37 concave lens ray diagram
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see large image of teeth of patients. (Teeth have to be placed between pole and focus) Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror to see a larger image of the face Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnace Ray Diagrams of Images formed by convex mirror
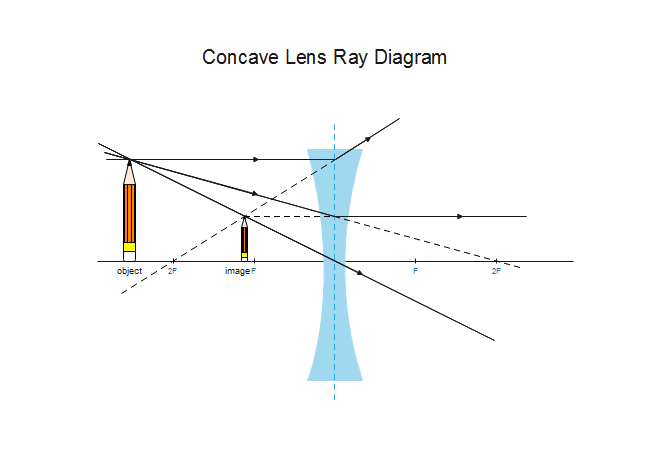
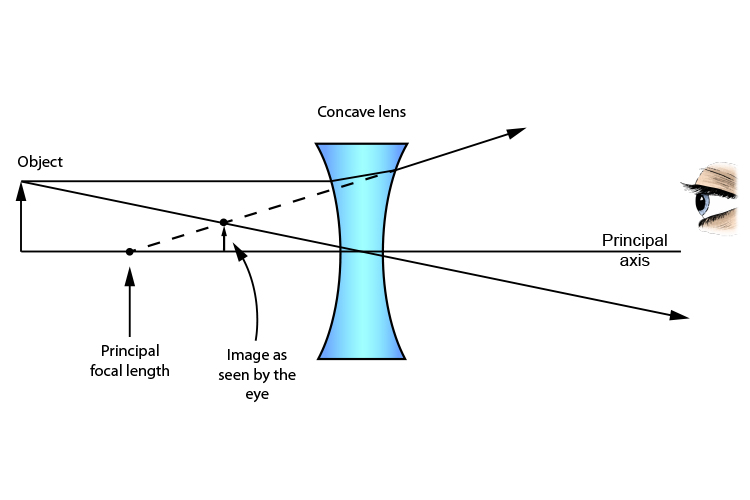
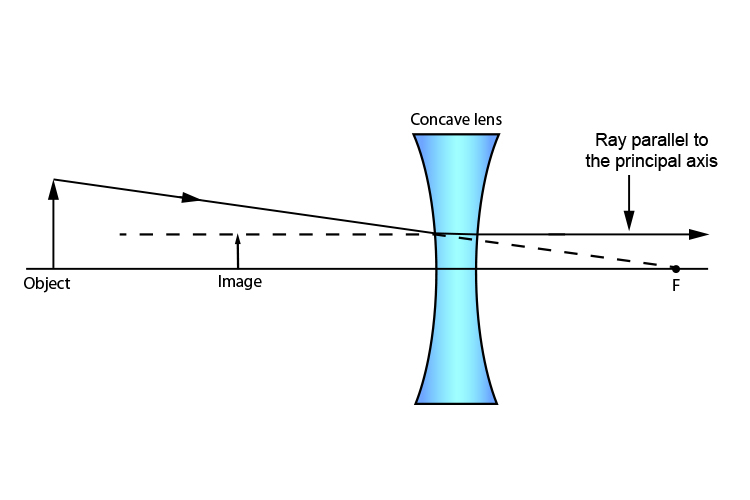
Step 1: The first ray of a concave lens ray diagram travels from the tip of the object parallel to the principal axis. When it emerges from the lens, it appears to come from the principal focus. F. Step 2: The second ray travels from the tip of the object through the optical centre of the lens, and is not refracted. F.
Concave lens ray diagram
Mirror Ray Tracing. Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. A third useful ray is that through the center of curvature since it is normal to the mirror and retraces its path backward.
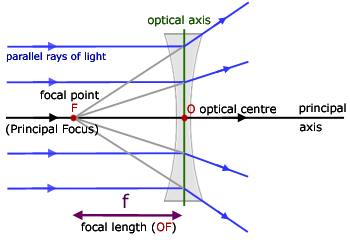
A concave lens is a piece of round glass that is thinner at the centre than at the edges. It bends the rays of light passing through it away from each other i.e. diverges them. Opticians use concave lenses to correct nearsightedness. They are also used in flashlights to magnify the light, and can be found in door viewers or peepholes. ...
The second ray goes straight through the center of the lens. The light rays don't converge, but the sight lines do. J.M. Gabrielse f Concave Lens (example) • F optical axis The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and refracts from the focal point. The second ray goes straight through the center of the lens.
Concave lens ray diagram.
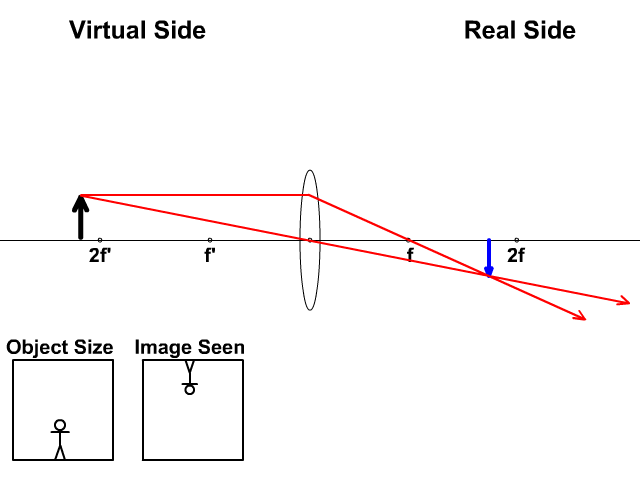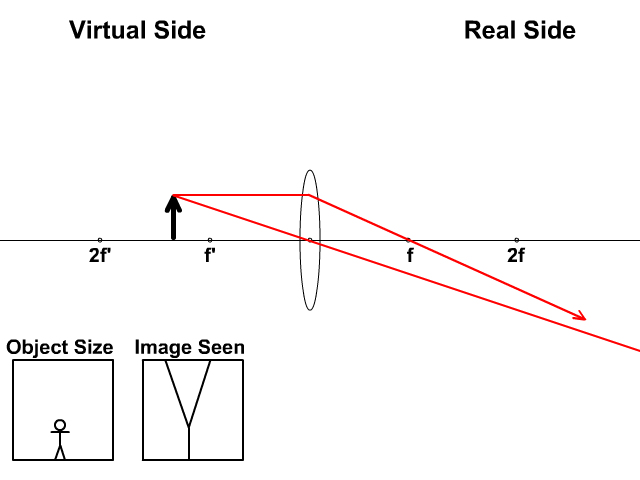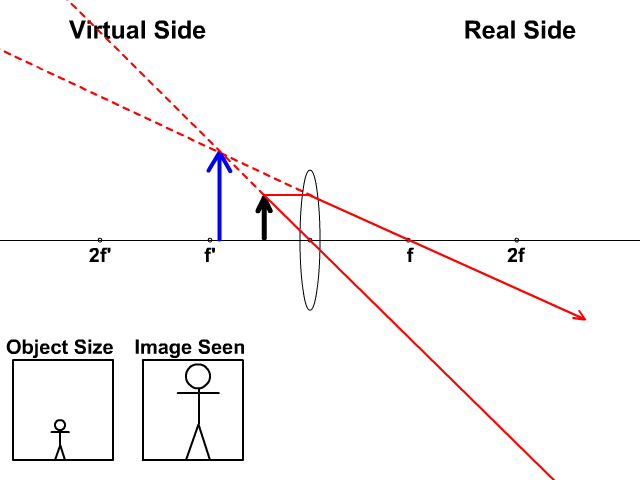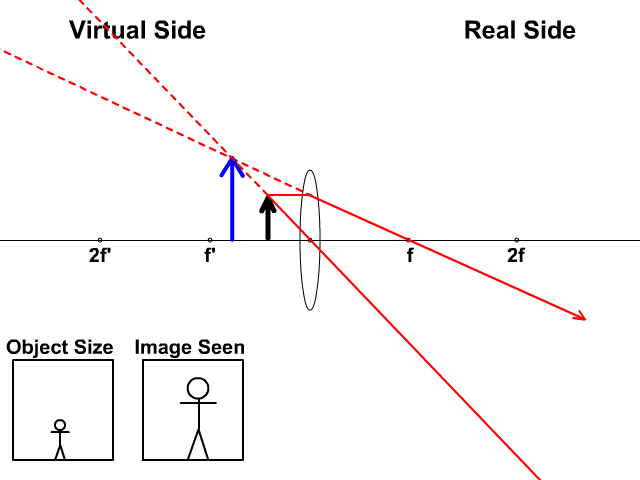
The takeaway here is that a concave lens will produce an upright, virtual image on the object side of the lens. Problem 4 : choose the correct ray diagram Now we have a concave mirror, which can either create a virtual upright image or a real inverted image depending on the location of the object.
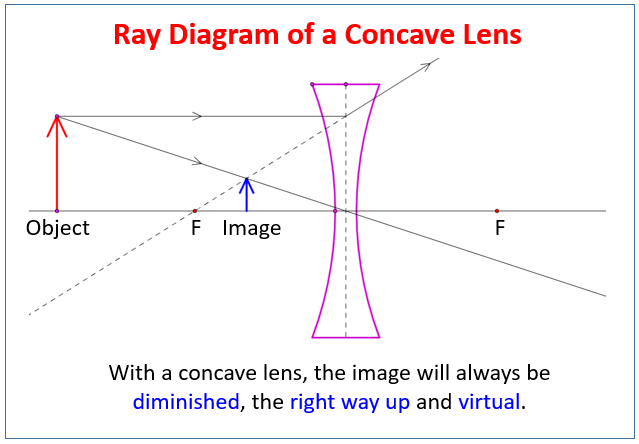
A ray diagram for a concave lens. In this diagram: "Ray 1" is traced backwards after being refracted by the lens. "Ray 2" is shown passing through the centre of the lens. This ray is also traced backwards. The diagram shows that a diminished virtual image is produced at the point that the 'traced' lines from "ray 1" and "ray 2" cross one another.
Ray diagrams for diverging (concave) lens. If an object is on one side of the concave lens, the concave lens can form the image of the object. If the position of the object on one side of the concave lens is known, how to draw the image formation of the object? Suppose an object is on the left side of the concave lens as shown in the figure below.
The ray diagram shown in Fig3. for diverging lenses was created using the rules given in Table. The first ray, parallel to the axis, appears to come from the focal point on the same side of the lens as the object. This ray is indicated by the oblique dashed line. The second ray passes through the center of the lens and is not refracted.
Find my revision workbooks here: https://www.freesciencelessons.co.uk/workbooksIn this video, we look at concave lenses. We explore how to draw a ray diagram...
Concave Lens Ray Diagrams Concave (diverging) lenses can also be used to form images, although the images are always virtual in this case If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a concave lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way:
So just remember, concave has the ... some place on the left side of this concave lens So I can put it, let me just stick it anywhere So let me just stick it right over there So, if I do and like always, we will do our two rays but with a concave lens, I'm only gonna do ...
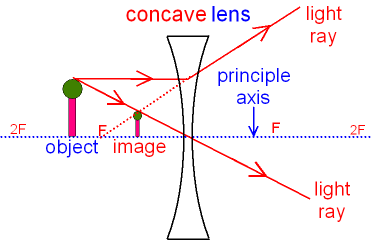
Ray diagram for an object viewed through a concave lens. For an object viewed through a concave. lens, light rays from the top of the object will be refracted. and will diverge. on the other side ...
June 15, 2020 - Other articles where plano-convex lens is discussed: microscope: Types of magnifiers: …of two simple lenses, usually plano-convex (flat on one side, outward-curved on the other, with the curved surfaces facing each other). This type of magnifier is based upon the eyepiece of the Huygenian ...
Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts NCERT Questions ...
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science.
The students can use a convex lens diagram to understand the ray's path after passing through a convex lens. The students may create a convex ray diagram by hand, but the process is lengthy, and at the same time, complicated. If the students fail to place the paths of the light properly, they may end up with a faulty convex lens ray diagram.
December 30, 2019 - Do you need help with your homework? On Toppr Answr you can scan any question, and get its answer instantly
Voronoi Diagrams with Cones; Juggling 13 Balls; Concave and Convex Lenses. Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave ...
Click Here for Full Physics Course: http://bit.ly/2CZXQui Convex and Concave Lenses are Spherical Lenses. We look at the Image Formation by these spherical l...
Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding...
This video shows you a simple method for drawing a ray diagram for a concave lens given the location of object. A ray diagrams helps you understand the chara...
This Hindi video explains how concave lens works i.e. how concave lens forms image using ray diagram.This video is mapped to CBSE class 10 Physics chapter Re...
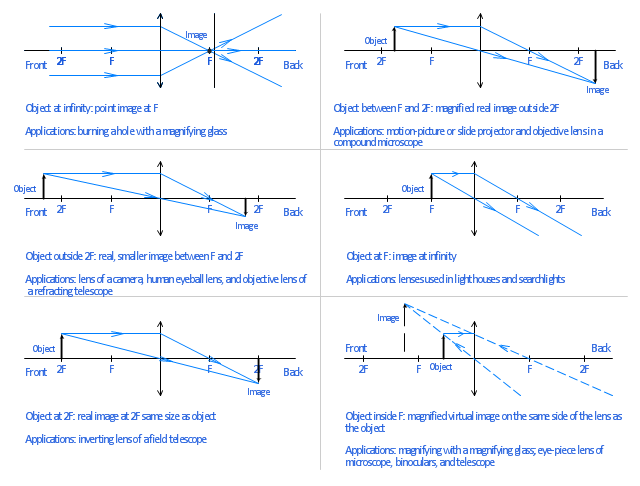
Here in this post, you will get Ray Diagrams for Images formed by convex & concave lenses as a Quick Reference.Image formation by lenses is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image. Ray […]
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length ... A concave lens is thinner in the middle than it is at the edges.
Ray tracing a convex lens: object inside focus The image appears larger (and farther away) than the object. This is a magnifying glass. (Remember: a magnifying glass is a convex lens.) Aside: near-sighted people need concave/diverging lenses; can a marooned myopic start a fire with his eye-glasses?
Convex lenses are also known as converging lenses since the rays converge after falling on the convex lens while the concave lenses are known as diverging lenses as the rays diverge after falling on the concave lens. In this article, we will learn about image formation by concave and convex lenses.
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider.
convex lens concave lens how to determine focal length ray diagrams image properties real virtual inverted size correction of eye defects causes of long-sight short-sight igcse/gcse 9-1 Physics revision notes
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
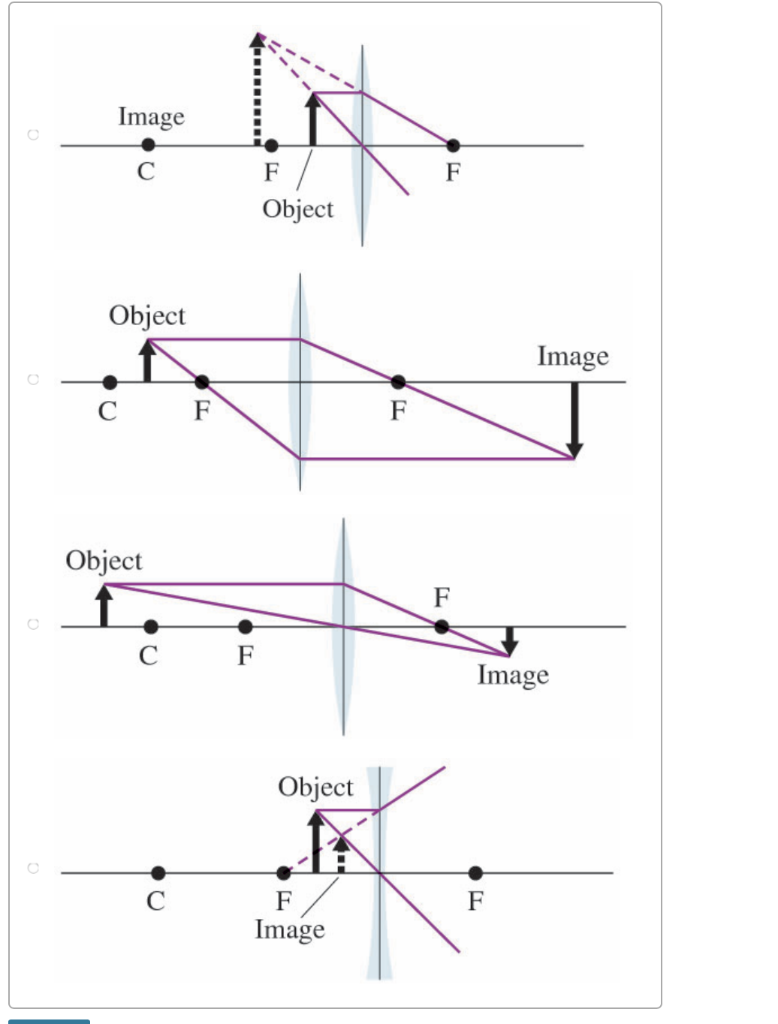
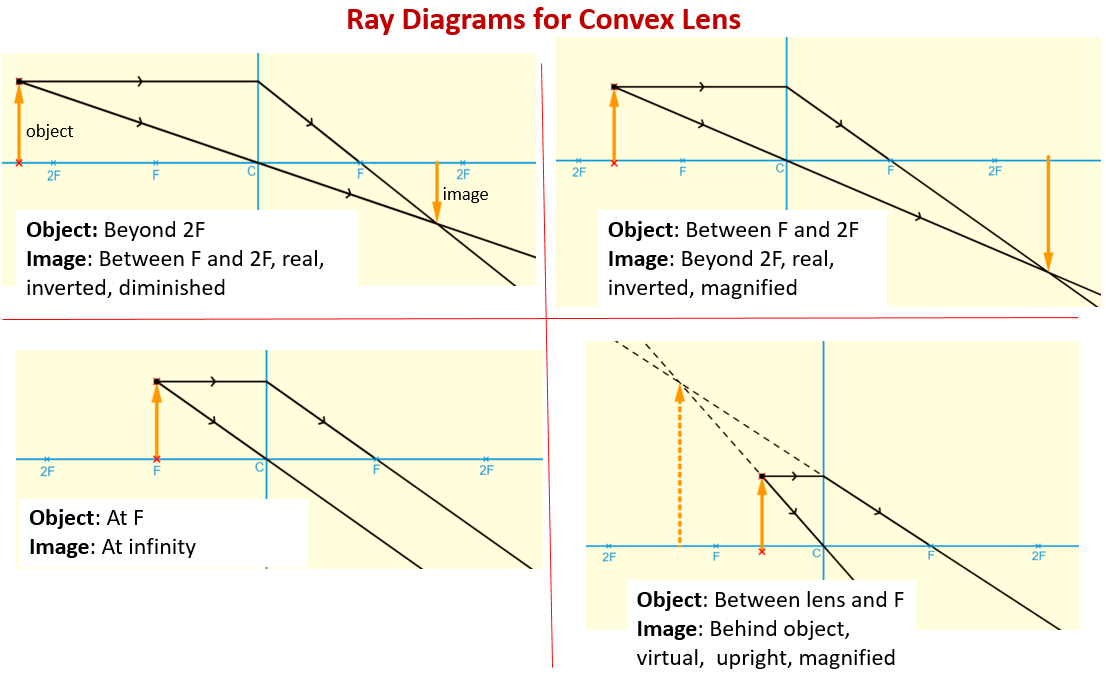
The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ...
Ray Diagram for an Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a concave mirror; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a concave mirror (i.e., in front of F). But what happens ...
With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens. Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
A concave lens is thinner in the middle than it is at the edges. This causes parallel rays to diverge. A concave lens separates but appears to come from a principal focus on the other side of the lens. In the concave lens ray diagram, a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with inward-facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. To create the diagram, a student should pick a point on ...
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.
The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length · The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image ...
The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.



















0 Response to "37 concave lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment