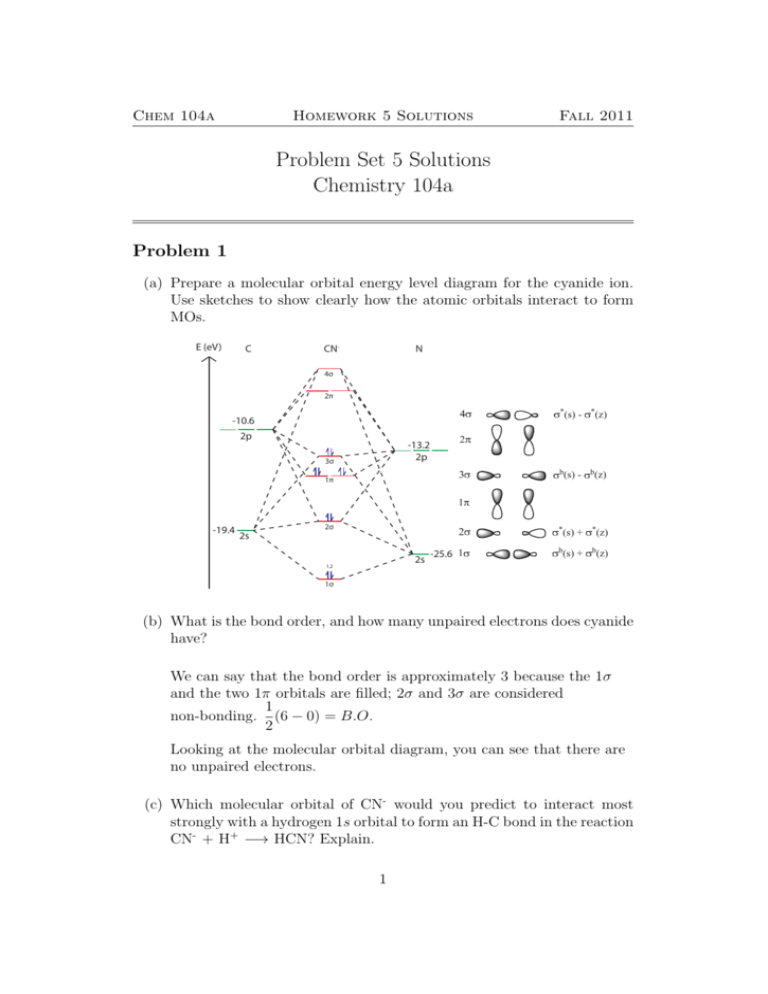
40 co molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital view of chemisorbed carbon monoxide. Click on the co molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Carbon monoxide lumo lowest unoccupied molecular orbital. In bacteria carbon monoxide is produced via the reduction of carbon dioxide by the enzyme carbon monoxide dehydrogenase an fe ni s ... Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ...
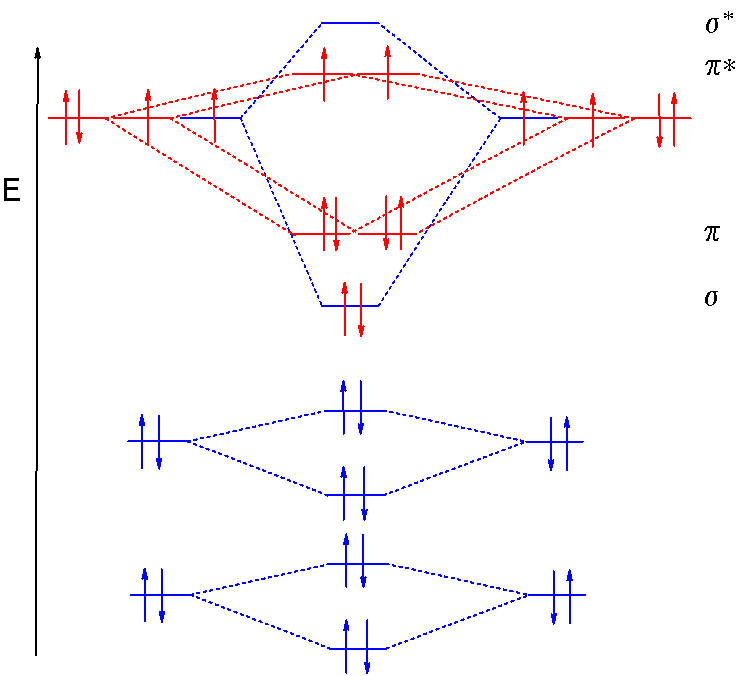
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.

Co molecular orbital diagram
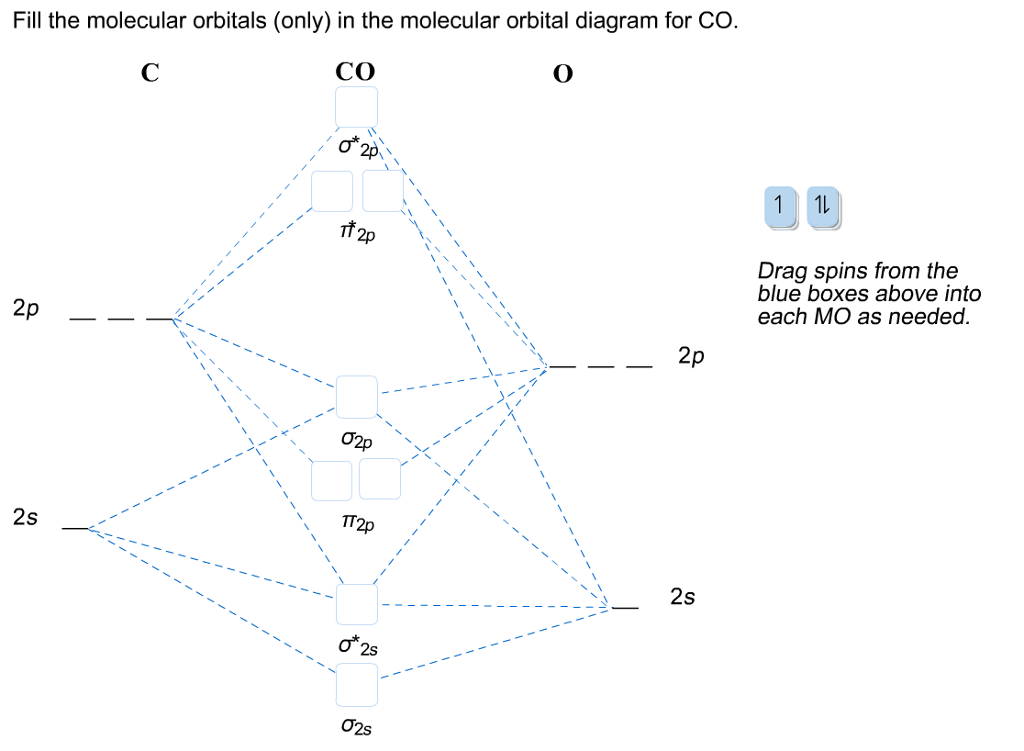
Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene Answer (1 of 10): The bond order of CO is 3. as Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N the bond order is 3, in acetylene H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order give... When the electronegativity of one atom is lower than the other, the more electronegative atom's orbitals are lower in energy. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. On the left you can see all of the orbitals. On the right, the total valence electrons (4 from C, 6 from O) have been added to the orbitals.
Co molecular orbital diagram. Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation. generic s-p valence MO diagram for carbon monoxide CO chain one can reasonably explain, that the HOMO of carbon monoxide must be of. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Molecular orbital diagram of co. The s orbitals and p z orbitals of both atoms are the correct symmetry to form σ interactions. Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. You have the here on this side you would have the energy so the energy is going up there. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
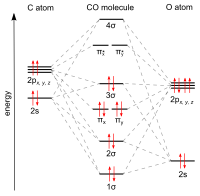
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen. A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram for short is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method (LCAO method) in particular. 32 Molecular Orbital Diagram For Co - Wire Diagram Source ... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... The molecular orbital diagram for CO molecule is shown in the following figure: (4) CN Molecule The electronic configuration of participating C and N atoms are: The total number of valence electrons is 9 and the electronic configuration of CN molecule can be written as:
May 09, 2018 · There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of carbon and 6.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. Which overlap is strongest? During the axial overlap of p-p orbitals, the electron density increases around the axis, so the bond formed is the strongest. Therefore, the strongest bond formed is when p-p orbital overlap occurs. Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- 2p ... Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... Molecular orbital diagram of CO and charge localisation. Ask Question Asked 1 year, 5 months ago. Active 1 year, 5 months ago. Viewed 110 times 4 1 $\begingroup$ MO diagram of CO. My question concerns the interpretation of the Molecular Orbital of CO. I think I find it clear how you build it but I have some concerns about how you rationalize it.
Molecular orbitals of carbon monoxide determined by LCAO. Carbon monoxide CO consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. The bond length is 1.128 Å. The molecular orbital Hamiltonian in this case is, rO r → O are the positions of the carbon atom and the oxygen atom and ZC eff = 3.25 Z eff C = 3.25 and ZO eff =4.55 Z eff O = 4.55 are the ...
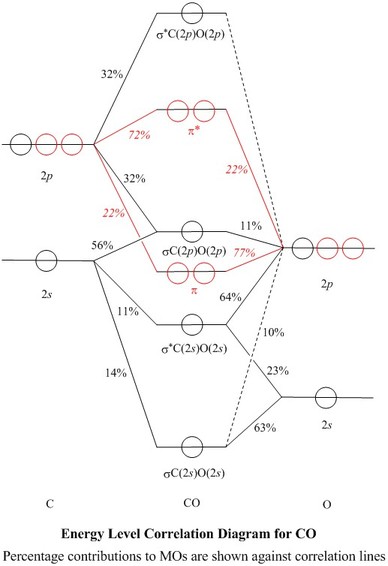
Molecular Orbitals for CO. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown The results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level.
Molecular orbital diagram of co. Tricky chemistry basics. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic ...
12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post, If you find it to be informative, pls share it and visit our website.
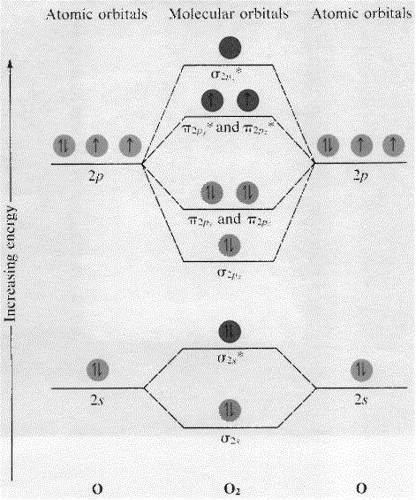
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions - Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2+, Rh2+, Ni3+, etc. . σ-ML4 Tetrahedral MO Diagram e. Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals.
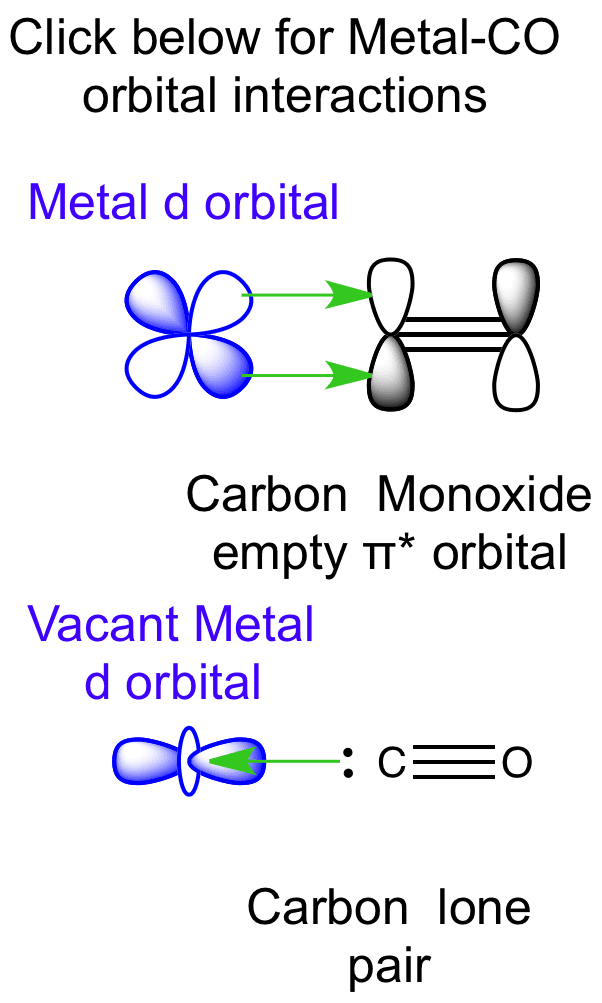
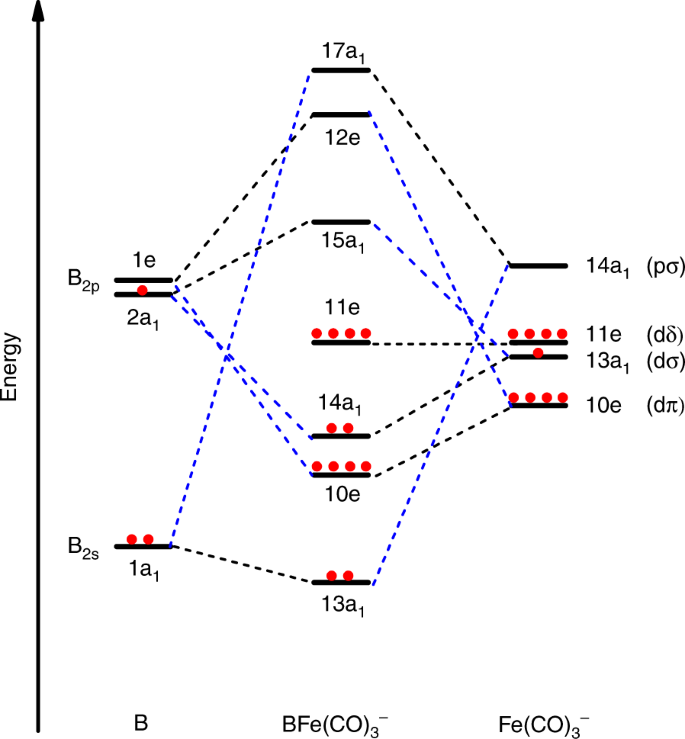
Point out key differences between the diagrams and use the diagram to explain why $\ce{CO}$ acts as a two-electron donor through carbon rather than through oxygen. Understandably, the key difference between these molecules is that $\ce{CO}$ is heteronuclear, and thus will have differences in energy between the molecular orbital and the atoms.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Monoxide (CO) The above image shows energy levels for the molecular orbitals of the carbon monoxide (CO) The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of showing how chemical bonding is taking place within a molecule.
diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO 2 in Figure 5.25.
Molecular orbital diagram of co. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic methods used by chemists and biochemists to analyse the molecular and electronic structure of atoms and molecules. This results in a larger energy difference between the resulting molecular orbitals ψ 1 and ψ 2 as shown in fig.
Also see here... Bond order for "NO"^+ Order by bond length: "NO", "NO"^(+), "NO"^(-) Is "CO" a Lewis acid? "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the ...
In the case of CO, the 2s atomic orbital on Oxygen is much lower in energy than the 2s atomic orbital in carbon. The discrepancy in energies allows the π2px & π2py bonding molecular orbitals to sink lower in energy than the “ σ*2s MO” in the MO diagram of CO.
Magnetic Behavior: If all the molecular orbitals in species are spin paired, the substance is diamagneti. But if one or more molecular orbitals are singly occupied it is paramagnetic. For Example, if we look at CO Molecule, it is diamagnetic as all the electron in CO are paired as in the figure below: Fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO
When the electronegativity of one atom is lower than the other, the more electronegative atom's orbitals are lower in energy. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. On the left you can see all of the orbitals. On the right, the total valence electrons (4 from C, 6 from O) have been added to the orbitals.

Lecture 26 Mo S Of Coordination Compounds Mlx X 4 6 1 Octahedral Complexes With M L S Bonds Only Consider An Example Of An Octahedral Complex Ppt Video Online Download
Answer (1 of 10): The bond order of CO is 3. as Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N the bond order is 3, in acetylene H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order give...
Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene





















0 Response to "40 co molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment