35 b2 molecular orbital diagram
A dihydrogen molecule contains two bonding electrons and no antibonding electrons so we have. bond order in H2 = (2−0) 2 = 1 bond order in H 2 = ( 2 − 0) 2 = 1. Because the bond order for the H-H bond is equal to 1, the bond is a single bond. A helium atom has two electrons, both of which are in its 1 s orbital.
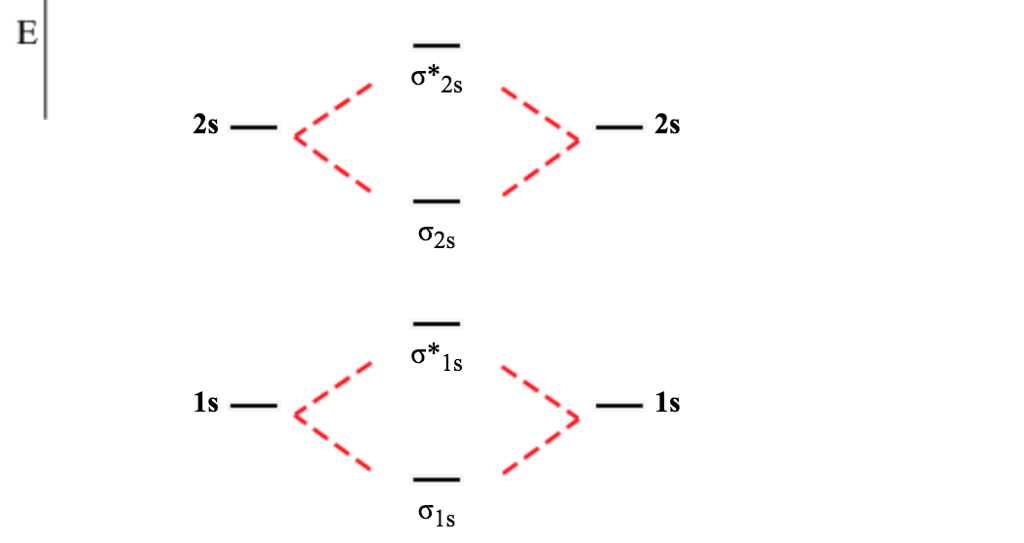
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Almost all stable molecules, larger than diatomic, have filled bonding and non-bonding molecular orbitals, and empty antibonding orbitals. B 2 H 6 has the correct number of electrons to fit this prescription, so is not electron-deficient in this sense, unlike BH 3, which has an empty non-bonding orbital.
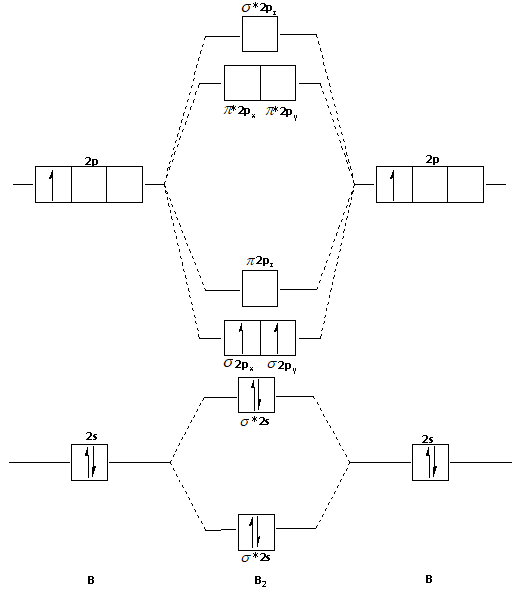
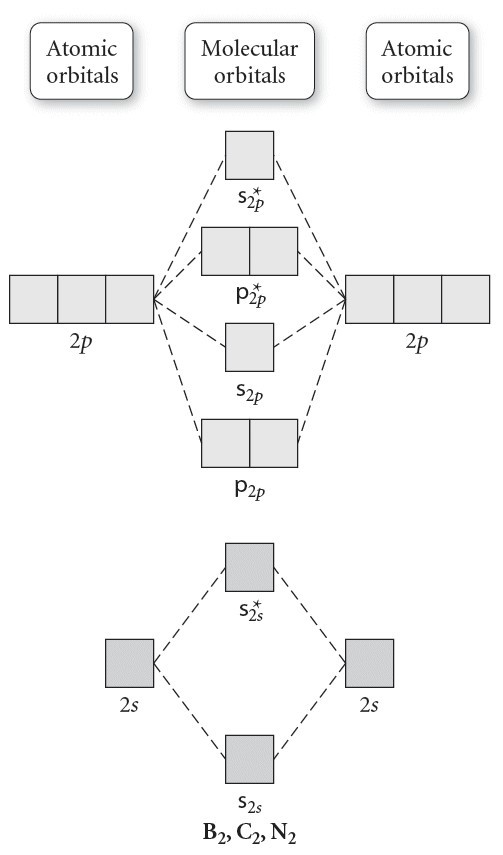
B2 molecular orbital diagram
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
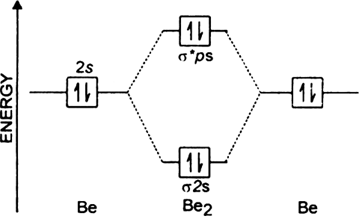
Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and ...
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
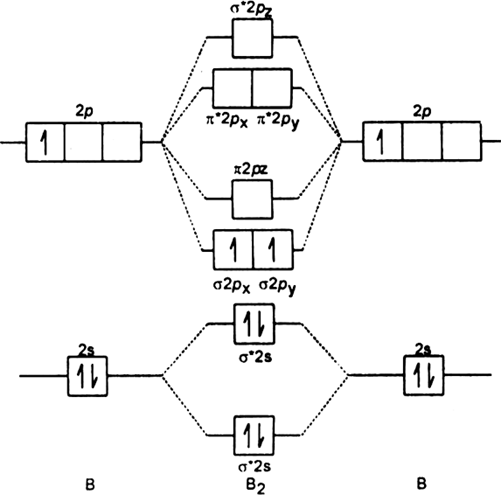
B2 molecular orbital diagram.
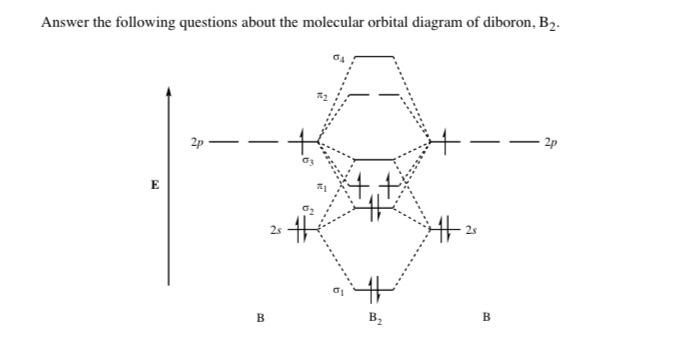
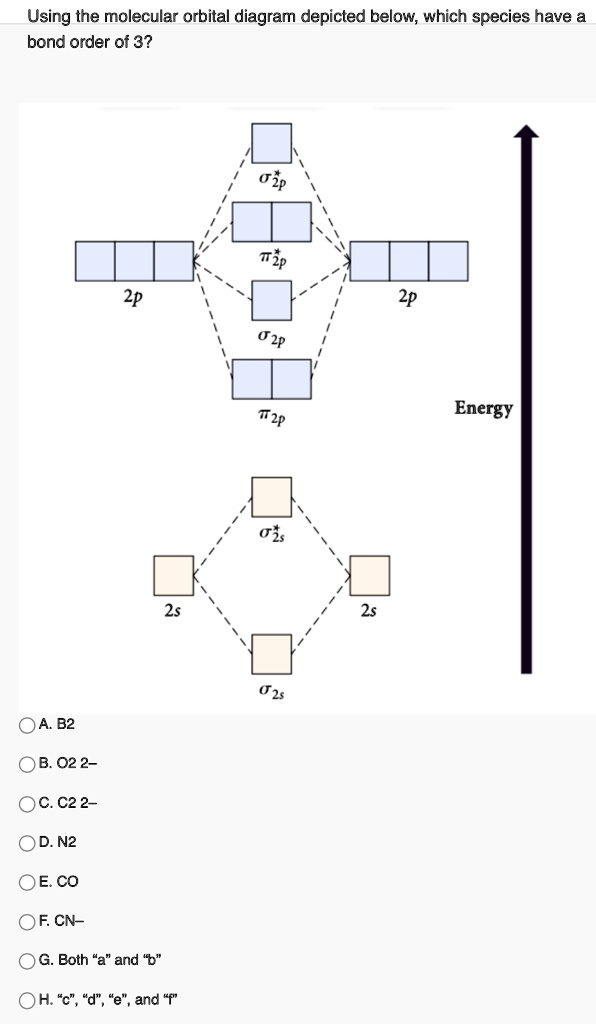
Question 2) Based on the molecular orbital diagram for NO, which of the following electronic configurations and statements are most correct? Question : Question 1) By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for B2, C2, N2, O2, and F2, predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic.
I disagree with Silvio Levy that the triplet ground state of $\ce{B2}$ is completely unexpected. The rationalisation also is not that difficult, and is known as s-p mixing. After all, ... The finished valence molecular orbital diagram is pictured below. Share. Improve this answer. Follow answered Aug 16 '18 at 16:33. Martin ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2. 13.03.2019 13.03.2019 7 Comments on Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2. Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence ...
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
22.05.2019 22.05.2019 1 Comments on Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. ... Be2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. Magnetic properties: Since each ...
May 18, 2021 by Admin. 1 So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. Nov 11, 2016.
MO diagrams explain why some molecules exist and others do not. By looking at the O2 molecular orbital diagram, we can see that oxygen has BO of 2 because it has 10 bonding and 6 anti-bonding. Experiments show that each O2 molecule has two unpaired electrons. We can also notice the magnetic property of diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
The molecular orbital diagram for [F-H-F]\(^-\) is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). Notice that all atomic orbitals, group orbitals (SALCs), and molecular orbitals are assigned a symmetry label that corresponds to each elements' symmetry under the \(D_{2h}\) point group. In other words, their labels correspond to Muliken Labels of individual ...
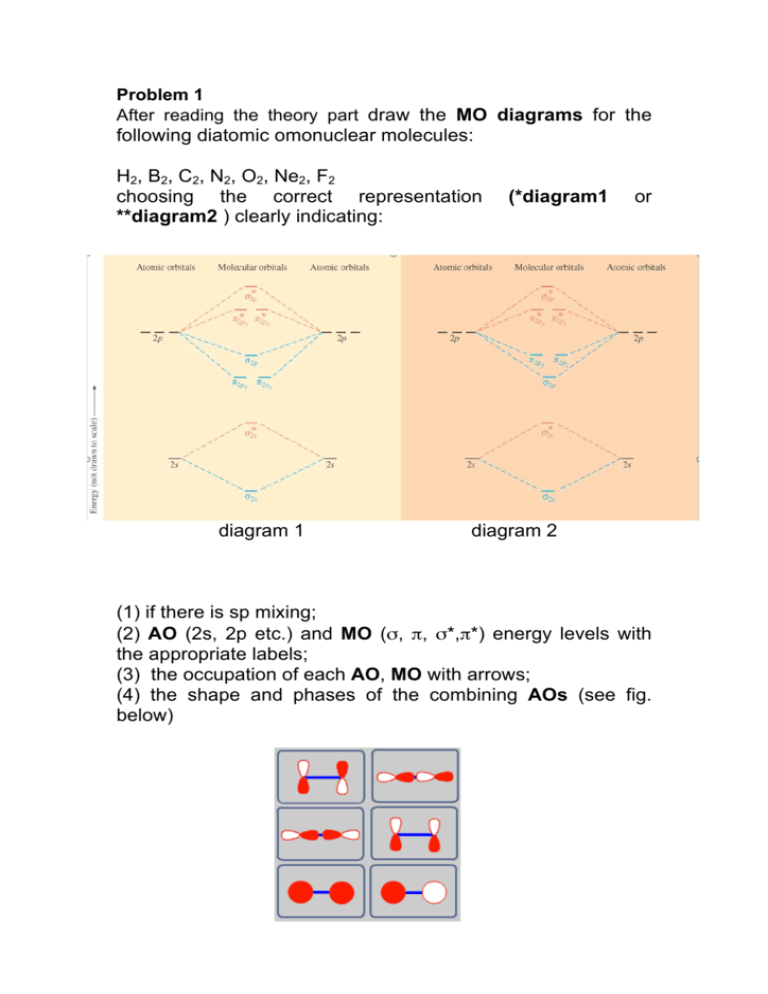
From the periodic table as we have already discussed the Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules of 1st two periods starting from Hydrogen to Neon. ...
B2 Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbital theory b2 this video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2 molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but ...
orbital. The electronic configuration for O 2 is: s 2s2 s* 2s2 s 2p2 p 2p4 p* 2p2. This electronic configuration indicates a bond order of 2, and the bond can be represented by O = O. There is no net bonding from the s 2s orbitals, because the number of bonding electrons equals the number of antibonding electrons.
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. In the formation of B2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the MO diagrams for B2.
30.06.2020 · So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
The valence molecular orbital diagram for Li2- is shown. The molecular orbital bond order for this species is equal to ____ and Li2- is _____stable than Li2. 1/2 ; less. the valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. Which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram? - B2- has a shorter bond than B2-The molecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2. …
The molecular orbital diagram for B 2 molecule is as follows: We know that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and the antibonds. Now, we have to calculate the bond order of B 2 molecule using the formula as follows: Bond order = 1 2 ( Number of electrons in BMO) − ( Number of electrons in ABMO) From the diagram, we can ...
The valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. - B2- has a shorter bond than B2-The molecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2.-B2- is paramagnetic. The MO diagram for the hydroxide ion -OH is shown.-The MO bond order is given by 2/2=1-there are 3 nonbonding MO's in this species-the -OH is a fairly stable species . Atomic orbitals that are not involved in …
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron.
B2 molecular orbital diagram. Answer to question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomi. Molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms in the molecule. Before we can draw a correlation diagram for b2 we must first find the in phase and out of ...
The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2 + (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired ... B2 molecular orbital diagram. Since bond order is zero be 2 molecule does not exist.
Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. This interaction introduces an element of s p mixing or hybridization into the molecular orbital theory. When p s mixing is allowed the energies of the σ2p and π2p orbitals are reversed. The two electrons from the b 2p orbitals now occupy separate degenerate π2p molecular orbitals and thus have parallel spins.
30.11.2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet. What is the molality of a 5. corresponds to the 1s orbital? (A) 1. Please select your changes regarding the highest energy level diagrams, the worksheet ionic compounds dot diagrams answers Draw and explain how to draw the contour diagram of your molecule. Bonds made with hybridized orbitals are called …
B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs.
⇒ A homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital in which the same atoms combine together. example- N2, O2, B2, etc. ⇒ A hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital in which different atoms combine together. example- CN, HF, NO, etc. Clearly, Cyanide (CN) lies in a hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital as it contains two different atoms. Also, using the …
11.11.2016 · So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. I always thought bond order corresponded to the number of bonds. That is, molecule held …
11.11.2014 · Re: M.O. Diagram for B2 Post by Chem_Mod » Tue Nov 11, 2014 11:21 pm As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond.
1 Answer. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals.
17.10.2018 · This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. …


















0 Response to "35 b2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment