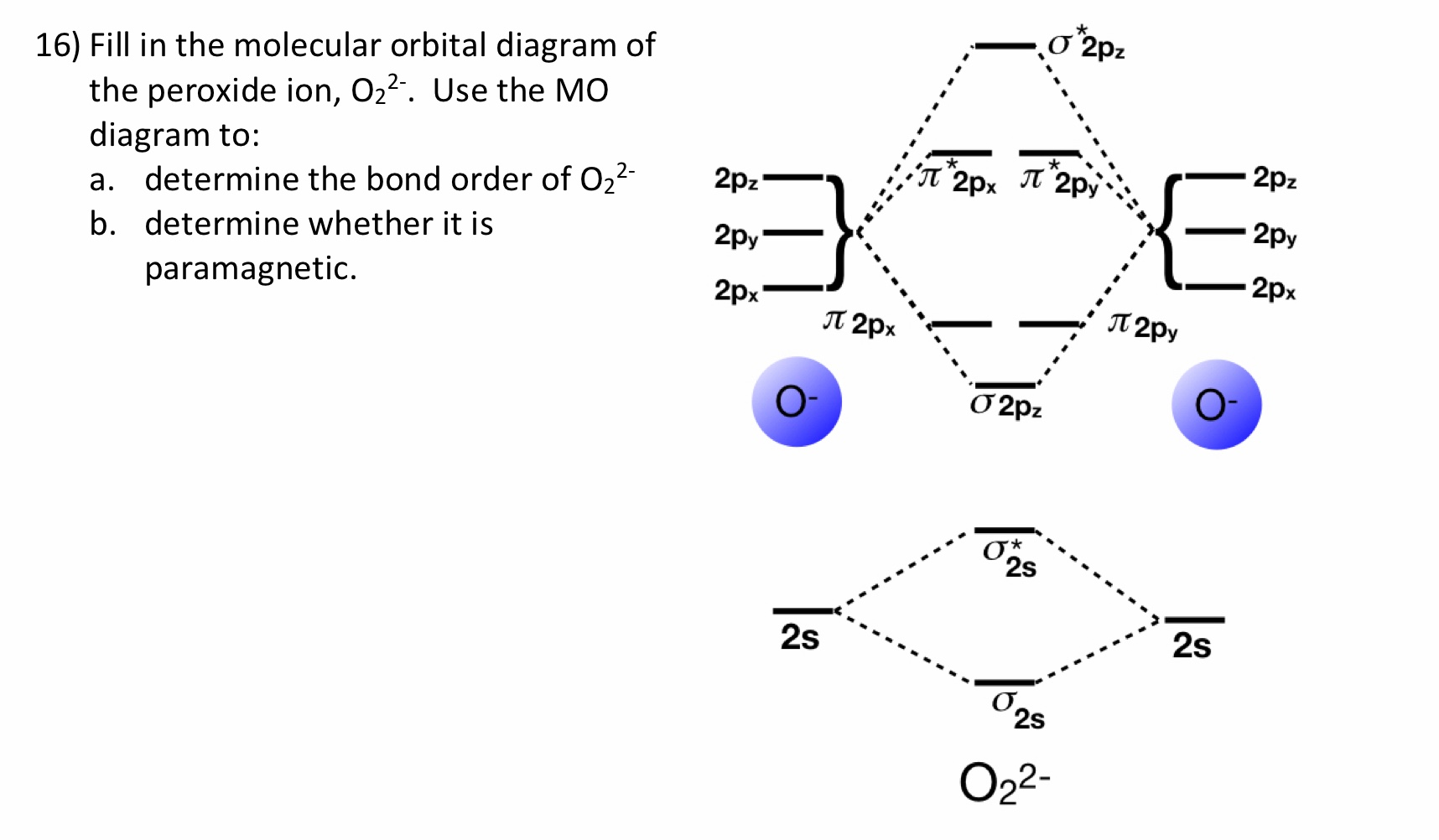
37 molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion
Inorganic Chemistry Cyanide Ion Non Bonding Lone Pair Chemistry - Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn : UNTPIKAPPS - Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn. Explain formation of O2 molecule with the help of MO diagram pls explain it soon !! - Chemistry - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure ... A fundamental factor in these molecular structures is the existence of electron pairs. These are electrons with opposed spins, allowing them to occupy the same molecular orbital without violating the Pauli exclusion principle (much like in atoms). Different molecular orbitals have different spatial distribution of the electron density.
The molecular orbital diagram of the BeCl2 molecule is drawn by the combination of Beryllium atomic orbitals and chlorine group orbitals. As there are two chlorine atoms and hence, first they combine to form group orbitals. The electronic configuration of Cl is [Ne] 3s23p5. Now, the 3s atomic orbital of one chlorine atom will combine with the ...
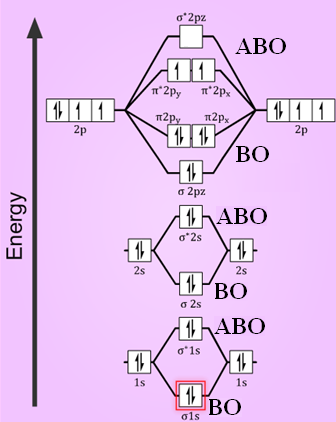
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion
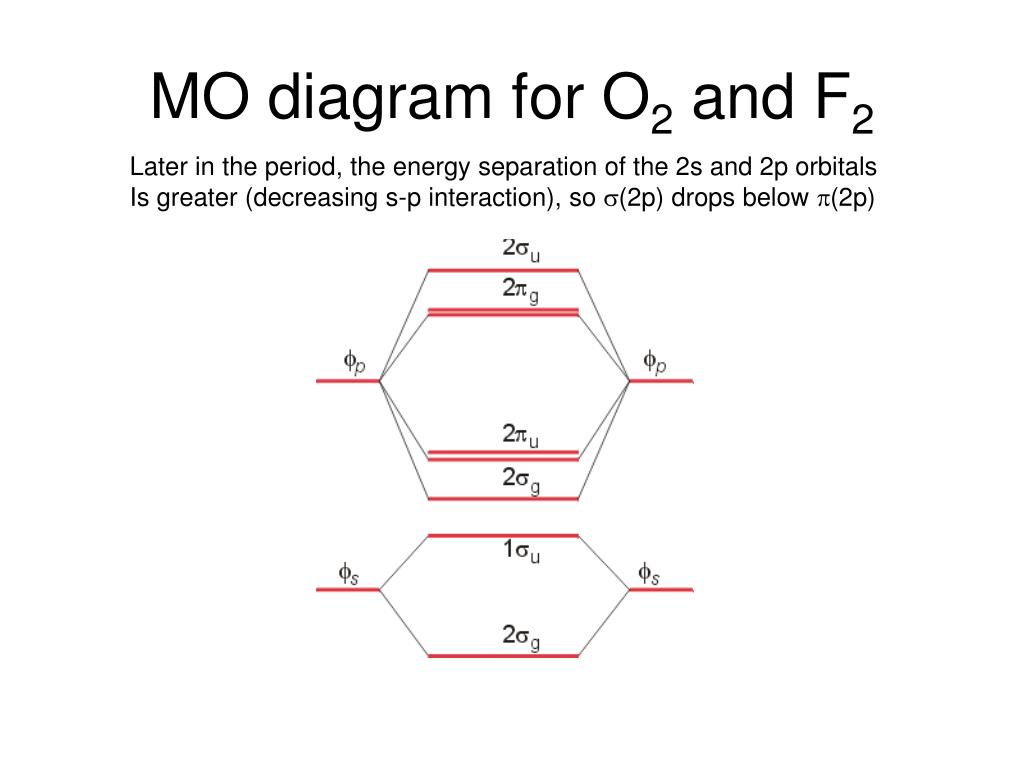
Shapes of s, p and d - orbitals, electron spin and spin quantum number. Rules for filling electrons in orbitals - Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configuration of elements, the extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals. Unit 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Sep 04, 2021 · Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. This switch in orbital ordering occurs because of a phenomenon called s-p mixing. s-p mixing does not create new orbitals; it merely influences the energies of the existing molecular orbitals. High entropy oxides are entropy-stabilised oxides that adopt specific disordered structures due to entropy stabilisation. They are a new class of materials that utilises the high-entropy concept first discovered in metallic alloys. They can have interesting properties due to the interactions at the electronic level and can be combined with other materials to make composite structures.
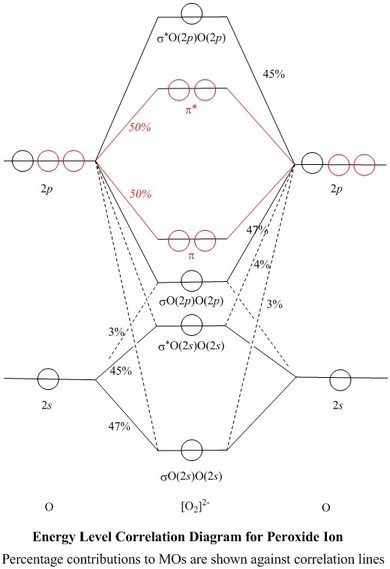
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion. A chemical bonding of several metallabenzenes and metallabenzynes was studied via an adaptive natural density partitioning (AdNDP) algorithm and the induced magnetic field analysis. A unique chemical bonding pattern was discovered where the M=C (M: Os, Re) double bond coexists with the delocalized 6c-2e π-bonding elements responsible for aromatic properties of the investigated complexes. The rule is applicable to the main- group elements, especially carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens, but also to metals such as sodium and magnesium. Valence electrons can be counted using a Lewis electron dot diagram. In carbon dioxide, for example, each oxygen shares four electrons with the central carbon. The unhybridized 2p orbital on carbon is perpendicular to the molecular plane. It is used for sideways overlap to form a π bond with the 2p orbital of oxygen. Oxygen is also sp2 hybridized in this molecule, but it forms only one σ bond as the other two sp2 hybrid orbitals are filled with lone pair electrons. 21. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr4. a. 0 lone pairs, square planar. b. 0 lone pairs, tetrahedral. c. 1 lone pair, square pyramidal. d. 1 lone pair, trigonal bipyramidal . 22. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of SCl2. a. 0 lone pairs, linear. b.
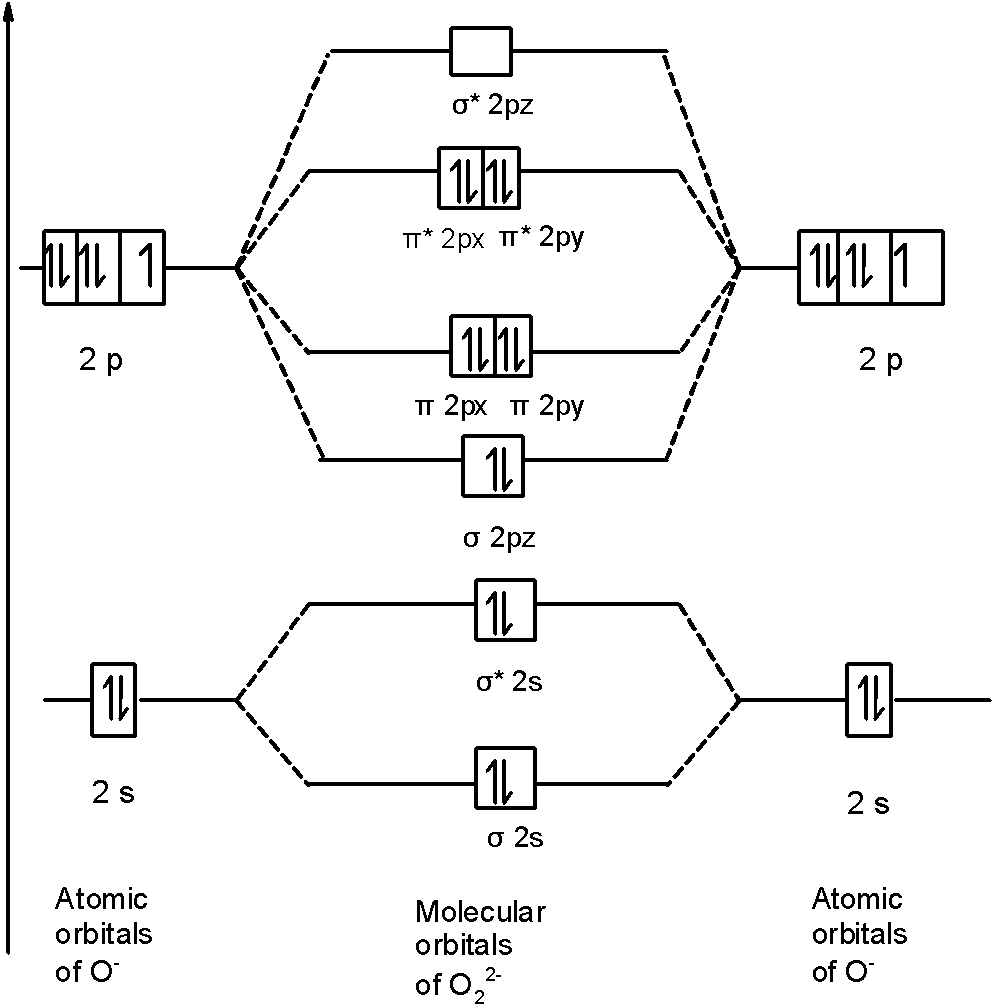
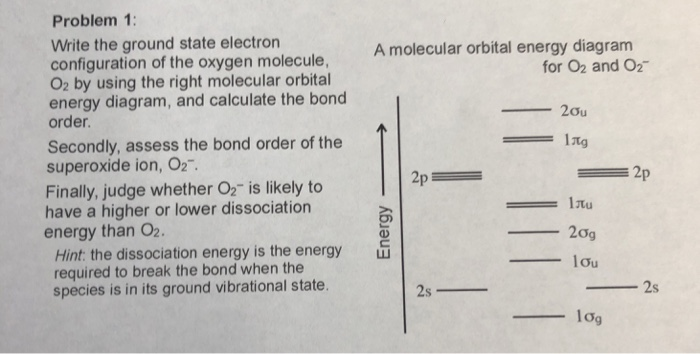
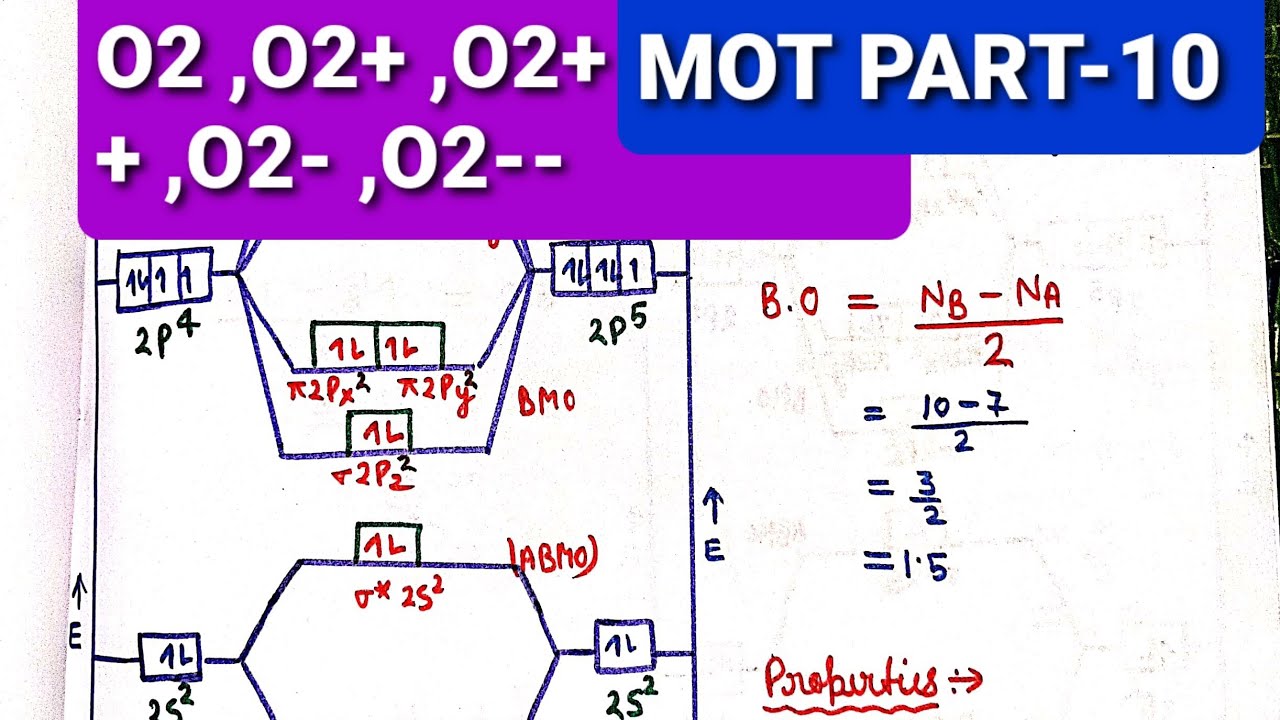
The number of electrons in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals of a molecule or molecular ion can be calculated from its electronic configuration. An electronic configuration , also known as an electronic structure, is the arrangement of electrons at different energy levels around an atomic nucleus. Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 . Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 ... Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3. Molecular orbital s: Orbital s that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbital s (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up Schrödinger wave equation for that molecule and then, solve it!!! Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker. These quizzes enable you to build your own molecular orbital diagram ...
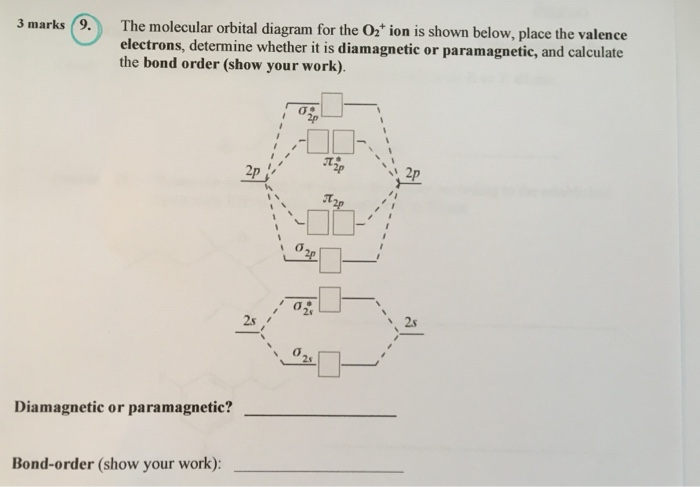
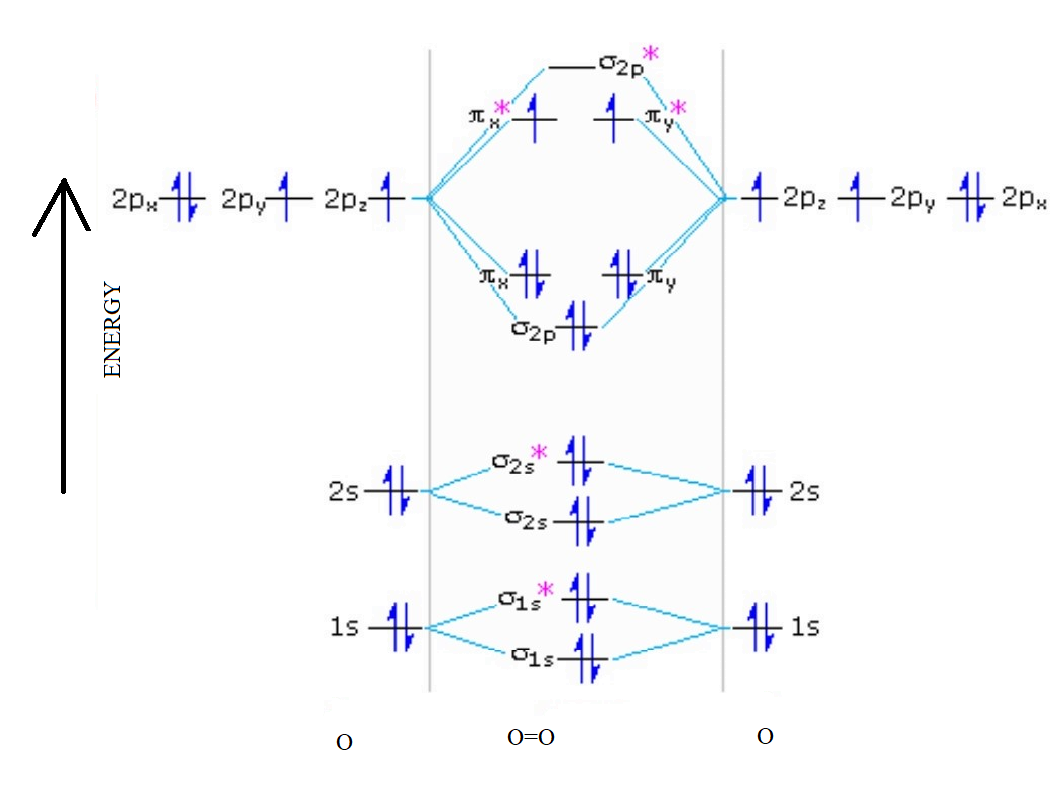
Mar 20, 2019 · Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... Greater the number of unpaired electrons present in the molecular or ion, greater is its paramagnetic nature. ... Diagram for O2+ is wrong because 2p atomic orbital of 2nd O atom will have only 3 e-. Reply. Mrs Shilpi Nagpal says. September 26, 2018 at 11:06 am. A major change is appreciated with an increase of electron population of the O 2 antibonding π* molecular orbital, which is filled by an electron from the C 6 H 6 occupied π molecular orbital. you could enjoy now is chapter 16 solubility and complex ion equilibria below. 11.3 Solubility - Chemistry Example 1. Application of Henry's Law At 20 °C, the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water exposed to gaseous oxygen at a partial pressure of 101.3 kPa (760 torr) is 1.38 × 10 −3 mol L −1.Use Henry's law to determine the ... In this article, we will study Chlorite ion(ClO2-) lewis structure, molecular geometry, hybridization, polar or nonpolar, bond angle, etc. Chlorite has a +3 oxidation state and is part of the chlorine oxides family. Chlorite is used in the paper, pulp, and bleaching of textiles. Properties of Chlorite ion. It has a molar mass of 67.452 g.
The Lennard-Jones potential (also termed the LJ potential or 12-6 potential) is an intermolecular pair potential.Among the intermolecular potentials, the Lennard-Jones potential is the potential that has been studied most extensively and most thoroughly.It is considered an archetype model for simple yet realistic intermolecular interactions. The Lennard-Jones potential models soft repulsive ...
unit iv: chemical bonding and molecular structure Valence electrons, ionic bond, covalent bond, bond parameters, Lewis structure, polar character of covalent bond, valence bond theory, resonance, geometry of molecules, VSEPR theory, concept of hybridization involving s, p and d orbitals and shapes of some simple molecules, molecular orbital ...
Molecular Geometry of Sulfur Trioxide (SO3) The above image clears that the bond angle among oxygen-sulfur-oxygen (O-S-O) atoms have to be more than 90°. Moreover, through the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory, the structure of sulfur trioxide (SO3) is found to be bent shaped or trigonal pyramidal or trigonal planar, where ...
Dinitrogen trioxide (N 2 O 3) is formed from the stoichiometric reaction between NO and O 2 or NO and N 2 O 4. Dinitrogen trioxide has an intense blue color in the liquid phase and a pale blue color in the solid state. Thermal dissociation of N 2 O 3, (8.4.7), occurs above -30 °C, and some self-ionization of the pure liquid is observed, (8.4.8).
NO2F Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity. NO2F, an inorganic compound, is named Nitryl Fluoride. It is a colorless gas and acts as a strong oxidizing agent. So, it can be used in the replacement of liquid oxygen, an oxidant in propellants of the rocket. NO2F can easily release its fluoride ion to other species in ...
A molecular-level understanding of how the electronic structure of metal center tunes the catalytic behaviors remains a grand challenge in heterogeneous catalysis. Herein, we report an ...
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air.Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl.It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.
Each oxygen atom has a pure 2p atomic orbital, which is perpendicular to its plane. Molecular orbitals are delocalized by linear combinations of these. orbitals do not affect the structure in a significant way. Carbon dioxide is another triatomic molecule.
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
There is one hydrogen atom in butanol that is connected to an oxygen atom at the end of the molecule, which is what allows for hydrogen bonding to occur (since O is in the NOF group, and a hydrogen atom bound to one of these three atoms results in the molecule being able to hydrogen bond).
Molecular orbitals of carbon monoxide. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining mo diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the molecular ion n 2. Individual atomic orbitals ao are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram ...
Electron configurat ion s of transit ion metal elements Hydrogen Z 1. Lithium Z 3. Ce 3 Xe4f 1. Iron which for ms ei the r the Fe 2 or Fe 3 ion s loses electrons as shown below. The Electron Configurat ion of Transit ion-Metal Ion s. CeriumIII leadII Ti 2 Am 3 Pd 2 For the examples that are transit ion metals determine to which series the y belong.
NO3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, and Hybridization. NO3 is a polyatomic ion with a negative charge. So, it is also referred to by the name of nitrogen oxoanion. The compound has its chemical name as nitrate formed after nitric acid looses a proton from it. Nitrate is an important source of nitrogen and oxygen.
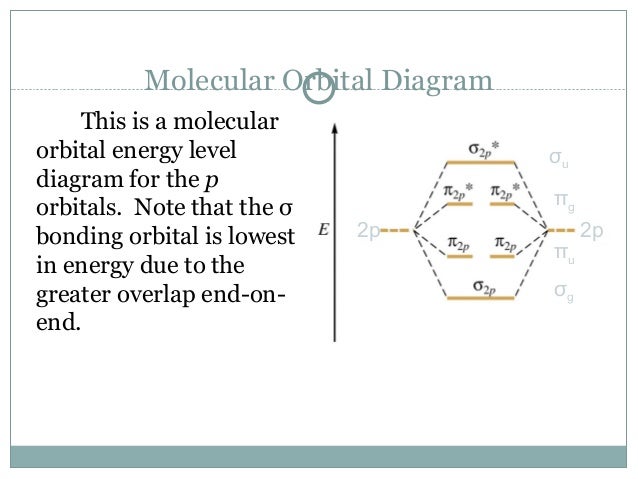
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
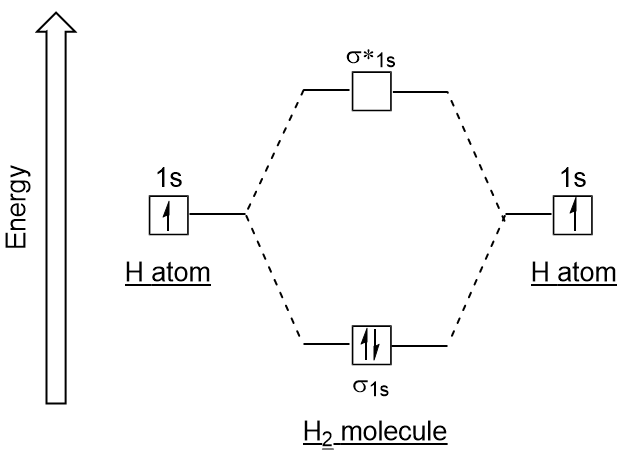
A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in the [latex]\sigma[/latex] 1s bonding orbital; the electron configuration is [latex]{\left({\sigma}_{1s}\right)}^{2}.[/latex] We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (Figure 7.7.10) in which a single upward arrow indicates one ...
Free radicals are extremely destructive atoms or molecules that bear one or more unpaired electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals. They are capable of causing detrimental health effects to the human body, such as DNA damage, protein breakdown, organ failure, cell death and cell membrane destruction, without discrimination [16, 21].Antioxidants are free radical trapping agents that can ...
Video Game Development: The Basic Skills you Need to Succeed. Digital Communications. 8 Gadgets that will Help you Relax and Unwind
Nov 17, 2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet
A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy than the original atomic orbitals.
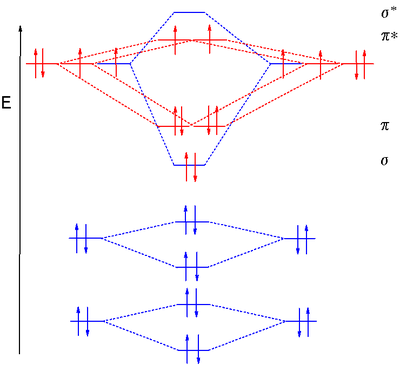
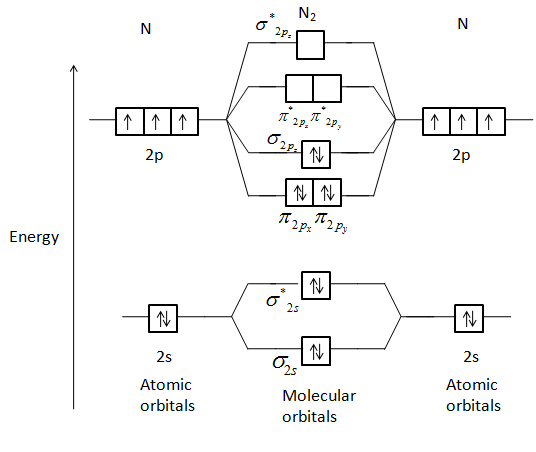
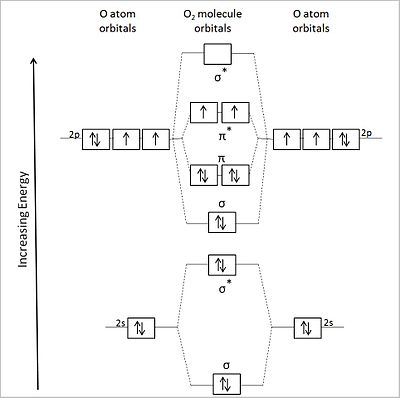
Sep 25, 2016 · The Lewis structure of #"O"_2# gives a misleading impression.. It shows that all the electrons in oxygen are paired, so oxygen should be diamagnetic.. Yet oxygen is paramagnetic.. The correct explanation comes from Molecular Orbital theory.. The atomic orbitals of the #"O"# atoms overlap to form the σ and π orbitals of the #"O"_2# molecule as shown in the diagram above.
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion 1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in the book "Symbolic Logic" (1881). 1834, introduced by English physicist and chemist Michael Faraday (suggested by the Rev. William Whewell, English polymath), coined from Greek ion ...
High entropy oxides are entropy-stabilised oxides that adopt specific disordered structures due to entropy stabilisation. They are a new class of materials that utilises the high-entropy concept first discovered in metallic alloys. They can have interesting properties due to the interactions at the electronic level and can be combined with other materials to make composite structures.
Sep 04, 2021 · Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. This switch in orbital ordering occurs because of a phenomenon called s-p mixing. s-p mixing does not create new orbitals; it merely influences the energies of the existing molecular orbitals.
Shapes of s, p and d - orbitals, electron spin and spin quantum number. Rules for filling electrons in orbitals - Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configuration of elements, the extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals. Unit 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure





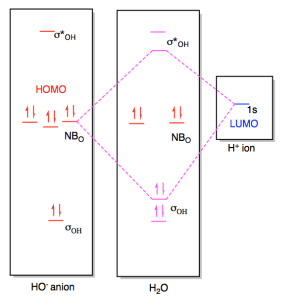




0 Response to "37 molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion"
Post a Comment