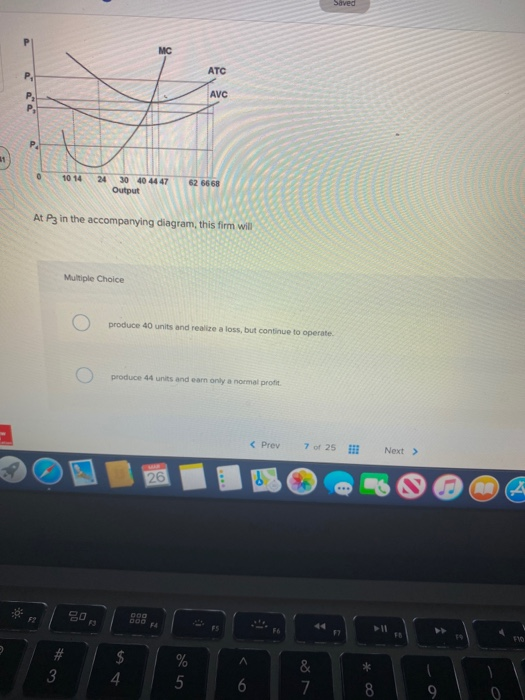
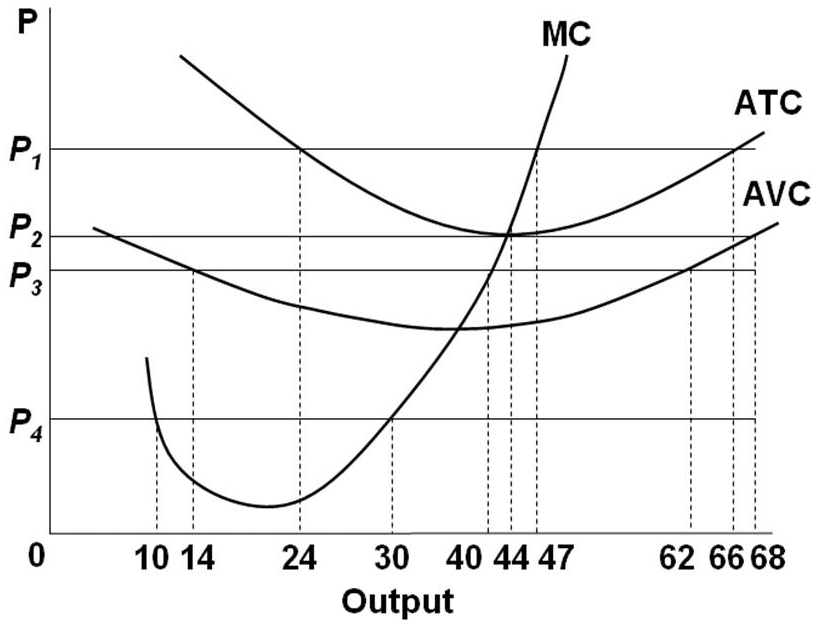
34 at p3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will
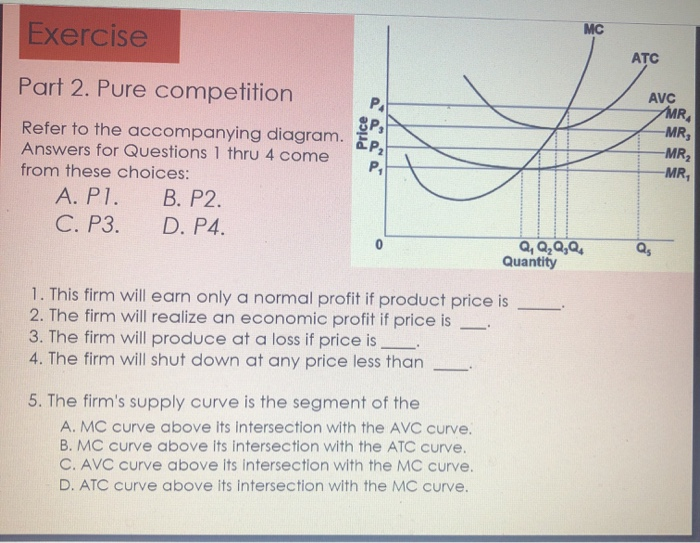
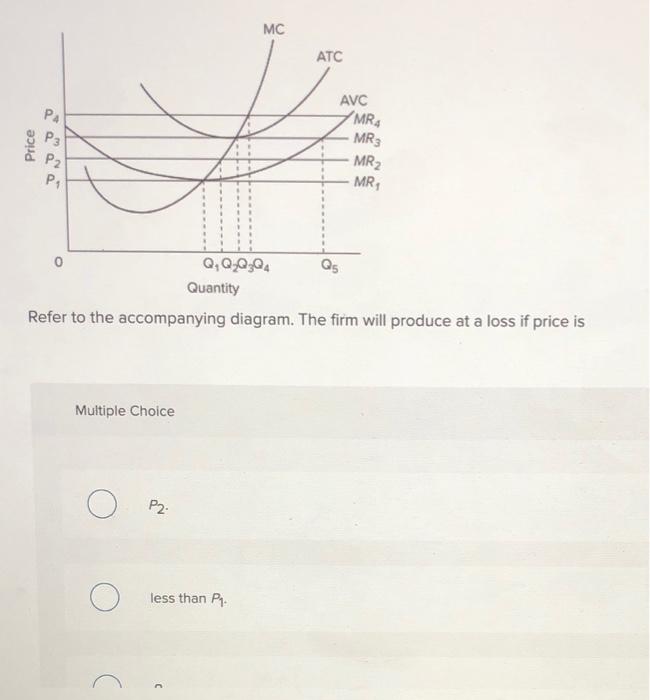
a. The firm shuts down immediately. The firm should shut down immediately when price is less than minimum average variable cost, the shut-down price. In the accompanying diagram, this is optimal for prices in the range from 0 to P1. b. The firm operates in the short run despite sustaining a loss.
system this diagram is describing - look at the diagram to get a feel for the symbols and notation of a data-flow diagram. Figure 6.1. An example data-flow diagram As can be seen, the DFD notation consists of only four main symbols: 1. Processes — the activities carried out by the system which use and transform information.
Question 1. SURVEY. 120 seconds. Q. The primary force encouraging the entry of new firms into a purely competitive industry is. answer choices. normal profits earned by firms already in the industry. economic profits earned by firms already in the industry. government subsidies for start-up firms.
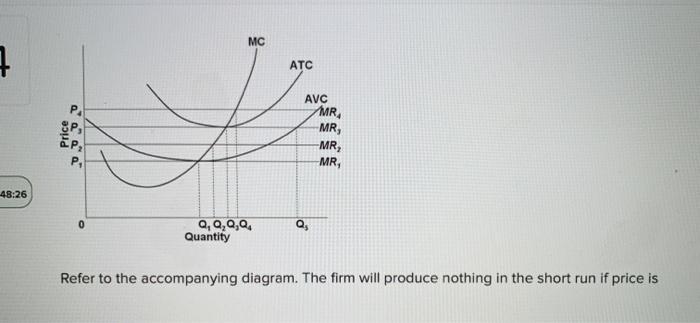
At p3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will
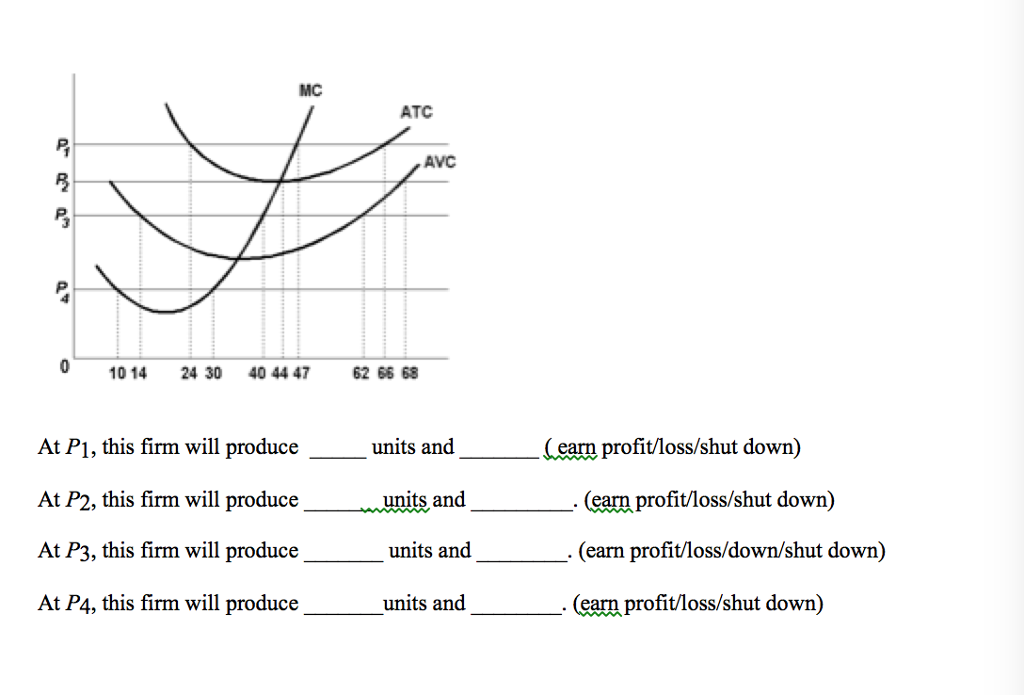
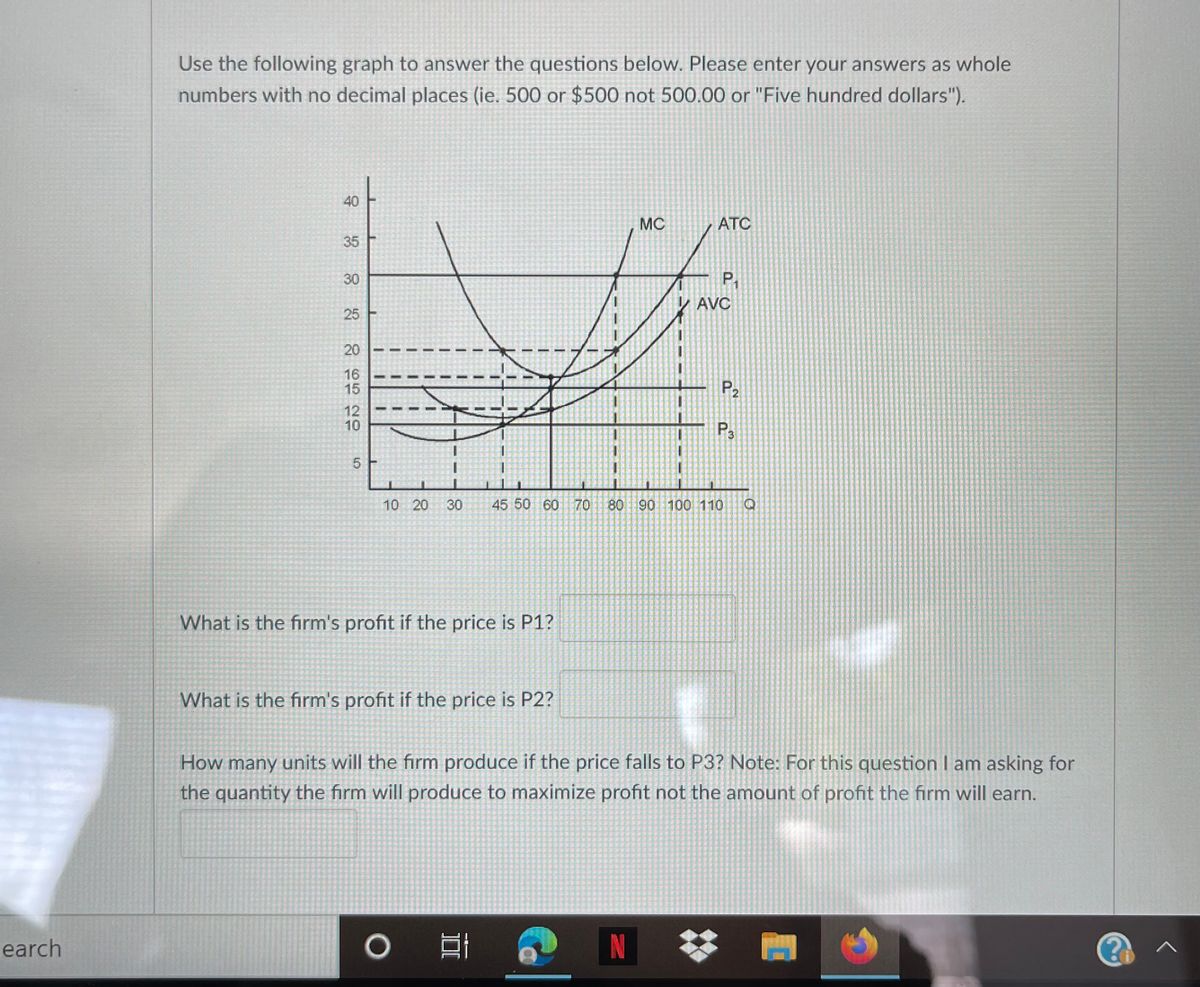
At P1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce. 47 units and realize an economic profit. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. produce 40 units and incur a loss. Total Product Average Fixed Cost Average Variable Cost Average Total Cost Marginal Cost. 1 $150.00 $25.00 $175.00 $ 25.00.
1) P> ATC, firm makes a profit, this case is shown in the above graph. 2) P< ATC, firm experience losses, see right graph below, total loss is the shaded area. 3) P=ATC, firm breaks even (profit=0), see left graph, point A is called the break-even point (the minimum point of ATC curve).
externally because P0 has no inbuilt pull-up resistors like P1, P2 and P3. P1(Port1)(Pins 1 to 9) and P2(Port2)(Pins 21 to 28) They are used as input/output pins. P3(Port3)(Pins 10 to 17) It is used as input as well as output port. No pull-up resistors are required in P3. Apart from input/output it also provides interrupts.
At p3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will.
Transcribed image text: ATC AVC 10 14 24 30 40 44 47 Output At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will Multiple Choice O produce 40 units and realiza loss, but continue to operate produced o produce 44 units and can only normal proth < Prev 7 of 25 Next > At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will Multiple Choice produce 40 units and realize a loss, but continue to operate O o ...
One firm produces the entire output of the industry . There are no close substitutes for the product . There are barriers to entry that protect the firm from competition by entering firms . 1.6.3 Monopolistic competition. is a market structure with: - Many firms - Each firm produces similar but slightly different products — called product ...
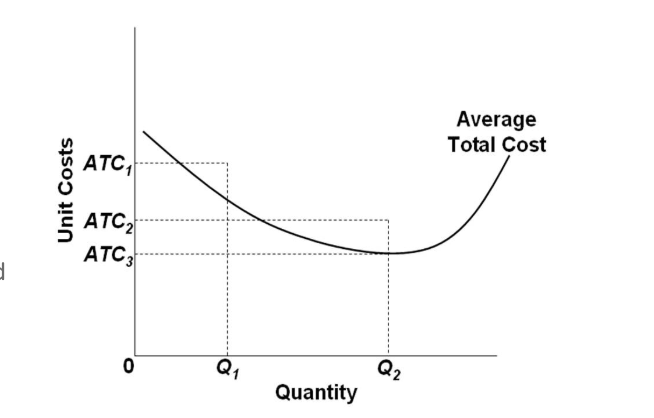
144. Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q2 at an average cost of ATC2, then the firm is: A. producing the profit-maximizing output, but is failing to minimize production costs. B. incurring X-inefficiency, but is producing that output at which all existing economies of scale might be realized.
Question 1 0.09524 out of 0.09524 points Correct Picture The diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. If in the long run the firm should produce output 0x, it should do it with a plant of size: Selected Answer: Correct #2. Answers: #4.
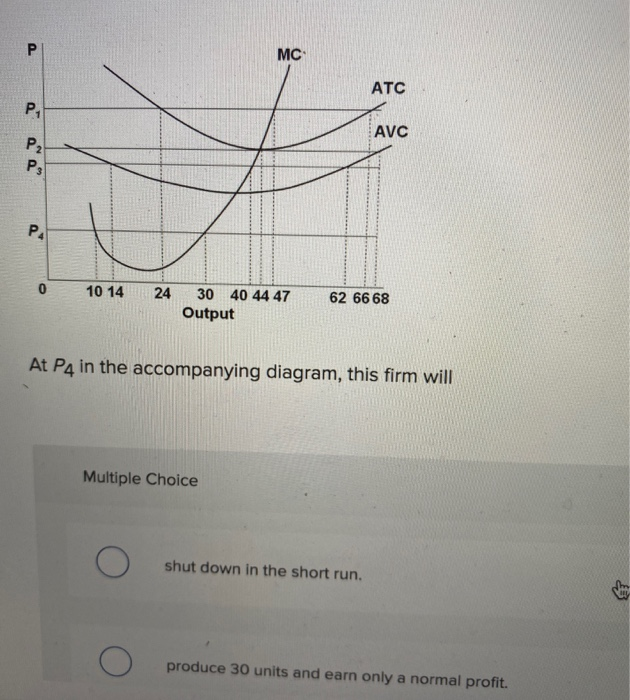
107. Refer to the above diagram. At P4, this firm will: A) shut down in the short run. C) produce 30 units and earn only a normal profit. B) produce 30 units and incur a loss. D) produce 10 units and earn only a normal profit. Answer: A. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 423-424 MI: 179-180 108. Refer to the above diagram. At P3, this firm will:
An important skill in microeconomics is the ability to find a firm's profit. Learn more about how to use a graph to identify the profit-maximizing quantity for a firm in a perfectly competitive market, and identify the area that represents the firm's profit or loss.
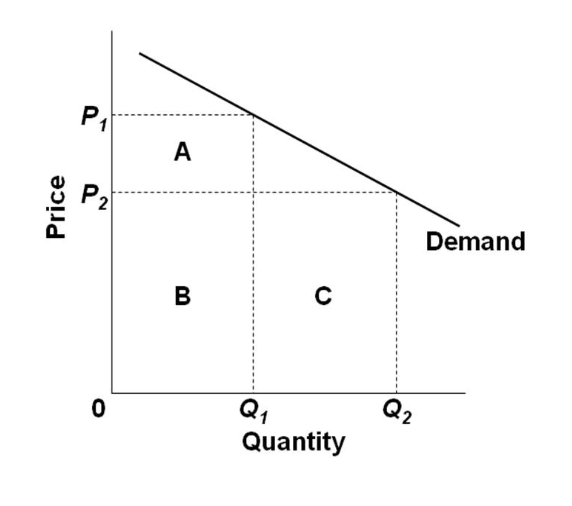
The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price= MR = MC, so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of 90, which is labeled as e in Figure 4 (a). Remember that the area of a rectangle is equal to its base multiplied by its height.
in the accompanying diagram. The equilibrium price is $6.50; at that price, the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied—11 million taxi rides per year. The demand and supply curves (D: 1 : and : S) illustrate this initial situation. b. With a price ceiling of $5.50, the quantity supplied is 9 million taxi rides and the quantity
At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. produce 40 units and realize a loss, but continue to operate. Refer to the accompanying diagram.
shows a monopoly firm that sells gadgets. If the firm acts to maximize profit, the firm will sell _____ units at a price of _____ per unit. a. Q 2; P 1 b. Q 2; P 5 c. Q 3; P 2 d. Q 4; P 3 e. Q 4; P 2 18. (Figure 61-5: A Gadget Monopoly) The graph shows a monopoly firm that sells gadgets. If the firm acts to maximize profit, the firm will earn ...
The firm's estimate of the demand for the product is P = 20 - 3(Q 1 + Q 2). How much should the firm plan to produce in each plant, and at what price should it plan to sell the product? First, notice that only MC 2 is relevant because the marginal cost curve of the first plant lies above the demand curve. Price Q 10 20 30 3.3 6.7 MR D MC1 ...
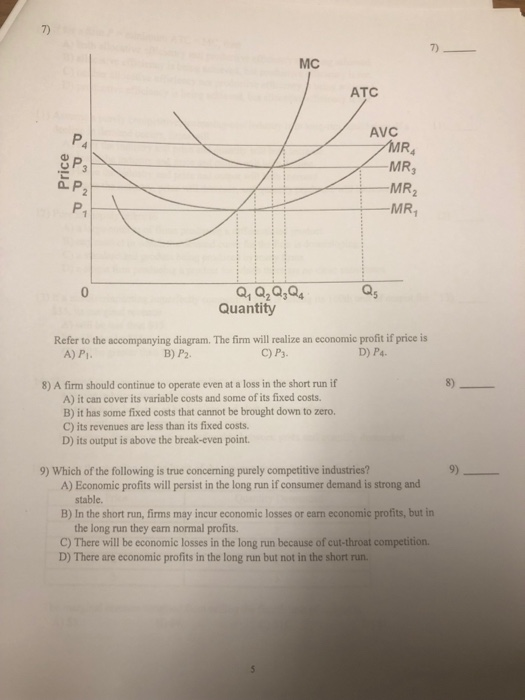
D. between P2 and P3. D. between P2 and P3. 47. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero. D. new firms will enter this industry. C. economic profits will be zero.
The long-run equilibrium occurs with supply curve S3, equilibrium price P3, industry output Q3, and firm's output q3. Thus, in the long run, profits are zero again and there are fewer firms in the industry. Figure 8. 11. a. Figure 9 illustrates the situation in the U.S. textile industry. With no international trade, the market is in long-run ...
14. Refer to the above data. If the firm's minimum average variable cost is $10, the firm's profit-maximizing level of output would be: A. 2. B. 3. C. 4. D. 5. 15. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit.
Determining the Highest Profit by Comparing Total Revenue and Total Cost. A perfectly competitive firm can sell as large a quantity as it wishes, as long as it ...
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
View Macroeconomics Quiz 13.pdf from ECO 3320 at University Of Dallas. 106. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the accompanying diagram. The firm will produce at a loss if price is less than P1.
2) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P3, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output F or shut down, as it doesnʹt matter which. C) produce output D.
Refer to the diagram. This firm will earn only a normal profit if product price is: a. P1 b. P2 c. P3 d. P4. c. P3. In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis. Refer to the information. For a purely competitive firm, marginal revenue graphs as a: a. straight ...
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produc A) 6 units at an economic profit of $7.98. B) 8 units at an economic profit of $16. C) 10 units at an economic profit of $4. D) 7 units at an economic profit of $41.50.
The V-diagram reveals that the largest shear force in the beam is -24 kN : segment CD The M-diagram reveals that the maximum bending moment is +48 kN·m : the 28-kN load at C. Note that at each concentrated force the V-diagram "jumps" by an amount equal to the force. There is a discontinuity in the slope of the M-diagram
120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
14. Assume the XYZ Corporation is producing 20 units of output. It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $10 per unit. Its total fixed costs are $100 and its average variable cost is $3 at 20 units of output. This corporation: A. Should close down in the short run. B. Is maximizing its profits.
Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q1 at an average total cost of ATC1, then the firm is: A. producing the potentially profit-maximizing output, but is failing to minimize production costs. B. incurring X-inefficiency, but is realizing all existing economies of scale. ...
A firm that can sell all of its output at the prevailing market price: ... a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply ...
Award: 1.00 point At P 3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce 14 units and realize an economic profit. produce 62 units and earn only a normal profit. produce 40 units and incur a loss. shut down in the short run.










![Solved 14 pts] QITI: Refer to the accompanying diagram and ...](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/8e6/8e6d69ca-5093-44e5-8bd5-1361f776ce24/image)



0 Response to "34 at p3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will"
Post a Comment