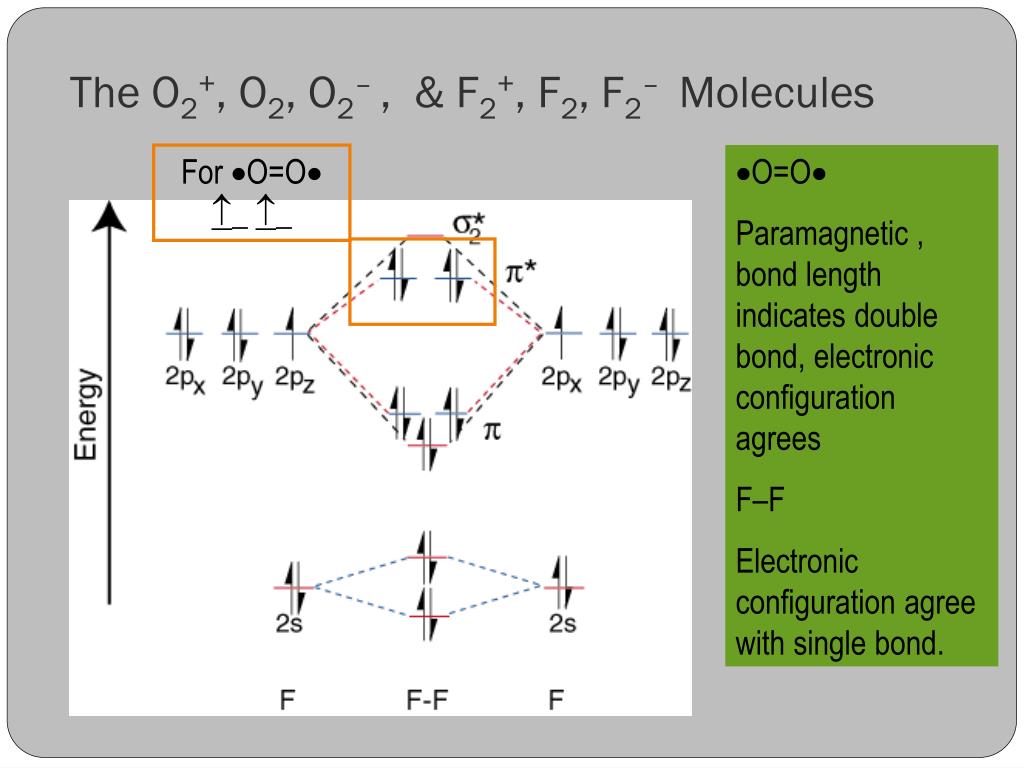
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order. - Bond order: In simple words, It can be stated that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and antibonds. Bond number also gives an indication of the stability of a bond. Lets calculate the bond order for ${N_2}$ : The total number of electrons present in the ${N_2}$ molecule is 14. Number of electrons in bonding orbitals : 8 Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ... 29 Sept 2017 — Bond order is 1 because their formula is total bonding electron - total antibonding electron /2 so lower shell which do not contain asterick(*) ...2 answers · 60 votes: O2 and F2 is an execption so their Z shell is down because of low energy level.but ...
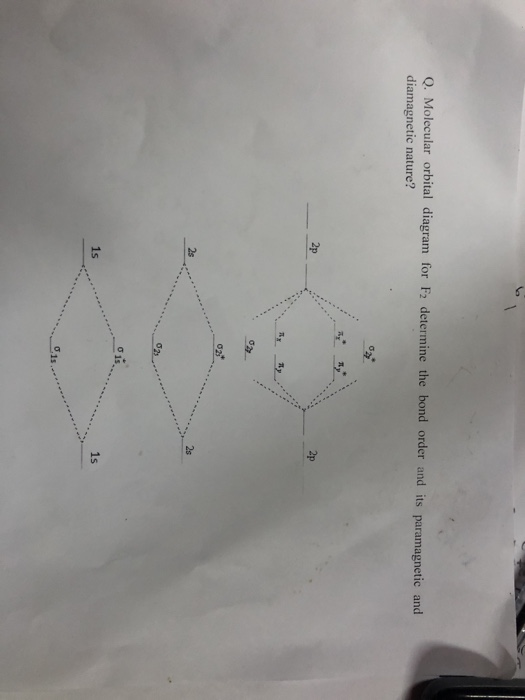
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order ... Now, from MO theory, let us calculate the bond order in the F2 molecule using the following formula. Bond order (BO) = 0.5 * (no. of electrons in bonding orbitals – no. of electrons in antibonding orbitals) For fluorine molecule, BO = 0.5 (8 – 6) = 1. The case of F2 is a simple one because of the symmetry and diatomicity of the molecule. For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————... If we draw the bond structure of the f2 molecule and distribute the bonding and antibonding electrons using the molecular orbital theory, then we can calculate the bond order of the molecule. In the case of a fluorine molecule has a total of 18 electrons and out of which 14 electrons are valence electrons.
#sigma# molecular orbitals are singly-degenerate, and #pi# molecular orbitals are doubly-degenerate. #sigma# molecular orbitals, in principle, get more stabilized upon overlap than #pi# molecular orbitals do. For example, an #ns//ns# overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this:
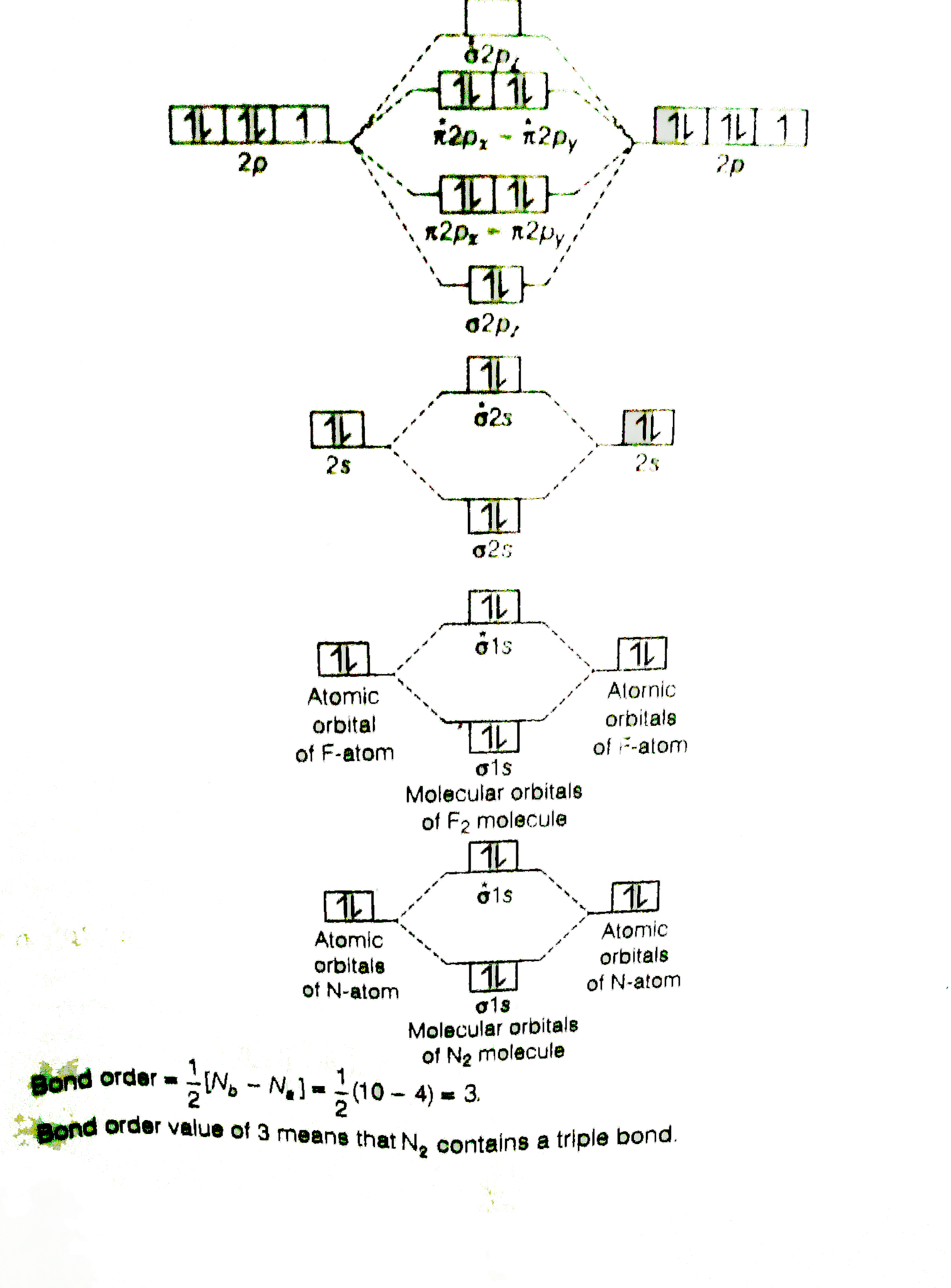
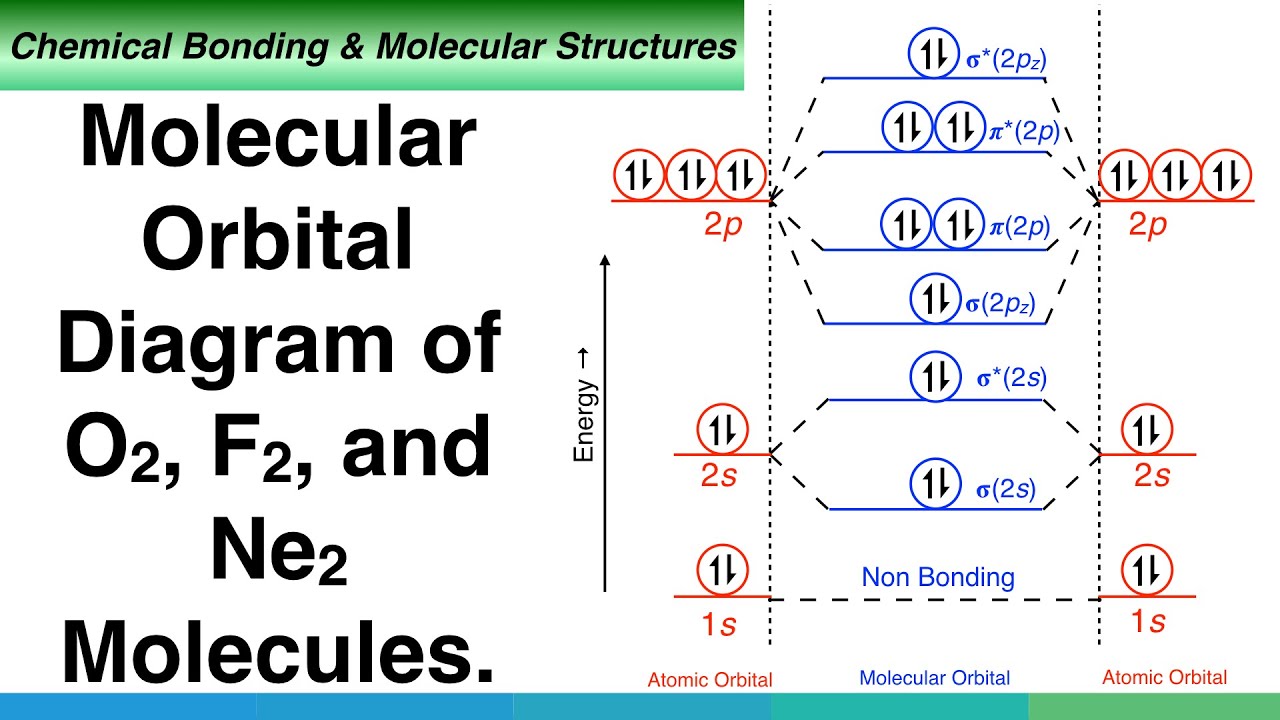
Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Bond
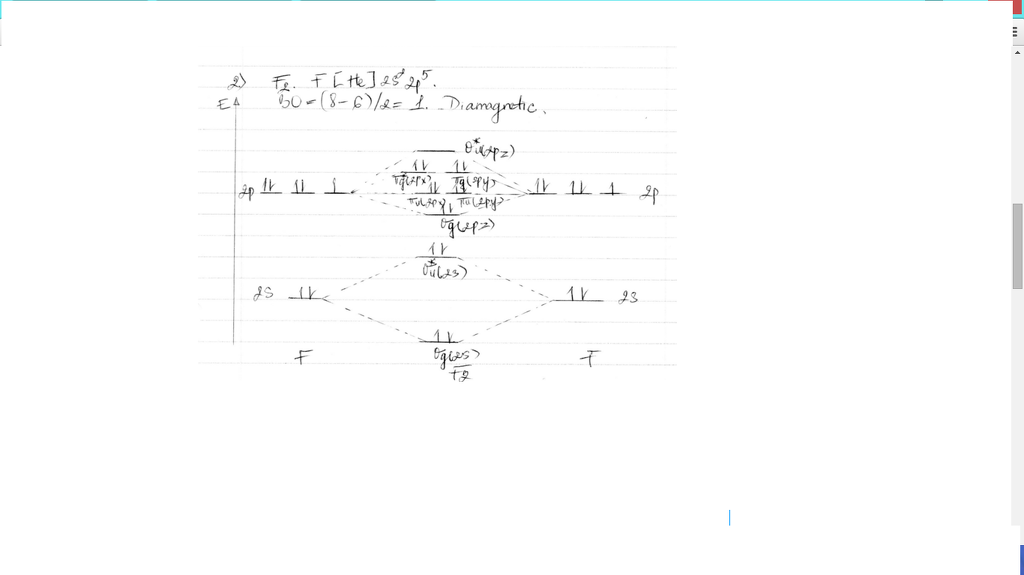
Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 And Find Out The Bond Order Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure 9820853 Meritnation Com



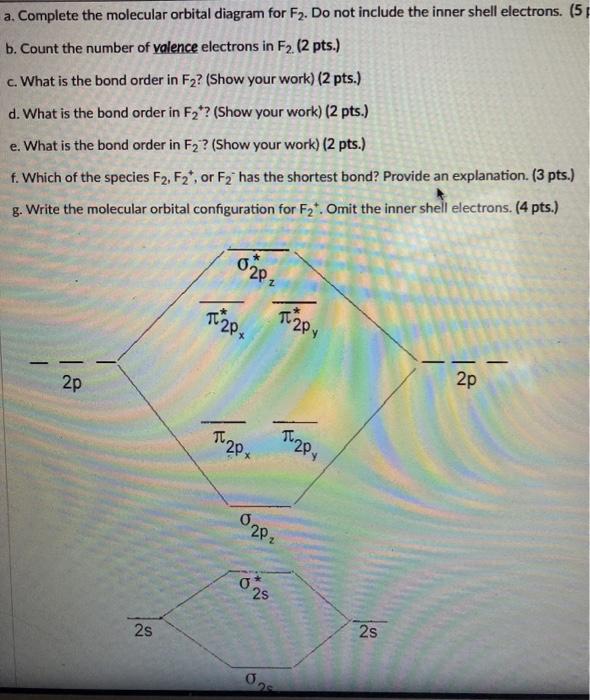








0 Response to "37 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment