38 c2 2 molecular orbital diagram
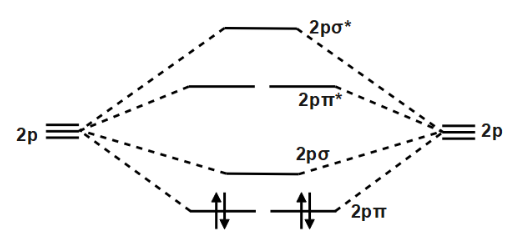
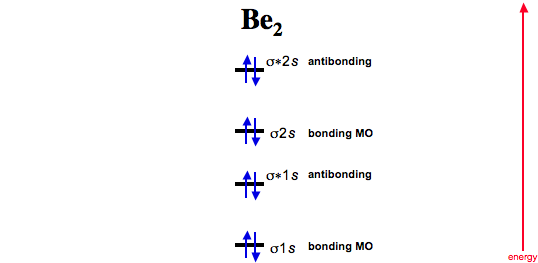
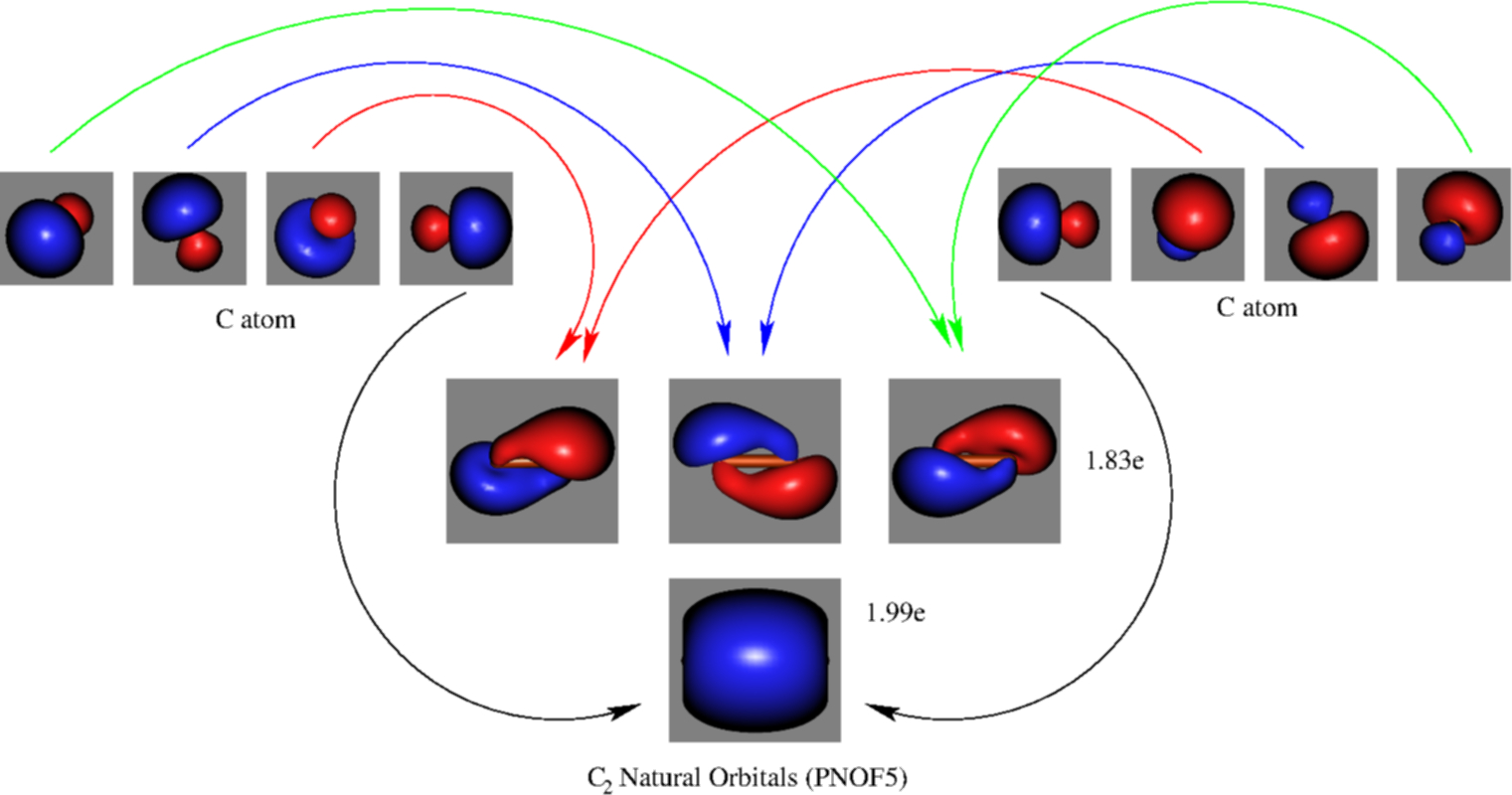
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 . The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n(2px) 2 n(2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons.
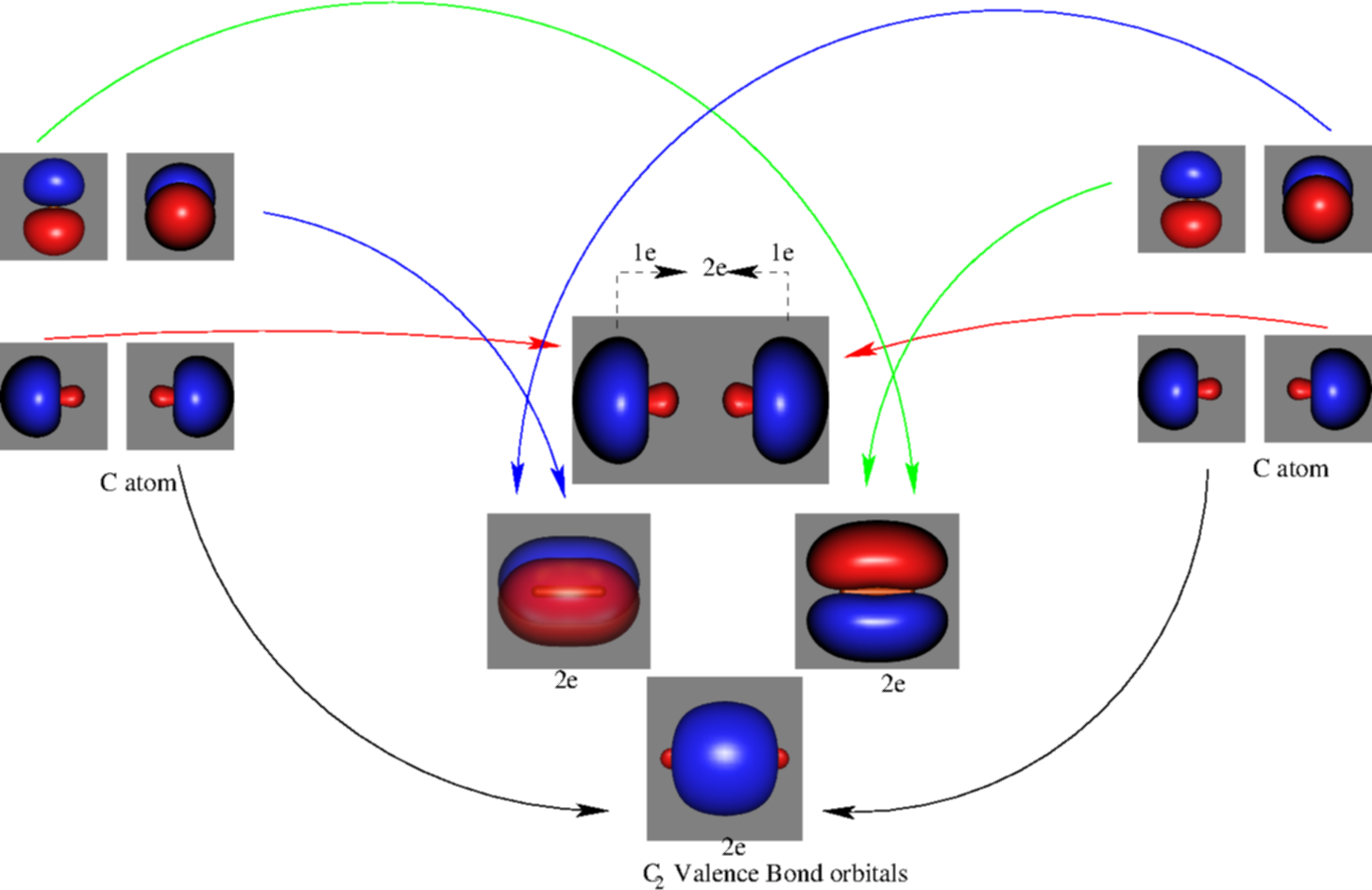
When two carbons atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.C2(2-) has a bond order of 3, so i...
C2 2 molecular orbital diagram
We will fill the 8 electrons in the molecular orbital diagram. The bond order for C 2 molecule is 2. Recall that the first covalent bond formed between two atoms is always a σ-bond. Since the bond order is 2, this corresponds to 1 σ-bond and 1 π-bond. Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ...
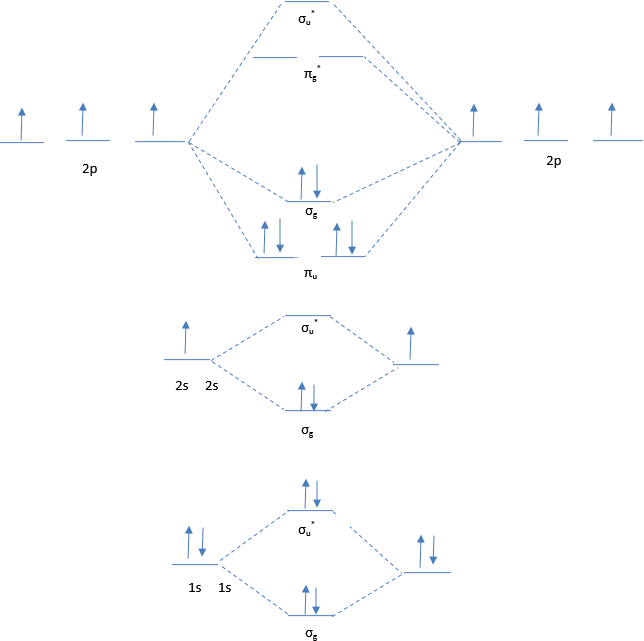
C2 2 molecular orbital diagram. The answer is C2- because of bond orders. When we draw the C2 MO, we have everything up till the PiPy Orbitlal filled, and the next orbital tht would be filled would be the sigma2Pz orbital. As for bond orders it is 1/2* [ (#e- in bonding orbitals)- (#e- in antibonding orbitals)] Doing this, normally just C2 is 1/2* [ (8)-4]=2. Example 2. Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11. The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be. Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron.
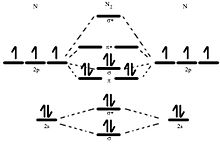
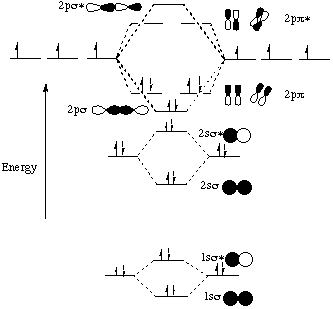
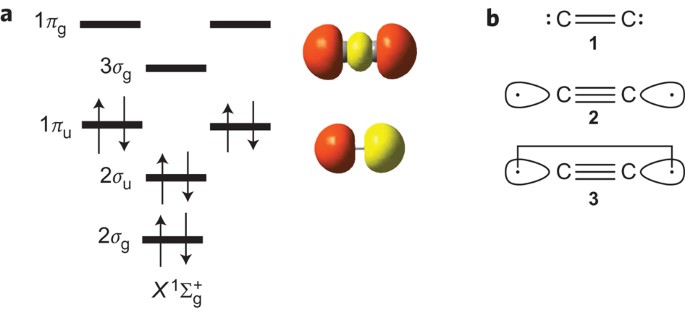
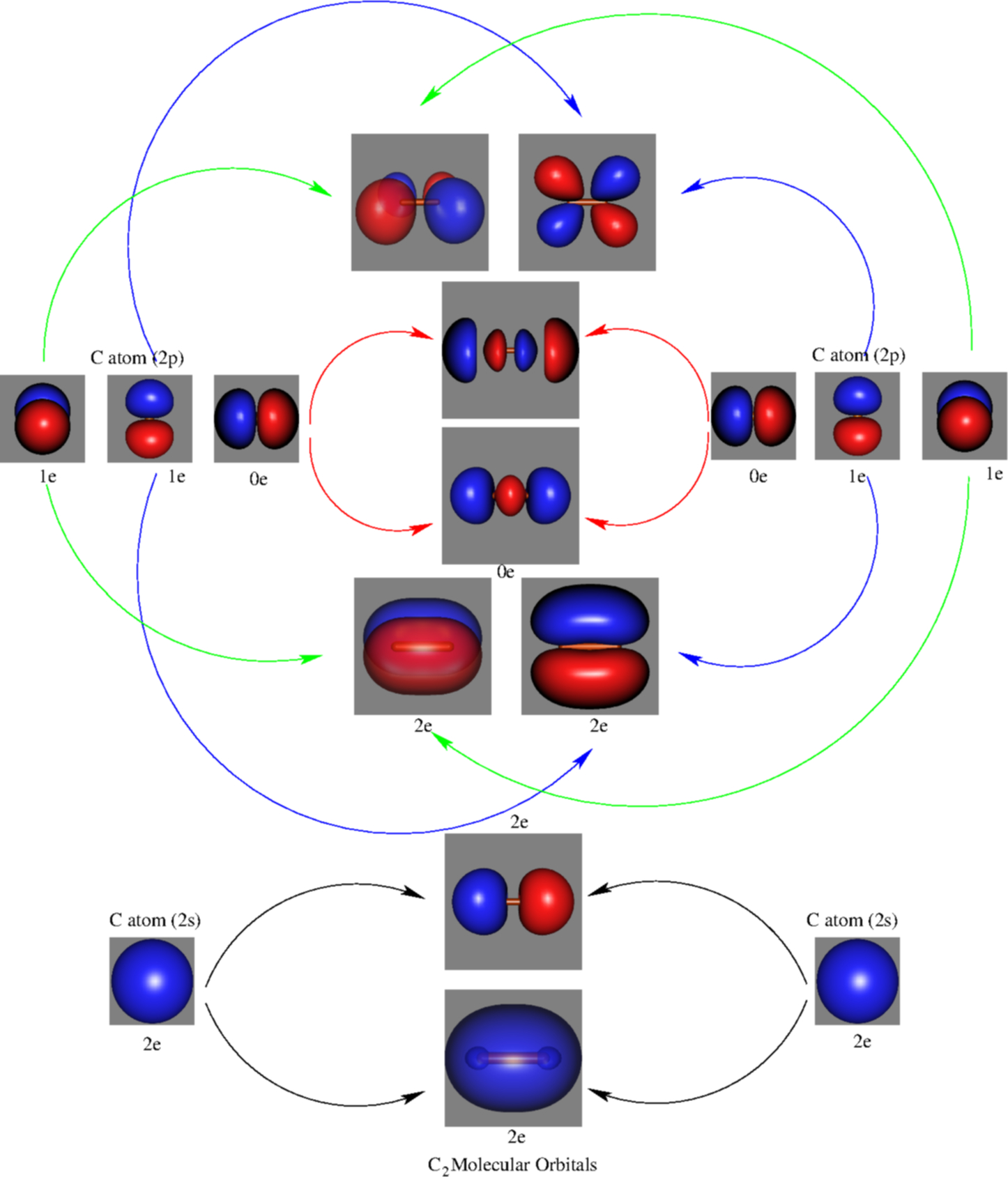
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Question: 12. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for C. The number of electrons in the 2p. molecular orbital is 1. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e.zero 13. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for C. The number of electrons in the C2, molecular orbital is 1 6.2 6.3 d. 4 e zero 14. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for N. From Molecular Orbital Diagram, which is most stable? A. C2 2-B. B2 C. B2 2+ D. N2 2+ E. C2 2+ A. C2 2-Which of the following molecules contains polar bonds but has a zero dipole moment? A. N2 B. NH3 C. CO2 D. BrCl E. CH3Cl. C. CO2. Which of the following statements is false? A. The rate of vaporization increases with increasing surface are. What is the molecular orbital configuration of C2? Looking at the appropriate MO diagram, we see that the π orbitals are lower in energy than the σp orbital. The valence electron configuration for C2 is (σ2s)2(σ∗2s)2(π2py,π2pz)4 ( σ 2 s ) 2 ( σ 2 s ∗ ) 2 ( π 2 p y , π 2 p z ) 4 .
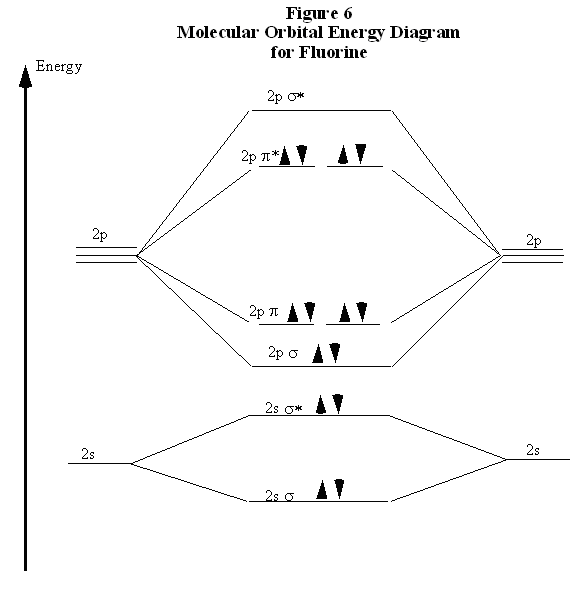
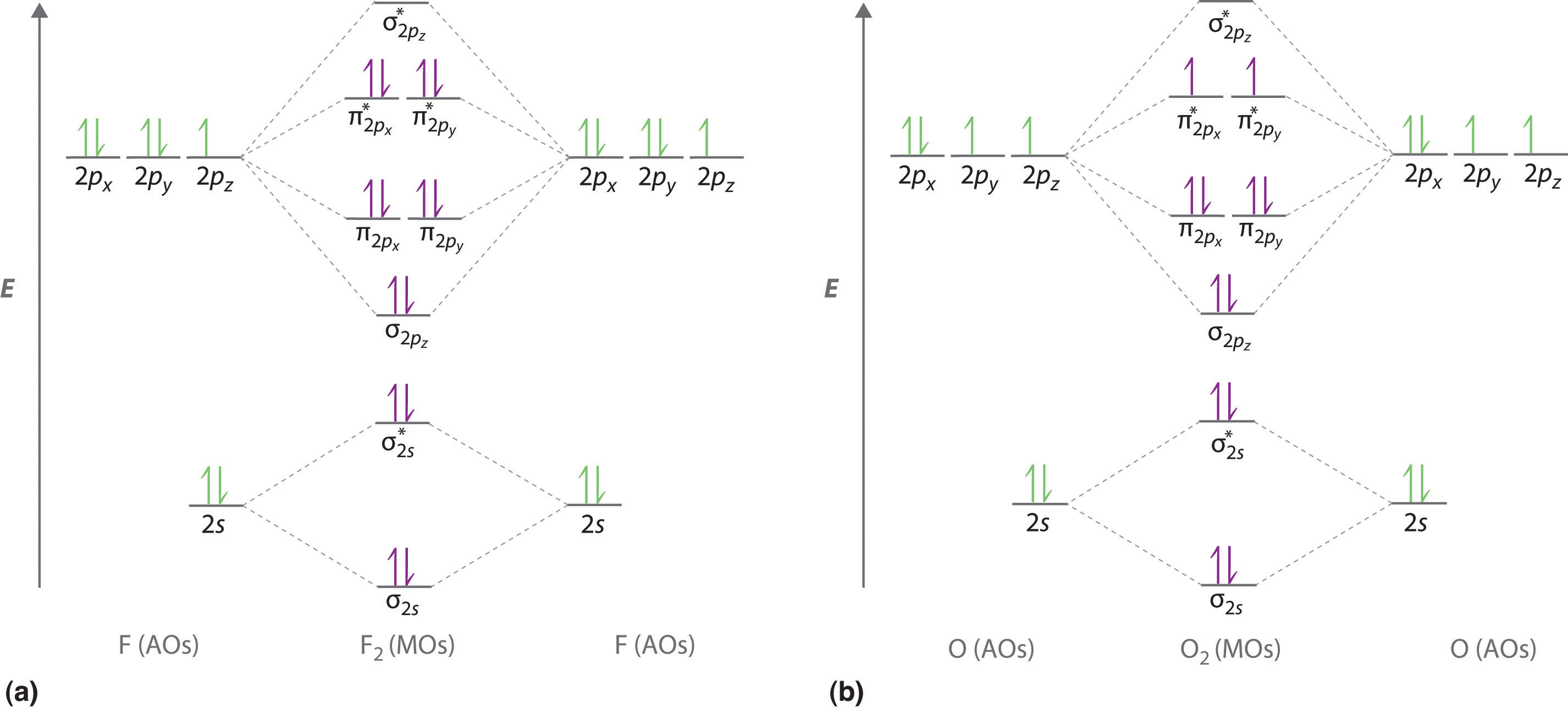
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2. From the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Answer. N 2 has a bond order of 3 and is diamagnetic. Example \(\PageIndex{3}\): Ion Predictions with MO Diagrams. Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in \(\ce{C2^2-}\). Will this ion be stable? Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... Subjects. Science. Chemistry Video Lessons Exam Reviews ACS Video Solutions Solutions Library. Organic Chemistry Video Lessons Exam Reviews ACS Video Solutions Solutions Library. Physics Video Lessons Exam Reviews Solutions Library. Biology Video Lessons Exam Reviews Solutions Library. The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
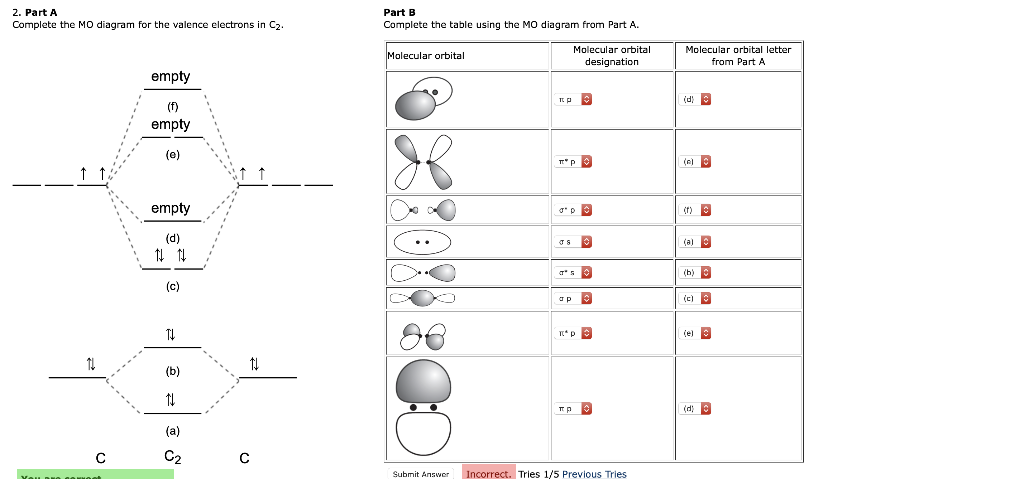
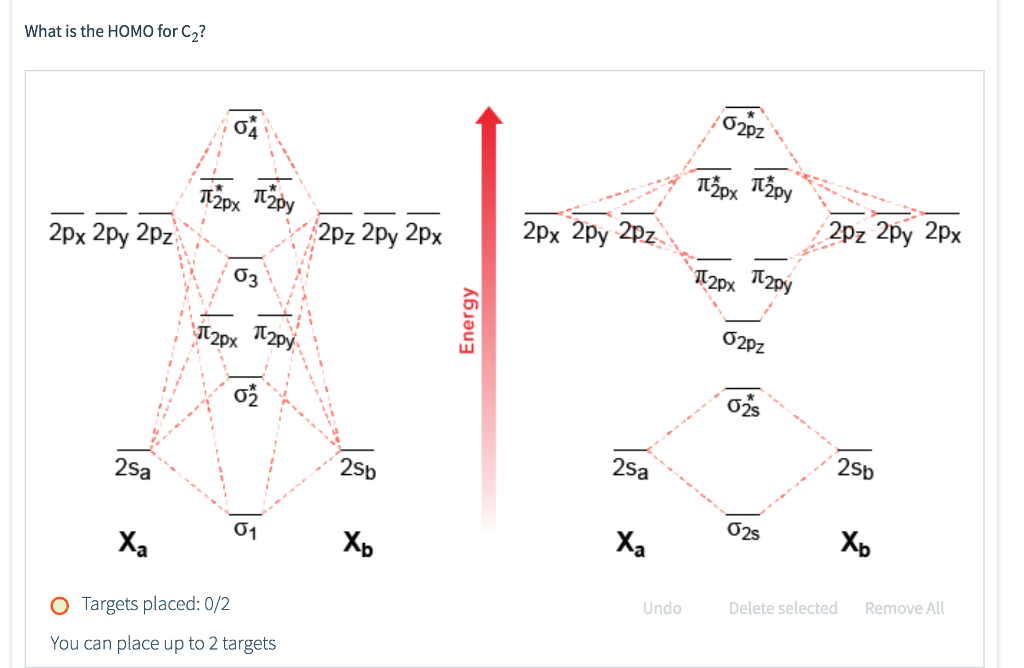
Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the C2 molecular ion. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons Energy Explanation Check ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the C2 molecular ion. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion ...
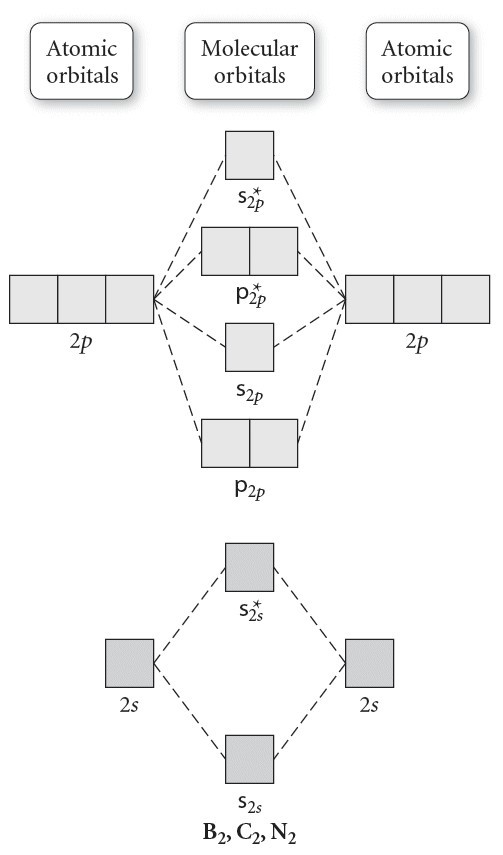
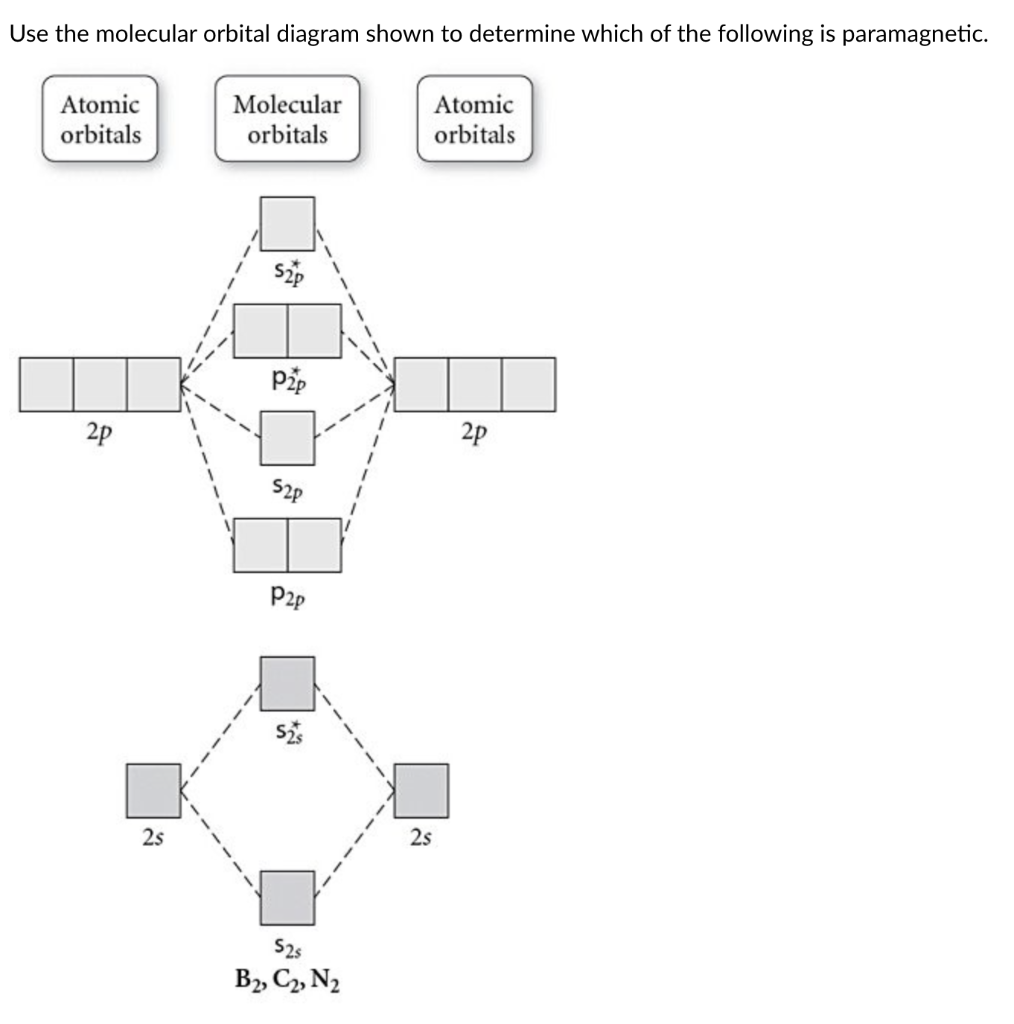
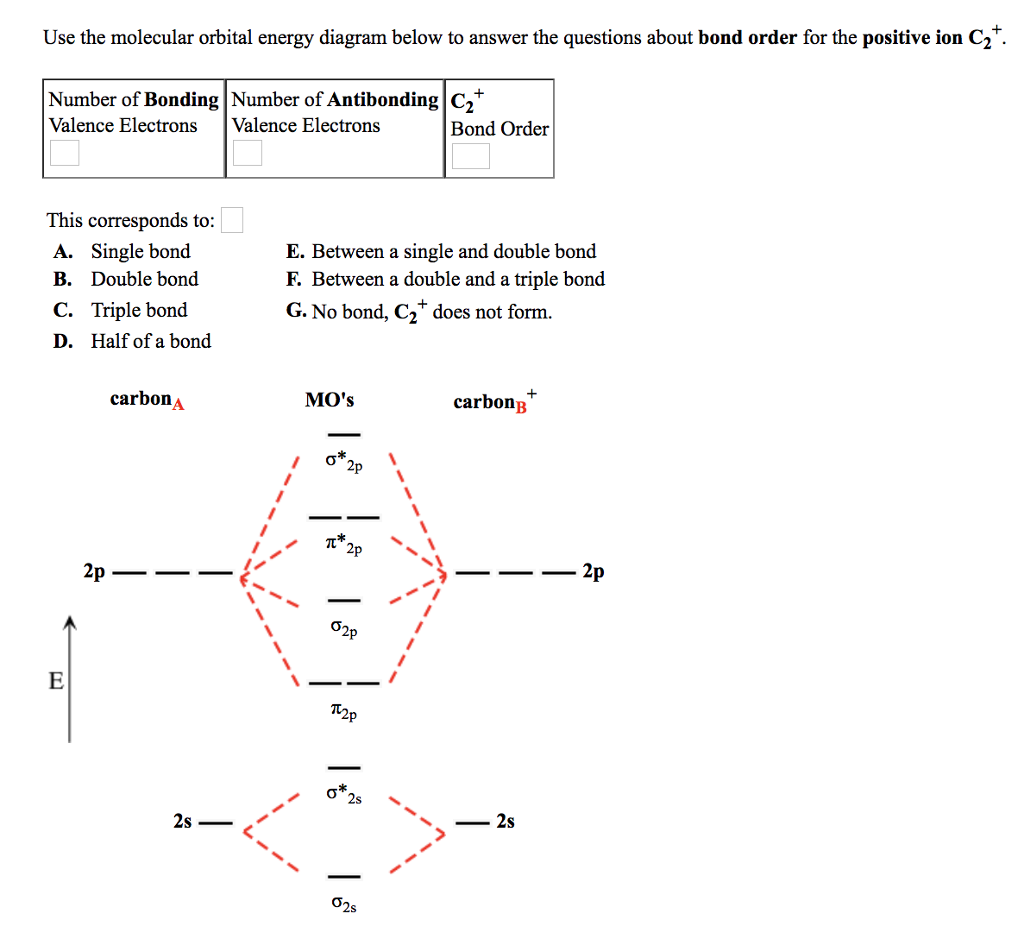
B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 Order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as CO. Mar 26, · This video shows the MO diagrams of the C2, N2, O2 and F2 molecules.A molecular orbital (MO) energy level diagram - Parkway C-2Use the molecular orbital ...
Answer (1 of 5): C2 exists, but only above 3,642 °C (6,588 °F) i.e. in vapor state
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.The ...
4 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus.
molecular orbital diagram for C2. number of electrons in the sigma2p molecular orbital is. 0. molecular orbital diagram for N2. number of electrons in the sigma2p molecular orbital is. 2. molecular orbital diagram for O2. number of elections in the pi*2p molecular orbital is. 1.
Answer (1 of 6): Short trick for bond order: C2- bond order is 12 * Example: This trick will work from total elctrone (8-20 )electrone.
Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9 . It is paramagnetic in nature. 6)Li2. Molecular orbital energy level of Li2.Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2 ...
Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer c2. For the ion c22. Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in cec22. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. N 2 has a bond order of 3 and is diamagnetic. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. Interact and form molecular orbitals. B calculate the bond order.
diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO 2 in Figure 5.25.
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ...
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
We will fill the 8 electrons in the molecular orbital diagram. The bond order for C 2 molecule is 2. Recall that the first covalent bond formed between two atoms is always a σ-bond. Since the bond order is 2, this corresponds to 1 σ-bond and 1 π-bond.
Solved 5 Draw Complete Molecular Orbital Diagrams To Compare The Bonding In C2 F2 And Cf A What Is The Bond Order Of Each B Which Of The Thre Course Hero
Solved 5 Draw Complete Molecular Orbital Diagrams To Compare The Bonding In C2 F2 And Cf A What Is The Bond Order Of Each B Which Of The Thre Course Hero







0 Response to "38 c2 2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment