38 mitochondria cellular respiration diagram
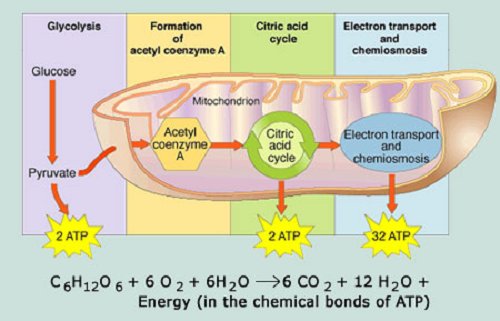
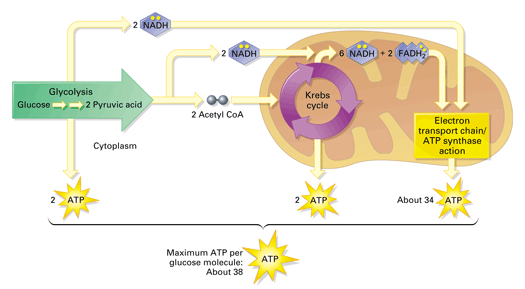
Function of Mitochondria. Mitochondria produce ATP through process of cellular respiration—specifically, aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen.The citric acid cycle, or Krebs cycle, takes place in the mitochondria.This cycle involves the oxidation of pyruvate, which comes from glucose, to form the molecule acetyl-CoA.Acetyl-CoA is in turn oxidized and ATP is produced. Thus, the total ATP yield in the cellular respiration process is 36 or 38 ATP molecules. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules.
These blank diagram s of Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, the Formation of Acteyl CoA, the Kreb's Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation are great for teaching the stages of photosynthesis with students.It is best used as a guided activity during which the teacher ex. Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration ...

Mitochondria cellular respiration diagram
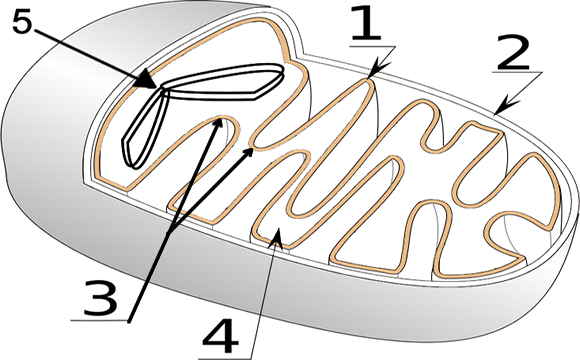
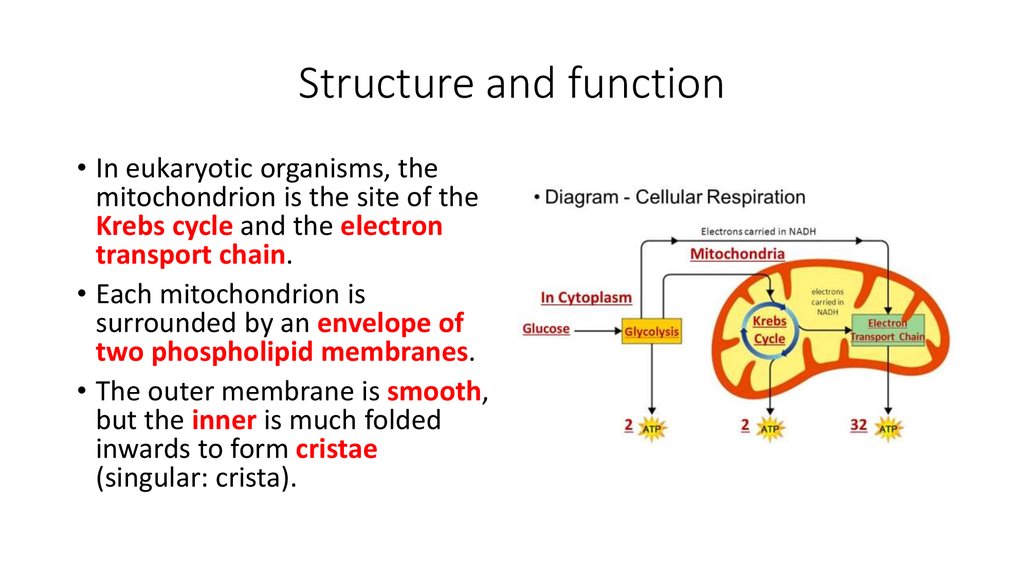
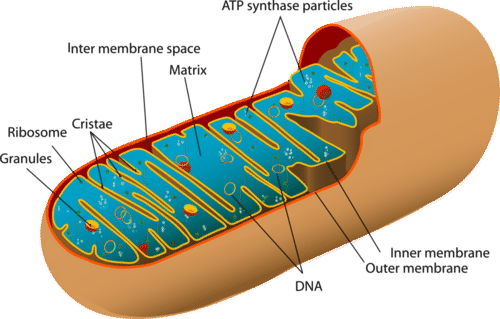
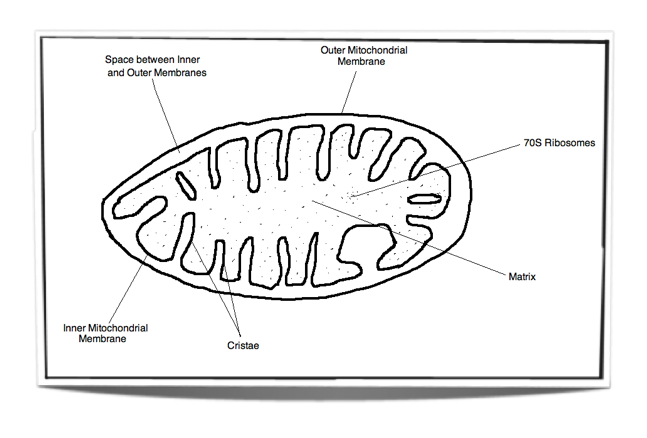
Mitochondria and Cellular respiration - an example of a metabolic pathway: It is difficult to describe mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) in terms of numbers and sizes because they are very dynamic organelles in living cells. Mitochondria continually fuse together, divide into smaller fragments The mitochondria are about the size of a bacterial cell and are often peanut-shaped. Mitochondria have their own DNA and a double membrane. The outer membrane (2) is smooth, while the inner membrane (1) is convoluted into folds called cristae (3) in order to increase the surface area. The matrix (4) is the space contained within the inner membrane. ... organelle in which the Kreb's Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain portions of cellular respiration take place. matrix. fluid inside the inner membrane of the mitochondria in which the Kreb's cycle takes place. cristae. folds of the inner membrane of the mitochondria. cellular respiration.
Mitochondria cellular respiration diagram. Mitochondria are now known to be more than the hub of energy metabolism. They are the central executioner of cells, and control cellular homeostasis through involvement in nearly all aspects of metabolism. As our understanding of mitochondria has expanded it has become clear that the structure, function and pathology of the 3 Cellular Respiration A cellular process that breaks down carbohydrates and other metabolites with the concomitant buildup of ATP Consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide (CO 2) Cellular respiration is aerobic process. Usually involves breakdown of glucose to CO 2 and water Energy extracted from glucose molecule: Released step-wise Many of the biochemical reactions involved in cellular respiration take place within the mitochondria. ... Mitochondria diagram explaining the structure of mitochondria. Structure of Mitochondria. The mitochondrion is a double-membraned, rod-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cell. Cellular respiration diagram mitochondria. The second worksheet has students identify the main reactants and products of cellular respiration as they relate to the mitochondrion. Atp is the energy currency of cells and is produced inside the mitochondria. Mitochondria are known as the 'powerhouse of the cell'.
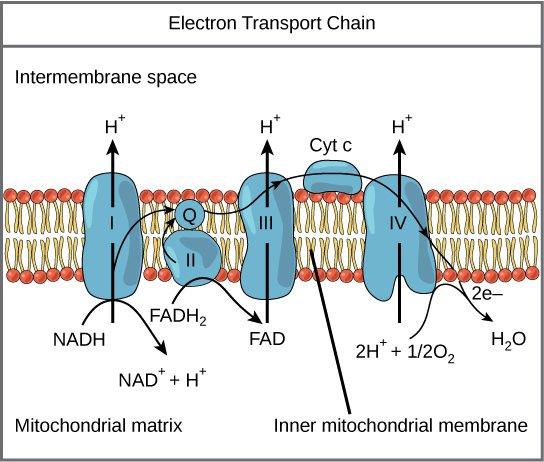
Mitochondria — Structure intermembrane space cristae inner membrane matrix What cells would have a lot of mitochondria? outer membrane THE CHEMICAL REACTION OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION oxidation C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP reduction STEP 1 How many carbons do you start with and how many are left in the products? Cellular respiration is a process that takes the energy from food and converts it into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is the energy currency of cells and is produced inside the mitochondria. the three-carbon compound that is produced during glycolysis and needed for both the aerobic and anaerobic pathways of cellular respiration that follow glycolysis Glucose A simple sugar that is an important source of energy. FlexBook® Platform + CK-12 Overview
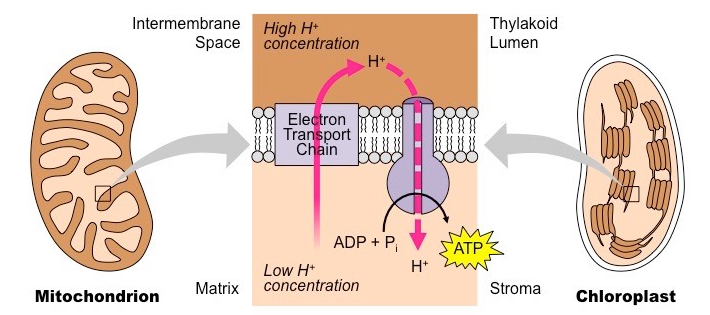
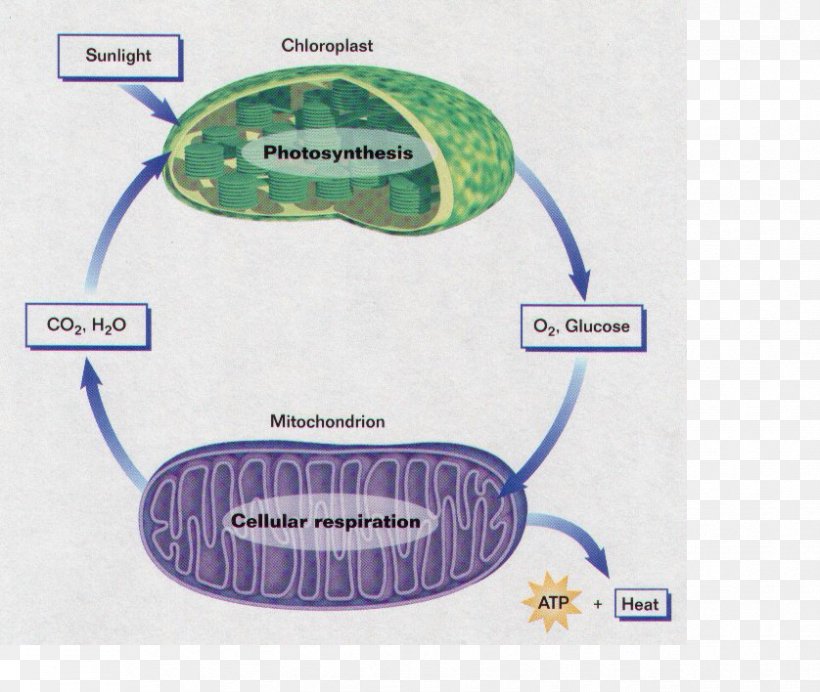
(Diagram 3.12) Mitochondria are the "power stations" of the cell. They make energy by "burning" food molecules like glucose. This process is called cellular respiration. The reaction requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide which is a waste product. The process is very complex and takes place in a large number of steps but the ... Mitochondria are energy-producing organelles found in most living cells. They use carbohydrates such as glucose in chemical reactions based on an electron transport chain and the citric acid cycle. The final products of these reactions are water and ATP, an energy-storage molecule. Overview Cellular respiration is the process of using oxygen in the mitochondria to chemically break down organic molecules such as glucose. This releases the energy stored in the bonds of glucose. In this process, molecules of water and carbon dioxide are released as waste products. This series of reactions produces 36 molecules of ATP! You can draw… Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Mitochondria. Mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion) are often called the "powerhouses" or "energy factories" of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy-carrying molecule.The formation of ATP from the breakdown of glucose is known as cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
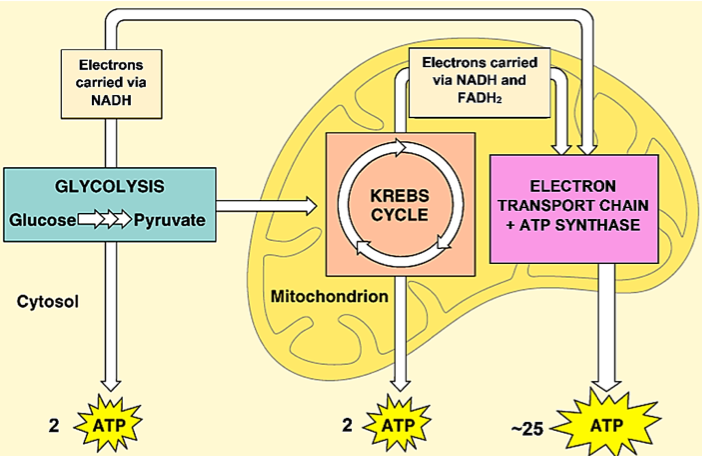
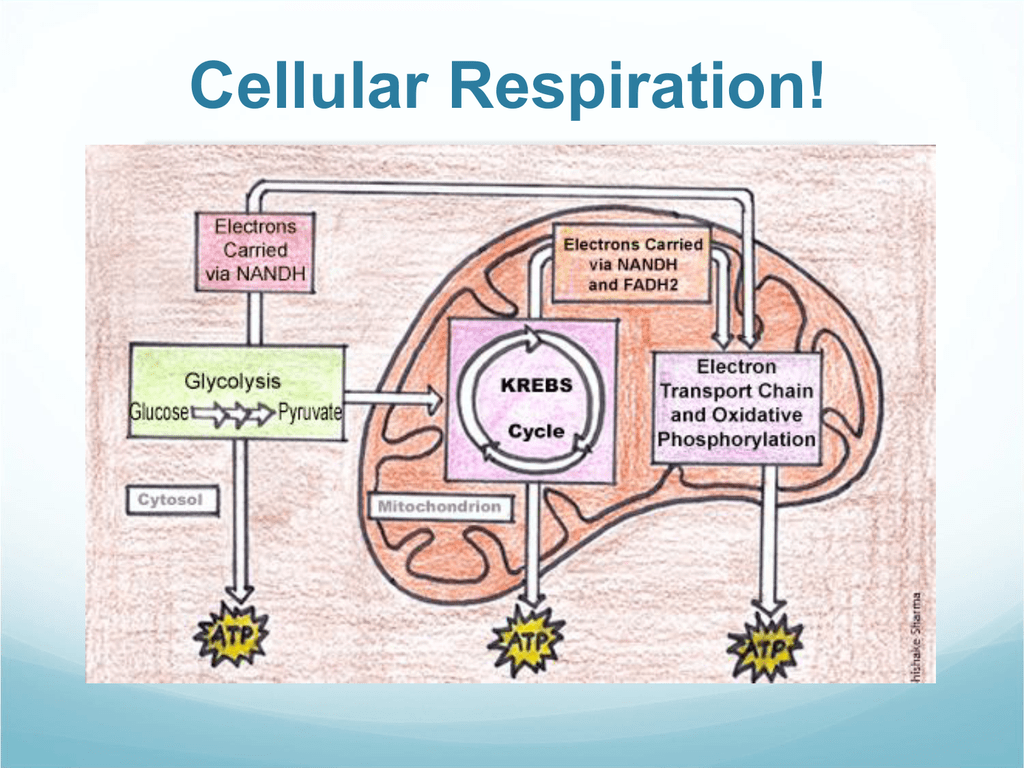
Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen. Electrons carried in NADH Pyruvic acid Glucose VE|ectrons carried in NADH and FADH2 ATP ATP Use the words below to label the diagram of cellular respiration on the lines provided. ATP electron transport chain glycolysis Krebs cycle mitochondrion
Cellular Respiration Review. ... MATCH THE LETTER IN THE DIAGRAM WITH THE LABEL: (You can use them MORE THAN ONCE or NOT AT ALL) ___ ___ ... Glycolysis happens outside the mitochondria in the . of the cell. happens when oxygen is present and includes glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and Electron transport. ...
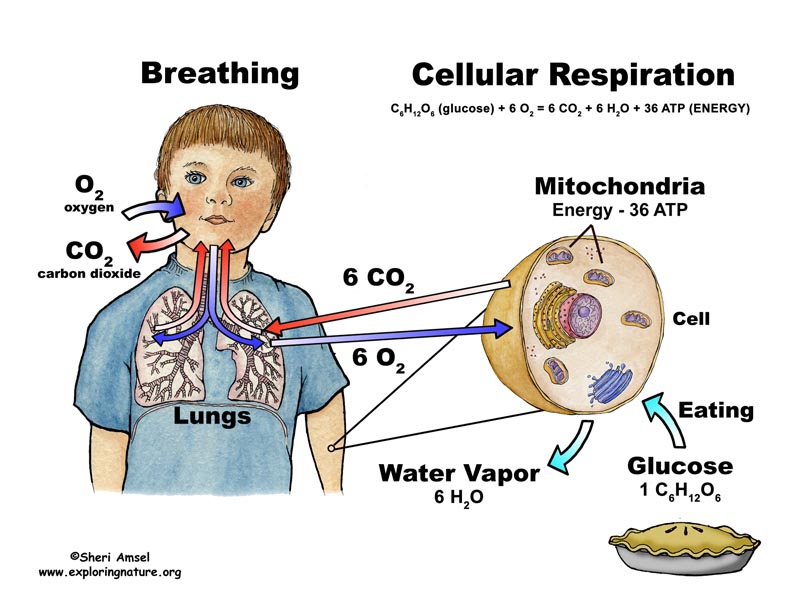
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration - an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration:
Mitochondria are a double-membrane-bound cell organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. In all living cells, these cell organelles are found freely floating within the cytoplasm of the cell. The diagram of Mitochondria is useful for both Class 10 and 12. It is one among the few topics having the highest weightage of marks and is majorly ...
A mitochondrion (/ ˌ m aɪ t ə ˈ k ɒ n d r i ə n /; pl. mitochondria) is a double-membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Mitochondria generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. They were first discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1880 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The mitochondrion is popularly ...
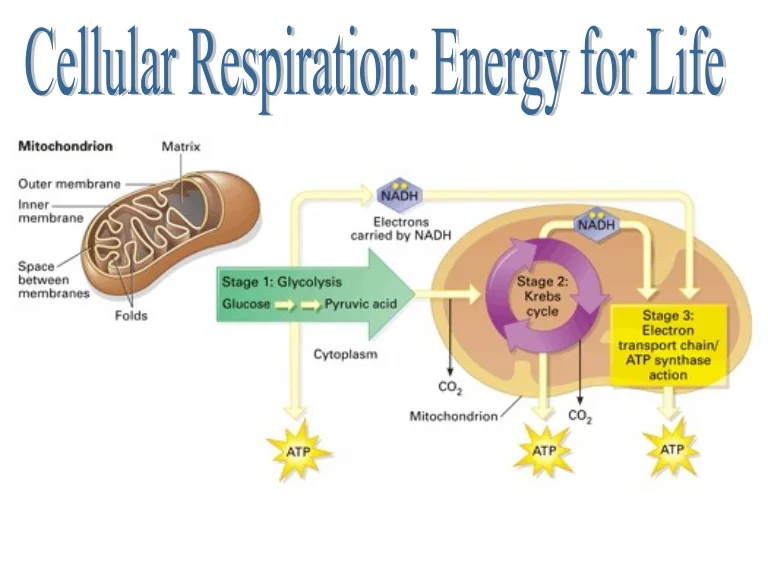
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Sep 9, 2018 - Two worksheets are included. The first is a simple worksheet that has students label the main parts of a mitochondrion. The second worksheet has students identify the main reactants and products of cellular respiration as they relate to the mitochondrion. Similar to my Photosynthesis and Chloroplast...
Glucose, a simple sugar, and other carbohydrates made by plants during photosynthesis are broken down by the process of aerobic cellular respiration (requires oxygen) in the mitochondria of the cell. This releases energy (ATP) for the cell. The more active a cell (such as a muscle cell), the more mitochondria it will have.
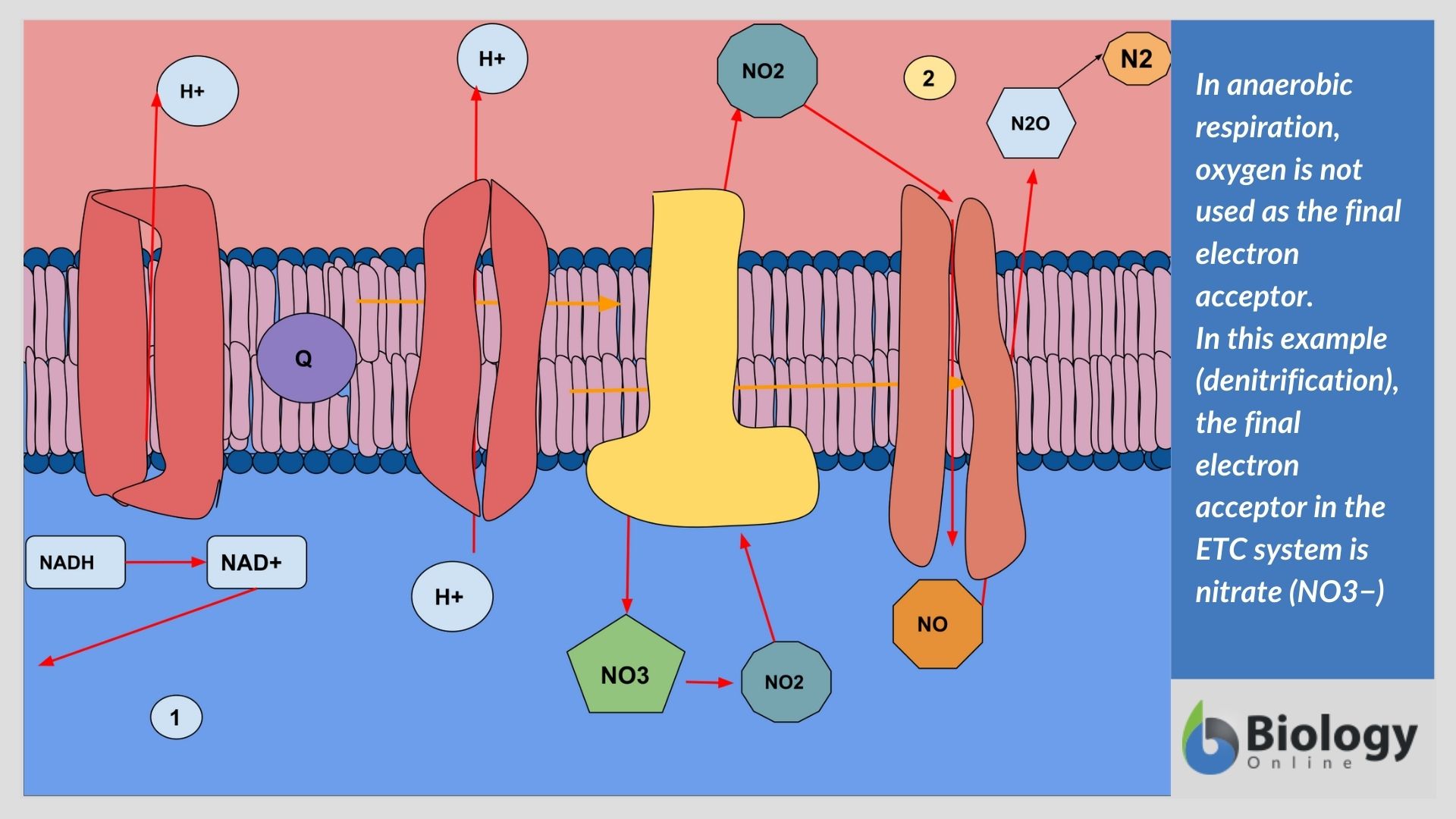
Apart from generating ATP molecules, the mitochondria also regulate cell growth and cell death, it signals the cells and generates heat. It plays a major role in cellular respiration. Anaerobic fermentation is another process by which ATP is generated in the body but anaerobic fermentation does not take place in mitochondria.
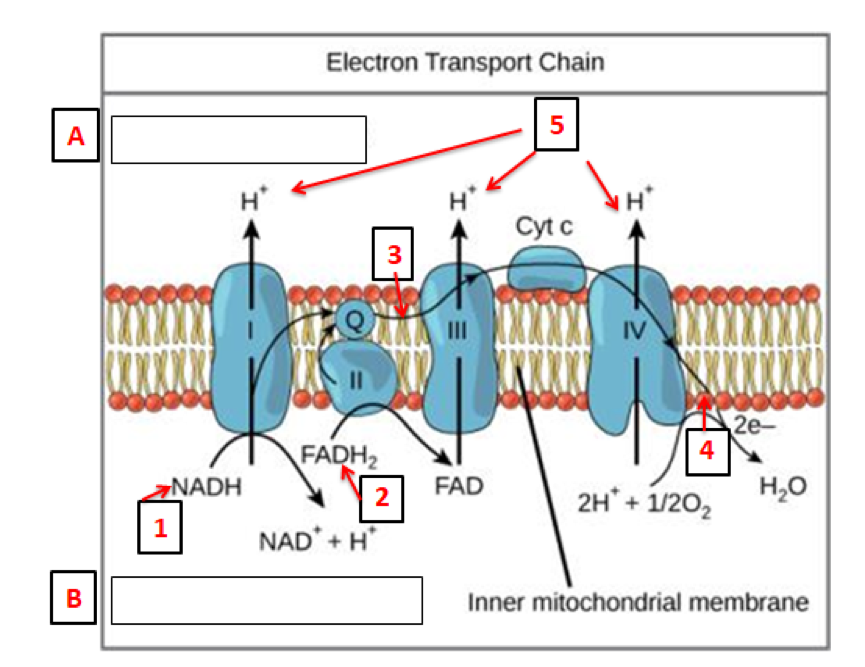
Mitochondria Cellular Respiration Diagram. cellular respiration diagram biologywise after successful pletion of the krebs cycle begins the electron transport chain as you can see in the diagram this stage is where energy is released in bulk in the process of cellular respiration it requires direct use of oxygen molecules this is also known as the oxidative phosphorylation process cellular ...
organelle in which the Kreb's Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain portions of cellular respiration take place. matrix. fluid inside the inner membrane of the mitochondria in which the Kreb's cycle takes place. cristae. folds of the inner membrane of the mitochondria. cellular respiration.
The mitochondria are about the size of a bacterial cell and are often peanut-shaped. Mitochondria have their own DNA and a double membrane. The outer membrane (2) is smooth, while the inner membrane (1) is convoluted into folds called cristae (3) in order to increase the surface area. The matrix (4) is the space contained within the inner membrane. ...
Mitochondria and Cellular respiration - an example of a metabolic pathway: It is difficult to describe mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) in terms of numbers and sizes because they are very dynamic organelles in living cells. Mitochondria continually fuse together, divide into smaller fragments














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)


0 Response to "38 mitochondria cellular respiration diagram"
Post a Comment