35 concave mirror ray diagram simulation
Ray 1 and 2. Ray 1 and 3. Ray 2 and 3. Draw the images formation using only two rays need to be adjusted to the object distance from the concave lens. If the object distance from the concave lens is as in the figure above, there are three ways to draw the image formation using only two rays.
Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. This is the currently selected item. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Cartesian sign conventions mirrors. Practice: Sign convention. Solved example: Mirror formula. Practice: Using the mirror formula.
Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Concave Mirror. Mirrors: 4 of 4 An interactive demonstration of the principal ray diagram of a concave mirror. link: view. type: simulation. system reqs: Flash player. author: Dr. Barbara Hoeling. design credits: Erick Zelaya, Developer

Concave mirror ray diagram simulation
Image Formation by Mirror - SimPHY - Interactive 2D Physics Simulator. A simple simulation to understand nature of image formed by convex and. concave mirrors. You can change position of image and focal length with. sliders to visualise corresposnding ray diagram and image formed by mirror. Mouse scroll to zoom, drag with mouse to pan.
Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams. Transcript. Let's explore the ray tracing technique to figure out the properties of images when things are kept in front of a concave or a convex mirror. Created by Mahesh Shenoy.
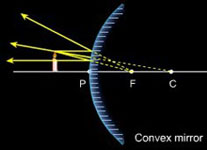
Problem Giancoli 32-21 (II) Show, using a ray diagram, that the magni cation m of a convex mirror is m = di/do, just as for a concave mirror. [Hint: Consider a ray from the top of the object that re ects at the center of the mirror.] Solution: See Fig.(6 ). Consider the ray re ects from the center of the mirror, and note that di < 0. tanθ = ho ...
Concave mirror ray diagram simulation.
Your browser does not appear to support HTML5. Try upgrading your browser to the latest version. What is a browser? Microsoft Internet Explorer Mozilla Firefox Google ...
This simulation allows you to manipulate objects in front of plane, convex and concave mirrors, to see the resulting ray diagrams and images. - Use the selector in the top left to change modes. - Camera can be translate and zoomed by dragging and pinching. PLANE mode: - drag the arrow by the center - rotate the arrow by either end CONCAVE ...
The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, and of real and virtual images. Students can use the animation to explore the reflection of light from a concave mirror and to investigate the position of the image formed by a concave mirror. Learning Goal: To show a ray diagram for a concave mirror. Interact
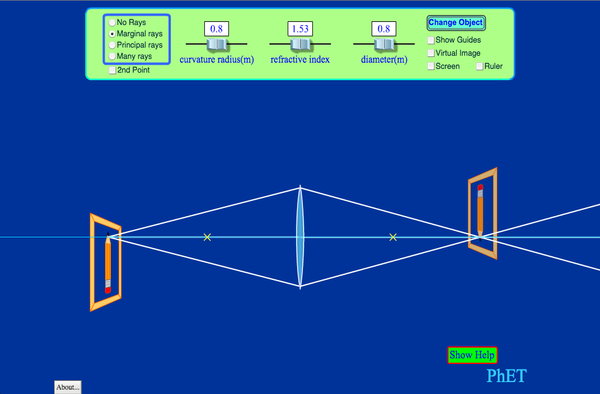
Ray Optics Simulation. An open-source web application to simulate reflection and refraction of light. ... The idealized "curved" mirror which obeys exactly the mirror equation (1/p + 1/q = 1/f). The focal length (in pixels) can be set directly. Glass. Simulate the the refraction and reflection of light on a surface. ...
One of a kind of simulation, Experiment & use in-depth explanations provided for clear concepts. Shows complete ray diagrams for all the positions for both concave & convex mirrors. Move the candle to different positions and a ray diagram automatically generates by itself. This animated physics (optics) software gives in-depth information about wavelenghts of light, refraction and dispersion ...
Spherical mirror has a single curvature radius R that is considered as positive for the concave mirror and as negative for the convex mirror. Lenses have two different curvature radii at both sides. The principal axis is a horizontal line drawn perpendicular to the mirror or lens through its center (see Fig. 1).
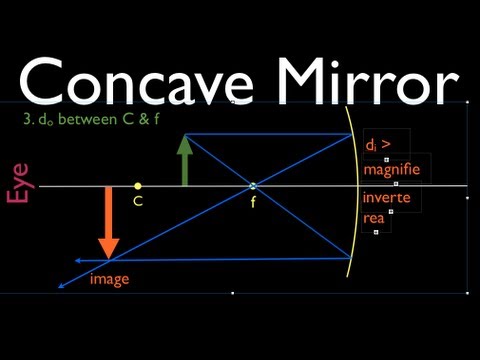
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
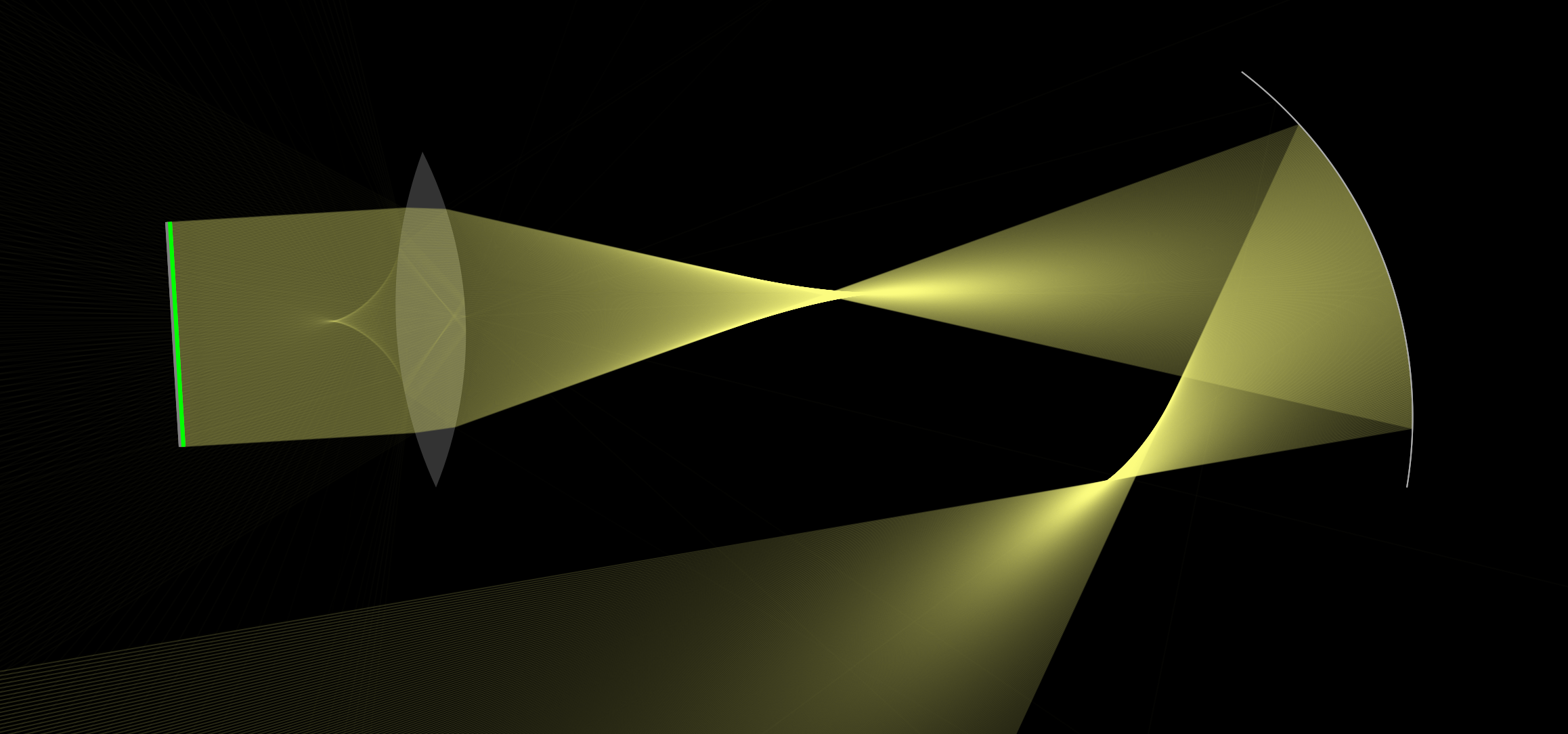
We are developing a project for optical lenses, mirrors, prism and optical-fiber experiments simulation. It will be like getting image and ray diagram for object's position from lenses (biconvex, biconcave, Plano-Convex, Convex-Concave, Meniscus, Plano-Concave), mirrors (concave, convex, plane), prism and optical-fiber.
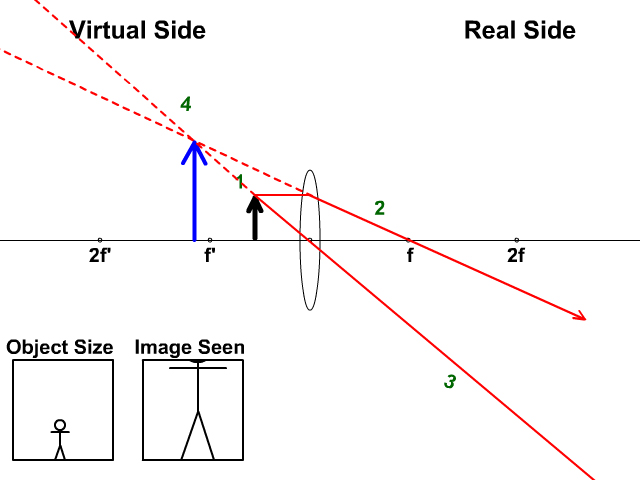
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
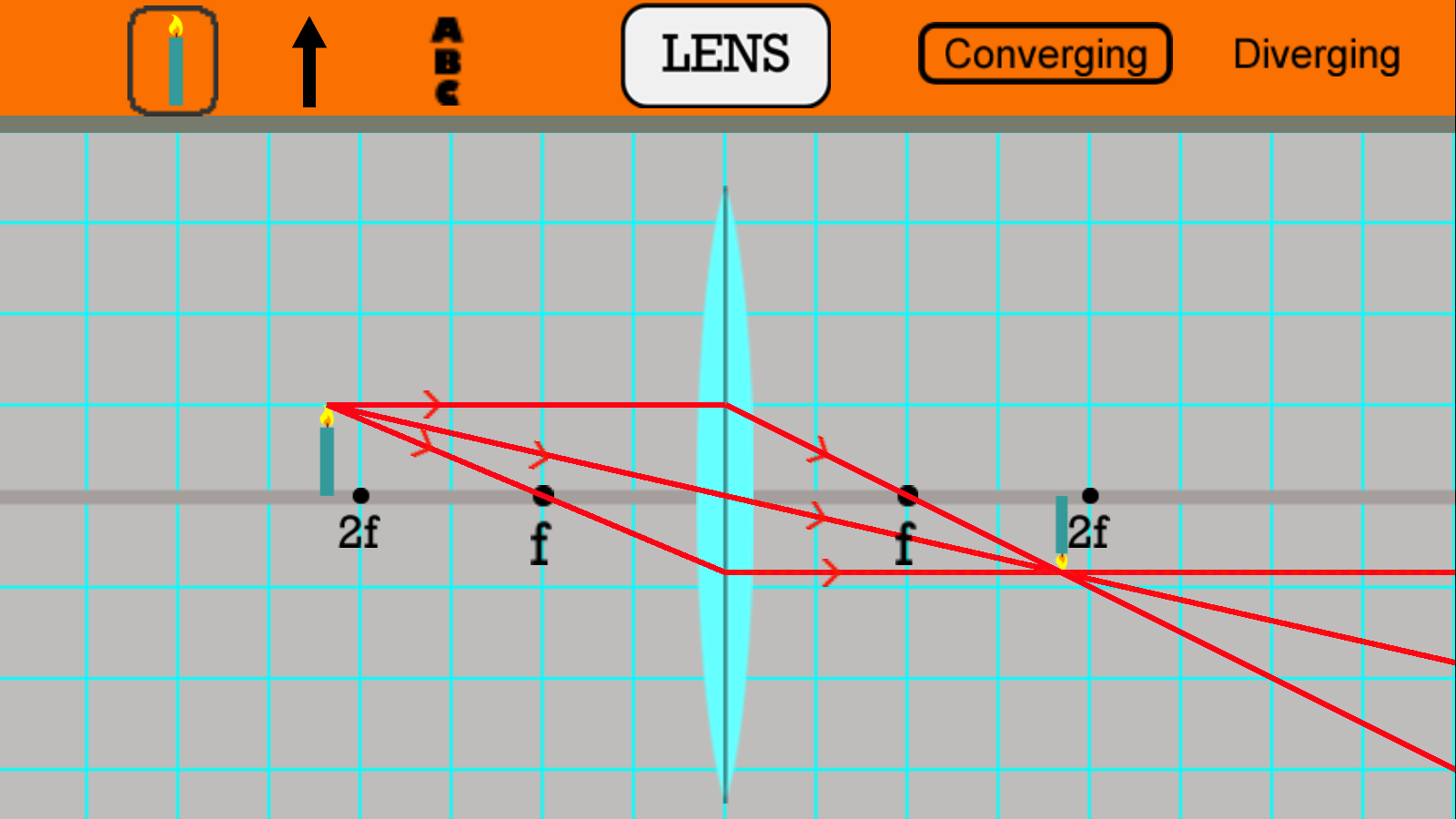
Curved Mirrors, Ray Diagrams, and Simulations Background Information Spherical mirrors may be concave or convex. Concave mirrors have the focal point (f) in front of the mirror, and convex mirrors have the focal point behind the mirror. In this equation, the symbols d o and d i represent the distances from the mirror to the object and to the image.
A concave lens is a piece of round glass that is thinner at the centre than at the edges. It bends the rays of light passing through it away from each other i.e. diverges them. Opticians use concave lenses to correct nearsightedness.
Ray Optics applets I have made. Image Formation in a Plane Mirror. Two People Looking in a Plane Mirror. Plane Mirror in 3D. Spherical Mirror Multiray. Concave and Convex Mirror Ray Diagram. Spherical vs. Parabolic Mirrors. Lenses. Lens Maker's Equation. Prism Dispersion. Lens Pair. Snell's Law for Spherical and Parabolic Lenses.
This collection of interactive simulations allow learners of Physics to explore core physics concepts by altering variables and observing the results. This section contains more than 70 simulations and the numbers continue to grow.
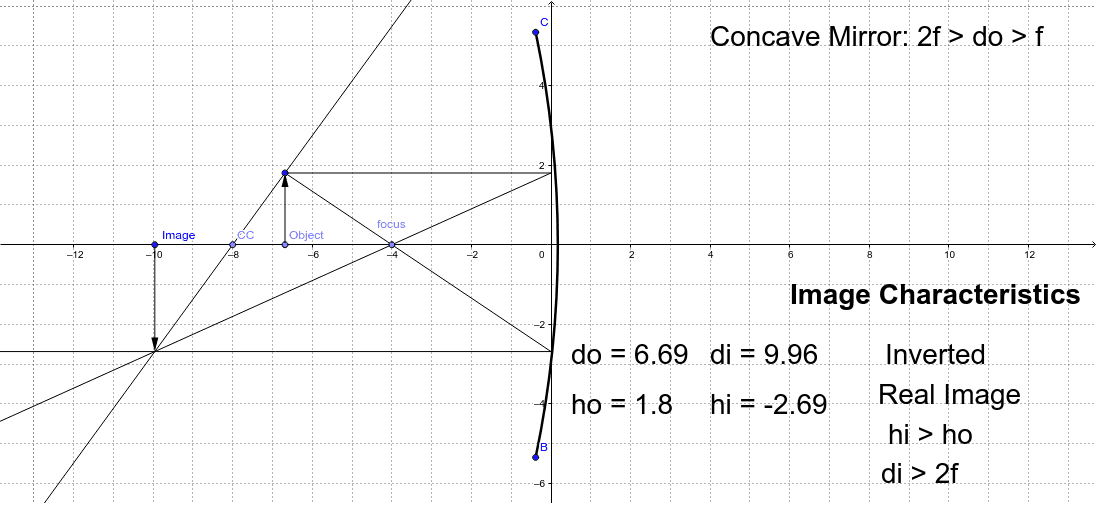
Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
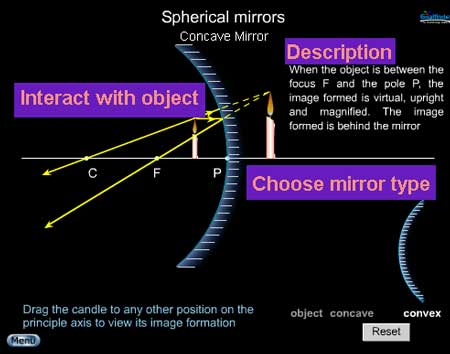
The Concave Mirror Images simulation provides an interactive experience that leads the learner to an understanding of how images are formed by concave ...
Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
Lens and Mirror Lab. Category. Optics, Physics. Change the location of the object and use the ray diagrams to determine the location of the image. The following lab was created by Nick Donovan. Thanks Nick! Recommended Lab:
The Name That Image Interactive is a skill-building tool that allows the learner to explore the characteristics of images formed by concave and convex mirrors. The learner is presented with the position of an object in front of a curved mirror and must decide which one of ~30 images is the corresponding image for that object position. When a learner makes a decision, feedback is immediate ...
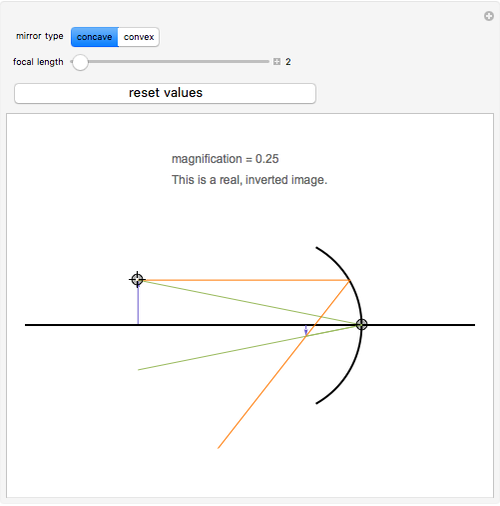
The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn. This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images.
These provide ray diagram of concave mirror to study and analyze nature of light passing through a concave mirror. You can basically adjust object position, object size, focal length, radius of curvature, and other parameters and perform concave mirror simulation.
The concave mirror differs greatly depending on whether the object is inside the focus of the concave mirror. If the object is in the focus of the mirror: It is a virtual image, the image looks larger than the real thing. And the image always stands straight. If the object is outside the focus of the mirror: It is a real image, which is ...
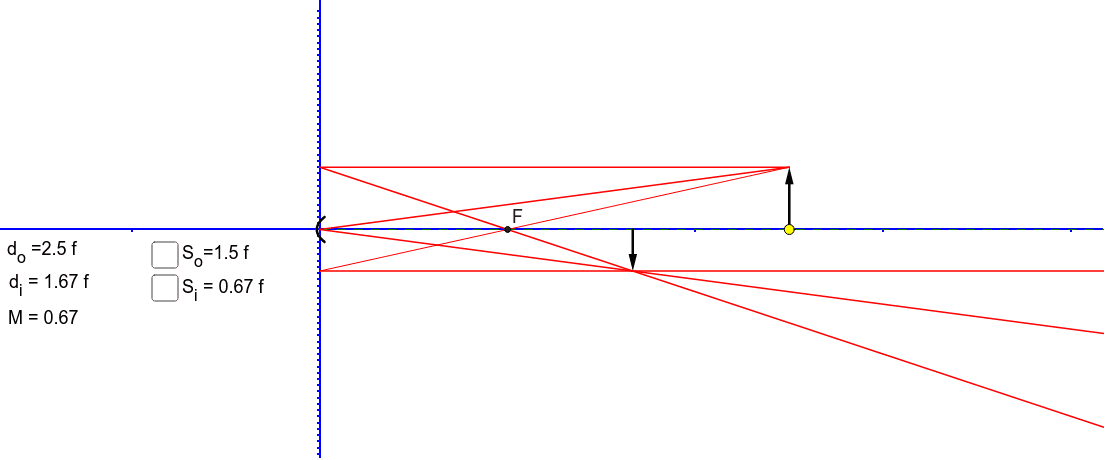
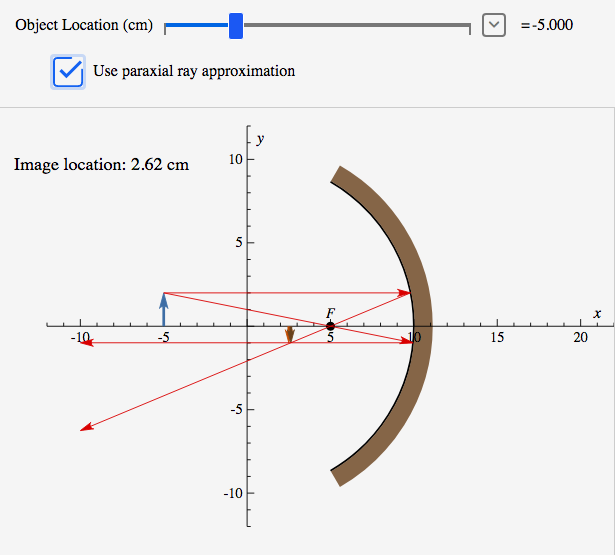
Concave Mirror ray diagram. This simulation shows a ray diagram for a concave mirror. Change the object position by dragging the yellow circle. Check the check boxes to show the distances S o and S i. F is the focal point. Light rays are shown in red, extensions to rays are shown as green dashed lines.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a concave mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, and of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle to move it along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size.













0 Response to "35 concave mirror ray diagram simulation"
Post a Comment