38 ray diagram convex mirror
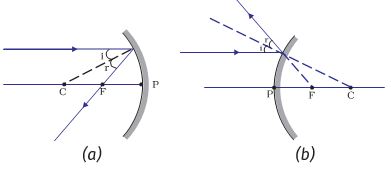
23.04.2020 · For a concave mirror , we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection For a convex mirror, since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis Rule 3 - Ray passing through Center of Curvature will follow the same path back after reflection One goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the double convex lens. Typically, this requires determining where the image of the upper and lower extreme of the object is located and then tracing the entire image. After completing the first three steps, only the image location of the top extreme of the object has been found. Thus ...
However, if one of the surfaces is flat and the other convex, then it is called a plano-convex lens. Difference between convex and concave lens: There is another type of lens known as concave lens. The major differences between concave and convex lens two are: CONVEX CONCAVE; This lens converges a straight beam of light. This lens diverges a straight beam of light. This lens is thicker at the ...
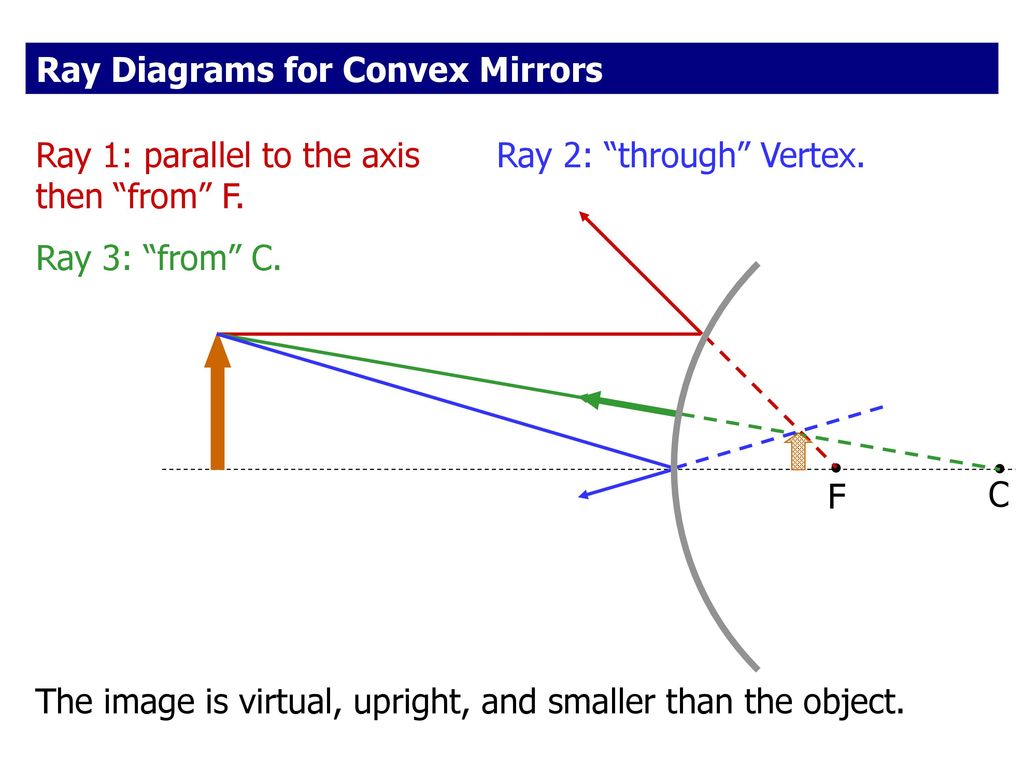
Ray diagram convex mirror
Convex Mirror: Convex mirror is a curved mirror for which the reflective surface bulges out towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards (diverging light rays) and therefore they are not used to focus light. The image is virtual, erect and smaller in size than the object, but gets larger (maximum upto the size of the object ... In this video from The Physics Classroom's video tutorial series, Mr. H demonstrates how to draw a ray diagram for objects located in front of convex mirrors... Your browser does not appear to support HTML5. Try upgrading your browser to the latest version. What is a browser? Microsoft Internet Explorer Mozilla Firefox Google ...
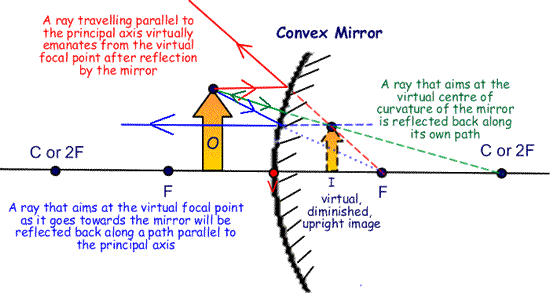
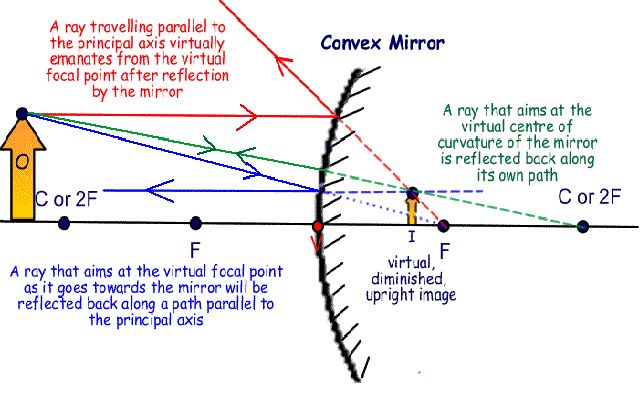
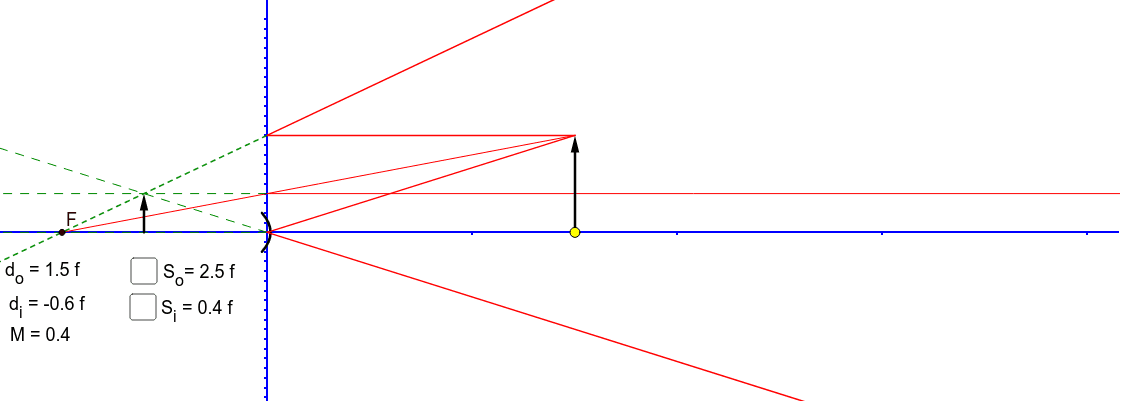
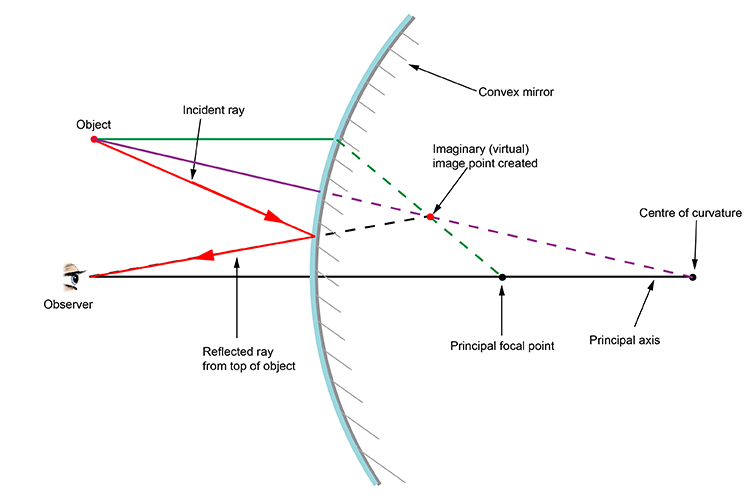
Ray diagram convex mirror. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. In case of a convex mirror any ... In this video I have taught how to draw ray diagrams of image formation by Convex Mirror in easy way. Convex Mirrors Mirror equation still holds, but: f& R now negative Virtual image, always upright. Liu UCD Phy9B 07 9 Summary: Signs ... Ray Diagram for Thin Lenses Ray 1 goes out from Q parallel to the axis & passes through F2. Ray 2 goes through the center of the lens unaffected
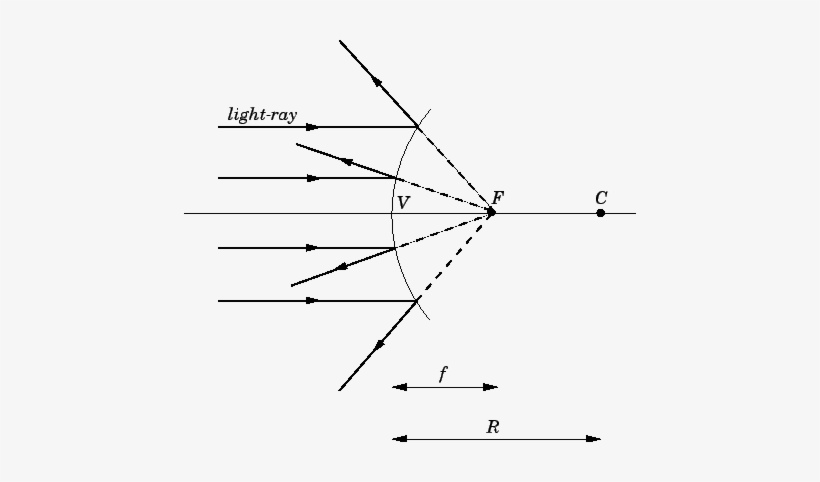
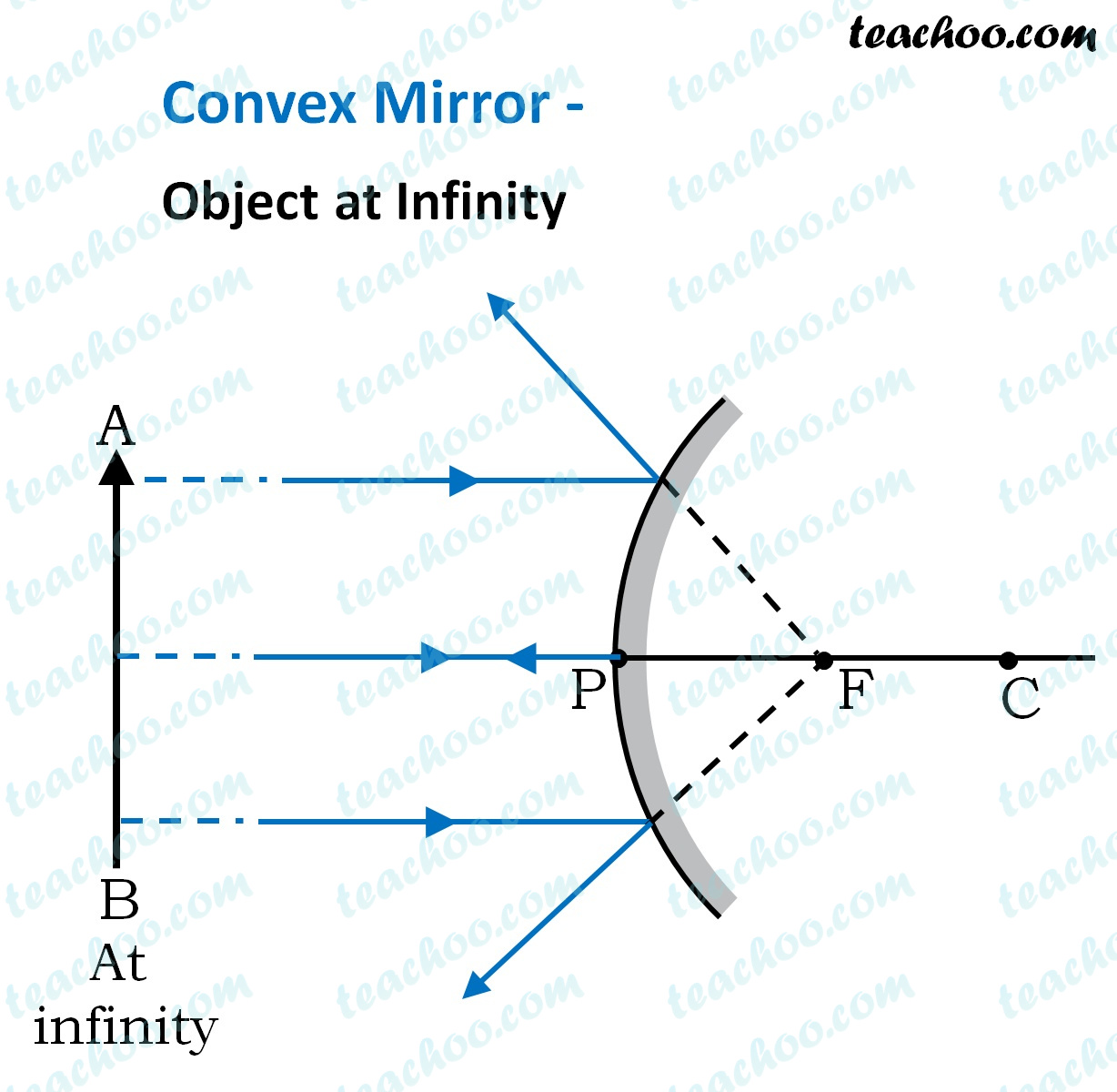
23.04.2020 · Concave Mirror - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 23, 2020 by Teachoo. For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis Since ray parallel to principal axis passes through the Focus ... 23 Apr 2020 — For a Convex Mirror,The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirrorSo, there will only be 2 cases.Between infinity and the pole P of the mirror: B...At infinity: At the focus F, behind the mirrorPosition of the object: Position of the image A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of ... 07.07.2020 · Convex Mirror Ray Diagram. Applications of Convex Mirrors. As side view mirrors in cars, buses, and trucks because the image formed is upright and small thus giving a wide field of view of the area toward the side of and behind the vehicle; As a security device in supermarkets, grocery stores, and convenient stores since the convex mirror gives a broad view of the area around corners ; At ...
The Physics Classroom » Curriculum Corner » Reflection and Mirrors » Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors. The document shown below can be downloaded and printed. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum. Visit the Usage Policy page for additional information. Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror. 28 Mar 2021 — Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams ... Two possibilities of the position of the object are possible in the case of a convex ...Position of object: Position of imageWithin focus(Between P and F): Behind the mir...Between F and C: Beyond CBeyond C: Between F and C A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size.
Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror. Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Guidelines for Rays Falling on the Concave and Convex Mirrors. When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely.
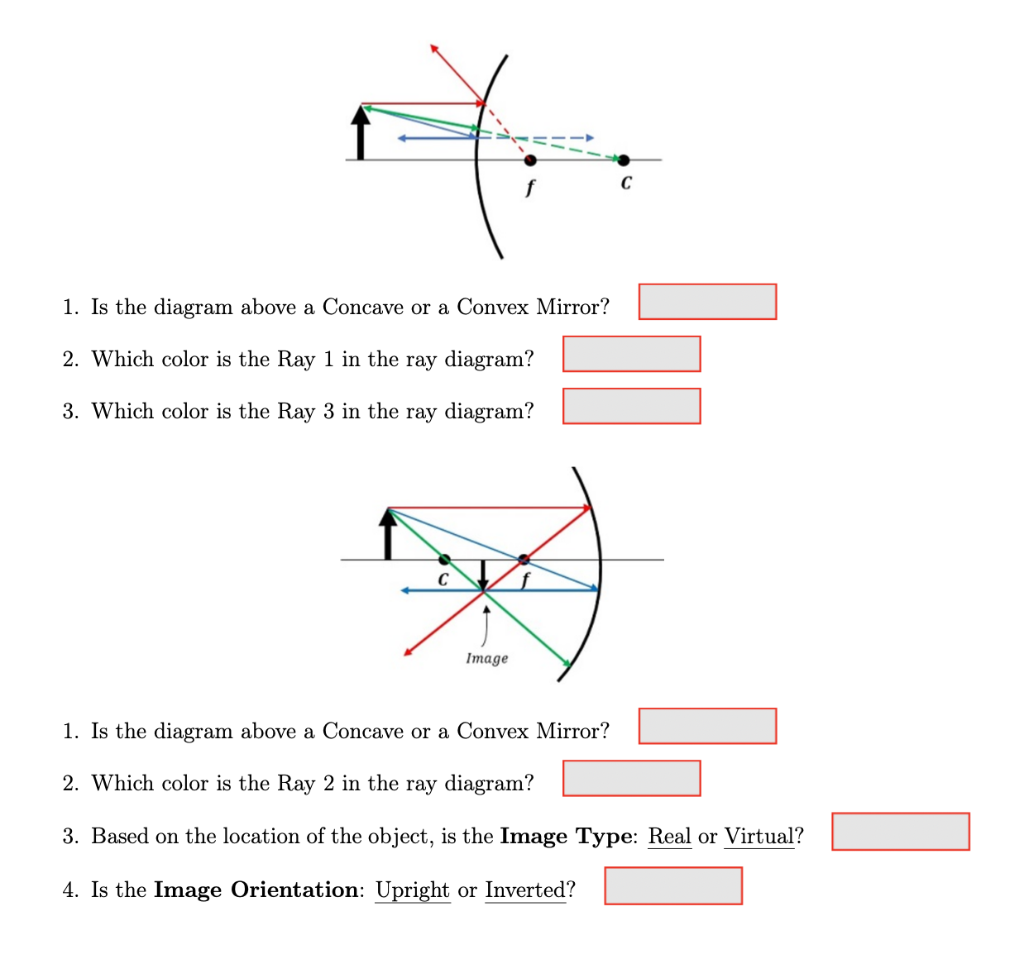
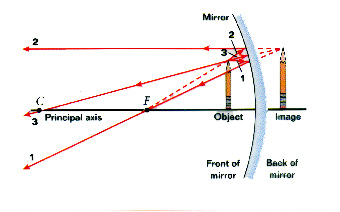
Ray diagrams can be used to determine the image location, size, orientation and type of image formed of objects when placed at a given location in front of a mirror. The use of these diagrams was demonstrated earlier in Lesson 3 and in Lesson 4.Ray diagrams provide useful information about object-image relationships, yet fail to provide the information in a quantitative form.
As the ray diagram shows, the image for a convex mirror is virtual, and upright compared to the object. A convex mirror is the kind of mirror used for security in stores, and is also the kind of mirror used on the passenger side of many cars ("Objects in mirror are closer than they appear."). A convex mirror will reflect a set of parallel rays in all directions; conversely, it will also take ...
Your browser does not appear to support HTML5. Try upgrading your browser to the latest version. What is a browser? Microsoft Internet Explorer Mozilla Firefox Google ...
In this video from The Physics Classroom's video tutorial series, Mr. H demonstrates how to draw a ray diagram for objects located in front of convex mirrors...
Convex Mirror: Convex mirror is a curved mirror for which the reflective surface bulges out towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards (diverging light rays) and therefore they are not used to focus light. The image is virtual, erect and smaller in size than the object, but gets larger (maximum upto the size of the object ...
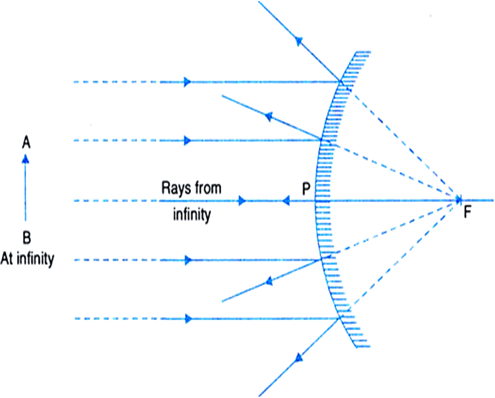
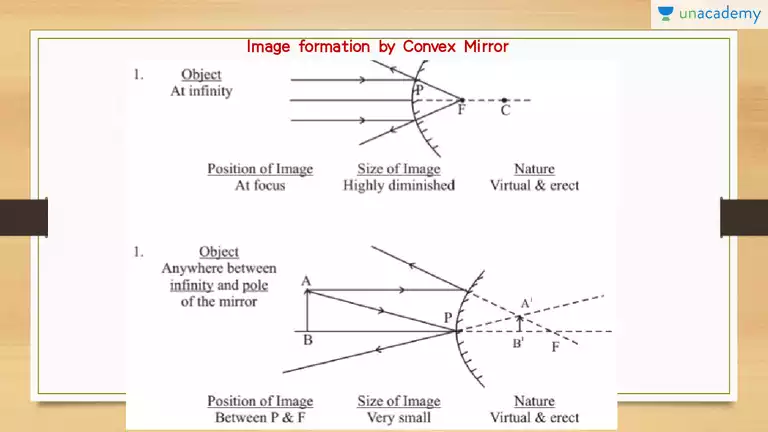
With The Help Of Ray Diagrams Explain The Formation Of Images By A Convex Mirror For The Following Position Of The Object I Object Between Pole And Infinity Ii Object At Infinity From Science
Draw And Explain The Ray Diagram Formed By A Convex Mirror When Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Concave And Convex Mirror Ray Diagrams By Dcaulf This Hand Drawn Cartoon Video Demonstrates How To Concave Mirrors Convex Mirror How To Memorize Things

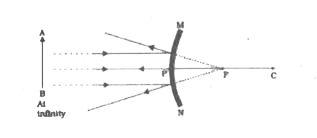
Draw A Labelled Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Image In A Convex Mirror When The Object Is At Infinity Mark Clearly The Pole And Focus Of The Mirror In The Diagram
Draw The Ray Diagram And Find The Position Nature And Size Of Image Formed By A Convex Mirror If The Object Is Placed I At Infinity Ii Between Infinity And The Pole


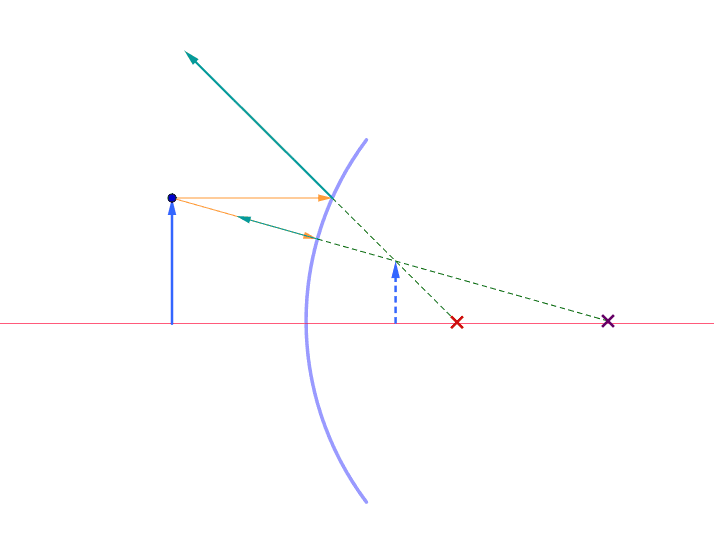











0 Response to "38 ray diagram convex mirror"
Post a Comment