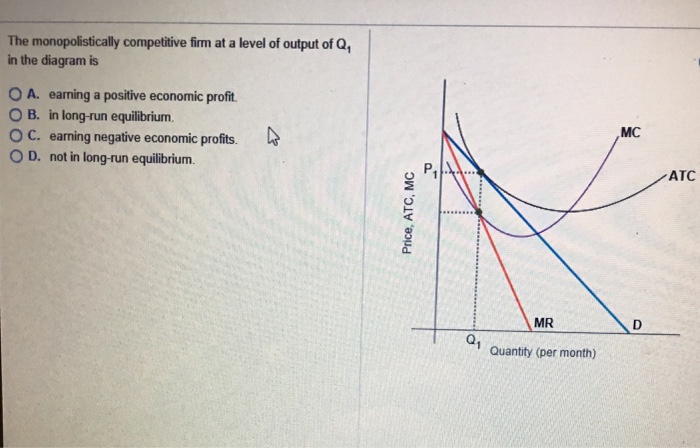
35 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
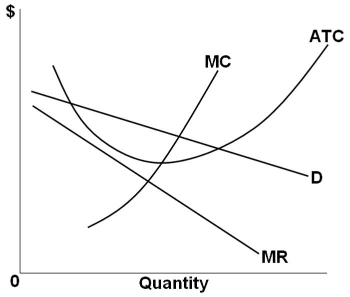
C)firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. D)no change in the number of firms in this industry. 31) Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: 31)____ A) loss of $320.
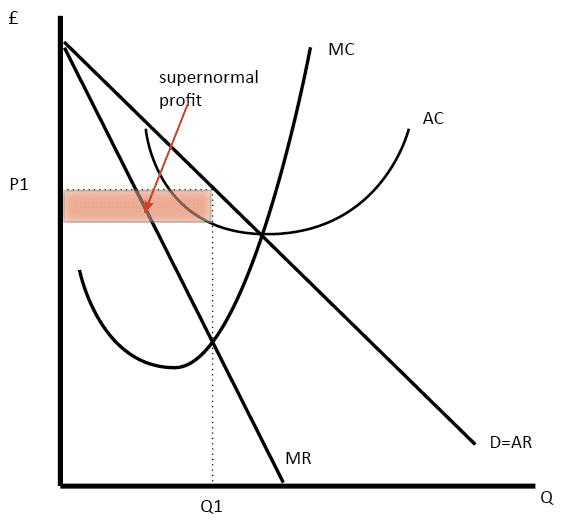
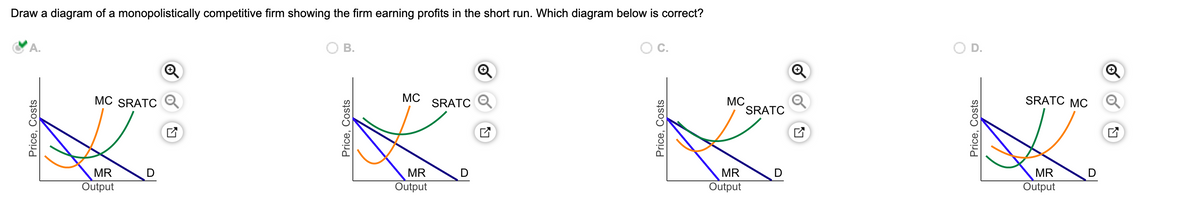
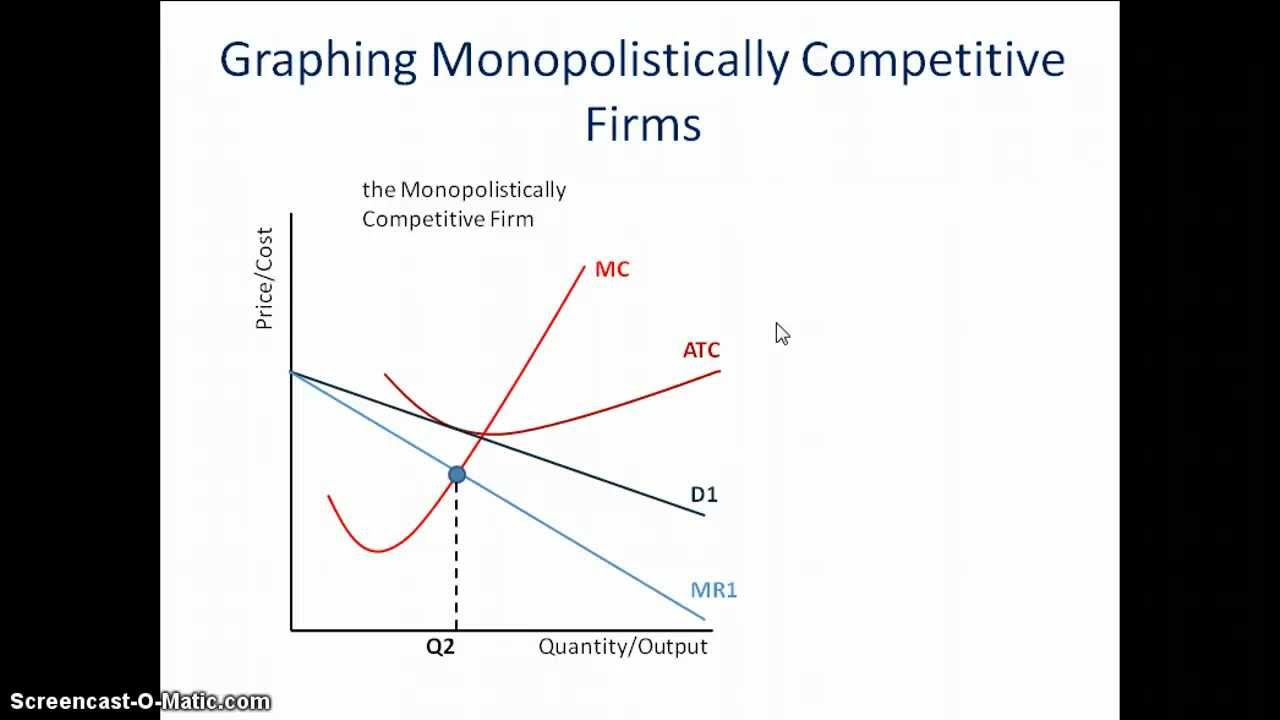
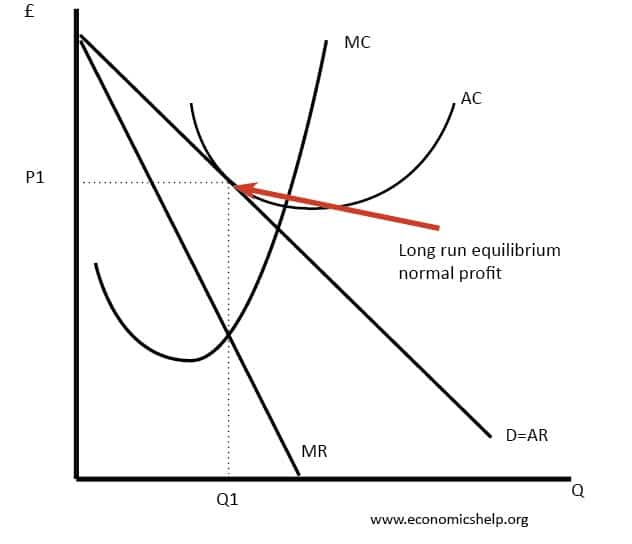
Diagram monopolistic competition short run In the short-run, the firm maximizes profit where MR=MC. This is at output Q1 and price P1, leading to supernormal profit. This profit per unit is less than what a monopolist makes. This difference is determined by the slope of the AR and the AC curve which is flatter than in the case of monopolist.
Suppose the market for fast-food value meals is monopolistically competitive, with many restaurants selling their own brand of food. Assume the restaurants in the industry behave optimally by maximizing profit. The figure to the right represents the market for one monopolistically competitive firm's value meals.
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
A monopolistic market is where one firm produces one product. A key characteristic of a monopolist is that it's a profit maximizer. A monopolistic market has no competition, meaning the monopolist...
Show a comparative analysis of incurring abnormal profits in a Monopolistically Competitive firm and Perfectly Competitive firm; with the help of a diagram. August 20, 2021 / in Samples / by Frank Main
If the firms in an oligopolistic industry can establish an effective cartel, the resulting output and price will approximate those of A. a purely competitive producer. B. a pure monopoly. C. a monopolistically competitive producer. D. an industry with a low four-firm concentration ratio.
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is.
A monopolistic market and a perfectly competitive market are two market structures that have several key distinctions in terms of market share, price control, and barriers to entry. In a...
C)firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. D)no change in the number of firms in this industry. 31) Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: 31)____ A) loss of $320.
In short run, a firm maximizes its profit when price is greater than average total cost, the firm is making a profit. In short run, a firm maximizes its profit when price is equal to marginal cost. 3.2. In Monopolistic competition, firms produce differentiated products, therefore, they are not price takers. The goods have inelastic demand. 4.1
Use a monopoly diagram for a representative monopolistically competitive firm to depict a long-run equilibrium. Understand how the market equilibrium changes upon opening to free trade. Assume that there are two countries, each with a monopolistically competitive industry producing a differentiated product.
Monopolistic competition refers to a market structure that combines the elements of both competitive markets, and monopoly. On the other hand, an oligopoly is a form of market structure where there are few firms that are independent, and vary their prices with respect to the prices of their rivals. SHORT RUN PROFITS IN MONOPOLISTIC MARKET STRUCTURE
A monopolistically competitive market is characterized by: · many buyers and sellers, · differentiated products, and · easy entry and exit. The monopolistically competitive market is similar to perfect competition in that there are many buyers and sellers who can enter or leave the market easily in response to economic profits or losses.
Demand Curve for the Monopolistically Competitive Firm. Monopolistic competition is a type of competition that exists in between two extremes. Perfect competition and the monopoly.. A perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is a horizontal line with infinite price elasticity.The demand curve of a monopoly firm is the demand curve for the industry, and it is downward sloping, indicating ...
Monopolistic competition is a market structure whereby there are many sellers or firms in the market or industry that offer similar products or services but not perfect substitutes. In other words, these many firms offer similar commodities but these commodities are not homogeneous or identical.
A monopolistically competitive firm faces a demand for its goods that is between monopoly and perfect competition. Figure 8.4a offers a reminder that the demand curve as faced by a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic or flat, because the perfectly competitive firm can sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price. In ...
C)firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. D)no change in the number of firms in this industry. 31) Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: 31)____ A) loss of $320.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: Question 4 options: a) $10. b) $13. c) $16. d) $19. Question 5 (4 points) Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: Question 5 options:
D) Each type of firm competes on product quality and price. Answer: C . 32) Excess capacity is the . A) difference between a perfectly competitive firm's and a monopolistically competitive firm's output. B) difference between a perfectly competitive firm's and a monopoly's output. C) output at the maximum point of the
Suppose the government places a sales tax on firms in a monopolistically competitive industry. Draw a diagram showing the short-run impact and the adjustment to the new long-run industry equilibrium. What happens to the equilibrium price and number of firms in the industry?
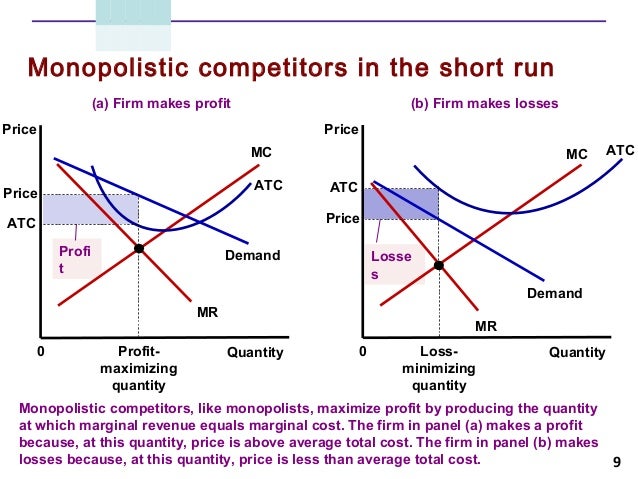
A significant difference between a monopolistically competitive firm and a purely competitive firm is that the former sells similar, although not identical, products. If monopolistically competitive firms in an industry are making an economic profit, then new firms will enter the industry and the product demand facing existing firms will
The model of monopolistic competition describes a common market structure in which firms have many competitors, but each one sells a slightly different product. Many small businesses operate under conditions of monopolistic competition, including independently owned and operated high-street stores, restaurants, hotels and pubs.
A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market is currently producing 100 units of output. It has average revenue of $10, average total cost of $8, and ficed costs of $200. What are the firm's profit, marginal cost, and average . Economics. you are hired as the consultant to a monopolistically competitive firm.
Draw a diagram depicting a firm that is making a profit in a monopolistically competitive market. Now show what happens to this firm as new firms enter the industry. Draw a diagram depicting a firm that is making a profit in a monopolistically competitive market. Now show what happens to this firm as new firms enter the industry.
C)firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. D)no change in the number of firms in this industry. 31) Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: 31)____ A) loss of $320.
C)firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. D)no change in the number of firms in this industry. 31) Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: 31)____ A) loss of $320.
B)monopolistically competitive firm. C)perfectly competitive firm. D)monopoly. 34) 35)In the figure above, assuming that the firm does not shut down, the firm will produce A)40 units. B)30 units. C)fewer than 20 units. D)20 units. 35) 36)In the figure above, assuming that the firm does not shut down, it will charge a price of A)$4. B)$3. C)$2 ...
3.1 Explain the three possible profit maximizing positions of perfectly competitive. firms in the short-run. 3.2 Describe the nature of the goods produced by a monopolistically competitive. firm. 4.1 Distinguish between the short-run aggregate supply curve and the long-run. aggregate supply curve.
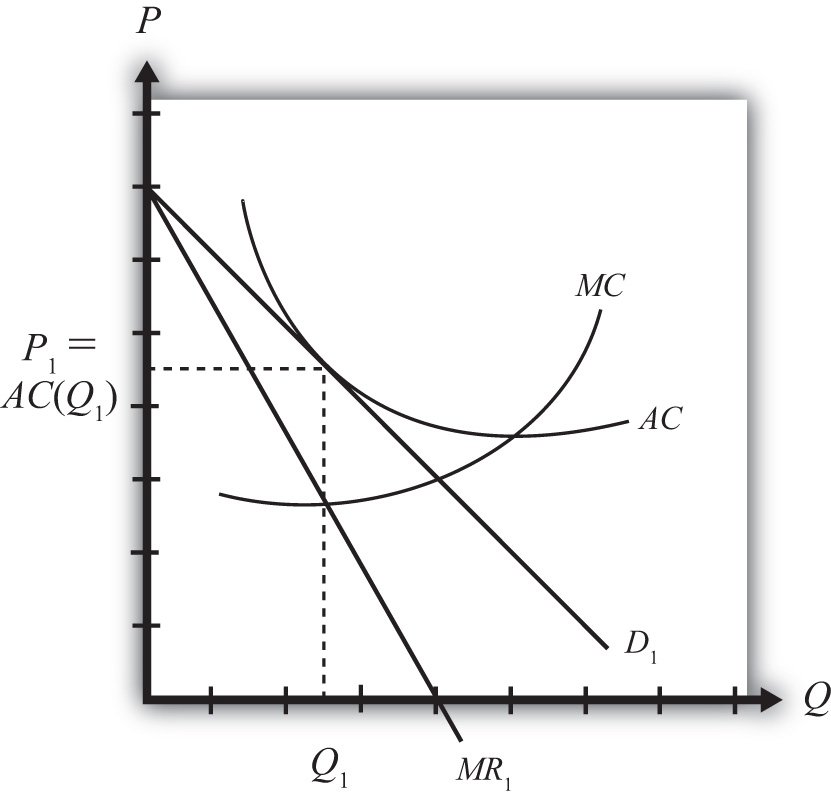
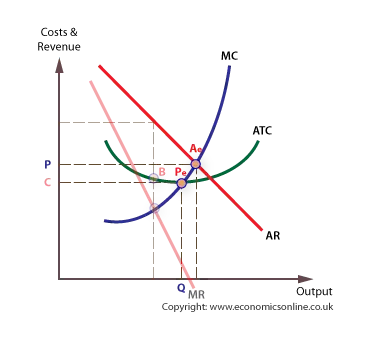
In monopolistic competition, firms operate where MR = MC, which is shown at quantity Q1 on the graph. However, the firm could produce up to where demand is equal to long-run marginal cost. This is because, at this point, the firm is producing at the exact cost the consumer is willing to pay.
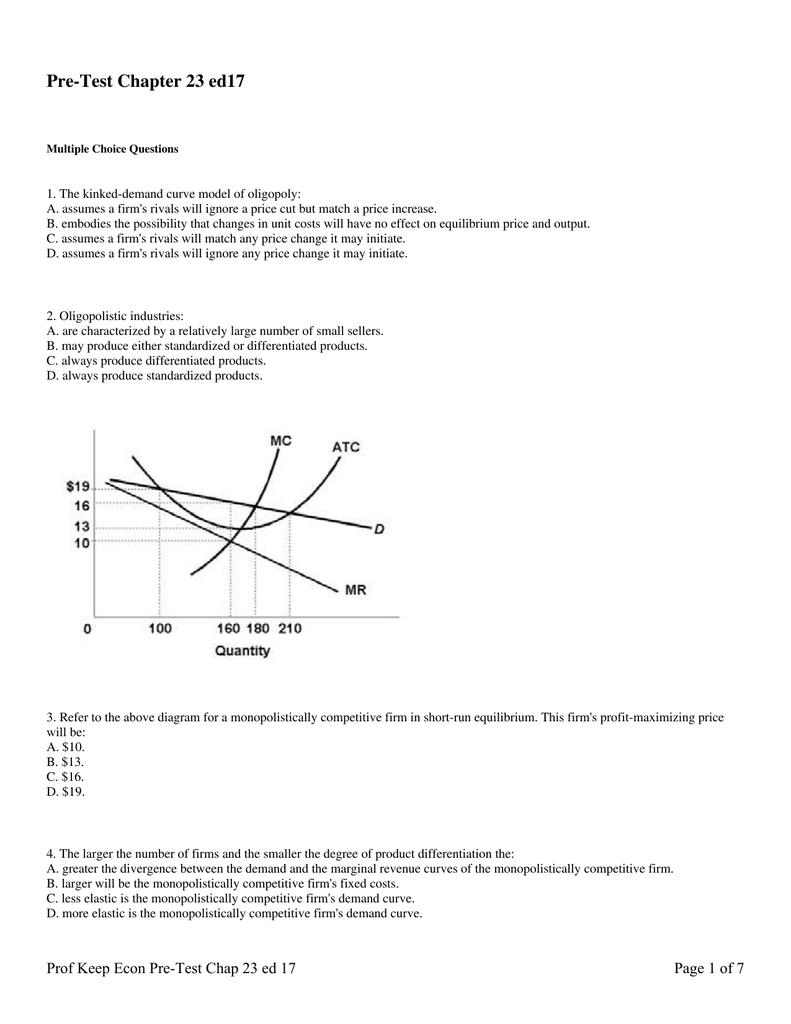
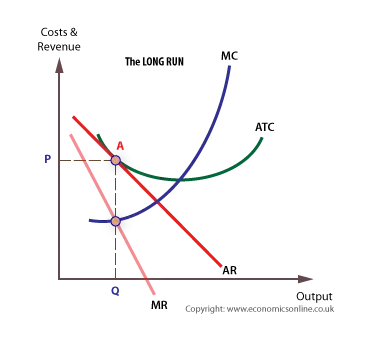
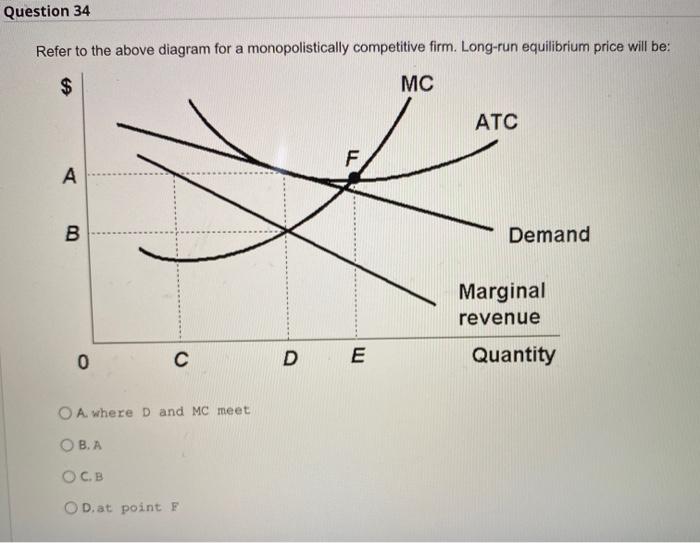
The diagram above depicts a monopolistically competitive firm in a state of long-run equilibrium. This firm maximizes its profit by producing an output level of Q'. The equilibrium price is P'. Since the price equals average total cost at this level of output, a typical firm receives a level of economic profit equal to zero.
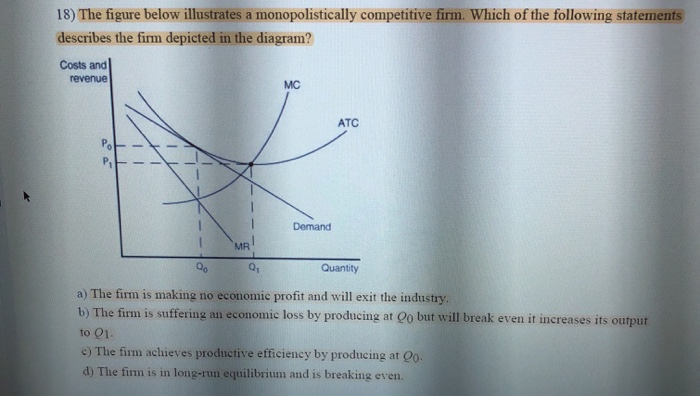
The following diagram shows the structure of cost and demand facing a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run. a. Identify the following on the graph and calculate each one. i. Profit-maximizing output levelii. Profit-maximizing priceiii. Total revenueiv. Total costv. Total profit or loss b. What is likely to happen in this industry in the long run?
The diagram below shows a typical monopolistically competitive firm when the industry is in long-run equilibrium. a. Explain why free entry and exit implies that the long-run equilibrium is at point A. b.
2 The diagram below shows the costs and revenues for a business. Which ONE of the following is the market structure shown in this diagram? A A monopolistically competitive firm B A firm which is a price maker C A perfectly competitive firm in the long run D A perfectly competitive firm in the short run 0 p Costs and revenues Output MC ATC
Note in the above diagram that firms would lose money if they produced more to achieve either allocative or productive efficiency. That most firms operate with excess capacity is evident when looking at most monopolistically competitive firms, such as restaurants and other retailers, where salespeople are often idle.










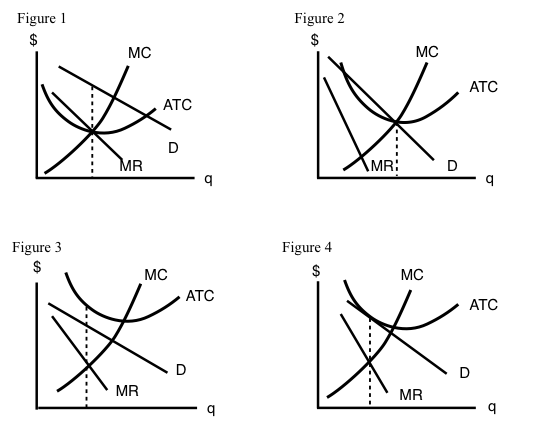





0 Response to "35 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is"
Post a Comment