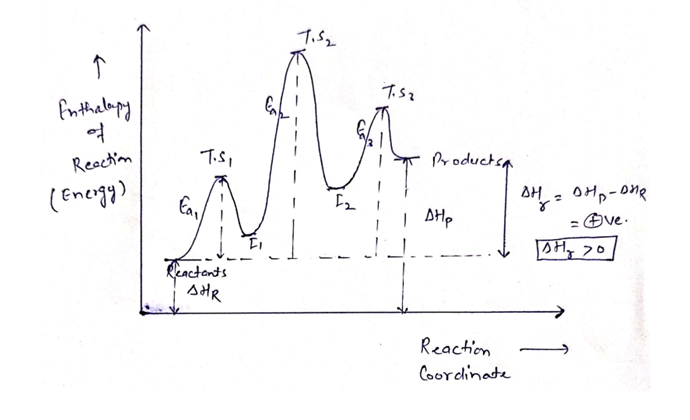
40 reaction coordinate diagram multistep reaction
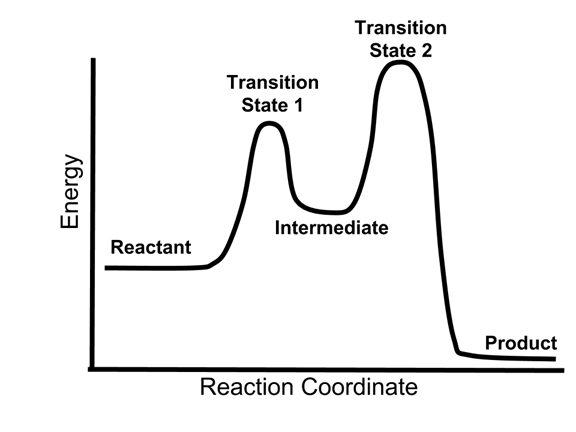
of inorganic or synthetic catalyst. In addition, different enzymes can work together, and catalyze a multistep reaction, of which each step is catalyzed by an individual enzyme. In biological systems, almost all chemical ... the reaction coordination diagram can be shown as in Fig 1, the starting point for either the forward ... Fig. 1 Reaction ... • Energy diagram: A graph showing the changes in energy that occur during a chemical reaction. • Reaction coordinate: A measure in the change in positions of atoms during a reaction. Reaction coordinate Energy Energy Diagrams 6 • Transition state ‡: - An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction.
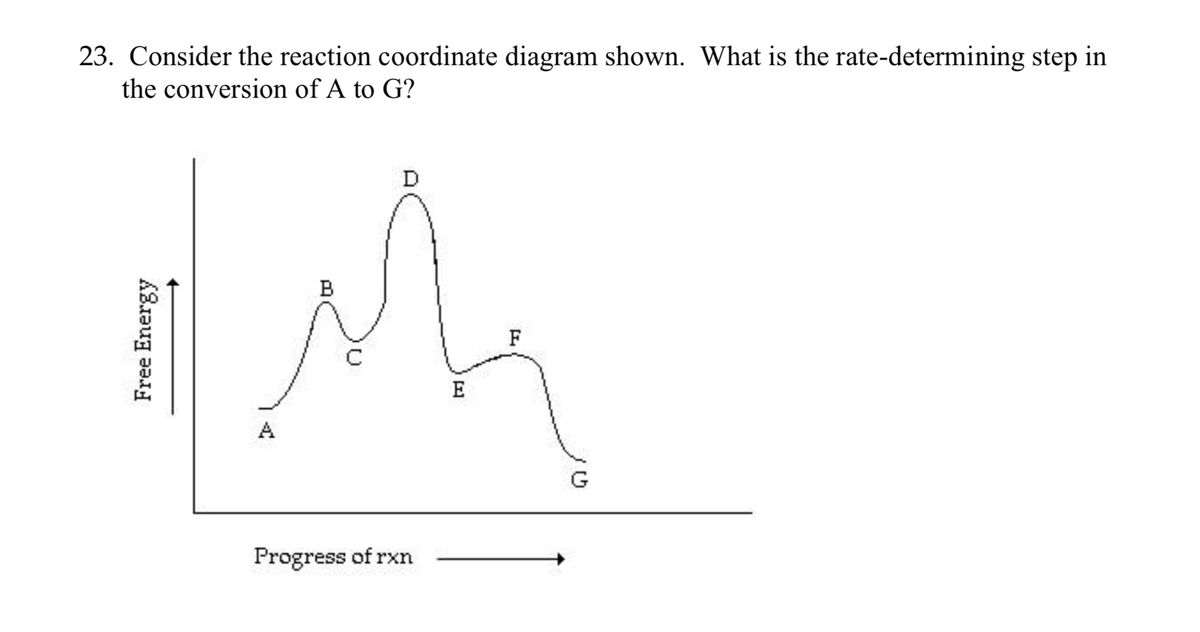
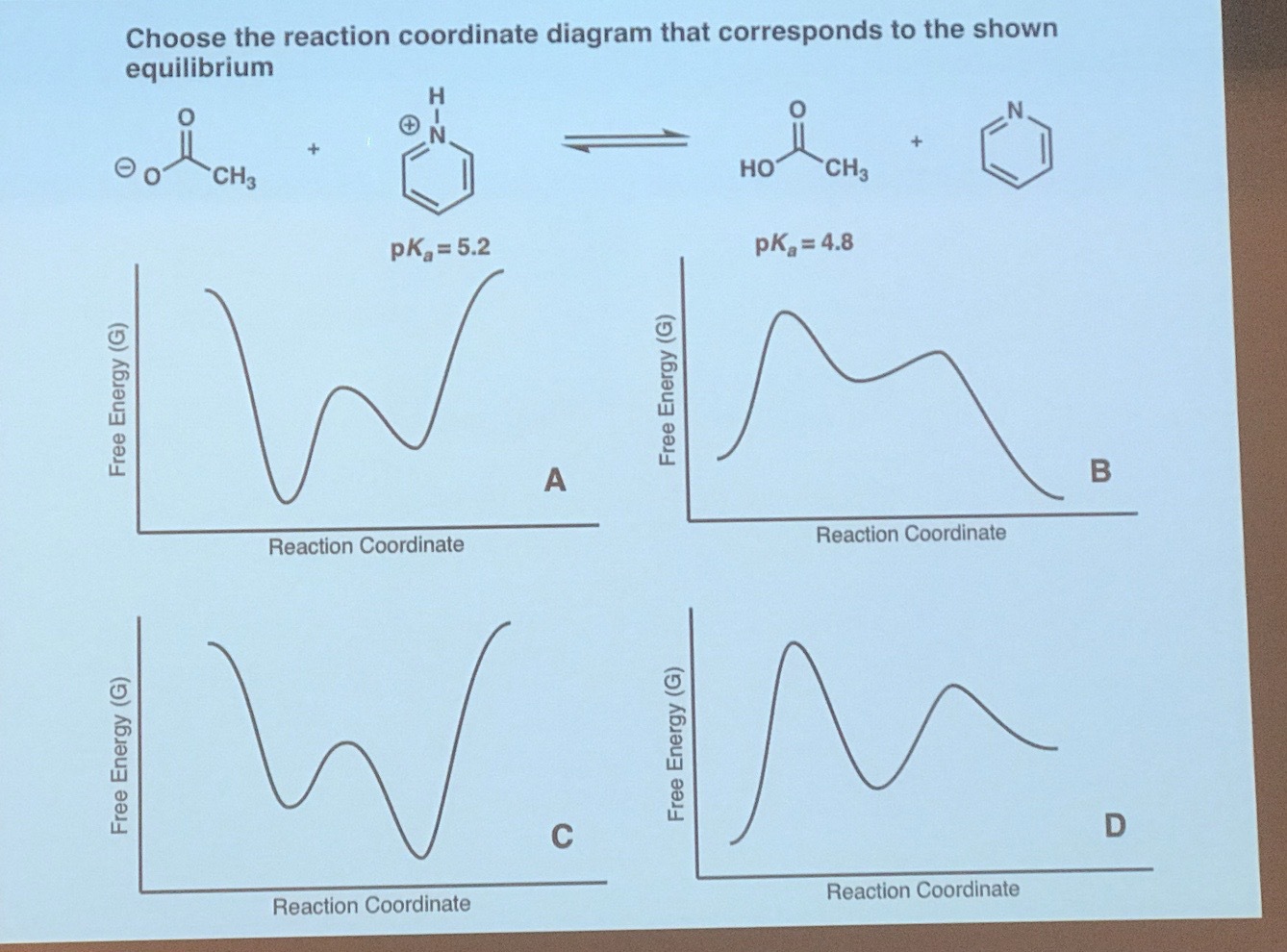
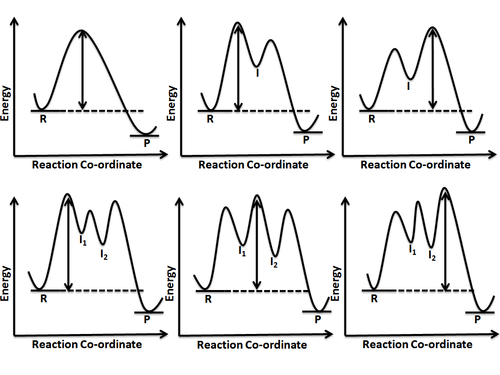
In a multistep reaction, the rate-determining step does not necessarily correspond to the highest Gibbs energy on the reaction coordinate diagram. [5] [3] If there is a reaction intermediate whose energy is lower than the initial reactants, then the activation energy needed to pass through any subsequent transition state depends on the Gibbs ...

Reaction coordinate diagram multistep reaction
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Figure 1.Reaction coordinate diagram for the NO 2 (g) + CO(g) → CO 2 (g) + NO(g) reaction.The sum of the two elementary reaction steps gives the net overall reaction—the NO 3 that is formed in step (1) is consumed in step (2), and one of the NO 2 consumed in step (1) is reformed in step (2).. The first step is much slower than the second step and is therefore the rate-determining step. Kinetics, equilibrium, and the reaction coordinate diagram (advanced topic). Chemical equilibrium is the state of constant composition attained when opposing reaction rates become equal. There is an essential relationship between reaction rates and chemical equilibrium, one that we can describe quantitatively.
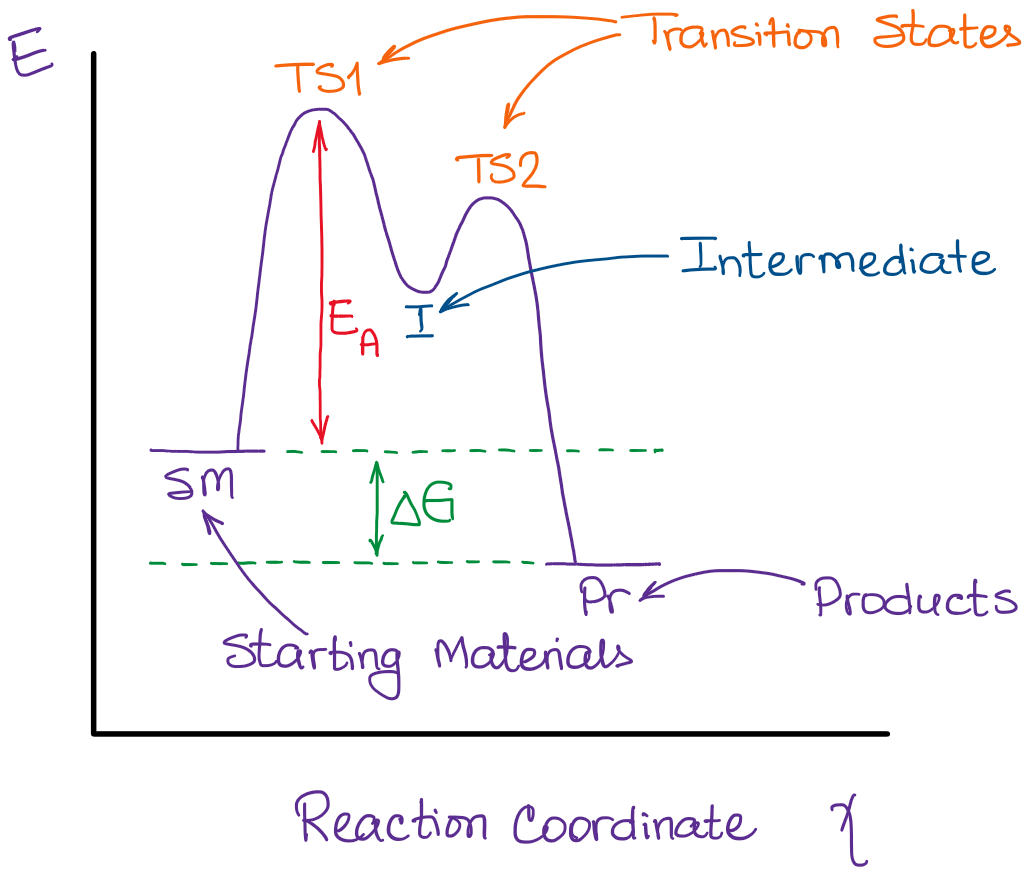
Reaction coordinate diagram multistep reaction. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Reaction coordinate diagrams show the energies of transition states, intermediates, reactants and products Reaction Coordinate G transition state reactant product intermediate intermediateany chemical structure that lasts longer than the time of a typical bond vibration, 10-13 to 10-14 s rate-determining step (rds) On this diagram we see: the x-axis that is a reaction coordinate: a loosely defined term meaning the reaction progress in the general direction from the starting materials or reagents (SM) to the products (Pr). the energy curve describing the energy states of the components at a certain point in the reaction. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the 'reaction coordinate', tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. Fig.7: Reaction coordinate diagram showing TS There may be more than one transition state for a reaction, generally for multi-step reactions. The local minima represent reactive intermediates and the local maxima are TSs (figure 8). The highest energy TS determines the overall reaction rate, and the step with highest energy TS is the
Reaction Coordinate Diagram of Ozone Photolysis The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction . Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction. Reaction path diagrams, as represented above, are a two dimensional slice of a multidimensional energy surface for the reaction. Conventionally, they are a plot of energy (in the rigorous case, free energy, G) versus the reaction coordinate. 6. Reaction Mechanism. The mechanism of a reaction is a stepwise description of how reactants are ... Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol -1 . In a reaction coordinate diagram, each step in a multi-step mechanism will have its own activation energy, resulting in an energy peak for each step. The rate-determining, or slow, step will have the largest activation energy. This can be seen in Figure 2 below. Figure 2. Reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction: NO 2 (g) + CO(g) → CO 2 (g
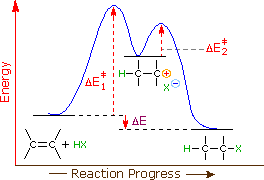
Define an elementary reaction, and state how it differs from an ordinary net chemical reaction. Sketch out an activation energy diagram for a multistep mechanism involving a rate-determining step, and relate this to the activation energy of the overall reaction. Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Involving Formation of an Intermediate ... energy barrier: Slowest step in a multistep reaction • If D = 2H reacts in the same way as 1H, what would be the most likely product of the following addition run under conditions that favor ... product. Then, draw the reaction coordinate for the reaction that ... Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1. According to Wikipedia: Given a reaction coordinate (energy diagram), the rate determining step can be determined by taking the largest energy difference between any starting material or intermediate on the diagram and any transition state that comes after it. That transition state will then be the rate-determining step of a given reaction.
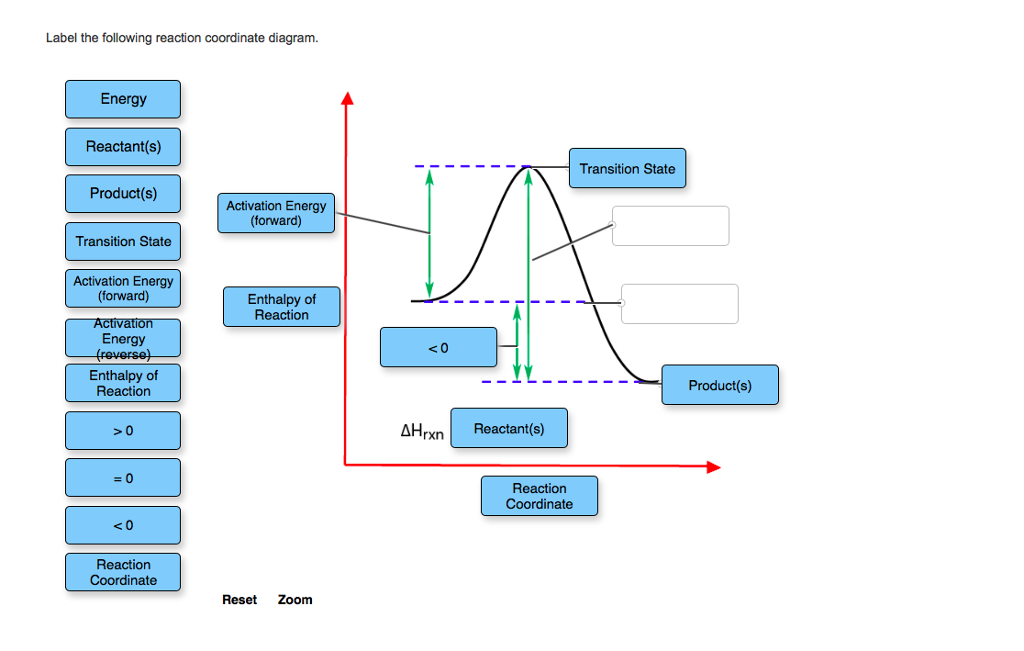
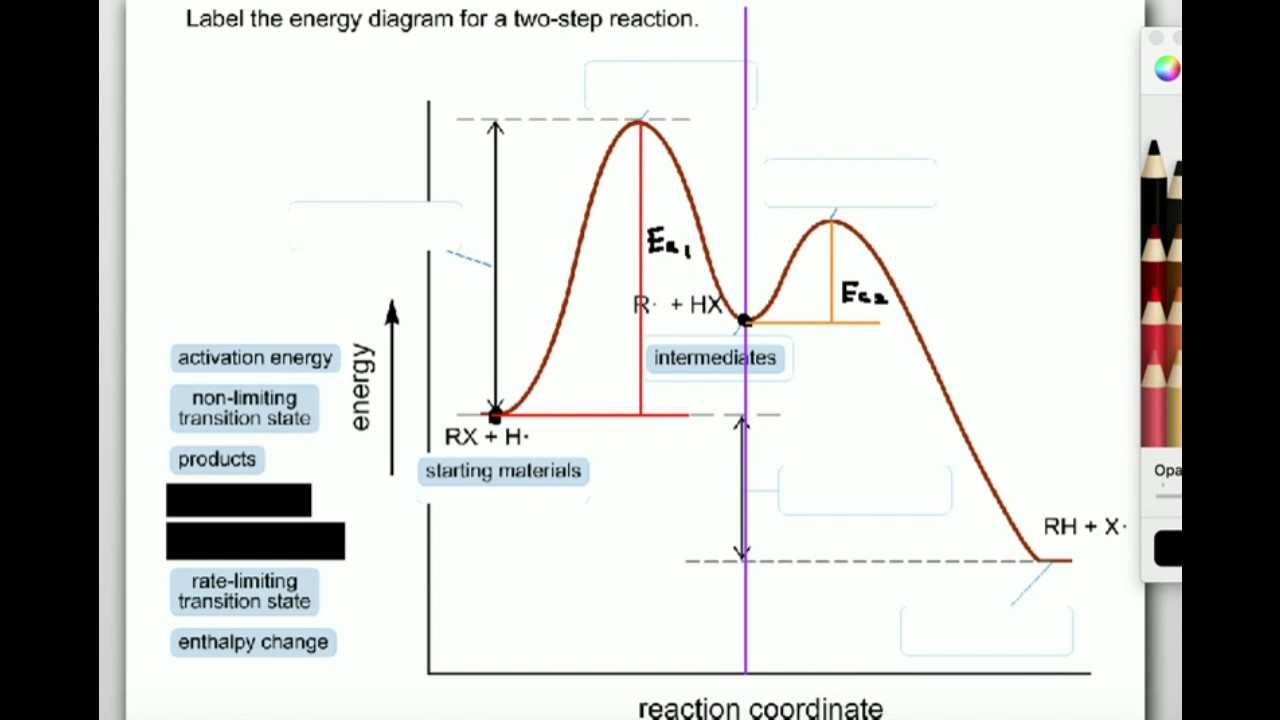
Label the following multi-step reaction diagram. Show transcribed image text. Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 99% (110 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.
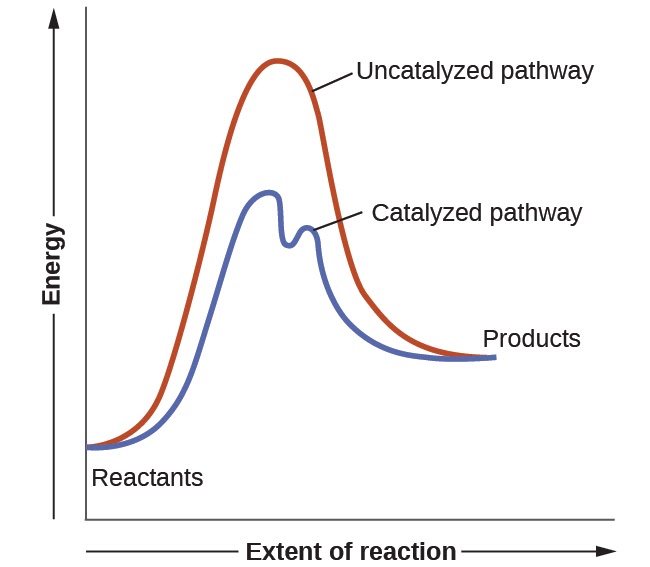
One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.
where the classical energy diagram says it shouldn't be able to occur! Reaction Coordinate! energy! Using classical energy diagram, a particle would move along the surface of the energy diagram! With tunneling, however, the particle could "cut" across the surface to generate a lower energy of activation! Therefore the k H /k D
Reaction coordinate diagrams. The intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC), derived from the potential energy surface, is a parametric curve that connects two energy minima in the direction that traverses the minimum energy barrier (or shallowest ascent) passing through one or more saddle point(s). However, in reality if reacting species attains enough energy it may deviate from the IRC to some extent.
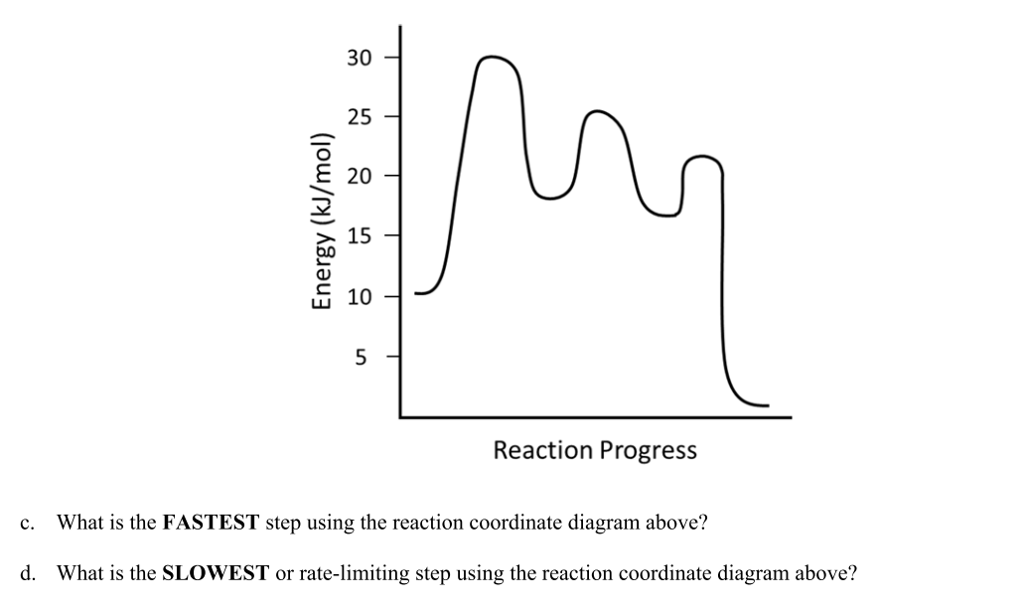
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams From Mechanisms: We can draw a coordinate diagram from a mechanism with more than one step, if we know the RATES of each step, and the ENTHALPY of the reaction… The LARGER the E A, the SLOWER the reaction, so the RATE DETERMINING STEP should have the HIGHEST E A. FASTER 'ssteps should have .
Need help preparing for the General Chemistry section of the MCAT? MedSchoolCoach expert, Ken Tao, will teach you what you need to know about reaction rate a...
Summary. A reaction mechanism is the sequence of elementary steps by which a chemical reaction occurs. A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is called a multistep or complex reaction. A reaction intermediate is a chemical species that is formed in one elementary step and consumed in a subsequent step.
Multistep Reactions! In a multistep reaction, the overall reaction rate is determined ! by the highest energy barrier along the reaction coordinate! Potential energy! Reaction Coordinate! E a (1)! E a (2)! E a (1) > E a (2)! Referred to as the rate determining step!
Collision theory states that molecules must collide to react. For most reactions, however, only a small fraction of collisions produce a reaction. In order for a collision to be successful, the reactant molecules must collide both with sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier and in the proper orientation to form any new bonds in the products.
The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants.
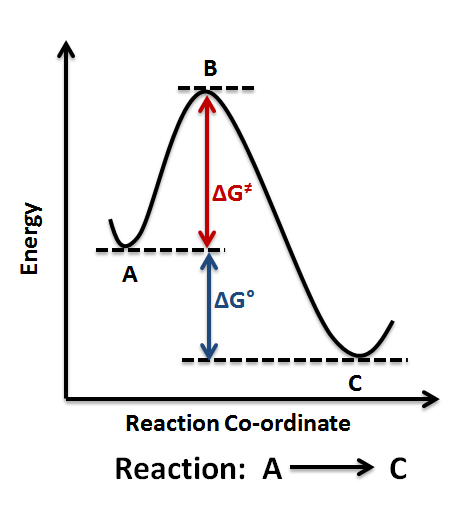
1! Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction
Kinetics, equilibrium, and the reaction coordinate diagram (advanced topic). Chemical equilibrium is the state of constant composition attained when opposing reaction rates become equal. There is an essential relationship between reaction rates and chemical equilibrium, one that we can describe quantitatively.
Figure 1.Reaction coordinate diagram for the NO 2 (g) + CO(g) → CO 2 (g) + NO(g) reaction.The sum of the two elementary reaction steps gives the net overall reaction—the NO 3 that is formed in step (1) is consumed in step (2), and one of the NO 2 consumed in step (1) is reformed in step (2).. The first step is much slower than the second step and is therefore the rate-determining step.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...




















0 Response to "40 reaction coordinate diagram multistep reaction"
Post a Comment