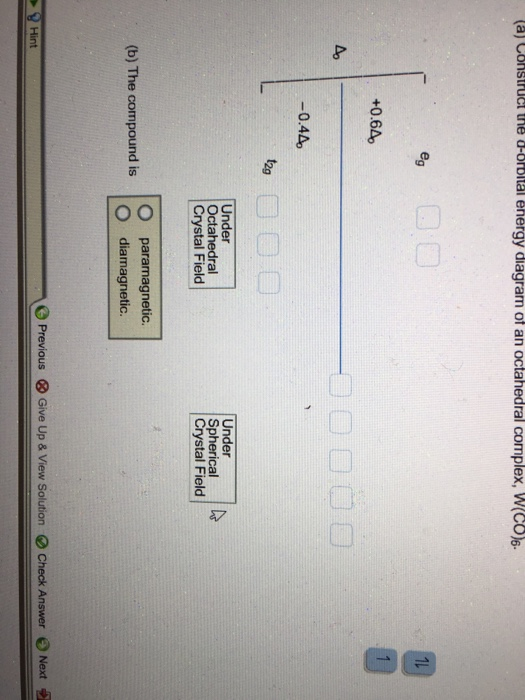
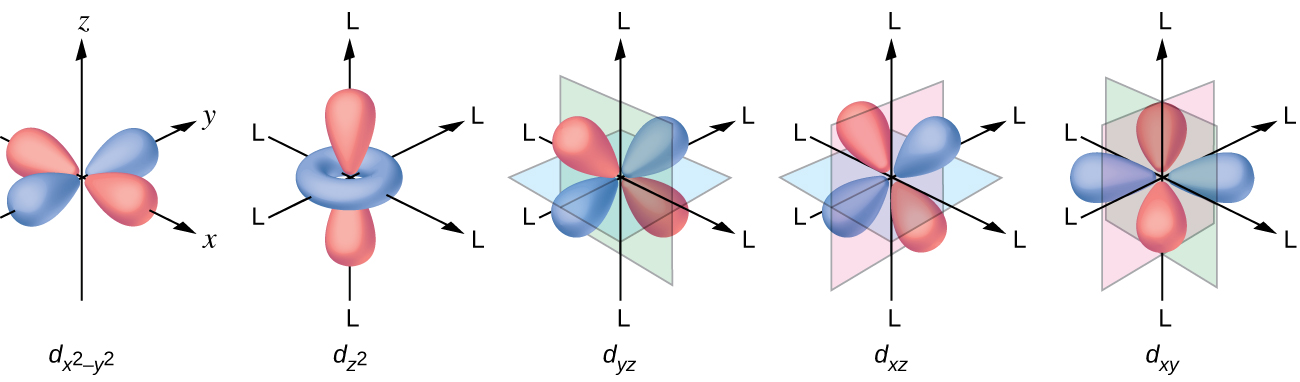
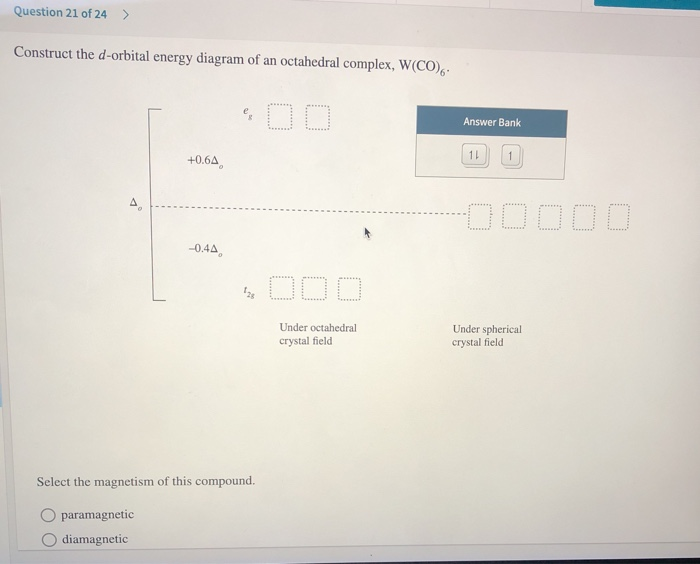
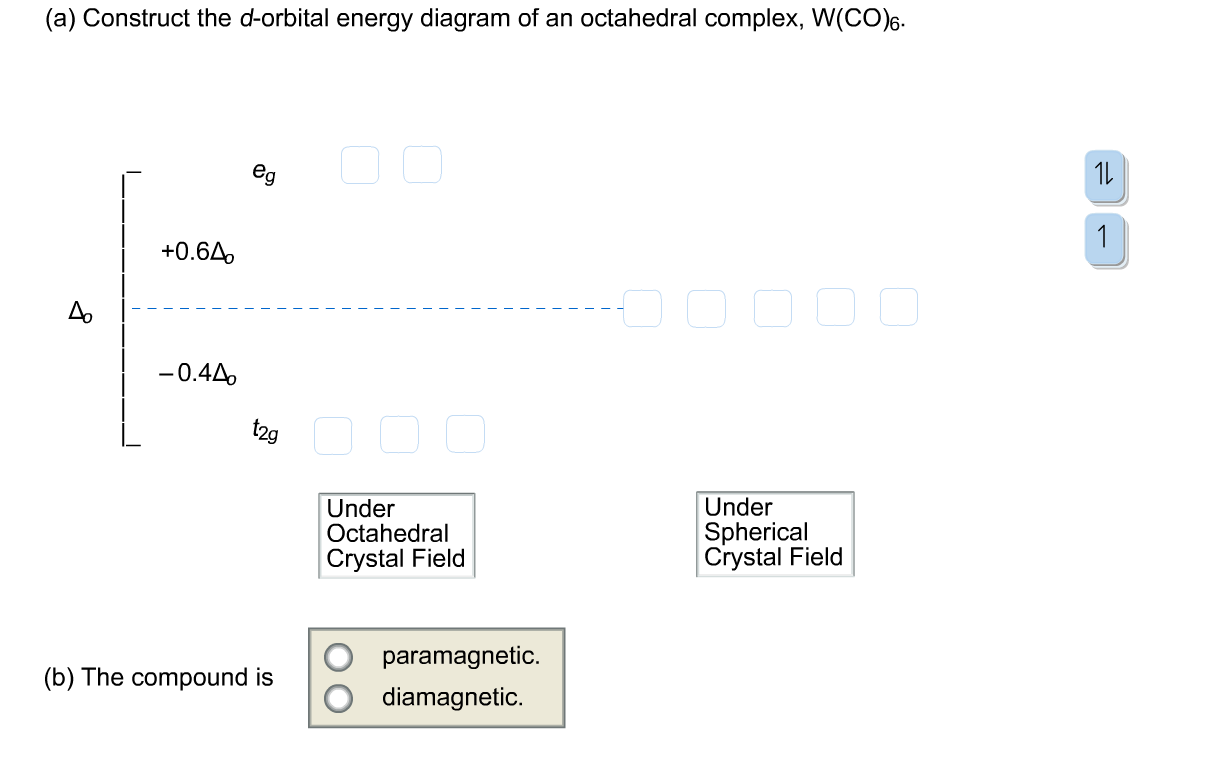
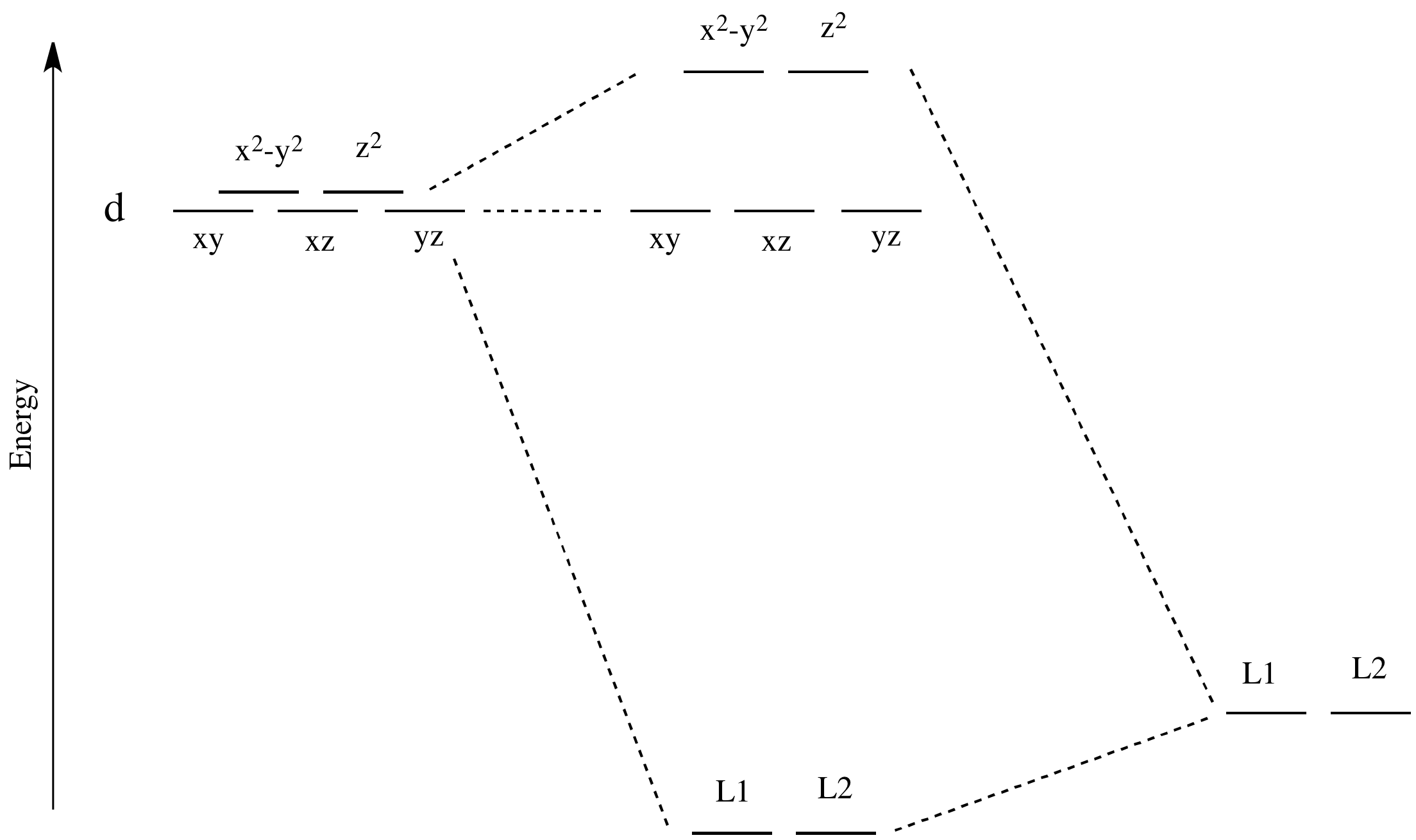
37 (a) construct the d-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, w(co)6.
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h ) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h ) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 − y 2 orbital s are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy , d xz and d yz orbital s.
This causes a splitting in the energy levels of the d-orbitals. This is known as crystal field splitting. For octahedral complexes, crystal ...6 May 2021 · Uploaded by Chuck Wight
Show transcribed image text Construct the cf-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, W(CO)6. (b) The compound is Construct the cf-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, W(CO)6. (b) The compound is order

(a) construct the d-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, w(co)6.
Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V (H2O)63+ Co (CN)63 - Mn (H2O)62+. A d1 octahedral complex is found to absorb visible light, with the absorption maximum occcurring at nm. a) Calculate the crystal-field splitting energy, Δ, in.
for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital character. metal d orbitals xz yz x2-y2 xy z2 1.125e 2.75e b. For consideration of L as a -acceptor in the axial position, the identical energy level diagram is obtained regardless of whether L is assigned to position 1 or 6. The xz and yz
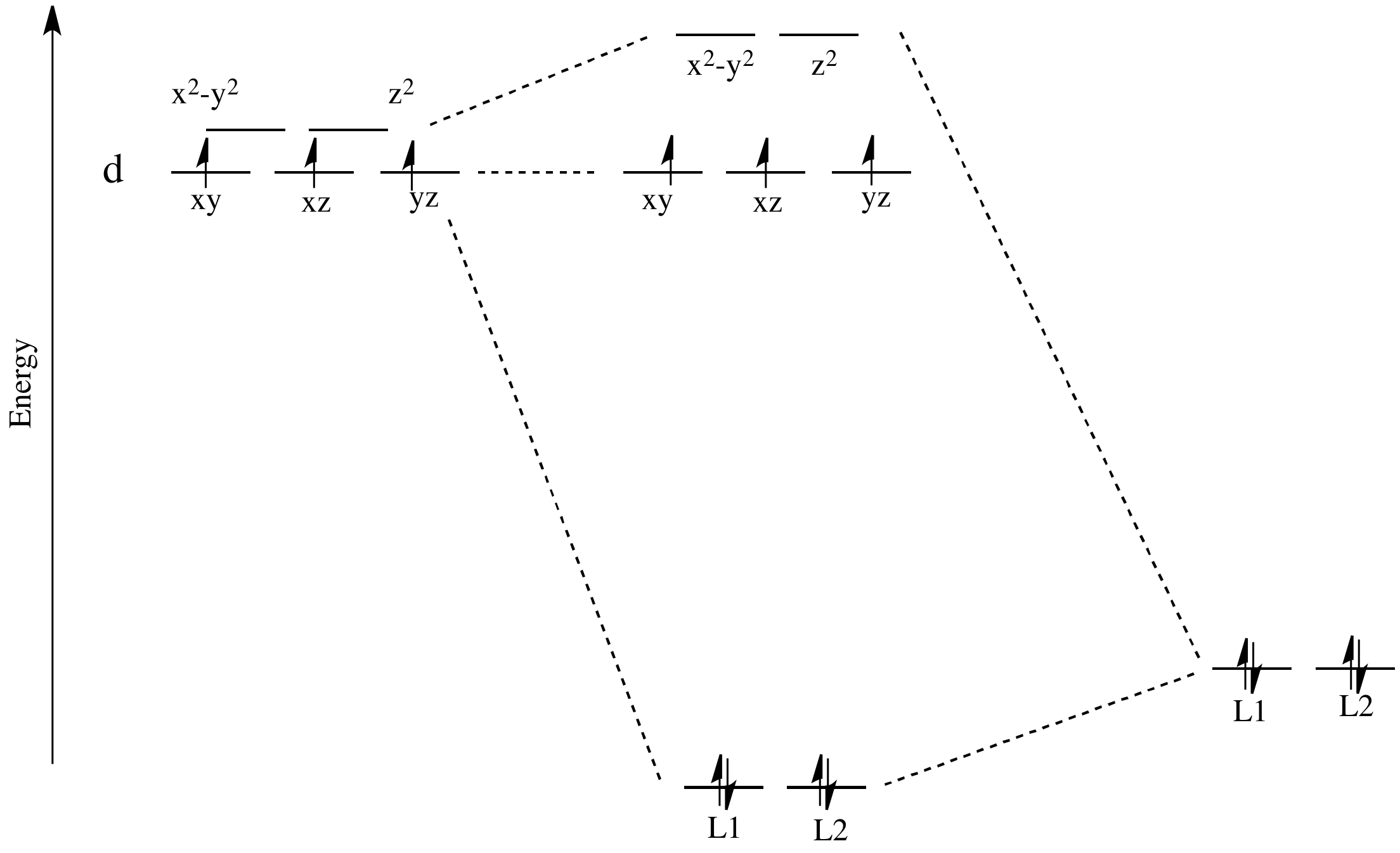
ligand-field splitting for this complex. W(CO) 5 absorbs light strongly at 25,000 cm-1. Assign the band to an electronic transition in W(CO) 6 and explain why the absorption is at lower energy than in W(CO) 6. With a loss of a CO ligand along the z-axis from W(CO) 6, the t 2g orbitals lose degeneracy as both the d xz and d
(a) construct the d-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, w(co)6..
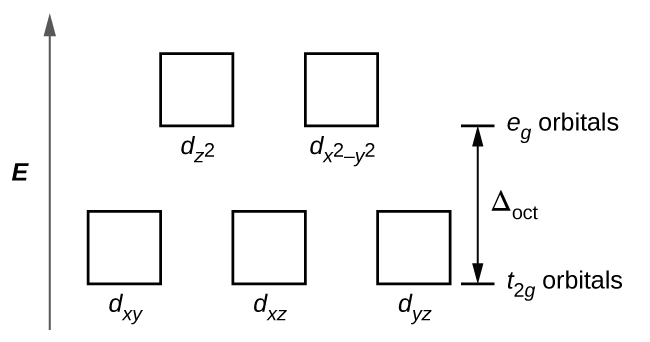
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ...
Transcribed image text: Construct the cf-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, W (CO)6. (b) The compound is. (a) construct the d-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, w(co)6. (c) Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for the C4v complex. The Cl atom lone pairs of electrons can form molecular orbitals with dxz and dyz. These metal atomic orbitals are ...
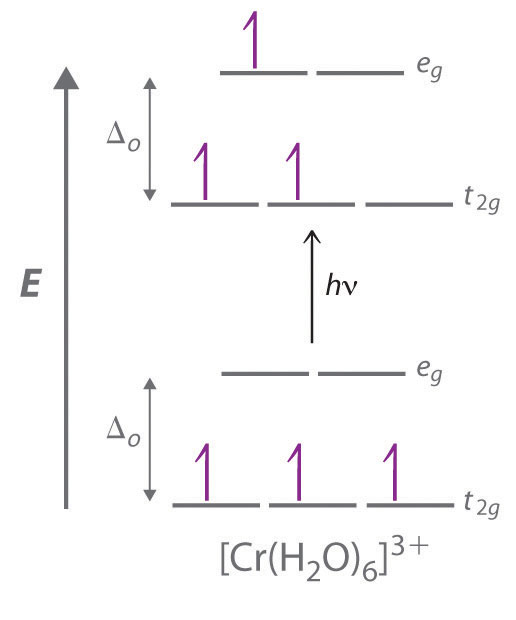
The octahedral complex [Ti(H 2 O) 6] 3+ has a single d electron. To excite this electron from the ground state t 2g orbital to the e g orbital, this complex absorbs light from 450 to 600 nm. The maximum absorbance corresponds to Δ oct and occurs at 499 nm. Calculate the value of Δ oct in Joules and predict what color the solution will appear ...
Figure 3-1 Molecular orbitals of Cr(CO) 6 (Only interactions between Ligand (σ- and π*) orbitals and metal d-orbitals are shown.) Simplified MO energy level diagram for Cr(CO) 6. Note the empty π* orbitals. Only three are involved in overlap with metal d orbitals.
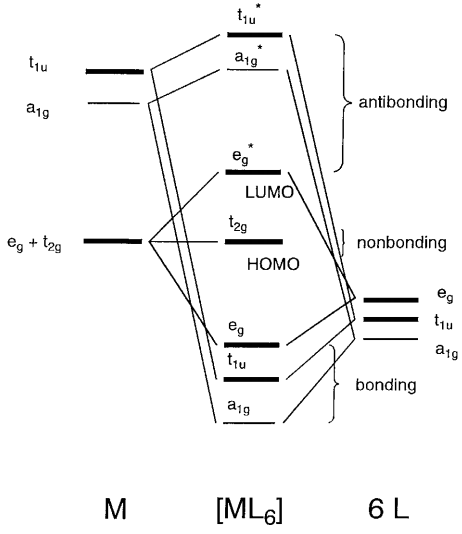
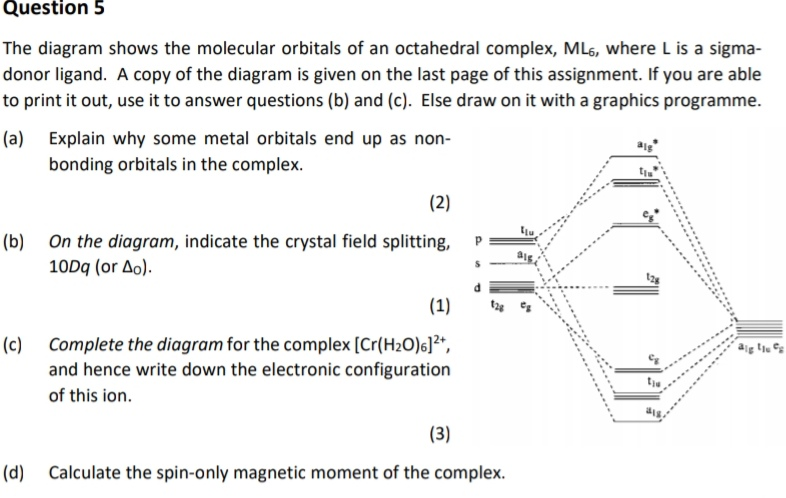
σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes Γσ= A1g+ Eg+ T1u Reading off the character table, we see that the group orbitals match the metal s orbital (A1g), the metal p orbitals (T1u), and the dz2and dx2-y2 metal d orbitals (Eg). We expect bonding/antibonding combinations. The remaining three metal d orbitals are T2gandσ-nonbonding. 5.
5.The energy of nonbonding orbitals remains the same. 6.The ionic character of the covalent bond arises from the difference in the energy of combining orbitals. 7.If the energy of a molecular orbital is comparable to an atomic orbital, it will not be very much different in nature from atomic orbital.
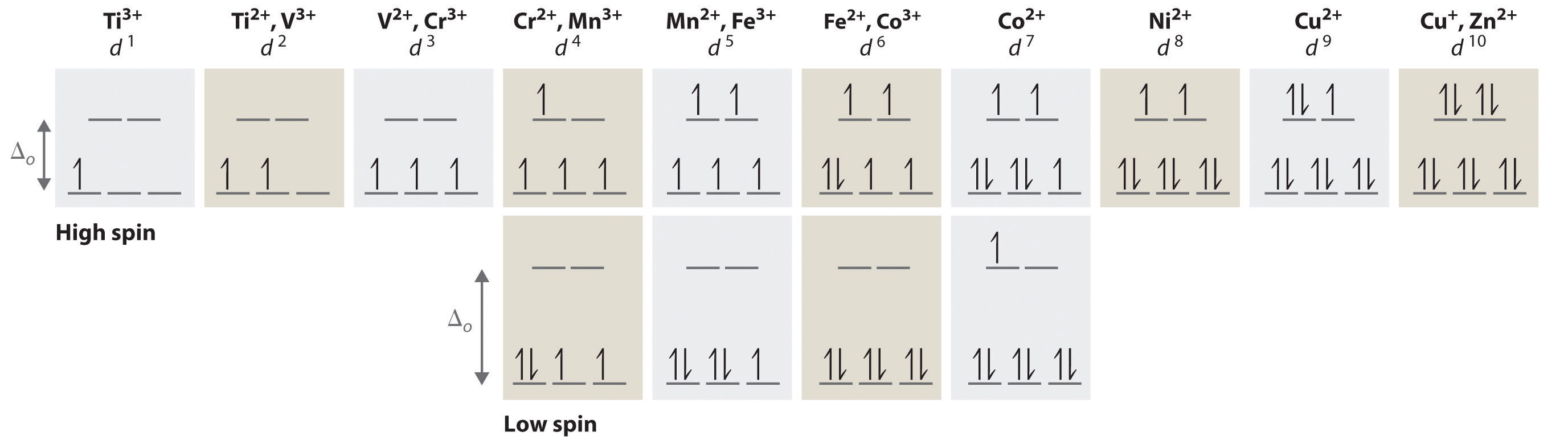
Identify the d-orbital diagram for a metal in an octahedral complex in each situation. Use the diagrams to specify the number of unpaired electrons. d electrons Spin state Diagram Unpaired electrons Answer Bank high AL | 1 _ 1 1 1 11 11 11 low 1 1 1 1 1 high 11 1 11 low high 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 low
Ans. Octahedral Trigonal prismatic ... d) [Cr(CO) 6] Ans. a) Each Cl ligand has a charge of ‐1, so 4 x ‐1 = ‐4 ... For a given multiplicity, the term with the largest value of L has the lowest energy, where L is the orbital angular momentum. 3) For a given term, in an atom with outermost sub‐shell half‐filled or less, the level with ...
t 2 - set of three orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) with higher energy e - set of two orbitals (d x 2 -y 2 and d z 2 ) with lower energy The crystal field splitting in a tetrahedral complex is intrinsically smaller in an octahedral filed because there are only two thirds as many ligands and they have a less direct effect of the d orbitals.
Theoretical chemistry research group focusing on development of methods, and calculations in the areas of ionic liquids, photochemistry and catalysis
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Other atoms that exhibit sp 3 d 2 hybridization include the phosphorus atom in PCl 6 −, the iodine atom in the interhalogens IF 6 +, IF 5, ICl 4 −, IF 4 − and the xenon atom in XeF 4. Figure 15. (a) Sulfur hexafluoride, SF 6, has an octahedral structure that requires sp 3 d 2 hybridization. (b) The six sp 3 d 2 orbitals form an octahedral ...

Lecture 26 mo’s of coordination compounds mlx (x = 4,6) 1) octahedral complexes with m-l s-bonds only consider an example of an octahedral complex.
Therefore, there cannot be any interaction between the three xy, xz, and yz orbitals and the σi orbitals on the ligands. In an octahedral complex, these three d orbitals therefore form a degenerate nonbonding set, located only on the metal (2-18 to 2-20). Principal ligand fields: σ interactions ...
a) (8 points) Qualitatively describe the ligand field (or crystal field) effect on the d orbital energies in a linear complex ML 2. Label the 5 d orbitals and the energy ordering you would expect, and show or explain why. The d z2 orbital extends toward the two ligands and will have the most overlap, leading to the orbital with the most
(d) tetrahedral complexes have larger crystal field splitting than octahedral complex Solution: (b, c) Aqueous pink solution of cobalt (II) chloride is due to electronic transition of electron from t2g to eg energy level of [Co(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+ complex.
(a) Construct the d-orbital energy diagram of octahedral complex [CoClol (b) How many unpaired electrons are there in [CoCl6l? Select answer 2g (c) Calculate the Ligand Field Stabilization Energy (LFSE) of this octahedral complex with respect to Ao Hint: consider the energy of electrons if placed in the following diagram. +0.6A Number 4o Under Octahedral Crystal Field Under Spherical Crystal Field
E.g. In case of octahedral d 9 configuration, the last electron may occupy either d z 2 or d x 2-y 2 orbitals of e g set. If it occupies d z 2 orbital, most of the electron density will be concentrated between the metal and the two ligands on the z axis. Thus, there will be greater electrostatic repulsion associated with these ligands than with ...
SCHEME 9.R.2 The d-orbital energy diagram for an octahedral complex, such as Fe(CN)g" . The d-orbitals split into two energy levels, and 2- In this particular complex, the Fe + ion has 6e, which occupy the three orbitals that are lowest in energy. Suggest the form that the orbital energy-level ...
D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3. Trigonal bipyramidal 4. Square pyramidal d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz 5. Square planar d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz d z2 d x2-yxy d yz d xz d z2 d x2-y2 d xy d yz d ...
Molecular orbital diagram corresponding to an octahedral MX N complex. Atomic levels of the transition-metal impurity, M, (ligand anions, X) are depicted on the left-hand (right-hand) side of the ... New bifunctional TCNQ-based material · New bifunctional TCNQ based material: [Co(terpy)2](TCNQ)3·CH3CN exhibits a high room temperature conductivity of 0.13 S cm−1 and an anomaly in ...
Magnetic Properties of Coordination Complexes μ eff = 2√S(S+1) = √n(n+2) BM If there is a possibility for contribution from the orbital angular momentum, μ= √L(L+1) + 4S(S+1) For a given value of the orbital quantum number l, the magnetic quantum number m can have any values from –l to +l and L = sum of m For d orbital electrons,orbital electrons, m = 2, 1, 0,2, 1, 0, -1, -2
How many unpaired electrons are there in [CoCl_6]^4-? Calculate the Ligand Field Stabilization Energy (LFSE) of this octahedral complex with respect to delta_0.1 answer · 1 vote: 3 ompained elechoj σ. octahed
Draw qualitative diagrams for the crystal-field splitting in (a) A linear complex ion ML2, (b) A trigonalplanar complex ion ML3, and (c) A trigonal-bipyramidal complex ion ML5. View Answer A B D E 10m 10m 5m 5m Draw the influence line for the moment at E when a unit point load moves from A to D.
(a) Which orbitals will be displaced from their position in the octahedral molecular orbital diagram by π interactions with the lone pairs of the Cl- ligand? (b) Which orbital will move because the Cl- ligand is not as strong a base as NH3? (c) Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for the C4v complex.
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. Consequently, the d x2-y 2 remains unoccupied ...
Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the d-orbital energy diagram of octahedral complex [CoCl_6]^4-. How many unpaired electrons are there in [CoCl_6]^4-? Calculate the Ligand Field Stabilization Energy (LFSE) of this octahedral complex with respect to delta_0. Question: Construct the d-orbital energy diagram of octahedral complex [CoCl_6 ...
This effect is particularly evident in d 9 configurations. The configuration in a octahedral complex would be t 2g 6 e g 3, where the configuration has degeneracy because the ninth electron can occupy either orbital in the e g set. A tetragonal distortion removes the degeneracy, with the electron of highest energy occupying the non degenerate d x 2 - y 2 orbital.
Therefore, the lower energy orbitals are completely filled before population of the upper sets starts according to the Aufbau principle. Complexes such as this are called "low spin". For example, NO2− is a strong-field ligand and produces a large Δ. The octahedral ion [Fe(NO2)6]3−, which has 5 d...
So the energy level diagram of their D orbital can be shown us one, 23 12 Only to violence to unpaid electrons are present. We have D X, Y, the Y, Z and T. The X. Mhm. For option B. We have cobalt with C. Two or full three or all charges negative fool. And the oxidation state of co bald in ...
Names: _ CHEM 312 1. Consider the octahedral compound SF6. a. Assign the symmetry labels to the sulfur 3s and. Sf6 molecular orbital diagram . The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. Fig. No. 5 Order of Energy Levels for Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen etc. This kind of energy reversal is due to mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals where the energy difference is ...
4 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus.
We rationalize this by saying there are no d orbitals close in energy to the valence 2s and 2p orbitals (2d orbitals are forbidden energy levels). However, for Row 3 and heavier elements, there are 3d, 4d, 5d, etc. orbitals that will be close in energy to the valence s and p orbitals. It is Row 3 and heavier nonmetals that hybridize d
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Construct the cf-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, W (CO)6. (b) The compound is.
Recap of molecular orbital theory. s-donor ligands (hydride complexes). Construction and interpretation of octahedral ML 6 molecular orbital energy diagram Lecture 3: p-acceptor ligands, synergic bonding, CO, CN-, N 2, Lecture 4: Alkenes and alkynes. Dewar-Duncanson-Chatt model. Lecture 5: M(H 2) vs M(H) 2, M n(O 2) complexes, O 2, NO, PR 3 ...
It is important to note that the splitting of the d orbitals in a crystal field does not change the total energy of the five d orbitals: the two e g orbitals increase in energy by 0.6Δ o, whereas the three t 2g orbitals decrease in energy by 0.4Δ o. Thus the total change in energy is. (1.2.1) 2 ( 0.6 Δ o) + 3 ( − 0.4 Δ o) = 0.
Transcribed image text: Construct the d-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, W(CO). Answer Bank +0.64, -0.44 WOOD Under octahedral crystal field ...
August 11, 2020 - The left over electron would need to pair up in one of the d orbitals (Notice that, in the chemistry of transition metal ions, the valence s and p orbitals are always assumed to be unoccupied). ... Things are very different in an octahedral complex, like K4[Fe(CN)6]. In that case, the d orbitals ...
good π acids or if the complex is cationic, e.g. Mo(CO)6 or [Mn(CO)6]+, because the CO-to-metal σ-donor electron transfer will be enhanced at the expense of the metal to CO back donation. • If the L groups are good donors or the complex is anionic, e.g. Cp 2W(CO) or [W(CO)5]2−, back donation will be encouraged, the CO carbon will lose its
d orbital functions can also be treated in a similar way E C 2 σ v (xz) σ ' v (yz) No change ∴ symmetric ∴ 1's in table y x Symmetry of orbitals and functions The z axis is pointing out of the screen! So these are representations of the view of the d z 2 orbital and d x 2-y 2 orbital down the z-axis. y x y x
Drawing the d-orbital electron energy diagrams of the undistorted complex [Co (en)3]Cl3 - 18127410
The easiest way to remember this convention is to note that there are three orbitals in the t2g set. The difference between the energies of the t2g and eg orbitals in an octahedral complex is represented by the symbol o. This splitting of the energy of the d orbitals is not trivial; o for the Ti(H2O)63...
Yeah, mm hmm. So let us start with option A. We have compound me sign night six three negative in this case Vanadium, which is we have a plus three oxidation state. And the violence shell configuration will be The valence shell configuration will be three D two.
The hint concerning the color of [Co(en) 2 Cl 2] + is useful because the enantiomerically resolvable form of this ion must be the cis isomer (the trans isomer is not optically active). This suggests that the violet salt, CoCl 3 ·4NH 3, must have a cis structure, as well, shown below.. The air oxidation of CoCO 3 gives the pink cis-chelate complex:. Addition of HCl causes an acid/base reaction ...




![d-orbital energy levels in planar [M II F 4 ] 2− , [M II (NH ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2020/DT/d0dt02022b/d0dt02022b-f1_hi-res.gif)













0 Response to "37 (a) construct the d-orbital energy diagram of an octahedral complex, w(co)6."
Post a Comment