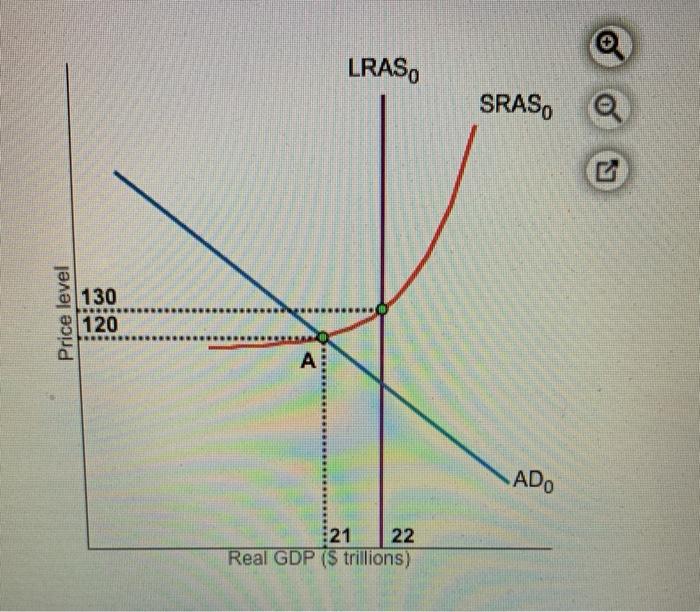
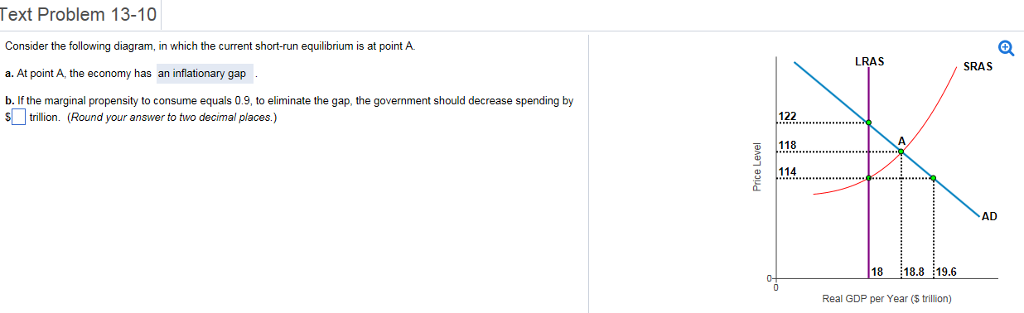
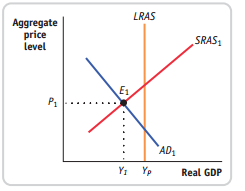
38 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.
3. Use the sticky-wage model of the short-run aggregate supply curve to work out the effects of the following changes on that curve: a. An increase in the target real wage, ω . Ans: The equation that we derived for the sticky-wage model was = ω P P Y F L e d rises even more than in the short run. This process continues until the long-run level of output is again reached. At the new equilibrium, point C, interest rates have risen to r3, and the price level is permanently higher. Note that, like monetary policy, fiscal policy cannot change the long-run level of output.
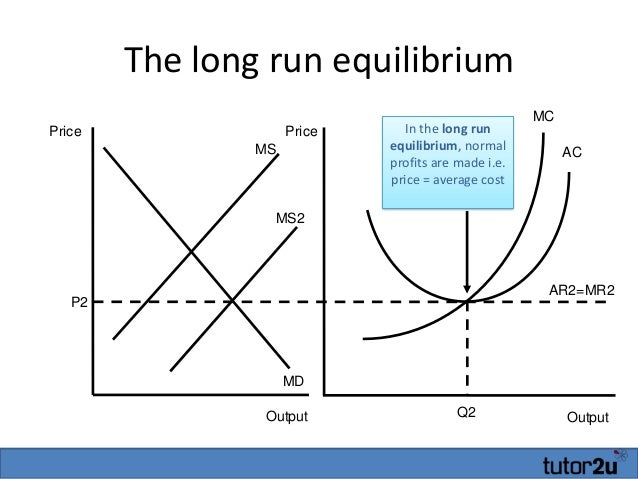
At this point, equilibrium price is OP 1 and industry supply is OQ 1. This is also long run equilibrium, to begin with. Hence, e 1 will be a point on the long run supply curve. ii. An upward shift in demand curve (D 3 D 4) will push the short run price to OP 2 at which the industry will supply OQ 2.

Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.
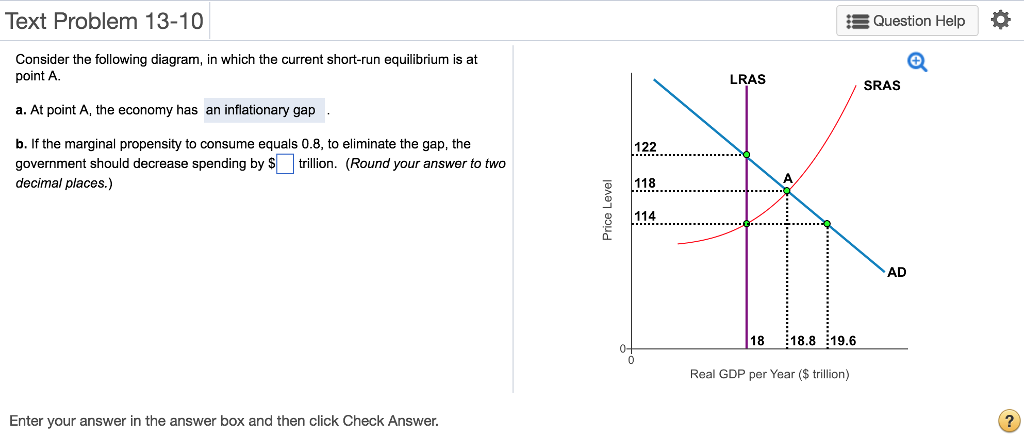
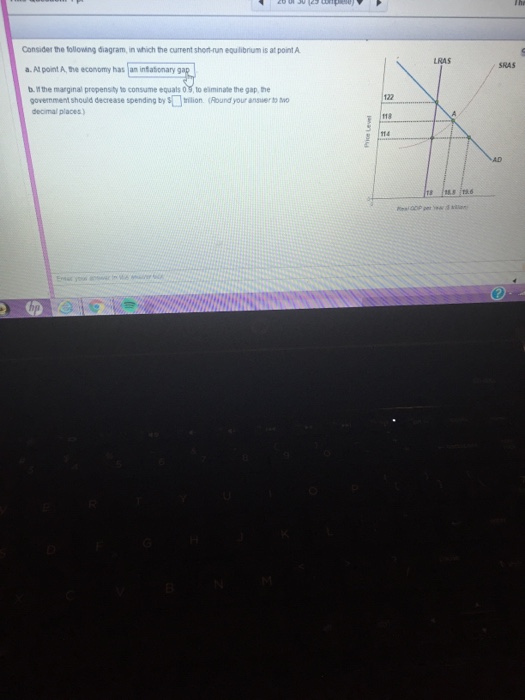
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has (an expectation gap / an inflationary gap / a recessionary gap) . If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $____ trillion. 1. shortrun equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has. 2. gap. 3. shortrun equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has. Assignment: 92 MyEconLab: Module Nine Homework Consider the following diagram, in which the current shortrun equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has. a recessionary gap 1 Answer to Consider the diagram below, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A, and answer the questions that follow. a. What type of gap exists at point A? b. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, what change in government spending financed by borrowing from the private sector could...
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.. View Homework Help - New Microsoft Word Document.docx from ECON 2302 at Collin College. Consider the following diagram, in which the current shortrun equilibrium is at point A. At point A. the 156 In the short run, in perfect competition, the loss per unit of output is PT and total loss for OM unit of output is PTSQ. The total loss PTSQ is the minimum loss that a firm can make under the given price - cost conditions. Since all the firms will be working under same cost conditions all would be in equilibrium at point T or output OM and every one will be making losses equal to PTSQ. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. (This is my answer, I think it's right). If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, calculate the change in governemtn spending that could eliminate the gap. $ ____ trillion. An increase in aggregate demand and a decrease in short run aggregate supply. Assume that the economy is in long run equilibrium. A shift in the aggregate demand curve will change. Only the price level in the long tun. Which of the following statements concerning economic growth is true? With long-run economic growth, there is an increase in ...
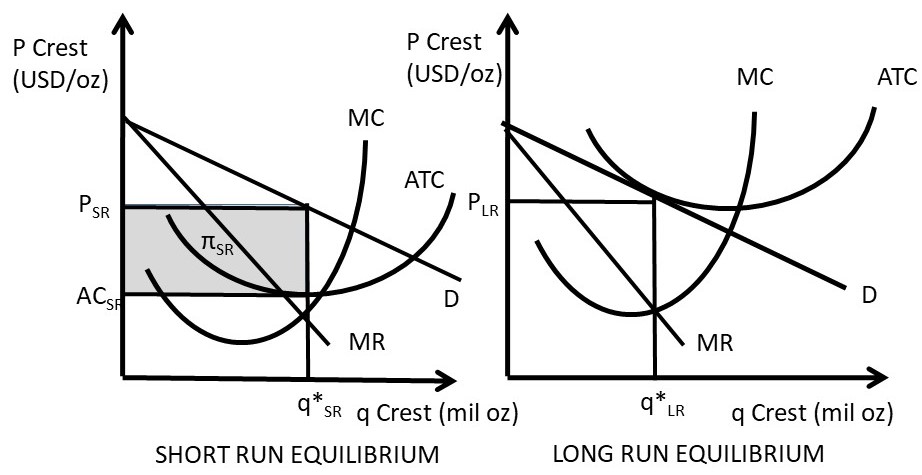
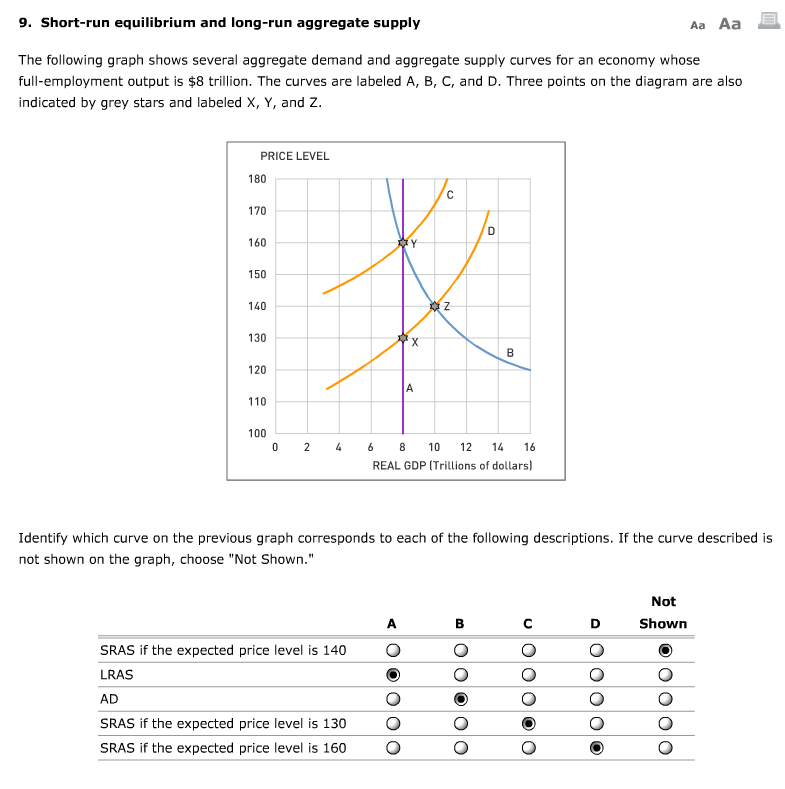
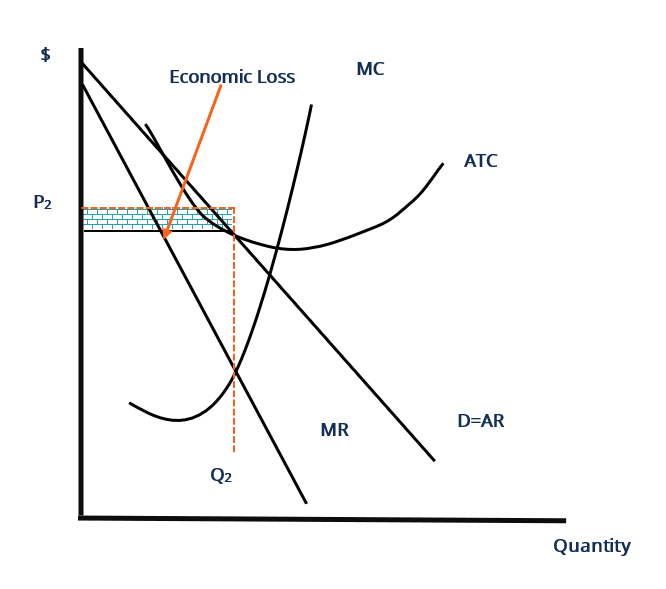
diagrams below depict the market demand and short-run supply curves for this industry and the ATC and MC curves of a representative firm — Lalinda Company. This industry is initially in long-run equilibrium. a) Show in the diagram above the industry's equilibrium price and output and Lalinda's equilibrium output. Consider an economy described by the following short run model. C = c 1(Y-T) I = b 0 + b 1Y- b 2i Md/P = C-a*i G = G 0 T = T 0 Ms = M 0 All the parameters (a, b 0,b 1, b 2, c 1) in the model are positive, and b 1+ c 1<1. We assume for simplicity that P=1. Important: Note that unlike in the short run model we have seen in class, money demand 2. (10 points) Assume the economy is in short-run macroeconomic . equilibrium at point E1 in the diagram at right. Based on the diagram, answer the following: Is the economy facing an inflationary or a recessionary gap? _____ What policies can the government implement to bring the economy back to long-run equilibrium? Quick Quiz - Pure Competition - Long Run 1. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct? 1. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. 2. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. 3.
Short-run equilibrium. An economy is in short-run equilibrium when the aggregate amount of output demanded is equal to the aggregate amount of output supplied. In the AD-AS model, you can find the short-run equilibrium by finding the point where AD intersects SRAS. The equilibrium consists of the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium output. (f) Draw the short-run Phillips curve that you found, labeling the coordinates of the points on it that correspond to points A and B above. Using point B, and the long-run equilibrium point we get the following short-run Phillips curve. Inflation rate . 1% Unemployment rate 2% B 5% 0% A 9-2 MyEconlab Module Nine Homework-Jennifer Brown Instruetor: Allyson Clarke Gource: M BA-502-Q 3225-17TW3-Clarke htps ://xlitemprod.pearsoncm g.coml apilv l/print/en-us/econ Assignment: 9-2 MyEconlab Module i Nine Homework i Jennifer Brown 2t10t17 Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. Suppose that an economy begins at the short-run equilibrium shown as point A in the figure to the right. Identify which of the other points on the diagram-points B , C, D, or E-could represent a new short -run equilibrium after the described events given below take place and move the economy away from point A.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has _____. b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.5 , to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $____ trillion.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap.. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.25 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $0.25 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places.
C) Wages would increase, causing the AS curve to shift to the right, reaching a new equilibrium at point E. D) Wages would increase, causing the AD curve to shift to the right, returning to the original equilibrium at point A. E) Potential output would decrease from 1000 to 900 and a new long-run equilibrium would be established at point D.
the diagram on the right. At the initial equilibrium (point A), there is now a surplus in the external sector because of the improvement in the balance of the current account. The central bank, therefore, buys foreign currency to eliminate the surplus and the domestic money supply increases. Graphically, the increase in
approach money market equilibrium in the short run (here) and the way we approached it in the long run (chapter 14). • In Chapter 14 we made the following long-run assumptions: In the long run the price level P is fully flexible and adjusts to bring the money market to equilibrium;
The short-run equilibrium in this economy is at point A, where AS and AD intersect. At this point, the goods market, the Pe financial market, and the labor market are all in equilibrium. If the equilibrium level P=1 of output equaled the natural level of output (and if the actual price level equaled the expected price level), the equilibrium ...
(a) Using a correctly labeled graph with both the short-run and long-run Phillips curves and the relevant numbers from above, show the current long-run equilibrium as point A. (b) Calculate the real interest rate in the long-run equilibrium. (c) Assume now that the Federal Reserve decides to target an inflation rate of 3 percent. What open-market
b. Suppose that Macroland experiences a negative demand shock. Graph the short-run changes in the original equilibrium that will occur because of this demand shock. On your graph, identify the new short-run equilibrium level of output (Y 2) and the new short-run equilibrium aggregate price level (P 2). Label any shifts in AD or AS clearly. c.
x One point is earned for showing a rightward shift of the AD curve. x One point is earned for showing the new equilibrium output and price level. (c) 2 points: x One point is earned for a correctly labeled graph of the short-run Phillips curve. x One point is earned for correctly labeling points A and B on the SRPC that indicate a leftward
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.25 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $.25 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places.

6 Short Run Perfectly Competitive Equilibrium Consider A Perfectly Competitive Market For Wheat In Chicago There Are Homeworklib
A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 "Changes in Demand and Supply" shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
1 Answer to Consider the diagram below, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A, and answer the questions that follow. a. What type of gap exists at point A? b. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, what change in government spending financed by borrowing from the private sector could...
1. shortrun equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has. 2. gap. 3. shortrun equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has. Assignment: 92 MyEconLab: Module Nine Homework Consider the following diagram, in which the current shortrun equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has. a recessionary gap
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has (an expectation gap / an inflationary gap / a recessionary gap) . If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $____ trillion.
Solved Include Correctly Labeled Diagrams If Useful Or Required In Explaining Your Answers A Correctly Labeled Diagram Must Have All Axes And Cu Course Hero

The Following Diagram Shows The Market Demand For Steel Use The Orange Points Square Symbol To Homeworklib

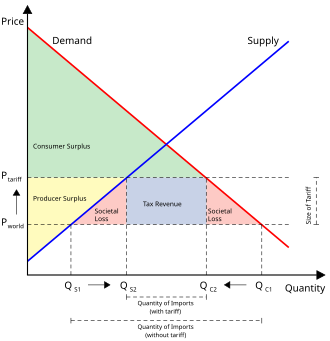
2 The Impact Of Fiscal Policy On The Balance Of Payments Recent Experience In The United States In Fiscal Policy Economic Adjustment And Financial Markets
















0 Response to "38 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a."
Post a Comment