39 meiosis crossing over diagram
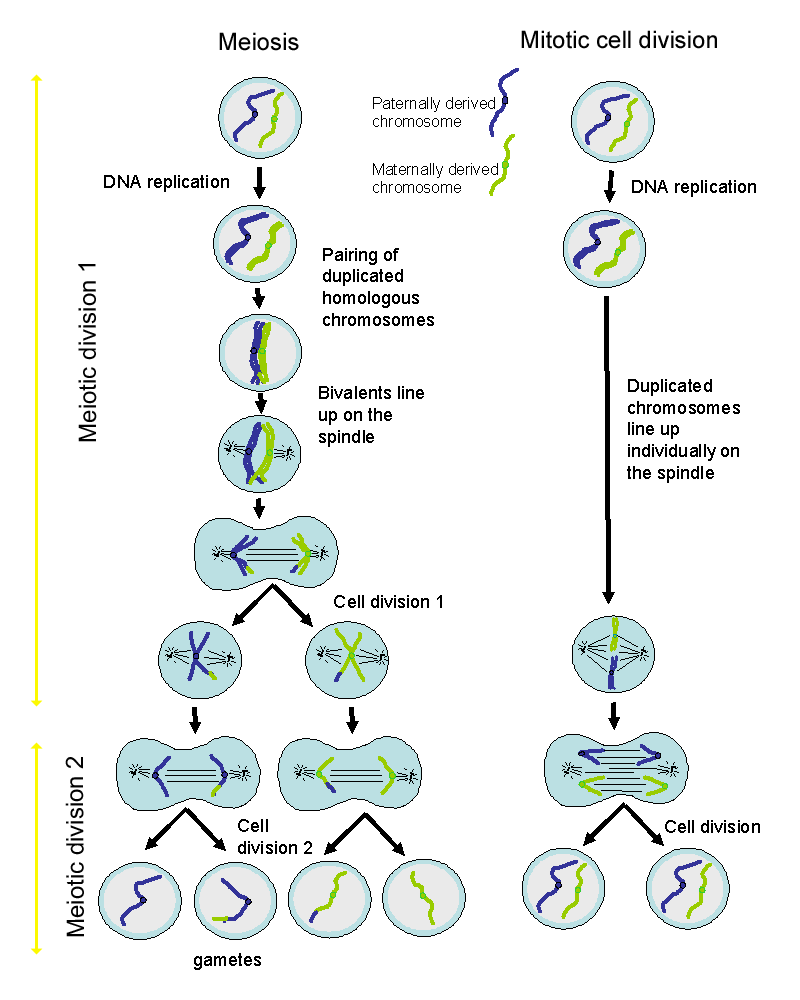
Meiosis is a rather long process than that of mitosis because it takes place in two cycles involving the separation of chromosomes. The process is longer due to the phases of prophase which takes place in two phases i.e prophase I and prophase II. Prophase I is quite complex which involves the pairing up... Meiosis is the process of cell division that halves the chromosome number and makes gametes Meiosis is a very technical process that is most easily described in diagrams and tables (see above Chromosomes condense, Crossing over occurs. Metaphase I. Homologous chromosomes pair up...
Meiosis, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each with half the number of chromosomes of the The process of meiosis is characteristic of organisms that reproduce sexually and have a diploid set of chromosomes in the nucleus.

Meiosis crossing over diagram
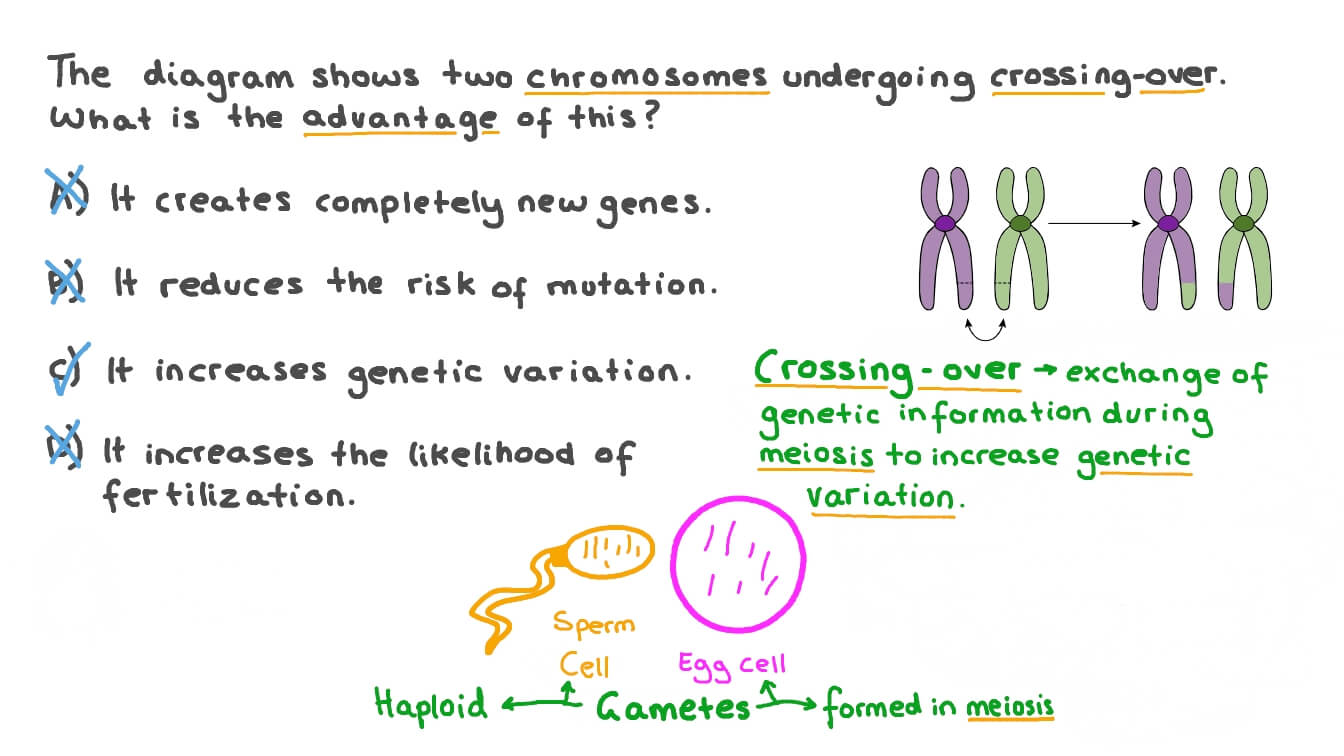
Crossing over is a biological occurrence that happens during meiosis when the paired homologs, or chromosomes of the same type, are lined up. ... And it's this crossing over that lets recombination across generations of genetic material happen, and it also allows us to use that information to find the... Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: crossing over, meiosis I, meiosis II, and genetic variation. Meiosis and genetic diversity. Fertilization terminology: gametes, zygotes, haploid, diploid. Chromosomal crossover in meiosis I.
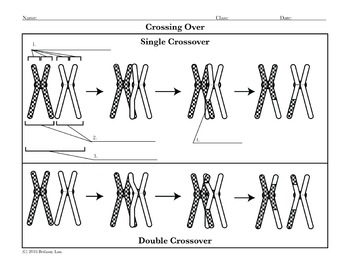
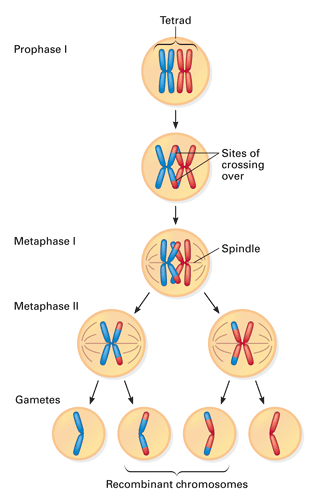
Meiosis crossing over diagram. Meiosis, Crossing Over. 1. Meiosis, Mechanism of Crossover, Significance in evolution. 16. Crossing over and Chiasmata • Chiasmata is the point where two homologous non- sister chromatids exchange genetic material during crossing over during meiosis. • Crossing over events dring meiosis help produce genetic variation. During prophase of meiosis I, the paternal homologous chromosome Crossing over occurs when a paternal chromatid exchanges part of itself with the maternal chromatid, so some alleles that were on one chromatid are now on the other. As an example, consider the meiosis II diagram above, which shows the end products of meiosis for a simple cell with a diploid number of 2n = 4 This diversity of possible gametes reflects two factors: crossing over and the random orientation of homologue pairs during metaphase of meiosis I. Cell Cycle Division: Part 2 - Meiotic Bead Diagrams (With Crossing Over). Prophase I: One chromosome from mother one from father come. Crossing over only occurs in meiosis I. Why do you use non-sister chromatids to demonstrate crossing over?
Crossing over results in a shuffling of genetic material and is an important cause of the genetic variation seen among offspring. Crossing over is a biological occurrence that happens during meiosis when the paired homologs, or chromosomes of the same type, are lined up. Learn meiosis cell division for A-level Biology. I explain the two mechanisms in meiosis that introduce genetic variation:Independent segregation and... Crossing over is essential for the formation of chiasmata, connections between homologs that become evident upon structural remodeling of Figure 1: Diagram of meiotic events during oogenesis in the C. elegans germ line. For simplicity, a single pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. Recombination/crossing over of chromosomes during prophase I. Below is a mitosis and meiosis Venn Diagram that summarizes all the key mitosis vs meiosis similarities and differences. On the left side of the diagram, you can see the key features of mitosis, on the right are the key features of...
Crossing over or shuffling of genes during meiosis is the major reason for genetic variation within species. Due to crossing over in meiosis, organisms may exchange genes and cause genetic variation in species. This variation serves the raw material of evolutionary process. Diagram of the meiotic phases. During meiosis, specific genes are more highly transcribed.[11][12] In addition to strong meiotic stage-specific expression of In this stage homologous recombination, including chromosomal crossover (crossing over), is completed through the repair of the double... Crossing over occurs in prophase 1 in meiosis (that's the one that creates gametes). Crossing over is a source of genetic variation. If you have taken any sort of high school biology you should know this, and if you're not taking a biology class why would you need to know this? Crossing Over in Meiosis. AP Biology Ch. Presentation Transcript. Crossing Over in Meiosis AP Biology Ch. 13 Ms. Haut. Crossing Over • Process by which parts of homologous chromosomes are interchanged • Crossing over and independent assortment are mechanisms that produce new...
Explain the process of "crossing over" in meiosis. How is it related to genetic diversity and genetic variability? Crossing over happens when the homologous chromosomes line up. When this occurs, the ends of the chromosomes may exchange segments of genetic material with their homologous pair.
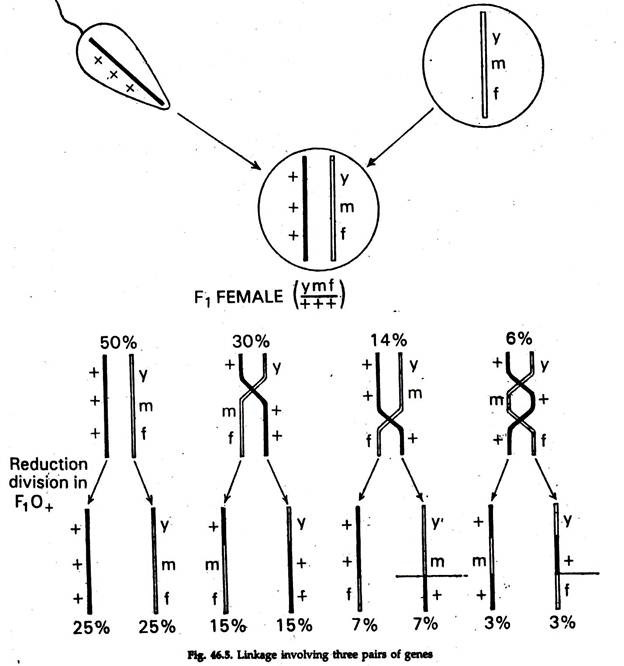
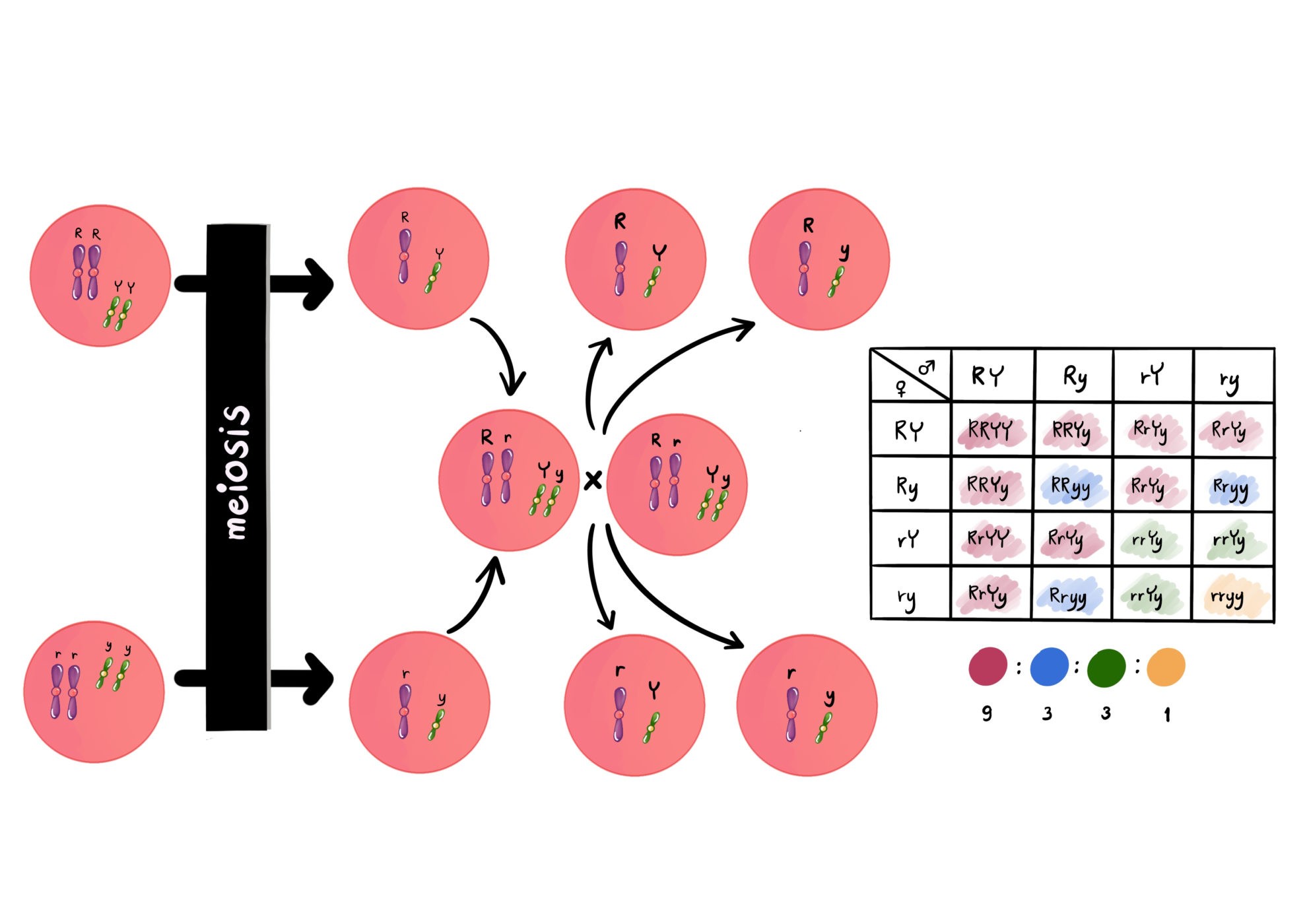
Mitosis: no crossing over & Meiosis: crossing over in prophase I. example / diagram of a cross involving all three alleles. 8. Describe the inheritance of ABO blood groups including an example of the possible outcomes of a homozygous blood group A mother having a child with a blood group O father.

What Is Crossing Over In Meiosis Crossing Over Example Recombination Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Display the crossing over diagram. Distribute Crossing over diagrams and markers to students. Share a brief animation, Meiosis: Crossing-Over. Be prepared to stop the video clip at different points to ask questions: What does sister mean in this context?

Which Diagram Demonstrates How Crossing Over Contributes To Genetic Variety During Meiosis A Answer Brainly Com
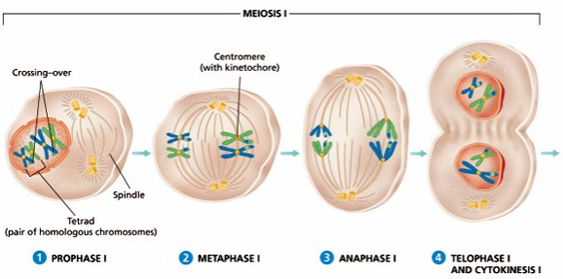
Phases of Meiosis. Meiosis Stages Diagram. The homologous chromosomes exchange parts of DNA with each other; this process is known as crossing over. The points of physical contact from which the genetic materials are exchanged are known as chiasmata.
Crossing over plays a critical role in increasing the genetic variation among offspring of sexual reproduction. It is important to understand how crossing over occurs and its consequences in meiosis. Look carefully at the diagrams depicting different stages in meiosis in a cell where 2n = 6. Assume...
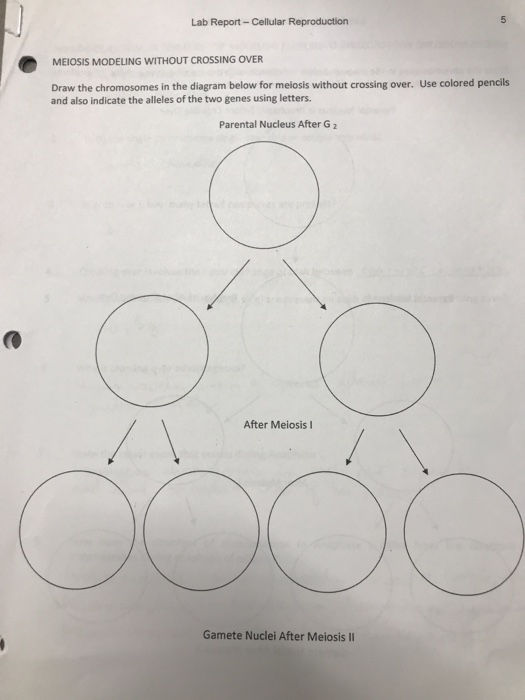
Meiosis and Crossing over. Published with reusable license by. After meiosis ends the chromatids break up into 4 haploids two that have not gone through crossing over (A)(B) and two that have (A)(b). If crossing over does not occur the genes will not be altered, meaning a clone of the parents would...
During meiosis, crossing over occurs during prophase I. It is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that results in recombinant chromosomes, which contribute to genetic diversity. During prophase I, each of the homologous pairs of chromosomes can be seen as...

Chromosomal Crossover Maternal Paternal Homologous Chromosomes Stock Vector Illustration Of Chromosome Chromatid 166675042
Crossing over occurs during prophase I, one of the longest phases of meiosis. Recombination or crossing over has rarely been observed during mitosis. It is completed before the cell proceeds to either metaphase I or to the second meiotic division.

Given Diagram Shows A Pair Of Homologous Chromosomes During Meiosis Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xii Piv C05 E01 060 Q01 Png Width 80 Maximum Crossing Over Will Occur Between Genes
Over time, however, crossing over leads to a greater variety of genes in a population and contributes to a diversity of characteristics and increased fitness of the population. Mitosis: Labeled Diagram. Just Now Westbranch.k12.oh.us Show details. Crossing-over and Recombination During Meiosis.
Meiosis I. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which homologous chromosomes are separated. P-I: Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs.
Click hereto get an answer to your question In meiosis, crossing over is initiated at. Pachytene stage is characterized by formation of synaptonemal complex which allows the exchange of genetic material between two homologus chromosomes by a process known as crossing over.
Meiosis has a narrow but significant purpose: assisting sexual reproduction. In mitosis, a cell makes an exact clone of itself. This process is what is behind the growth of children into adults, the healing of cuts and bruises, and even the regrowth of skin, limbs, and appendages in animals like geckos and lizards.
How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: crossing over, meiosis I, meiosis II, and genetic variation. Meiosis and genetic diversity. Fertilization terminology: gametes, zygotes, haploid, diploid. Chromosomal crossover in meiosis I.
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells.
Crossing over is a biological occurrence that happens during meiosis when the paired homologs, or chromosomes of the same type, are lined up. ... And it's this crossing over that lets recombination across generations of genetic material happen, and it also allows us to use that information to find the...
















0 Response to "39 meiosis crossing over diagram"
Post a Comment