36 ray diagram convex lens
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. We have already learned that a lens is a carefully ground or molded piece of transparent material that refracts light rays in such a way as to form an image. Lenses serve to refract light at each boundary. As a ray of light enters a lens, it is refracted; and as the same ray of light exits the lens, it is refracted again.
6.12.2019 · A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially with a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm. The two are kept at 15 cm from each other. A point object lies 60 cm in front of the convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image by the combination. Determine the nature and position of the image formed. Answer:
Ray diagram convex lens
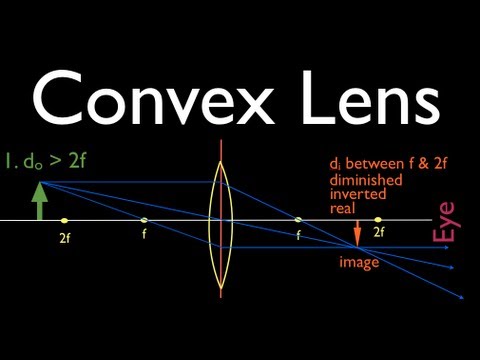
Easy and interesting way to understand the concept of image formation of an object by convex lens.Published on 3 March 2021 Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
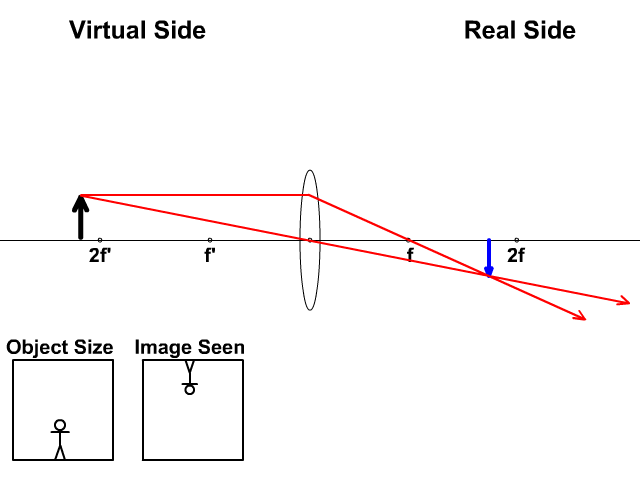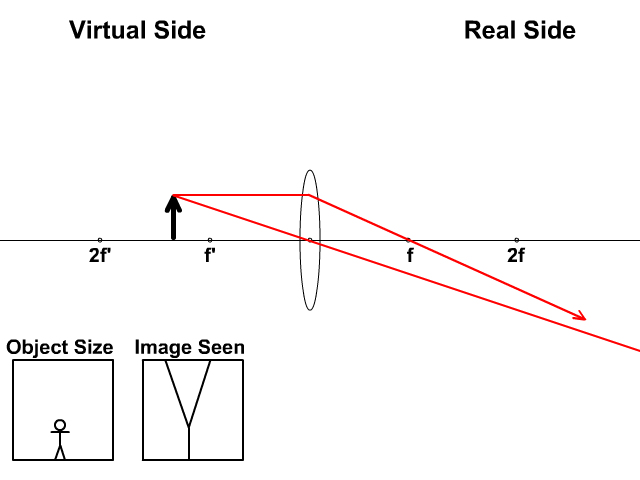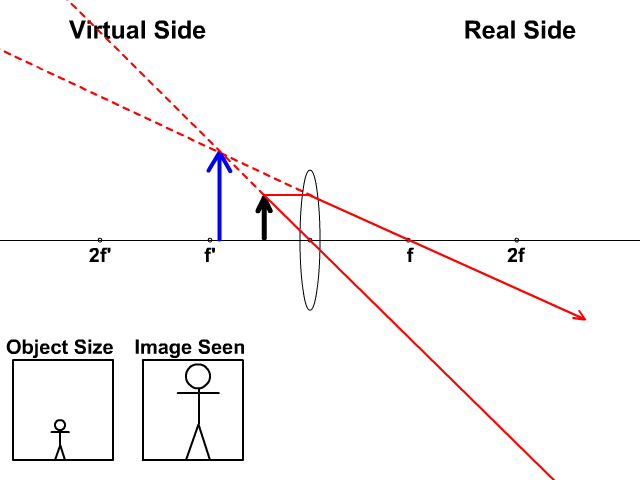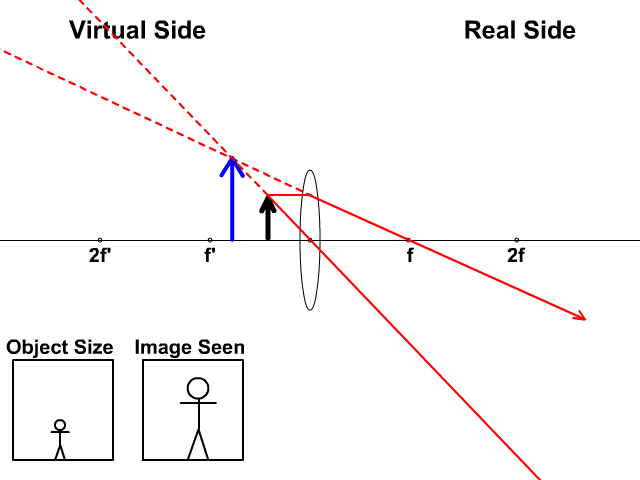
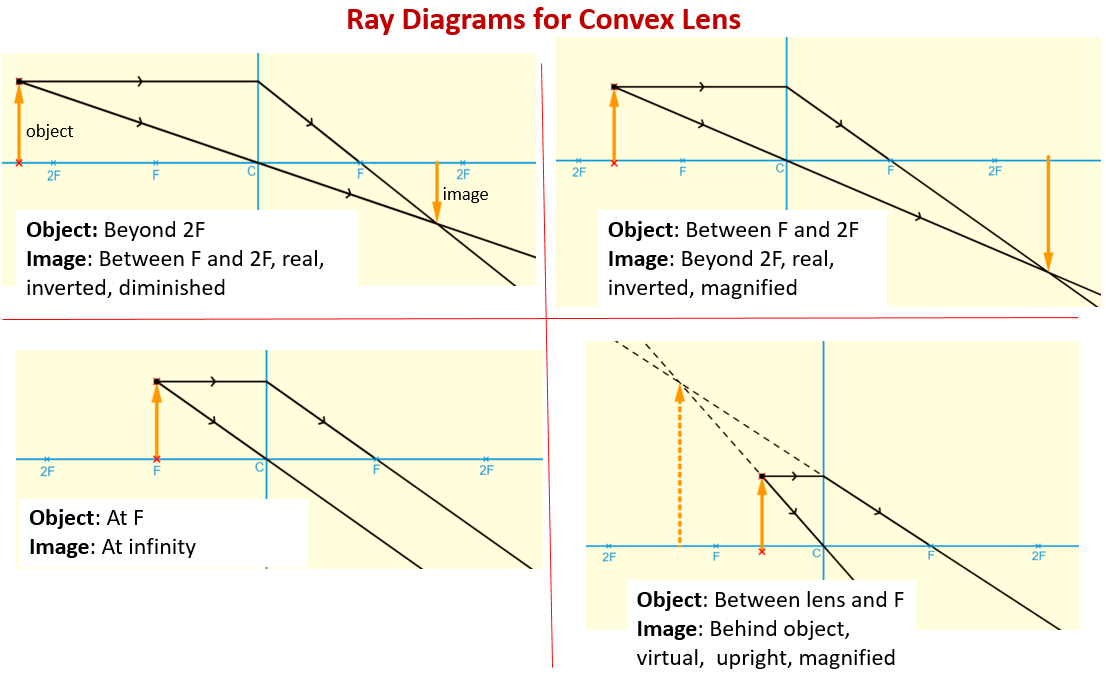
Ray diagram convex lens. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the ... The word lens comes from lēns, the Latin name of the lentil, because a double-convex lens is lentil-shaped.The lentil plant also gives its name to a geometric figure.. Some scholars argue that the archeological evidence indicates that there was widespread use of lenses in antiquity, spanning several millennia. The so-called Nimrud lens is a rock crystal artifact dated to the 7th … When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel ...
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ... There are two types of lenses, they are a convex lens and a concave lens. The images obtained from these lenses can be either a real image or a virtual image. Below is an experiment to find the image distance for varying object distances of a convex lens with ray diagrams. Refraction Through a Lens | Ray Diagrams of a Convex Lens | ICSE Class 10 Physics | Umang Vedantu Class 9 and 10. Abhishek sir will take you through ICSE Cla... Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
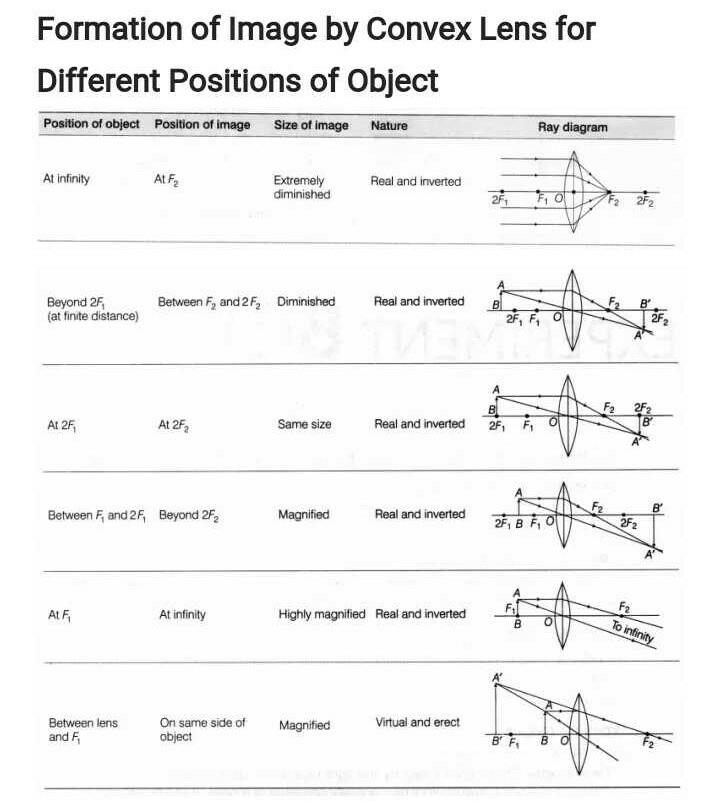
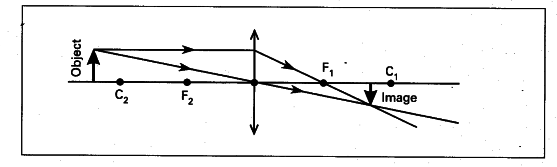
The image formation by convex lenses using ray diagram depiction can be briefly explained as follows, When the object is placed at infinity: When the object is placed at infinity, the image formed by the convex lens will be at the second focus, F2. The nature of the image obtained will be a real image and it will be in inverted form. Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation. For a both convex and concave lens, we see that ray passing through Optical center emerges without deviation. Next: Convex Lens - Ray diagram→. Facebook Whatsapp. The diagram showing the refracted ray can be viewed by clicking the View Diagram button below. View Diagram The solution to Example A is given as an example. Try Example B on your own and click on the See Answer button to check your answer. See Answer Answer: 34.7 degrees. Measure the angle ... The convex lens ray diagrams give people an idea about the position of the image and the object. The students can also have ideas about the nature of the lens. They can also know how the light rays experience a change in path due to a convex lens's presence there. People can use the convex lens ray diagram to understand the nature, size, and image position. But, it is difficult for the ...
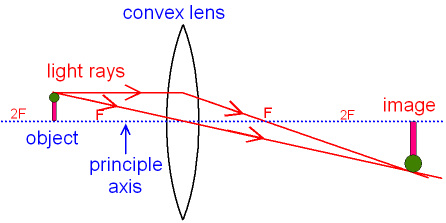
Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be loaded into the projector upside down so the ...
Convex Lens - Ray diagram Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts ...
The convex lens shown has been shaped so that all light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side of the lens. (The axis is defined to be a line normal to the lens at its center, as shown in Figure 1.) Such a lens is called a converging (or convex) lens for the converging effect it has on ...
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by Teachoo. For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis Since ray parallel to principal axis passes through the Focus Both rays ...
Method for drawing ray diagrams – convex lens. A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find the location of the image that would be created on a screen you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "The two rules of refraction for converging lenses". The only ...
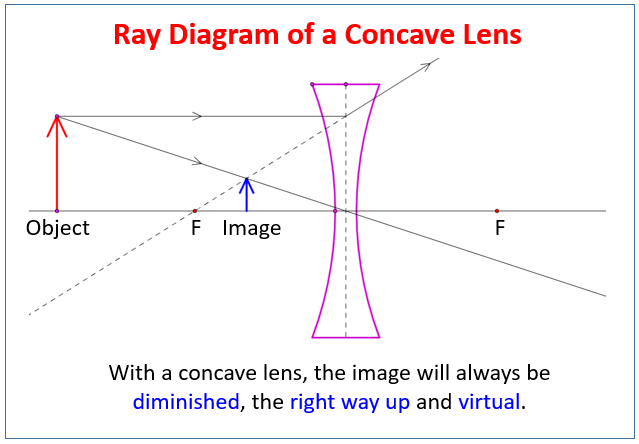
10.12.2019 · A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction. Any incident ray of light that passes through the focus of the lens before getting refracted will emerge parallel to the principal axis on refraction.
Ray diagrams for convex lenses are based on the principle that convex lenses converge light rays passing through them. The following points are to be kept in mind while drawing ray diagrams for convex lens:-A ray of light passing through the optical center of a convex lens passes through the lens undeviated. A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, on passing through the lens, gets ...
Ray tracing diagram for convex lens. "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than ...
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
The convex lens is a lens that converges rays of light that convey parallel to its principal axis (i.e. converges the incident rays towards the principal axis) which is relatively thick across the middle and thin at the lower and upper edges. convex lens can converge a beam of parallel rays to a point on the other side of the lens.
The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram Concave Lens - Ray diagram You are here. Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts ...
Uses of convex lens. These are used for a variety of purposes in our day-to-day lives. For example, The lens in the human eyes is the prime example. So the most common use of the lens is that it helps us to see. Another common example of the use of this type of lens is a magnifying glass. When an object is placed in front of it at a distance ...
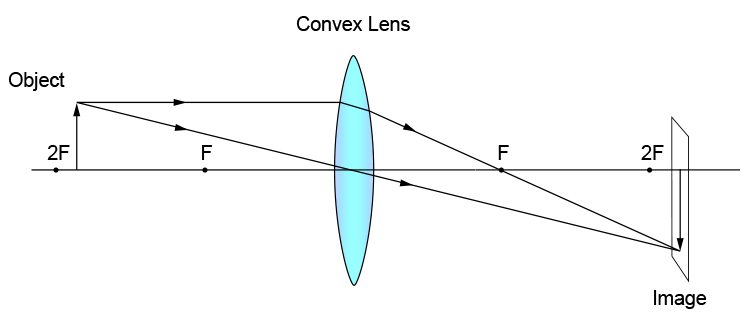
Section 1: Introduction (Refraction and Lenses) 4 Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an example for aconvex lens: F The image of the top of the object is formed where the light rays cross. In a perfect lens all the rays from a point on the object will
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis after reflection. For a concave mirror , we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection. For a convex mirror, since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis.
A worksheet to construct ray diagrams to show where images are formed by a converging (convex) lens and a diverging (concave lens). Aimed at AQA GCSE Physics. Although, may also be useful for other boards/A-Level. Answer sheet available! Both word and pdf worksheets available. Feedback greatly received - particularly constructive ways to improve.
Shows what happens to parallel light rays when they reflect off a concave and convex mirrors and what happens when they pass through concave and convex lense...
ICSE CHAPTER 5 (B)
In X-ray optics, gamma ray optics, and neutron optics, a collimator is a device that filters a stream of rays so that only those traveling parallel to a specified direction are allowed through. Collimators are used for X-ray, gamma-ray, and neutron imaging because it is difficult to focus these types of radiation into an image using lenses, as is routine with electromagnetic radiation …
The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
Easy and interesting way to understand the concept of image formation of an object by convex lens.Published on 3 March 2021





















0 Response to "36 ray diagram convex lens"
Post a Comment