38 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.
Discuss the parts of a rib and rib classifications. The thoracic cage (rib cage) forms the thorax (chest) portion of the body. It consists of the 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum ( Figure 7.5.1 ). The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12). The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. Apr 16, 2016 — Part b transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide gas exchange involves the transport of two respiratory gases oxygen and carbon dioxide. Drag the ...
The actual sites of gas exchange within the lungs are the. ... thick secretions that are difficult to transport. ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the major components of the respiratory system. Upper respiratory system (top to bottom): nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx ...

Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.
OR 6. a) Write a short note on : i) Minimum Gas-liquid ratio for absorber ii) Murphee stage efficiency. b) Ammonia gas is to be removed from its mixture with air by scrubbing with water in a packed tower. A gas mixture entering the column contains 6% NH3 (Vol%) and rest air (Vol.), water free of NH 3 enters in the column in countercurrent ... Heroes and Villains - A little light reading. Here you will find a brief history of technology. Initially inspired by the development of batteries, it covers technology in general and includes some interesting little known, or long forgotten, facts as well as a few myths about the development of technology, the science behind it, the context in which it occurred and the deeds of the many ... The Slow Carbon Cycle. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity, carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks, soil, ocean, and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle. On average, 10 13 to 10 14 grams (10-100 million metric tons) of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange.. Figure 10.2.2 - Muscle Fiber: A skeletal muscle fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, which contains sarcoplasm, the cytoplasm of muscle cells. A muscle fiber is composed of many myofibrils, which contain sarcomeres with light and dark regions that give the cell its striated appearance. Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures involved in respiratory epithelium function. Mastering A and PAssignment Unit 5 - Respiratory System Art-labeling Activity Figure 17.5 Anion channel Oland Secondary active transport of Facilitated diffusion of CI ECF pical Mucus layer Id One model of se Watery saline layer Paracellular diffusion of Na drawn by ... Virtually all nitrogen in the atmosphere occurs in the form of nitrogen gas (N 2, sometimes referred to as dinitrogen), which is present in a concentration of 78%.Other gaseous forms of nitrogen are ammonia (NH 3), nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO 2), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O). These trace gases typically occur in atmospheric concentrations much less than 1 ppm, although there may be ... 1. Air enters through the nose or mouth. 2. Air travels down the trachea and then enters the bronchi. 3. Air travels down smaller and smaller bronchioles. 4. Air reaches small sacs called alveoli. Drag each label to the appropriate location on this diagram of the human respiratory system.
There is lots of room in the air for it to have (but not “hold”) more moisture, because air is a gas, water vapor is a gas, and there’s lots of empty space between gas molecules. Also, water vapor molecules are whizzing around at about 600 miles per hour, so there’s really no “holding” them anyway. 15.3 Hearing Audition (Hearing) Hearing, or audition, is the transduction of sound waves into a neural signal that is made possible by the structures of the ear (Figure 15.3.1).The large, fleshy structure on the lateral aspect of the head is known as the auricle.Some sources will also refer to this structure as the pinna, though that term is more appropriate for a structure that can be moved ... 8.1 The Concept of Homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to physiologically regulate its inner environment to ensure its stability in response to fluctuations in external or internal conditions.The liver, the pancreas, the kidneys, and the brain (hypothalamus, the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system) help maintain homeostasis. Search the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more. Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking for.
Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: Solution A catalyst does not affect the energy of reactant or product, so those aspects of the diagrams can be ignored; they are, as we would expect, identical in that respect. Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Reset Help Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT Airways CO2 is transported dissolved in plasma, bound to hemoglobin or as HCO3 Alveoli of lungs CO₂ O₂ O2 diffuses from alveolus to capillary co, so O2 diffuses into cells Cellular respiration determines 02 ... Google's free service instantly translates words, phrases, and web pages between English and over 100 other languages. A diving cylinder or diving gas cylinder is a gas cylinder used to store and transport high pressure gas used in diving operations.This may be breathing gas used with a scuba set, in which case the cylinder may also be referred to as a scuba cylinder, scuba tank or diving tank.When used for an emergency gas supply for surface supplied diving or scuba, it may be referred to as a bailout ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and functions of the nephron. (Refer to the posted image at the right for labeled answers) What is the primary driving force for glucose transport into proximal tubule cells? Sodium concentration gradient allows secondary active transport of glucose.
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation are tightly coupled to each other. The enzymes and intermediates of the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation are located in organelles called mitochondria. The oxidation of carbohydrates is the source of over 50% of the energy used by cells.
Label the mechanisms of carbon dioxide transport. (Refer to the posted image for labeled answers) Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the mechanisms involved in the transport of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the processes of reabsorption in the tubular epithelium. Submit My Answers Give Up Correct Help Reset Low concentration High concentration Secondary active transport of and glucose Secondary active transport of and glucose High concentration High concentration Apical membrane Apical membrane ...
Identify the different epithelia of the body, and describe the chief function(s) and location(s) of each. An epithelium (ep″ ı˘-the ′le-um; "covering") is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity (Figure 4.1). Epithelial tissue occurs in two different forms:
2.3 Cell structure and function (ESG4S) Section 3: Cell Structure and Function. In this section the learners now expand their knowledge and learn the various cell structures and related functions. The roles of the organelles within the cells need to be introduced and relate structure and location of organelles to their function.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange Learn this topic by watching Gas Transport in the Blood II: Carbon Dioxide Concept Videos All Anatomy & Physiology Practice Problems Gas Transport in the Blood II: Carbon Dioxide Practice Problems
Question: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the processes of reabsorption in the tubular epithelium. This problem has been solved! ... Sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule Primary active Low Na concentration Leak channel transport of Na (c) Sodium-linked reabsorption Glucose and Nat SGLT 缄. GALUT " Apical membrane ...
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the classes of epithelia. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the classes of epithelia ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange Learn this topic by watching Gas Transport in the Blood II: Carbon ...
It is the owner’s responsibility to use the recreational vehicle for its intended purpose as described above and to observe and comply with all proper operating practices, instructions and safety regulations listed on the safety labels or in the owner’s manual, and/or operating practices, and …
Biology. Biology questions and answers. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange ResetHel CO2 diffuses out of pulmonary capillaries CO2 O2 Airways CO2 diffuses into systemic capillaries Alveoli of lungs co, o O2-rich blood 02 CO2-rich blood 02 diffuses from alveolus to capillary Blood flow to and from ...
Founded in 2002 by Nobel Laureate Carl Wieman, the PhET Interactive Simulations project at the University of Colorado Boulder creates free interactive math and science simulations. PhET sims are based on extensive education <a {0}>research</a> and engage students through an intuitive, game-like environment where students learn through exploration and discovery.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the path a secretory protein follows from synthesis to secretion. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Glycolysis citric acid cycle and electron transport. Identify the type of mutation that has led to each result shown.
That is: NFP = GBHP - [CHP + BCOP] = 10 mm Hg. Or: NFP = 55 - [15 + 30] = 10 mm Hg ( Figure 25.4.1 ). Figure 25.4.1 - Net Filtration Pressure: The NFP is the sum of osmotic and hydrostatic pressures. A proper concentration of solutes in the blood is important in maintaining osmotic pressure both in the glomerulus and systemically.
Apr 5, 2015 — Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. ANSWER: 1/11 4/11/2015 Ch 18 HW Correct ...
Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Dalton's Law Each gas in a mixture of gases exerts its own pressure as if no other gases were present Pressure of a specific gas is partial pressure P x Total pressure is the sum of all the partial pressures Atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg) = P N2 + P O2 + P H2O + P CO2 + P other gases
Identify the symbols on a military map. a. Use the legend, which should identify most of the symbols used on the map. b. Identify each object by its shape on the map. Note: For example, a black, solid square represents a building or a house; a round or irregular blue item is a lake or pond.
Terms in this set (33) Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. the diaphragm and rib muscles contract. Which statement is correct? In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells.
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells within the pancreas. It is responsible for regulating movement of glucose from the blood into cells. This article will consider the structure of insulin, how it is synthesised and secreted, its actions on the body and clinical conditions that are associated with faults in its production.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange. Reset Help Systemic circulation PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT Airways ...1 answer · 0 votes: The sequence of carbon dioxide transport in body - 1. Carbon dioxide is released from mitochondria. Carbon dioxide is released from mitochondria ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identity aspects of gas transport and ... is close contact with pulmonary capillaries in order for that exchange Tokyo.5 answers · 4 votes: Due to its partial pressure gradient, carbon dioxide diffuses from cells into tissue fluid ...
Such coupled reactions are referred to as redox reactions. The metabolic processes glycolysis, Kreb's Cycle, and Electron Transport Phosphorylation involve the transfer of electrons (at varying energy states) by redox reactions. Passage of electrons from compound A to compound B.
appropriate model or diagram. Size, Location, and Orientation The modest size and weight of the heart give few hints of its incredible strength. Approximately the size of a person's fist, the hollow, cone-shaped heart weighs less than a pound. Snugly enclosed within the inferior mediastinum (me″de-as-ti′num), the
The Slow Carbon Cycle. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity, carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks, soil, ocean, and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle. On average, 10 13 to 10 14 grams (10-100 million metric tons) of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year.
Heroes and Villains - A little light reading. Here you will find a brief history of technology. Initially inspired by the development of batteries, it covers technology in general and includes some interesting little known, or long forgotten, facts as well as a few myths about the development of technology, the science behind it, the context in which it occurred and the deeds of the many ...
OR 6. a) Write a short note on : i) Minimum Gas-liquid ratio for absorber ii) Murphee stage efficiency. b) Ammonia gas is to be removed from its mixture with air by scrubbing with water in a packed tower. A gas mixture entering the column contains 6% NH3 (Vol%) and rest air (Vol.), water free of NH 3 enters in the column in countercurrent ...




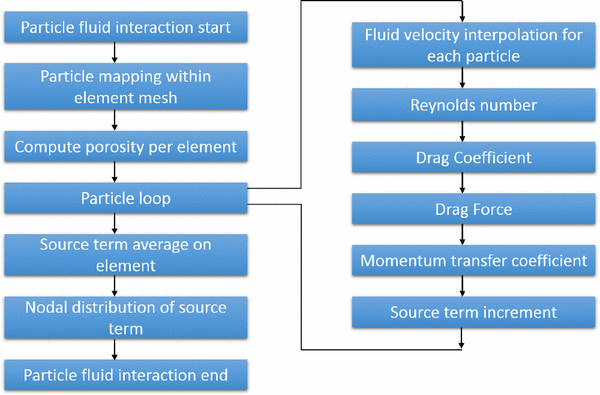





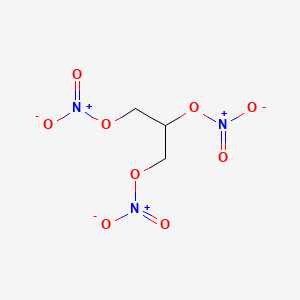




0 Response to "38 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas transport and exchange."
Post a Comment