38 c2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
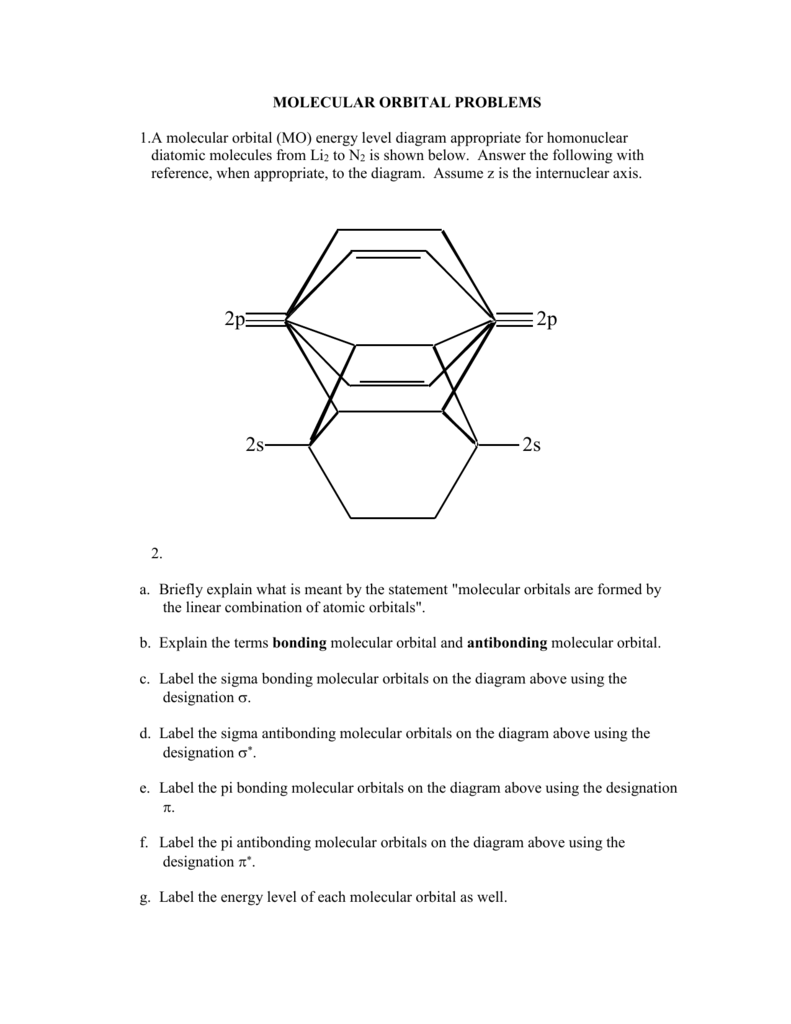
Chapter 1: Molecular Orbital Concepts A. Concepts of MO Theory. 1. Strong Covalent Bonds. Consider the pi bond of ethene in simple molecular orbital terms (The qualitative results would be the same for any pi or sigma bond. The nitrogen atom can be described as utilizing sp3 hybrid orbitals in the nitrogen trifluoride molecule. The bond dipoles in NF3 oppose the effect of the unshared pair of electrons. The NF3 molecule is more polar than the NH3 molecule.
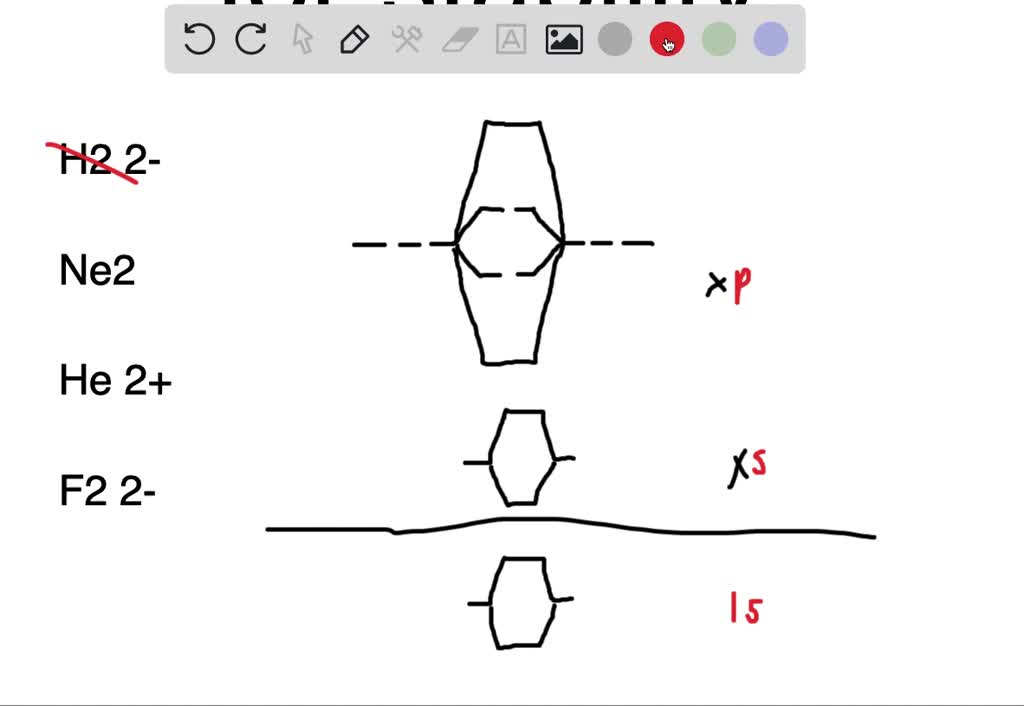
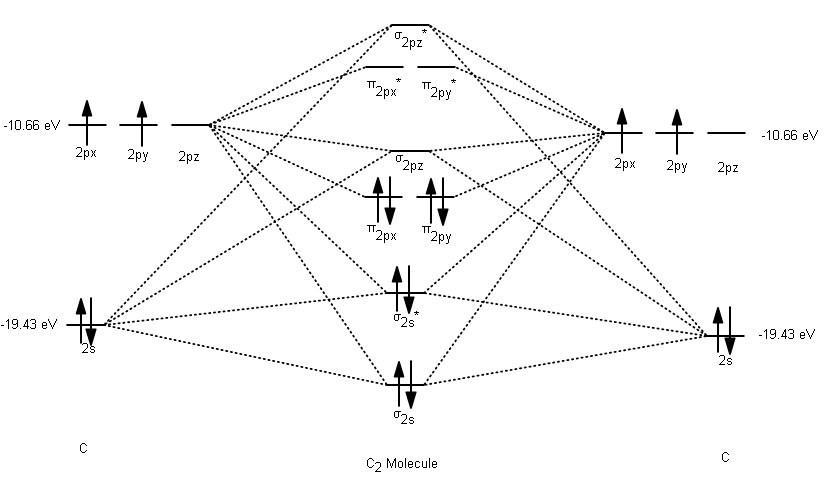
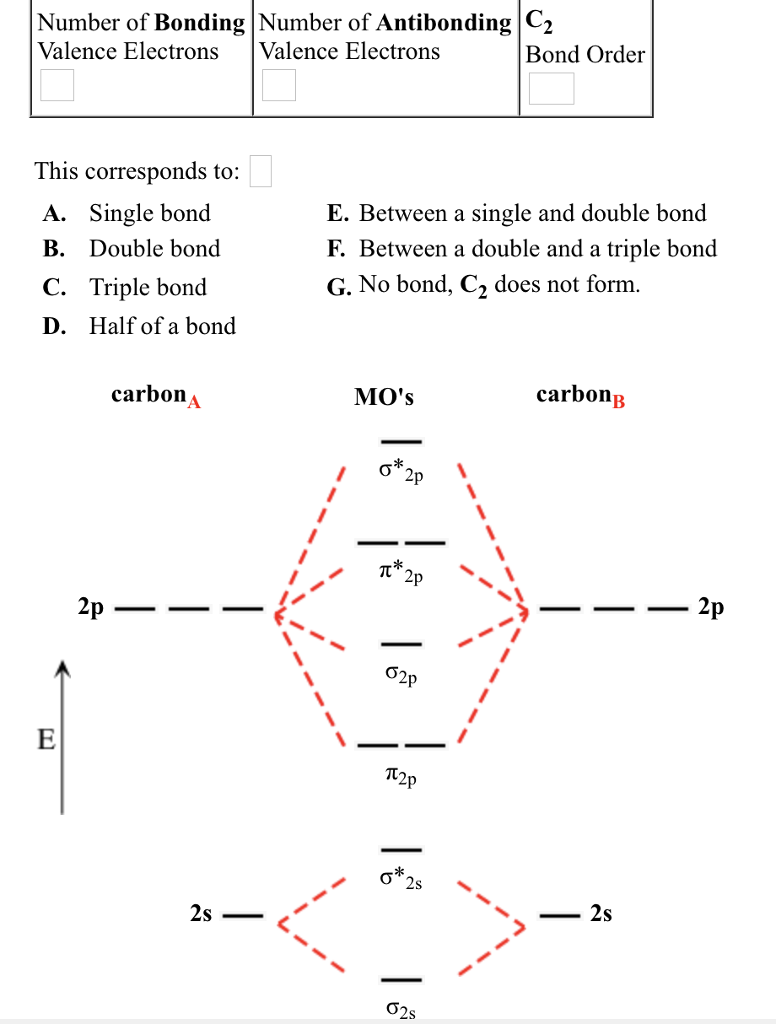
The answer is C2- because of bond orders. When we draw the C2 MO, we have everything up till the PiPy Orbitlal filled, and the next orbital tht would be filled would be the sigma2Pz orbital. As for bond orders it is 1/2* [ (#e- in bonding orbitals)- (#e- in antibonding orbitals)] Doing this, normally just C2 is 1/2* [ (8)-4]=2.

C2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
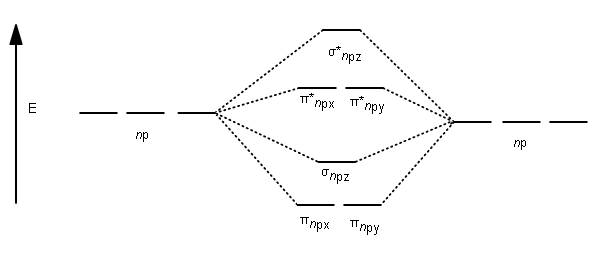
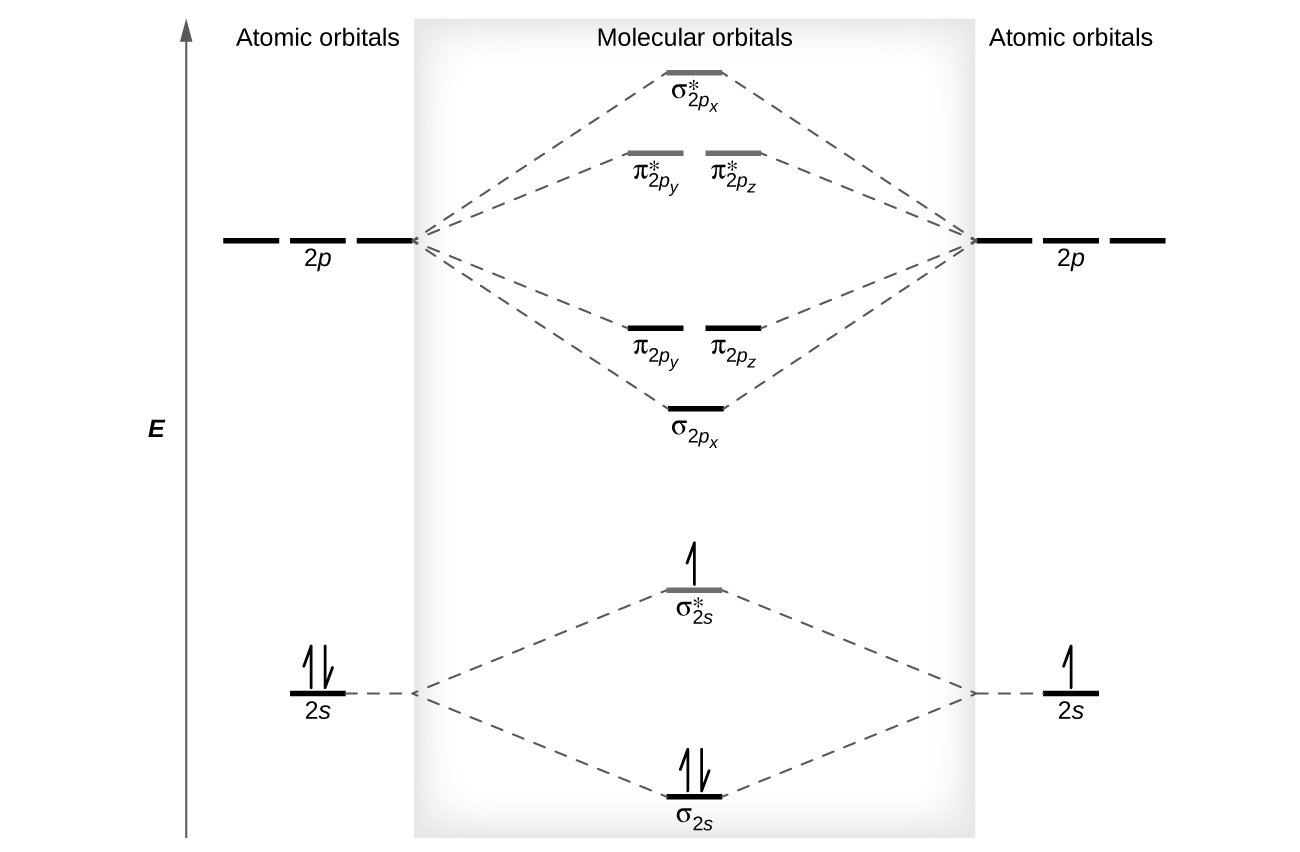
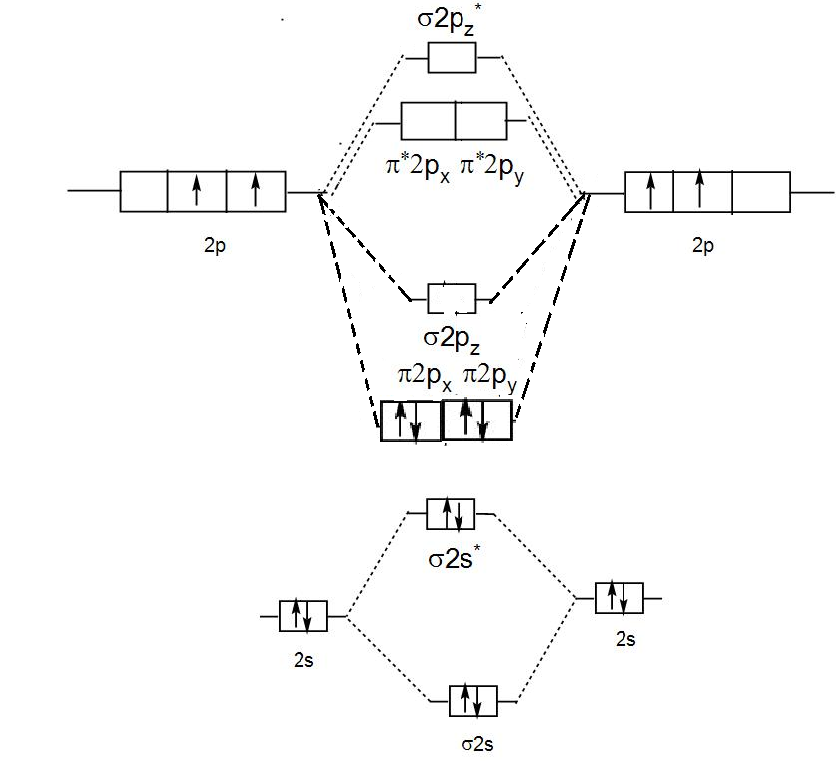
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c. 15-08-2012 · The bond strength of the C-H that’s being broken is usually within 10 kcal/mol of the bond strength of the C-H that’s being formed. What we call “instability” of various carbocations (e.g. secondary, aryl, etc.) is really just another word for high electron affinity, which means that the more “unstable” the neighboring carbocation, the more energy will be released when it completes ...
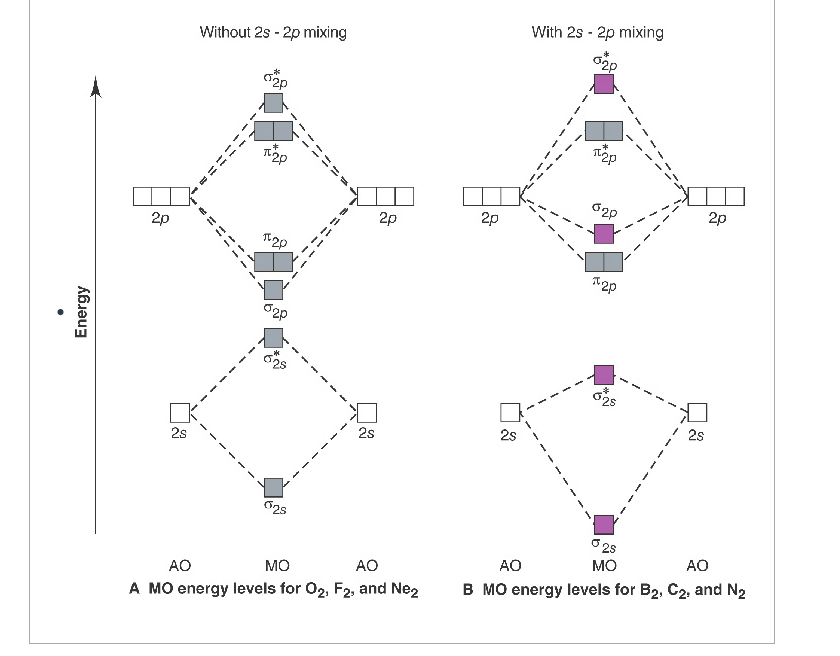
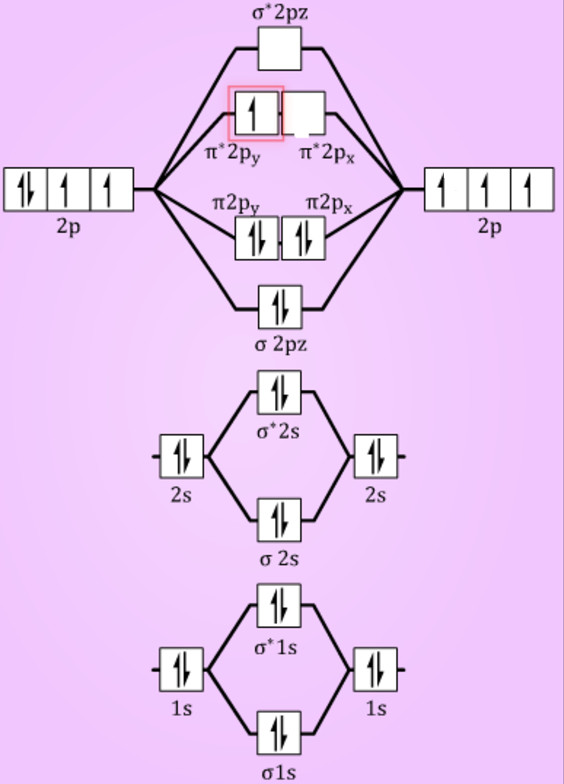
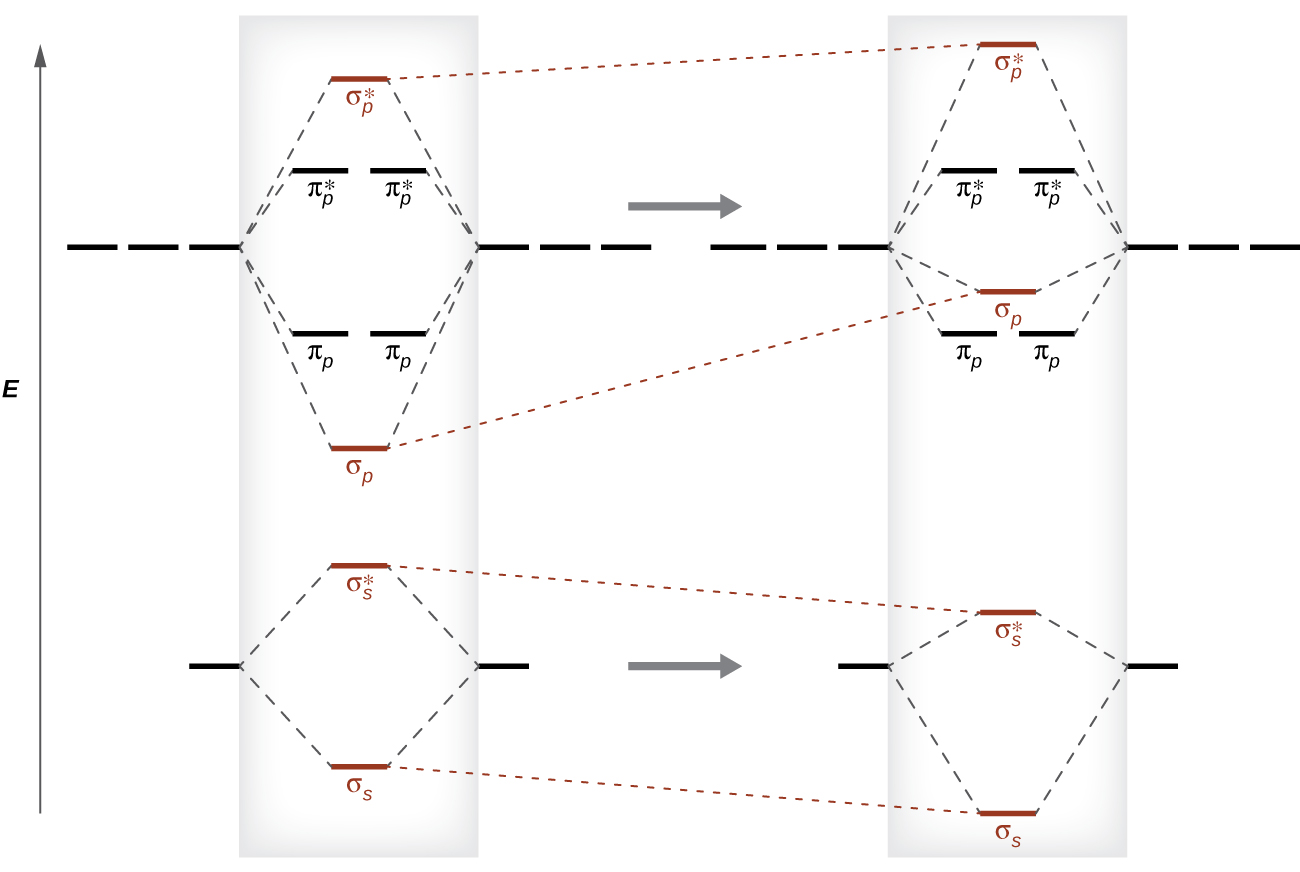
C2 molecular orbital diagram bond order. In the formation of B 2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. MO electronic configuration: Bond order: Here Nb = 4, Na = 2 Bond order = The two boron atom is B2 molecules are linked by one covalent bond. Question 2) Based on the molecular orbital diagram for NO, which of the following electronic configurations and statements are most correct? Question : Question 1) By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for B2, C2, N2, O2, and F2, predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. Antibonding orbital is type of molecular orbital (MO) that weakens the chemical bond between two atoms, whereas bonding orbital is used in molecular orbital (MO) theory to describe the attractive interactions between the atomic orbitals of two or more atoms in a molecule.Thus the bond order of C2^- is 1/2 x (9-4) = 2.5 The bond order of C2− ... The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n(2px) 2 n(2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons.
This diagram should be to scale. If necessary, you can omit the two lowest molecular orbitals from the diagram. Write the molecular orbital configuration for your molecule. Calculate the bond order for your molecule. Jen B2 Jeff OH- Mike F C2 Laura Li2 Jill Be2 Cody N2 Diana CO Kevin BF Wai BH Mike S NH Ly HF Jake SH Melissa F2 C2 molecular orbital diagram. In the mo approach each carbon atom has four valence orbitals namely a 2s and three 2p. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2. The result is. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. Bo 1 2 bonding e anti bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 lcao mo theory also predicts correctly that o2has two unpaired electrons. Bond Order. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The net contribution of the electrons to the bond strength of a molecule is identified by determining the bond order that results from the filling of the molecular orbitals by electrons. Answered: 4. Write a molecular orbital diagram,… | bartleby. 4. Write a molecular orbital diagram, determine the bond order, and predict the magnetism for the following: C2- b. H22- а. с. Nez+ с. 022+. Please answer and write it in understandable handwriting please.
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory is the final theory pertaining to the bonding between molecules. In contrast to VSEPR and valence bond theory which describe bonding in terms of atomic orbitals, molecular orbital theory visualizes bonding in relation to molecular orbitals, which are orbitals that surround the entire molecule. The purpose of MO theory is to fill in the gap for some behavior that ... 15-11-2021 · Trimeric acylphloroglucinols (T-ACPLs) are a subclass of the large class of acylphloroglucinols—derivatives of 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene containing an R–C=O group. T-ACPL molecules contain three acylphloroglucinol moieties linked by methylene bridges. Many of them are present in natural sources and exhibit biological activities, often better than the corresponding … The bond order refers to half the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in the molecule. The smaller the bond order the longer the bond length and vice versa. The specie having the least bond order is C2+ with a bond order of 1.5. This specie certainly has the longest bond length also. Hence the answer. For Ne 2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 schematron.org each MO an appropriate label. Determine the electron configuration and bond order for each, and rank the three species in order of increasing bond order% (1). The bond order is the difference in the number of ...
on C22- Molecular Orbital Diagram. The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the C2 molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. It is sigma2s (2)sigma2s* (2)sigma2p (2)pi2p (4)pi2p* (4) Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion. Check me out.
Drag the formulas to the appropriate magnetic bin :C2^2+,Li2-,B2^2-asked by defferan on November 19, 2008 Chemistry Hi!! Bond-order and Magnetic Behavior of Diatomic Species without Molecular Orbital Theory chemical bonding, bo nd order, paramagnetic, diamagnetic, m olecular orbital theory. KO2Sol. If the bond enthalpies of A2, AB & B2 are `in ...
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
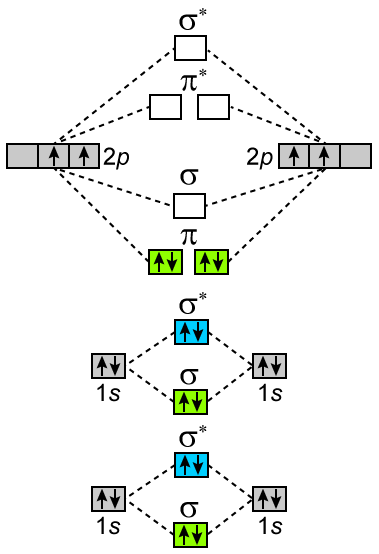
Electron Configurations and Bond Orders Just as with atoms, we can write a molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O-O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons.
Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in ce c2 2. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. N 2 has a bond order of 3 and is diamagnetic. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. Interact and form molecular orbital s. B calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Consider the h 2 ...
Answer (1 of 6): O2 2- bond order = 1 O2 - bond order = 1.5 O2 bond order = 2 O2+ bond order = 2.5 O2 2+ bond order =3 I hope it’ll work out :)
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
Therefore, the bond order of C2 C 2 molecule is 2 and it will have a double bond. Therefore, the bond order of H2 H 2 molecule is 1 2. 1 2. Molecular orbital electronic configuration of N 2 N 2 [σ(1s)]2,[σ∗(1s)]2,[σ(2s)]2,[σ∗(2s)]2,[π(2px)2] [ σ ( 1 s)] 2, [ σ ∗ ( 1 s)] 2, [ σ ( 2 s)] 2, [ σ ∗ ( 2 s)] 2, [ π ( 2 p x) 2] B.O ...
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the C2(2+) molecule. The bond order of C2(2+) is also calculated and the meaning of t...
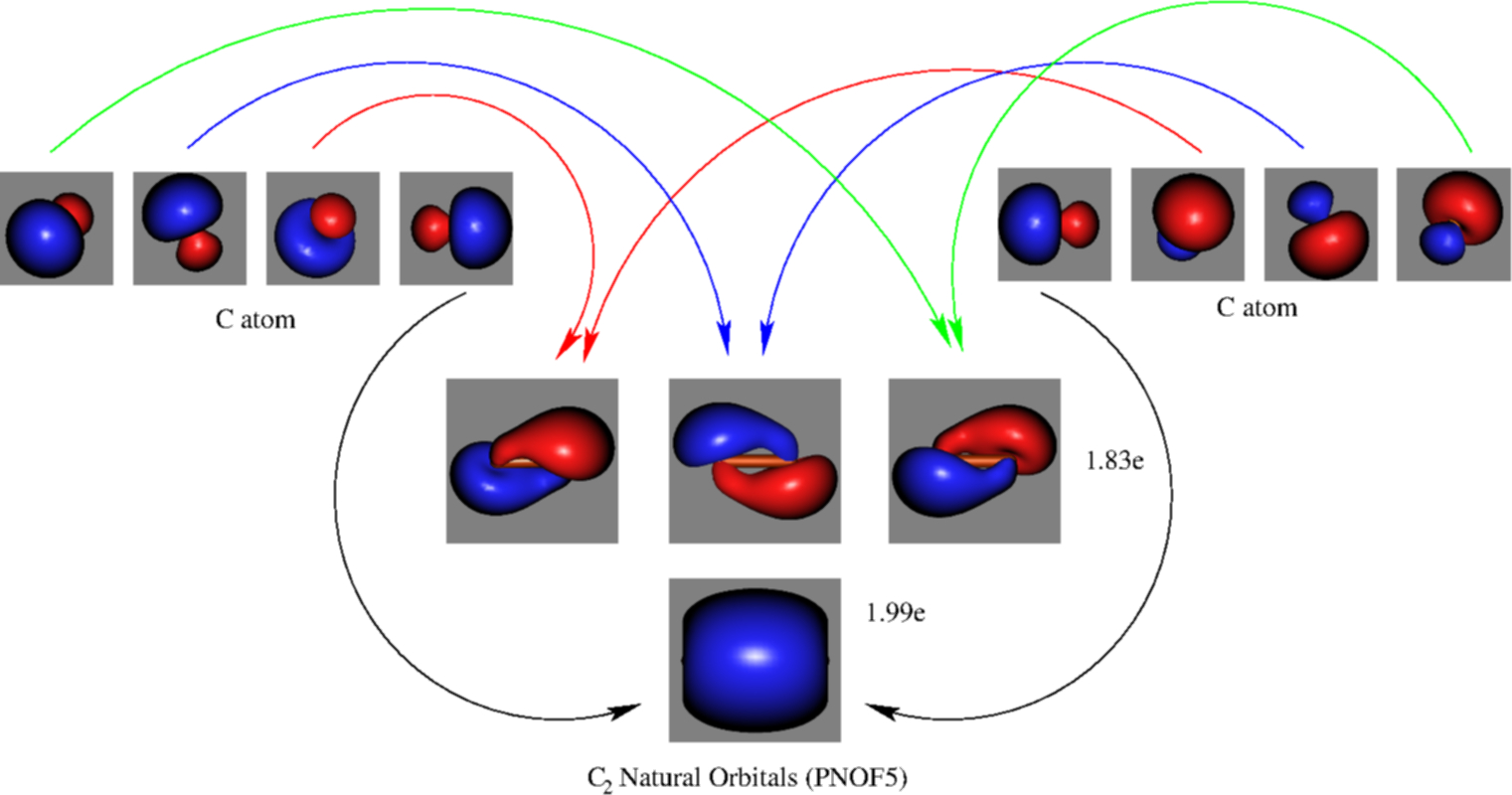
The formal bond order calculated with these orbitals and occupation numbers is 2 (resulting from 6 electrons in bonding orbitals and 2 in an antibonding orbital). How many bonds does C2 have? The analysis of the CASSCF wavefunctions in conjunction with the effective bond orders of the multiple bonds shows that there are four bonding components ...
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
Answer (1 of 6): Bond order is the number of Chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond. In a Covalent Bond ( as in case of C2 ) between two atoms, a single bond has a bond order of one, a double bond has a bond order of two, a triple bond has a bond order of th...
Bond order of C2- = 1/2 (7 - 2) = 5/2 = 2.5 Bond order of C2 = 1/2 (6 - 2) = 2 Highest bond order means highest bond energy and shortest bond length. So, the highest bond order with highest bond energy and the shortest bond length is found in C2-. So, the order starting with the highest bond order is = C2- > C2 > C2+.
Stereoisomers. As defined in an earlier introductory section, isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. When the group of atoms that make up the molecules of different isomers are bonded together in fundamentally different ways, we refer to such compounds as constitutional isomers.For example, in the case of the C 4 H 8 hydrocarbons, most of the isomers are ...
The bond order is Figure The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory.
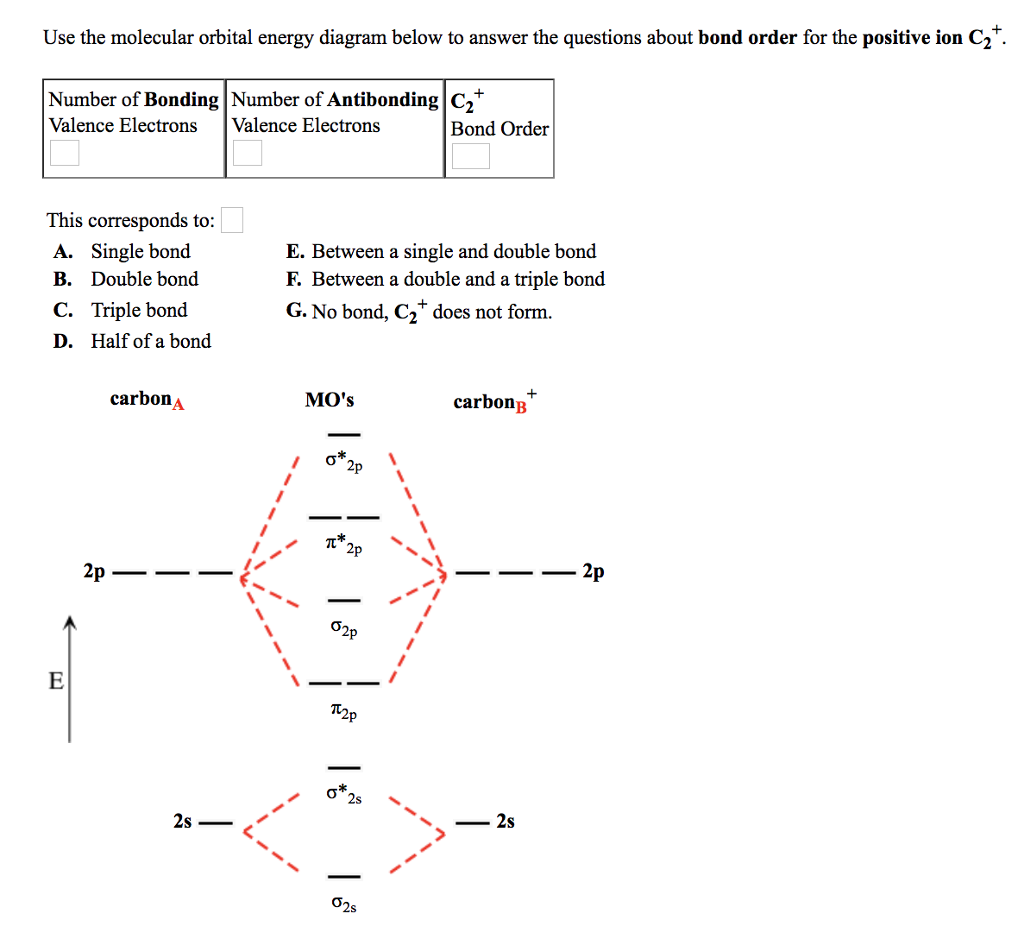
Use the filled in molecular orbital diagram for a neutral C2 molecule shown below to answer the following questions: Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals 14 1- 2p E os 1 1L 28 2s Choose... 2 What is the bond order for the cation of the Cz molecule (C2+)?
15-08-2012 · The bond strength of the C-H that’s being broken is usually within 10 kcal/mol of the bond strength of the C-H that’s being formed. What we call “instability” of various carbocations (e.g. secondary, aryl, etc.) is really just another word for high electron affinity, which means that the more “unstable” the neighboring carbocation, the more energy will be released when it completes ...
d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c.
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...












0 Response to "38 c2 molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment