35 square planar orbital diagram
26.12.2021 · Square pyramidal: 87° 4: 2: Square planar: 90° As we discussed in the lewis structure, that each carbon atom forms 3 bonds, 2 with neighboring carbon atoms and 1 with the hydrogen atom. Therefore, carbon has 3 bonding electron pair which corresponds to Trigonal planar geometry. Hence, the 3D structure of benzene will be as below. The trigonal planar …
22.11.2021 · The square-planar R n+1 Ni n O 2n+2 phases are identified on the phase diagram by their formal 3d electron count. AFI, antiferromagnetic insulator; SC, superconductor. AFI, antiferromagnetic ...
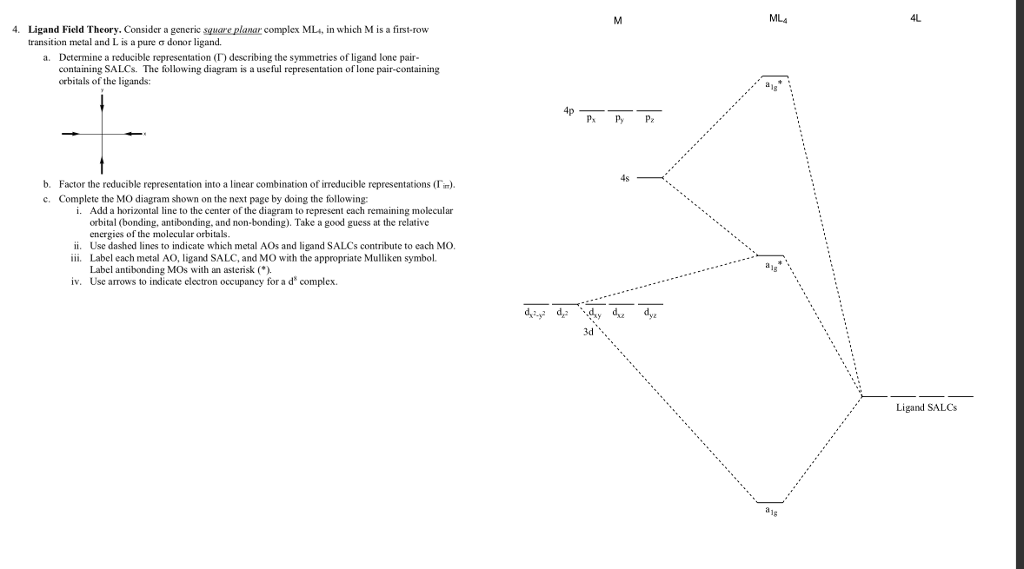
I have this homework problem in Inorganic and I am not sure where to being. I really appreciate any insight you can provide! The question reads: Find the symmetries of the sigma-bonding p-orbitals in [MnBr*_4_*]^- . What valence orbitals on the metal will interact with the symmetries of the simga-bonding ligand orbitals? This is my thought process so far: I initially thought that [MnBr*_4_*]^- was tetrahedral, providing a T*_d_* point group. I tried to draw a VSPER structure to double check t...
Square planar orbital diagram
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
If it were to adopt a square planar geometry, the electrons will be stabilised (with respect to a tetrahedral complex) as they are placed in orbitals of lower energy. However, this comes at a cost: two of the electrons, which were originally unpaired, are now paired: $\hspace{30 mm}$ (source: Wikipedia) and on top of that, there are additional steric repulsions introduced by moving the …
Our teacher told us this trick to tell if complex is going to be square planar. We are considering the fact that the coordination no. is 4. If the metal has a $\ce{d^7}$, $\ce{d^8}$ or $\ce{d^9}$ configuration along with a strong field ligand or $\ce{d^4}$ with weak field ligand then complex will be square planar otherwise tetrahedral.. One exception i have come across for this is …
Square planar orbital diagram.
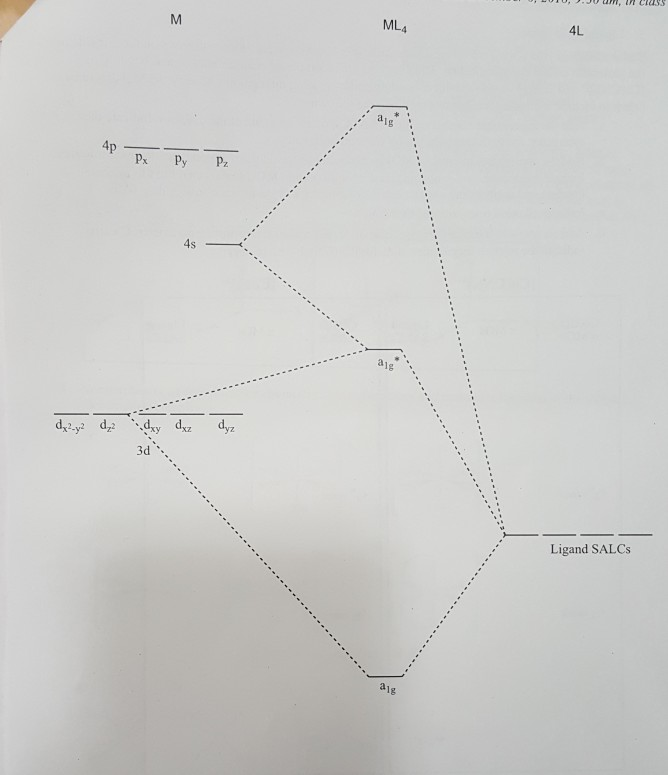
form tetrahedral, square planar or pyramidal geometries. MOT for the tetra coordinated complexes can be utilized to construct the molecular orbital diagrams ...12 pages
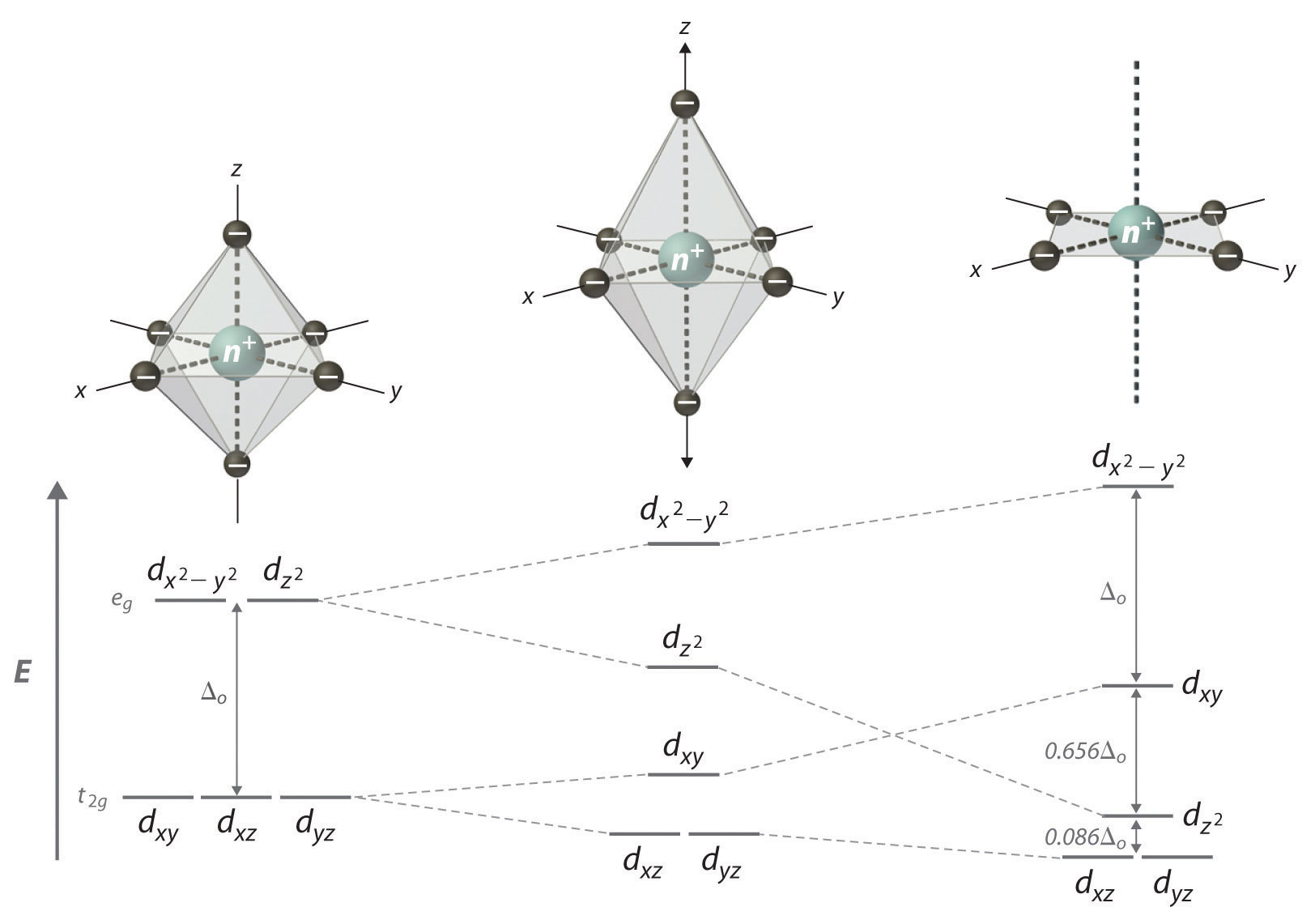
Feb 09, 2018 · The crystal field theory can be extended to square-planar complexes, such as Pt( NH3)2Cl2. The splitting of the d orbitals in these compounds is shown in the figure below. diagram. return to top. Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal 4. Square pyramidal d z2 dx2-y2 d xy d yz d xz. 5.
Predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following: a. a tetrahedral d6 ion b. \[Co(H2O)6\] 2+ c. \[Cr(H2O)6\] 3+ d. a square-planar d7 ion I'm having trouble solving this type of problem. I have the following questions regarding the answers: 1) How did they determine what was low spin and high spin? For B, I'm puzzled as H2O falls in the grey zone of the spectrochemical series (according to my professors notes, but I have seen sources that don't agree), so it could ...
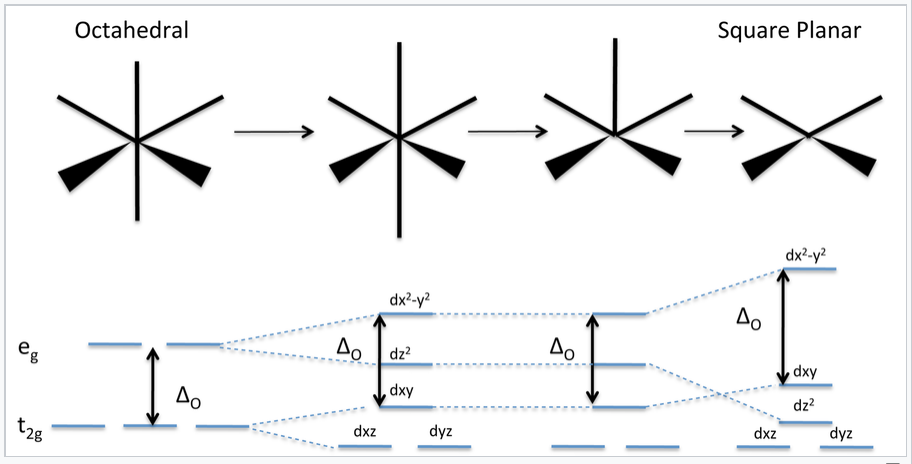
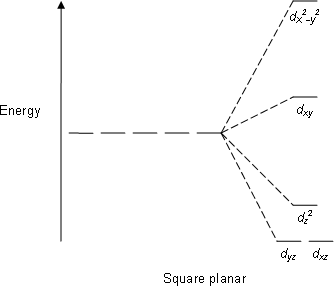
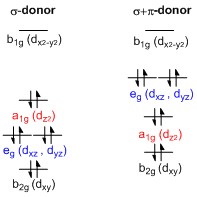
In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is the most destabilized and is left unfilled.
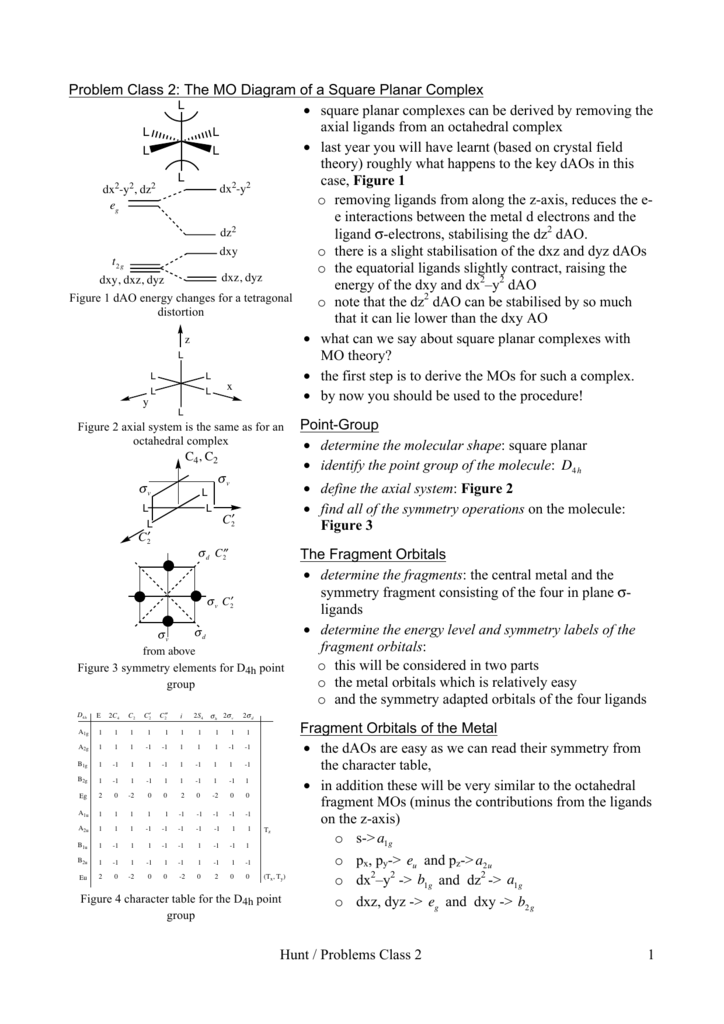
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. When the two axial ligands are removed to generate a square planar geometry, the d …
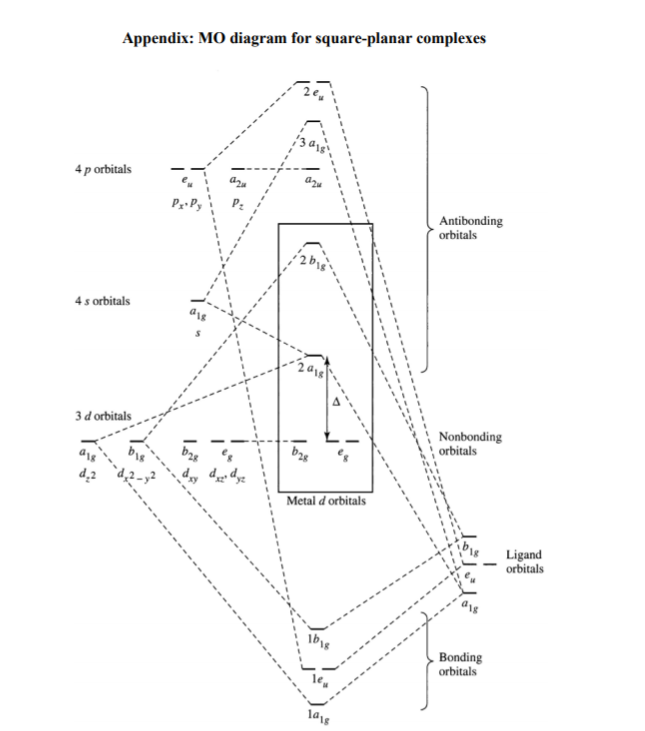
Molecular Orbital Theory – Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar Complexes The crystal field theory fails to explain many physical properties of the transition metal complexes because it does not consider the interaction between the metal and ligand orbitals. The molecular orbital theory can be very well applied to transition metal complexes to rationalize the covalent as well …
If I wore a stretchy wrist band with magnets on the inside, pressed up against my skin, would it eventually start to accumulate iron in my blood vessels and clog them?
Apr 18, 2014 · Description. This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. The students generate ligand-group orbitals (LGOs) for the set of 4 H (1s) orbitals and then interact these with carbon, ultimately finding that such a geometry is strongly disfavored because it does not maximize H/C bonding and leaves a lone pair on C.
by J Börgel · 2016 · Cited by 21 — The presentation of d-orbital splitting diagrams for square planar transition metal complexes in textbooks and educational materials is ...
10.05.2021 · In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is ...
This was the last question on an exam I just took. Skimmed the question in a hurry, just wrote down some bullshit about how Zn^2+ is d8 therefore square planar is most likely, then I regurgitated some tangentially related gibberish about coordination numbers and came out with a worthless answer with no time left on the clock. Now that I'm not rushing it, I'm thinking that I should have calculated the changes in CFSE (or shit, LFSE maybe? Is that possible? god damn it) for the different geometri...
We find that the square planar complexes have the greatest crystal field splitting ligand field (left diagram) and the tetrahedral field (right diagram).D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3.
Spin states when describing transition metal coordination complexes refers to the potential spin configurations of the central metal's d electrons. In many these spin states vary between high-spin and low-spin configurations. These configurations can be understood through the two major models used to describe coordination complexes; crystal field theory and ligand field theory, …
Jahn-Teller, Square Planar Complexes, Orbital Overlap Method, and Electron Counting Chapter 10 and Section 13.3 Monday, November 30, 2015. Jahn-Teller Distortions Jahn-Teller Theorem: electron configurations with unequal occupancy of degenerate orbitalsare not stable. d4HS A complex with such a configuration will undergo a Jahn-Teller distortion to lower its energy. no …










![d-orbital energy levels in planar [M II F 4 ] 2− , [M II (NH ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2020/DT/d0dt02022b/d0dt02022b-f1_hi-res.gif)




0 Response to "35 square planar orbital diagram"
Post a Comment