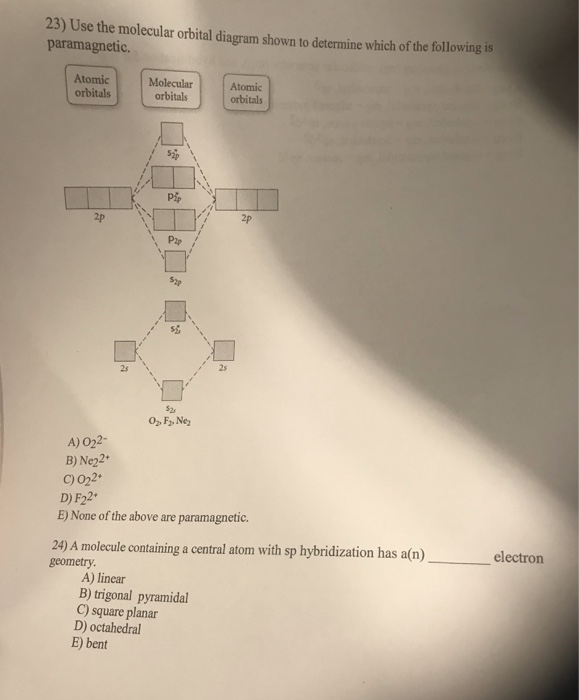
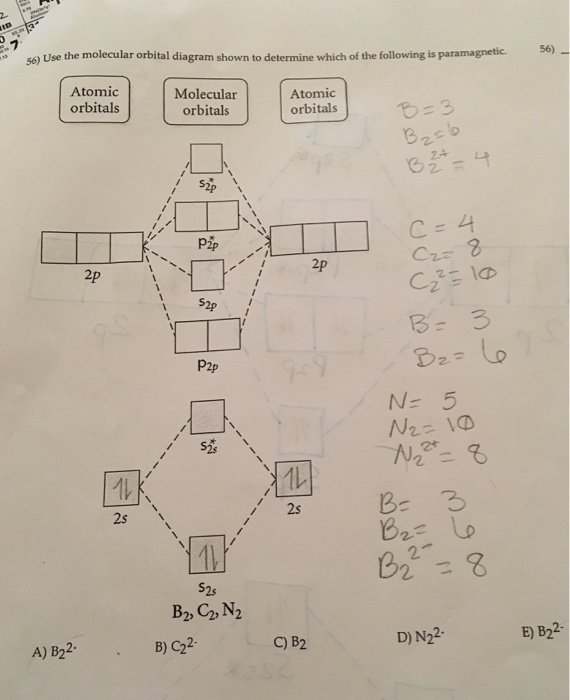
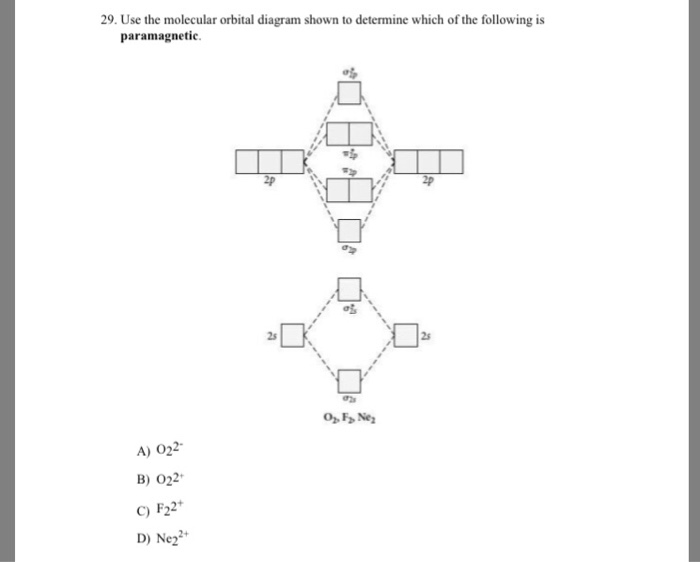
39 draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
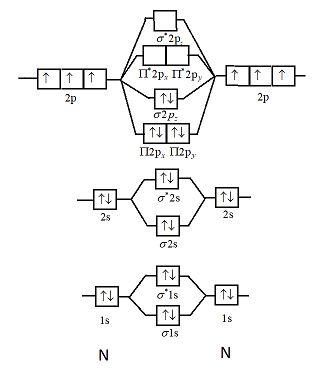
1. Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule B. 2. For full credit on MO diagrams, • label increasing energy with an arrow next to the diagram. • pay attention to whether the question asks for valence electrons or all electrons.
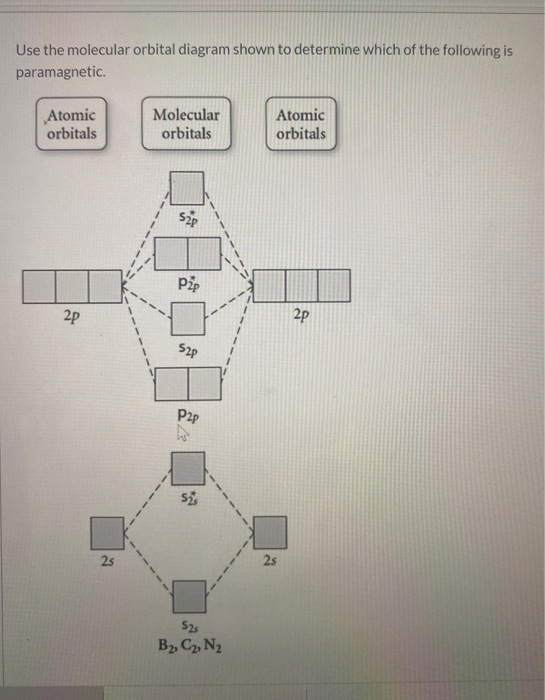
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. asked Jul 15, 2019 in Chemistry by brittanyr9777. general-chemistry. Nitrogen can lose an electron to form N2+. Given the molecular orbital configuration of N2 [core] (σ2s)2 (σ *2s)2 (π2p)4 (σ2p)2 is N2+ diamagnetic or paramagnetic? asked Jun 30 ...
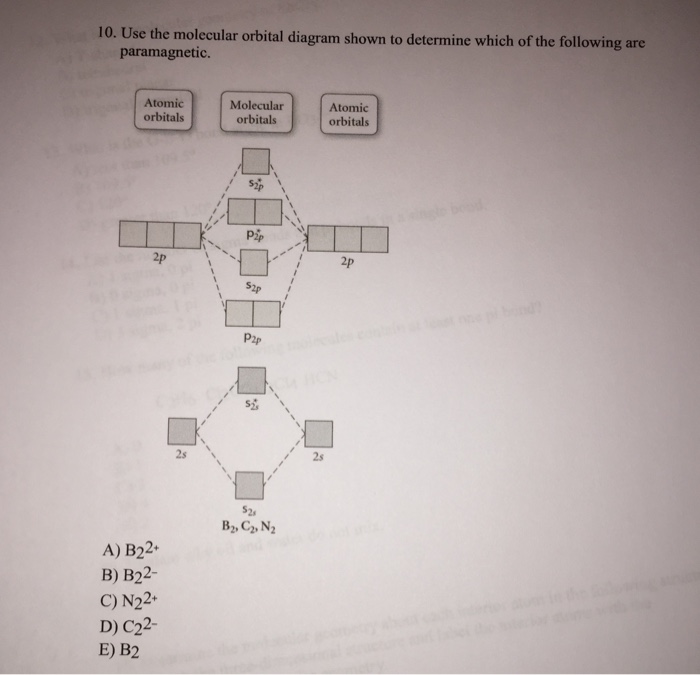
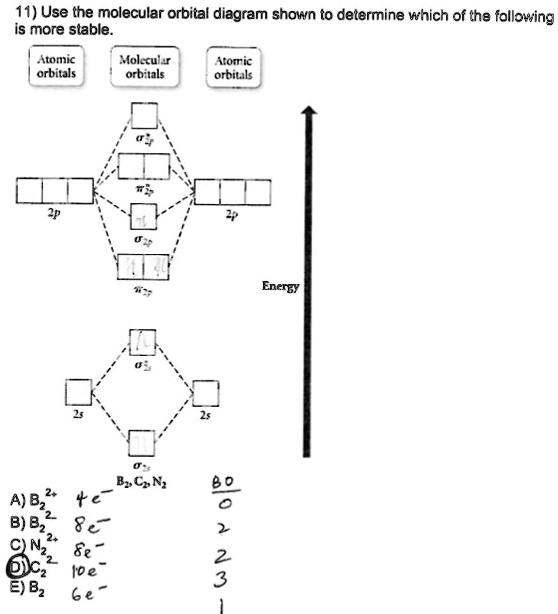
E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) C2^2+ B) N2^2+ C) B2

Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
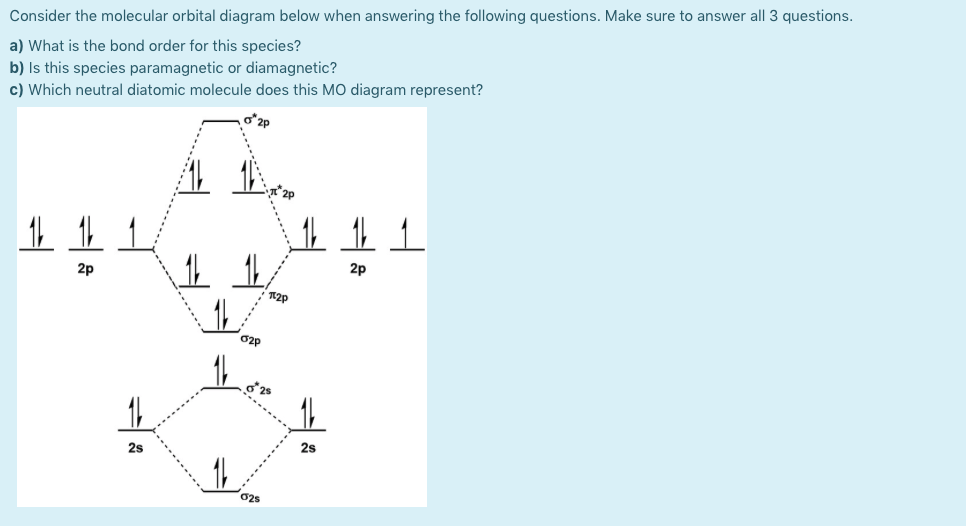
By constructing a molecular orbital picture for each of the following molecules determine whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Paramagnetic materials those with unpaired electrons are attracted by magnetic fields whereas diamagnetic materials those with no unpaired electrons are weakly repelled by such fields.
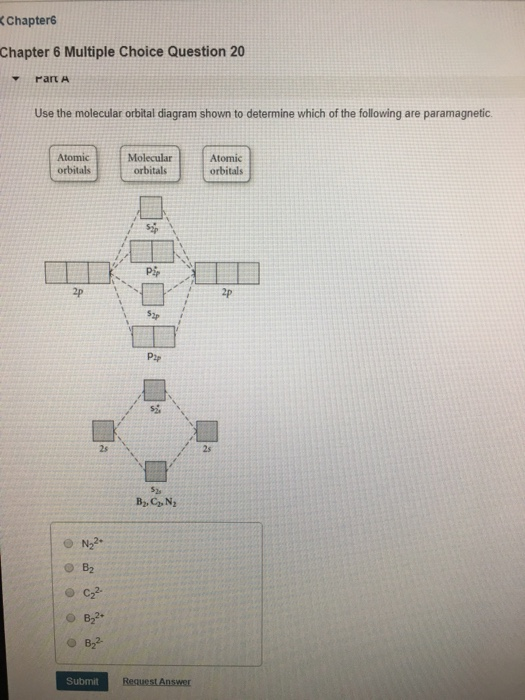
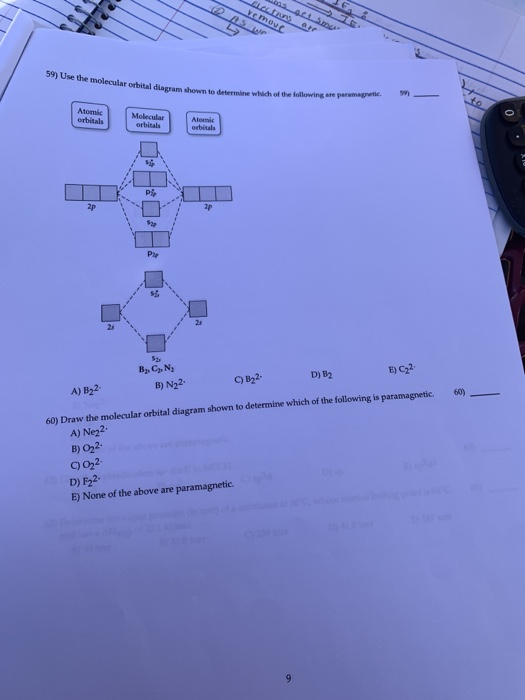
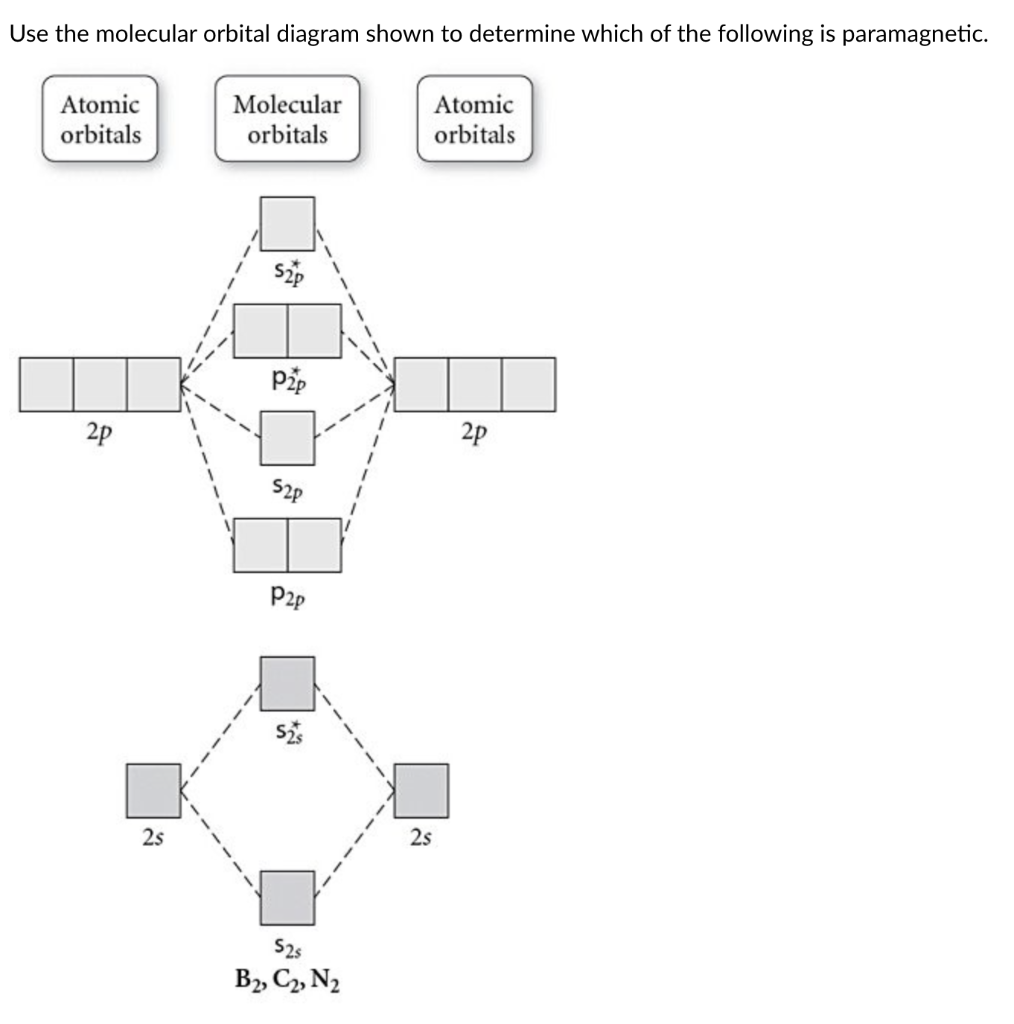
Transcribed image text: 6. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic B,2 B, C2, B22 and N22.
pollutants. A molecular orbital diagram of this species is shown below. Core orbitals are omitted. Marks 8 Using arrows to indicate electrons with their appropriate spin, indicate on the above diagram the ground state occupancy of the atomic orbitals of O and H, and of the molecular orbitals of OH. In the provided boxes on the above diagram ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic..
How to Make the Molecular Orbital Diagram for B2- (Bond Order, Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic). Principia. Principia. 1 answerThe MO diagram of the NF molecule can be drawn as below. The energies of the atomic orbital of N and F are different. The atomic orbital s of F are.... 1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in ...
B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Start your trial now! Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals.
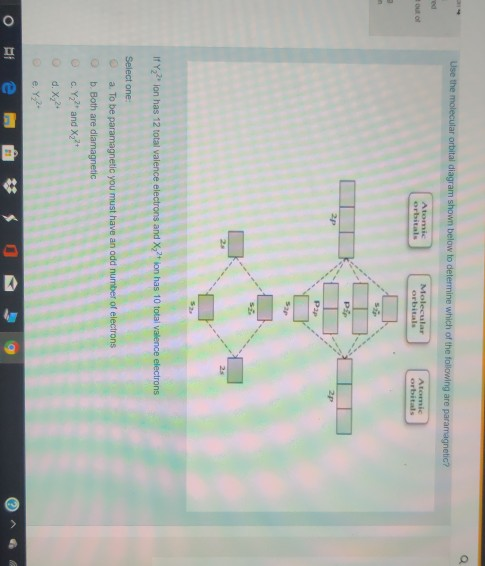
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. N22 b22 b22 b2 c22. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in energy than the separate atomic ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is MOST stable. A) B2^2+. B) C2^2+. C) N2^2+. D) C2^2-Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. C) O2^2+ Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. B) B2.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Answer to Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. N22+ B22+ B B2 CeV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of the lowest energy ...
Draw the best Lewis structure for BrO4⁻ and determine the formal charge on bromine. A) -1 B) +1 ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. A) F2 B) F22⁺ ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) O22⁻ ...
FREE Answer to Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. N22+ B22+...1 answer · Top answer: Electronic configuration of nitrogen is as follows N (7): 1s'2s 2p Nitrogen has five valence electrons, two electrons in 2s orbital and remaining 3 are ...
Construct the molecular orbital diagram of NO + and calculate for the bond order and determine if its paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Determine if there's an unpaired MO (paramagnetic or diamagnetic)
Sign In to Writing (Essays) Science. Chemistry Q&A Library Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Start your trial now!
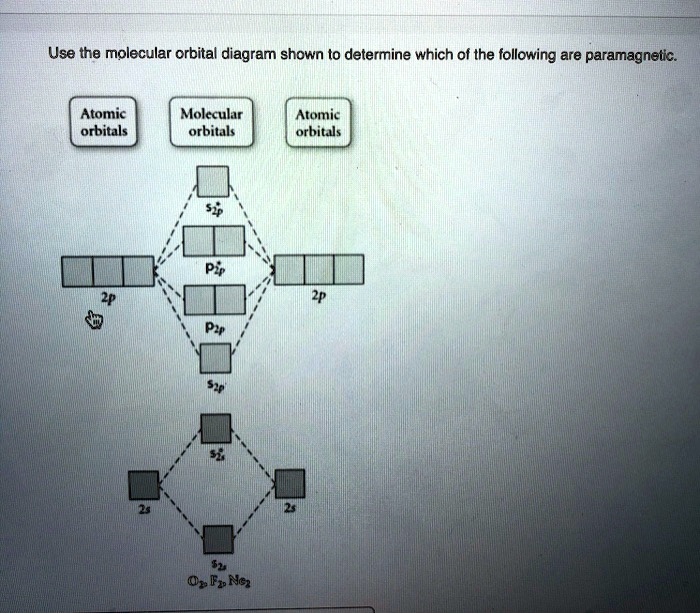
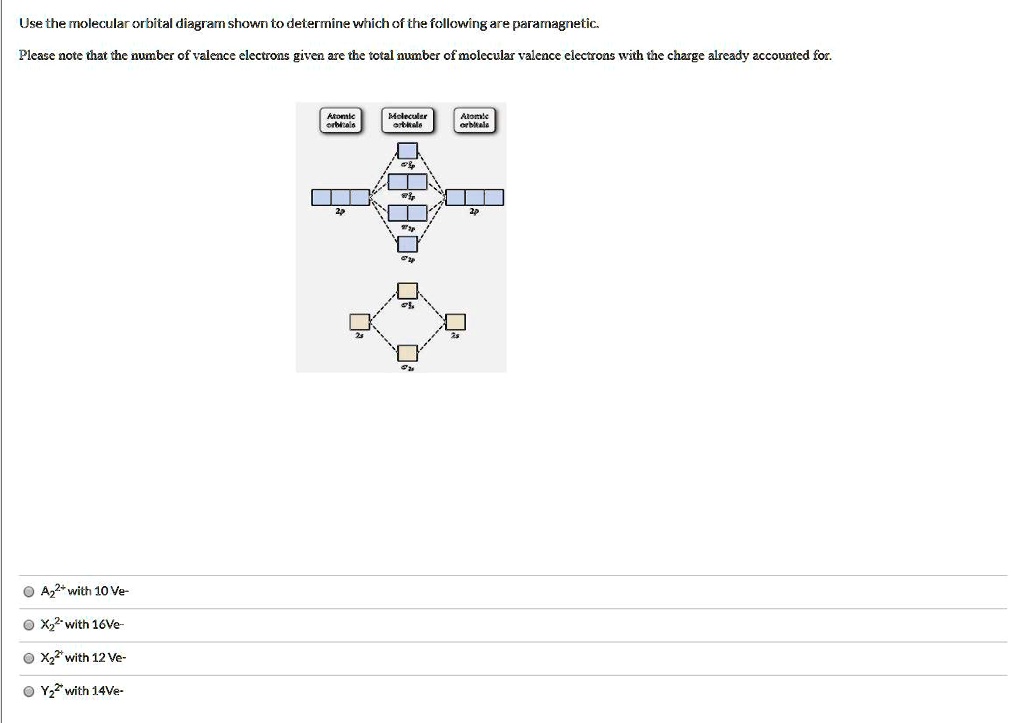
Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. O22+ Ne22+ F22+ O22- ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Answer options: Ne22+ O22- F22+ O22+ None of the above are ...
Transcribed image text: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. (a) O^2-_2 (b) Ne^2+_2 (c) O^2-_2 (d) ...
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A. Ne 22+ B. O 22+ C. F 22+ D. O 22- E. None of the above are paramagnetic. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos.
Molecular orbital diagram for c2 2-. The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively. B2 has two unpaired electrons with the same spin and there for e is paramagnetic. C2 and N2 are... This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the C2 ( 2-) molecule.

Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a) n22+ b) b2c) b22+d) c22-e) c22+
A asdfasdf b asdfasdf c asdf d f2 2 e none of the above are paramagnetic. Molecular Orbital Diagram Wikipedia 1 draw the molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following is most stable. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Fill in the mo diagram that corresponds to each of ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic.Answer options:B2B22+N22+C22-B22-Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic.Answer options:B2B22+N22+C22-B22-
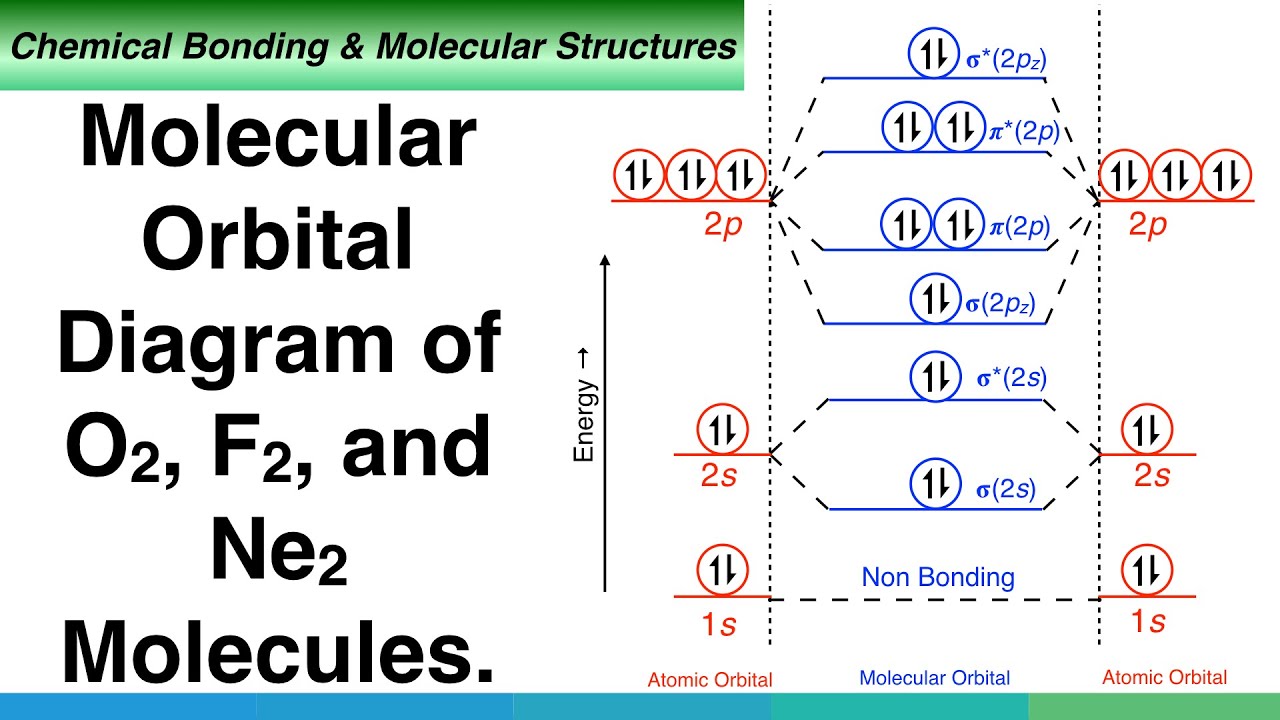
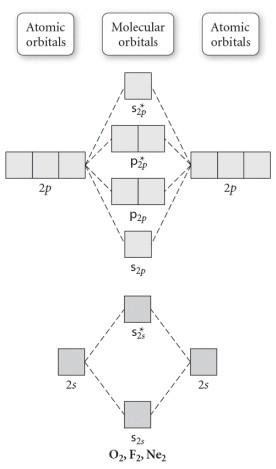
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetica. None of the above are paramagnetic. A o22 b ne22 c o22 d f22 e none of the above are paramagnetic. B b2 identify the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs ...
Transcribed image text: Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. O 0,2 O F₂2+ O Ne 2+ O 0₂2+ None of ...
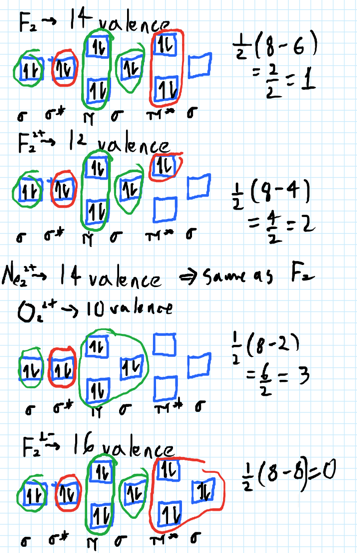
1 answera. Only B2 B 2 is paramagnetic. All the others are diamagnetic. Their MO diagrams are shown below. b. For CO, the...
Use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which is most stable a o22 bf2 c f22 d f22 e ne22 a. A asdfasdf b asdfasdf c asdf d f2 2 e none of the above are paramagnetic. Label each and each and every molecular orbital with its call sigma pi and position the accessible electrons interior the perfect atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...
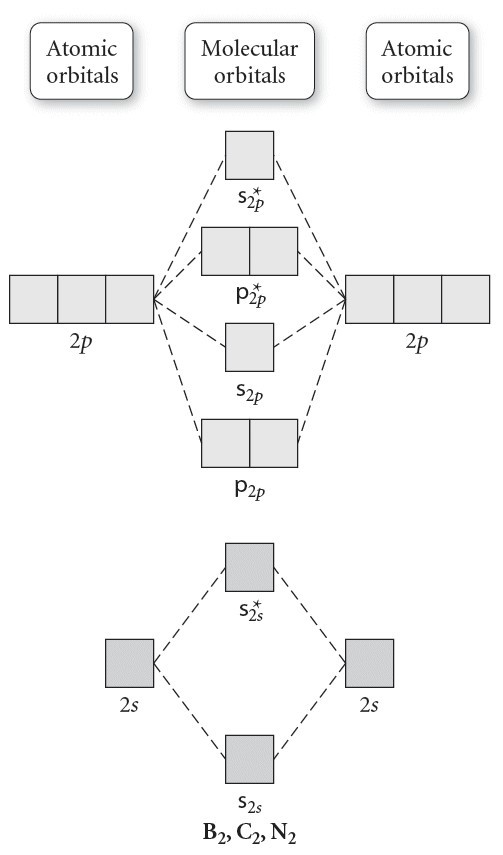
The molecular orbital diagrams for molecules and ions are drawn from the order of increasing energies shown in the molecular orbital configuration. Always remember that the number of molecular orbitals formed must be equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were combined in the molecule.
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures.
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. 38 a b2 b c22. C o22 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. 3 draw the molecular orbital diagram needed and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A n 2 2. D c 2 2. C b 2 2.
Draw the Molecular orbital Diagram Shown to Determine which Of the Following is Most Stable. use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable 38 a b2 b c22 use the molecular orbital question draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to answer to draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to ...

Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.a. ne22+ b. o22+ c. f22+ d. o22- e. none of the above are paramagnetic.
2. The bond order of a homonuclear diatomic molecule can be decreased by. removing electrons from a bonding MO or adding electrons to an antibonding MO. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) N2^2+. B) B2^2+. C) B2^2-. D) C2^2-. E) B2.
Also see here... Bond order for "NO"^+ Order by bond length: "NO", "NO"^(+), "NO"^(-) Is "CO" a Lewis acid? "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the ...
Transcribed image text: 6. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B2, B, C, B and N, Molecular ...
















0 Response to "39 draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic."
Post a Comment