40 moody diagram friction factor
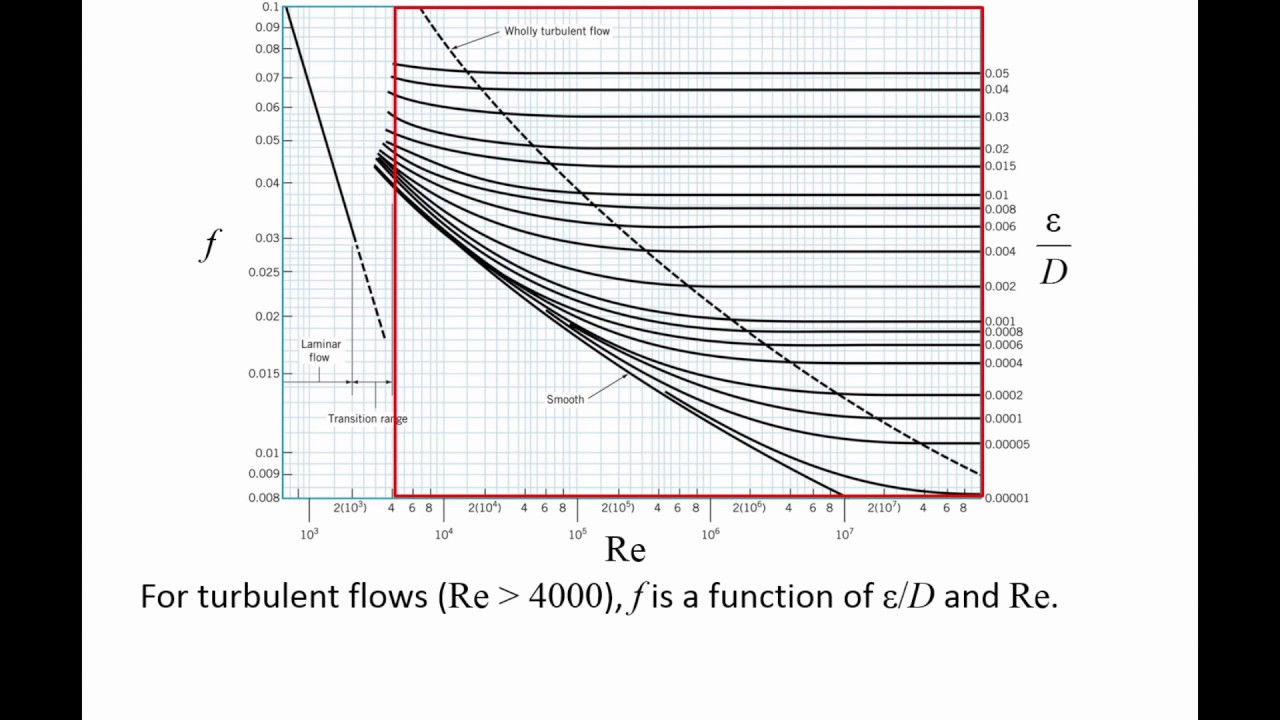
friction factor, f, rather than a graph like the Moody diagram. There are indeed equations available that give the relationships between Moody friction factor and Re & ε/D for four different portions of the Moody diagram. The four portions of the Moody diagram are: i) laminar flow (Re < 2100 - the straight line at the left side of the Moody ...
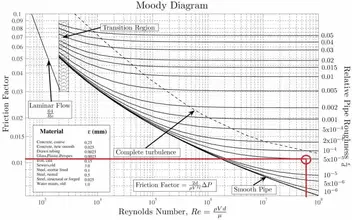
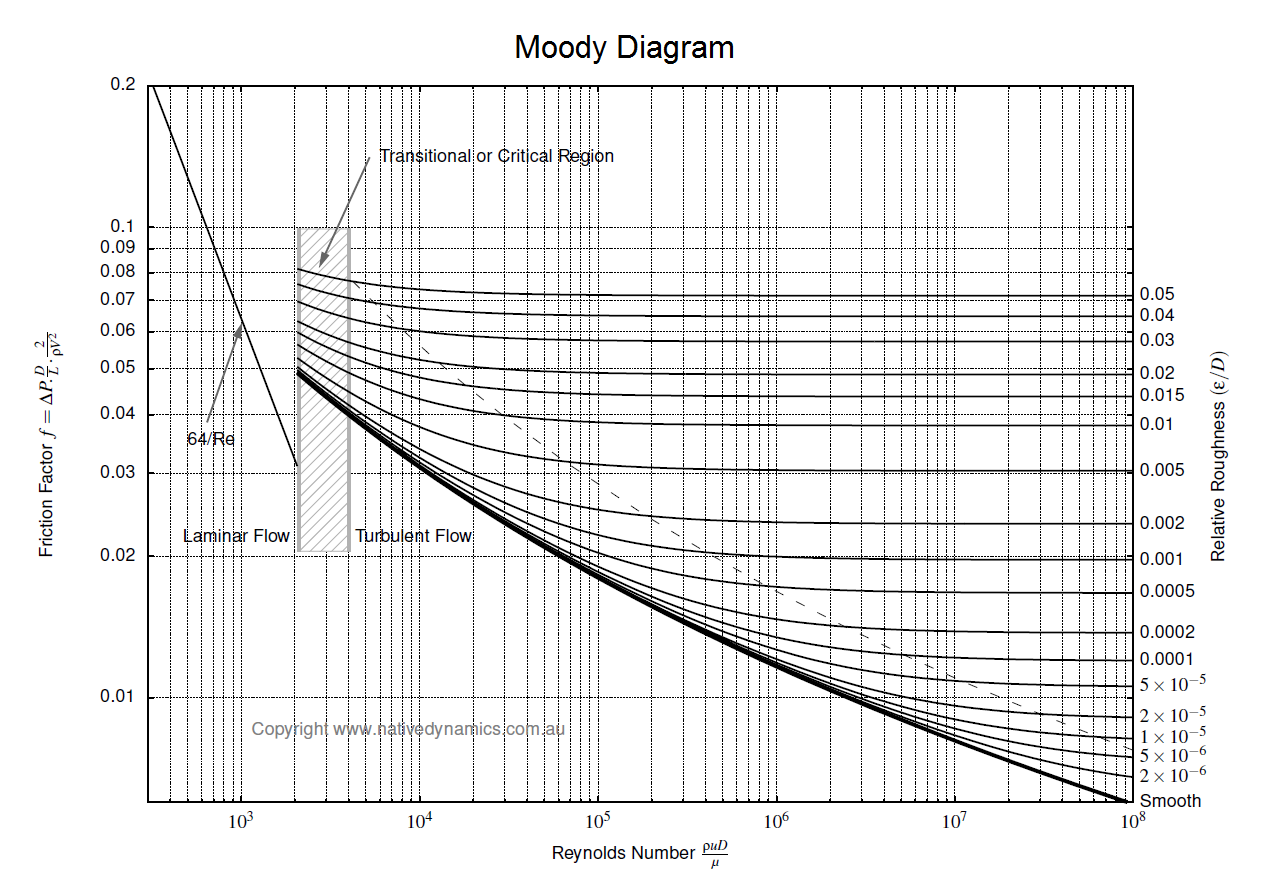
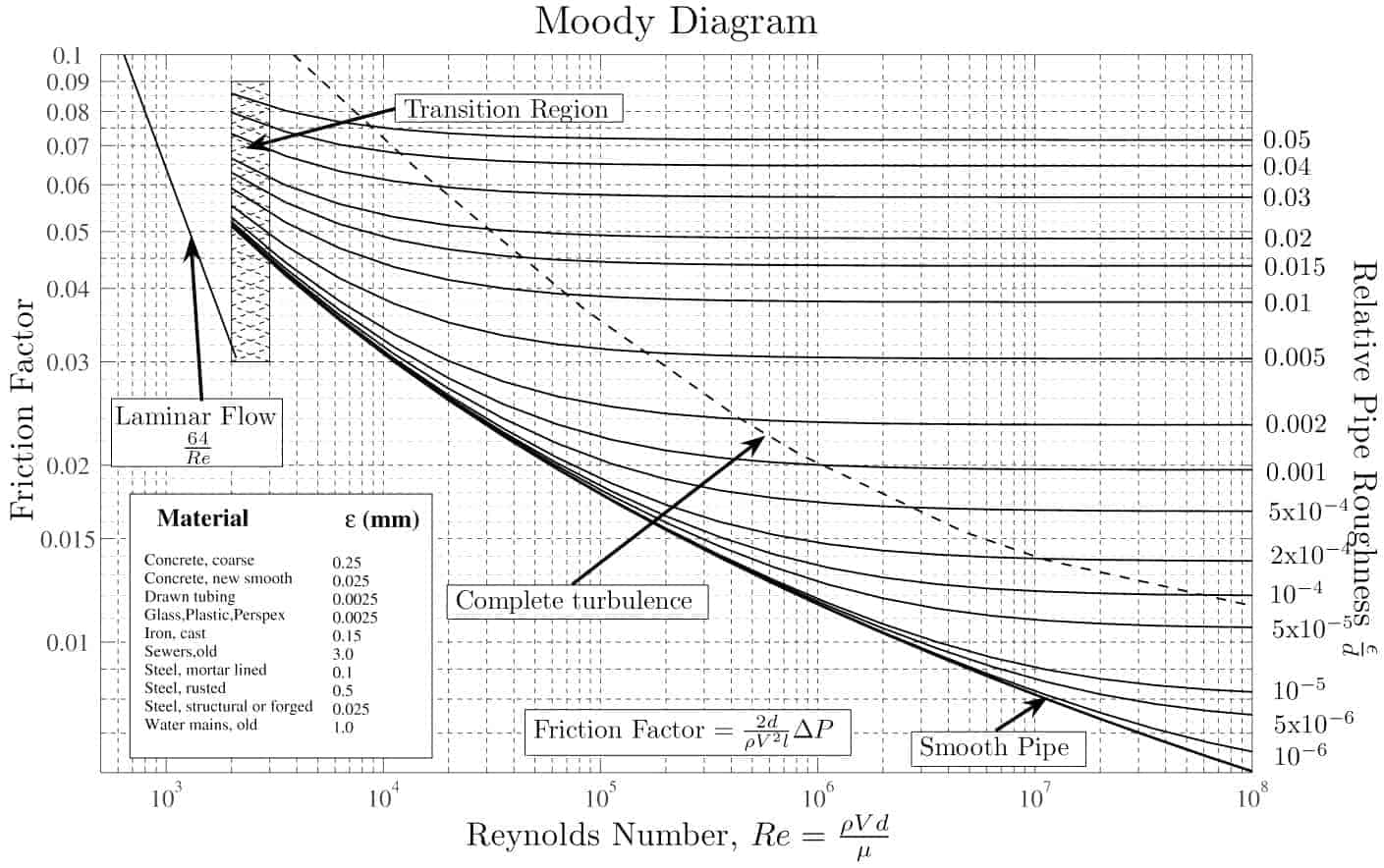
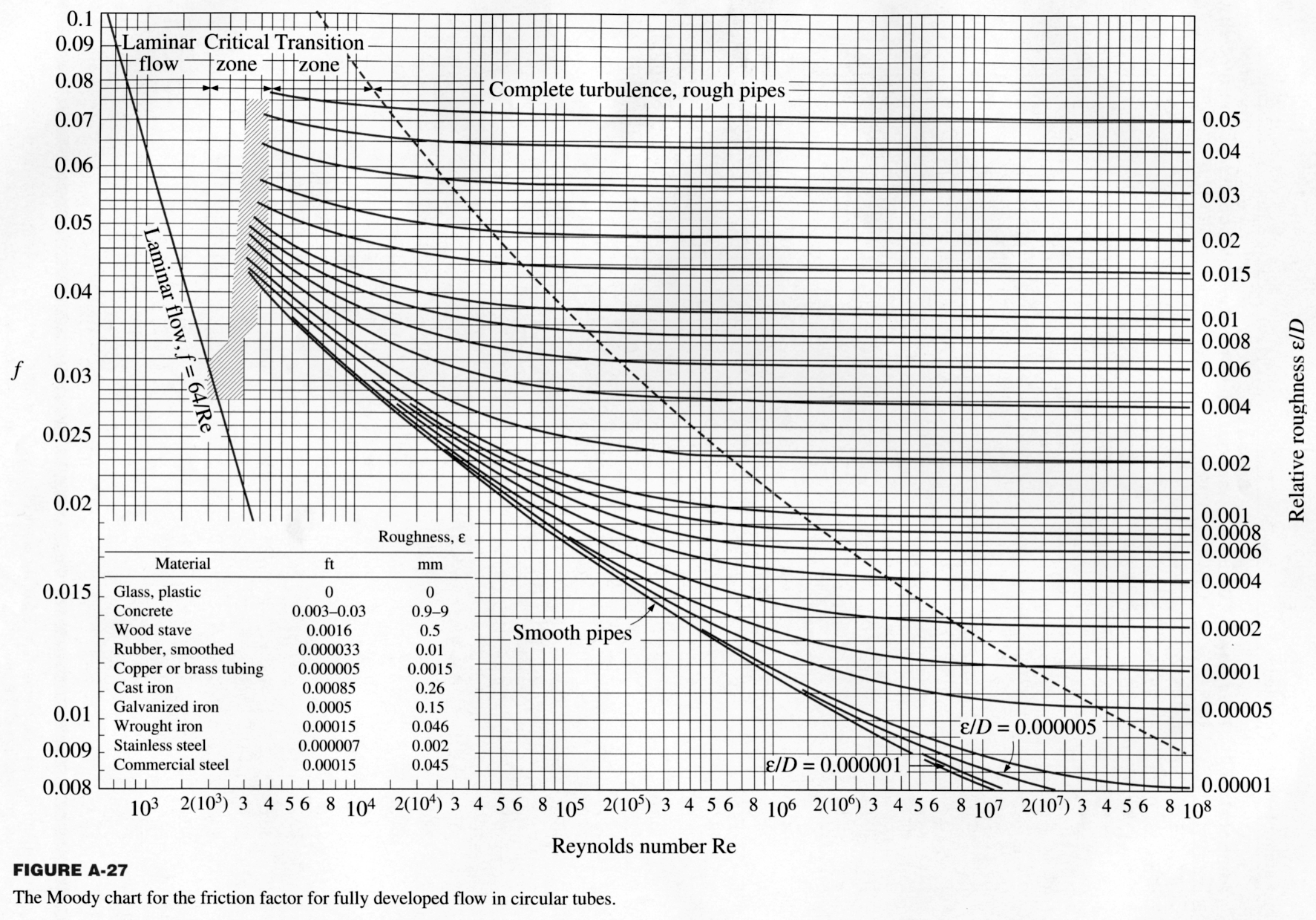
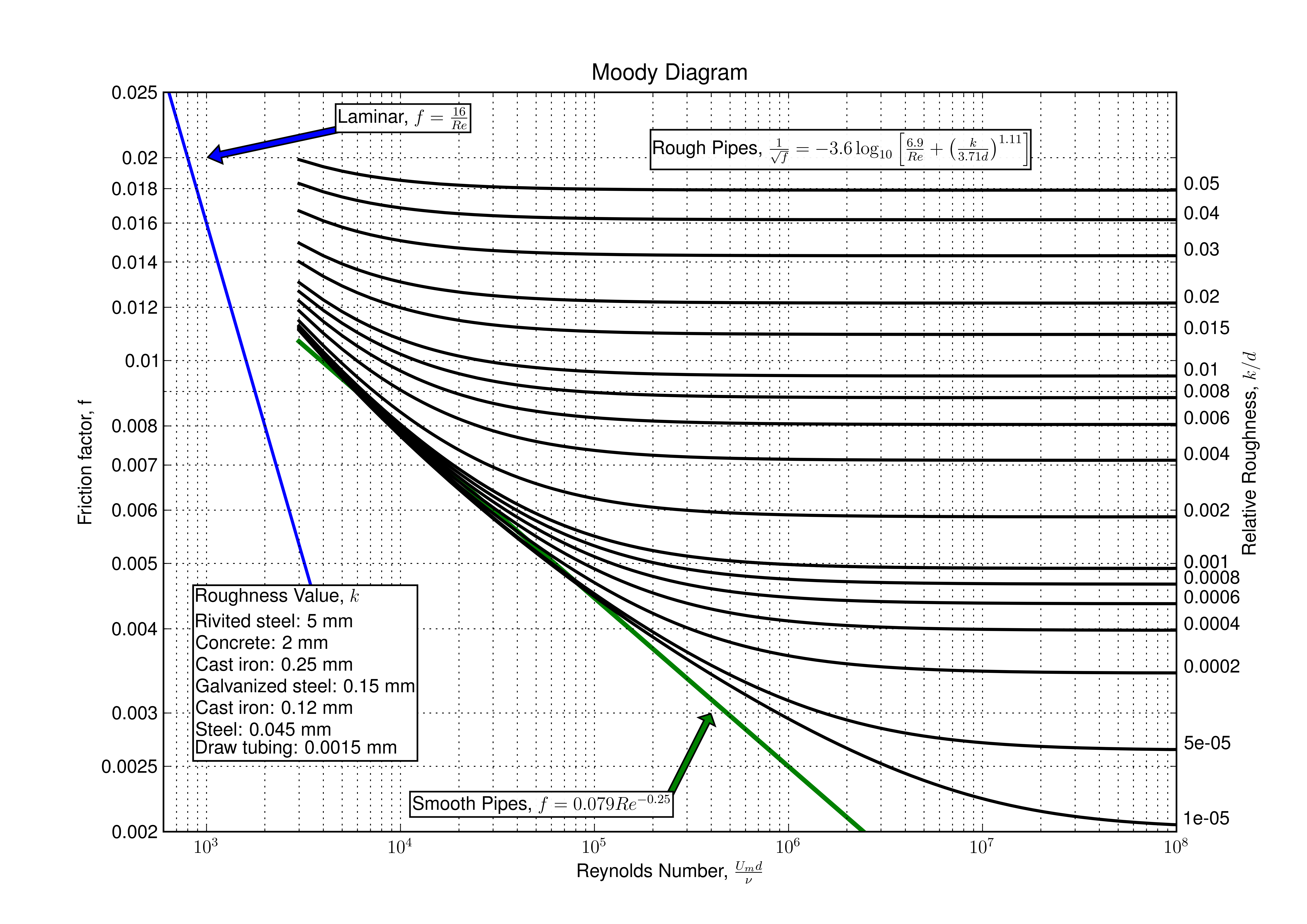
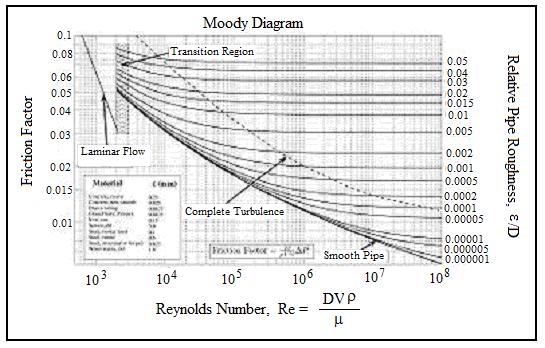
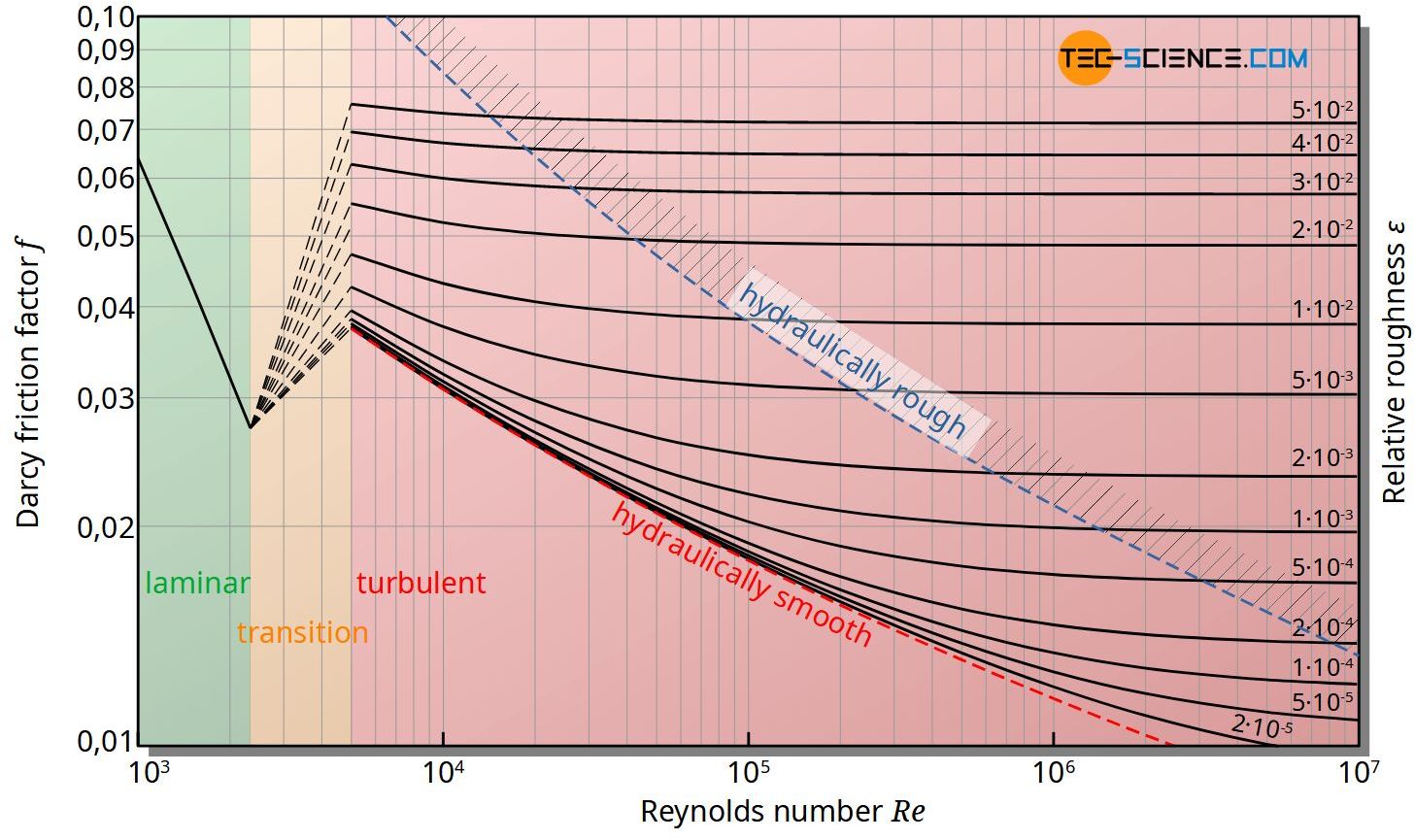
Moody Diagram The Moody diagram (also known as the Moody chart) is a graph in a non-dimensional form that relates the Darcy friction factor, Reynolds number, and the relative roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe. Source: Donebythesecondlaw at the English language Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0,
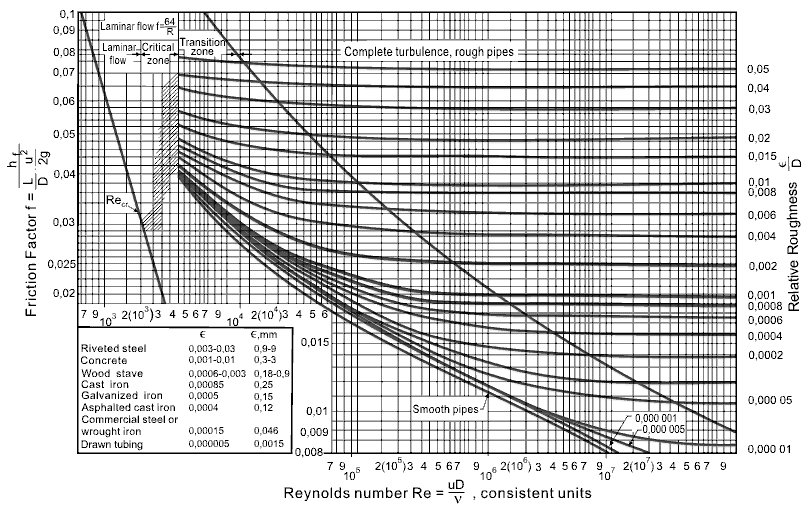
common method of obtaining a value for f is graphically, from the Moody friction factor diagram, first presented by L. F. Moody in his classic 1944 paper in the Transactions of the ASME. (Ref. #1). The Moody friction factor diagram, shown in the diagram below, is now available in many handbooks and textbooks and on many websites.
Moody diagram friction factor
The Moody friction factor is generally accepted and used in pressure drop calculations. Some texts, including API RP 14E, use the "Fanning" friction factor, which is one-fourth the value of the Moody friction factor. Confusion between Moody and Fanning friction factors is a common source of error.
A Spreadsheet as a Friction Factor Calculator - The use of a spreadsheet is an attractive alternative to the Moody diagram for determining a value of the Moody friction factor for specified values of Reynolds number, Re, and roughness ratio, /D.
Nov 23, 2021 · This calculator utilizes Moody's approximation to determine the Darcy friction factor. Moody's approximation or otherwise known as Moody equation is given as: f = 0.0055 ( 1 + (2 * 10 4 * k/D + 10 6 /Re) 1/3) This approximation is valid for flow regimes where Reynold's number is between 4,000 and 5*10 8, and pipes with a k/D ratio less than 0.01.
Moody diagram friction factor.
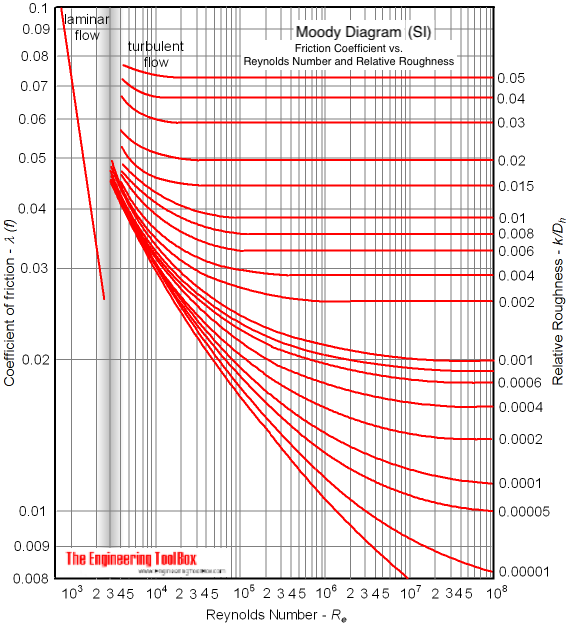
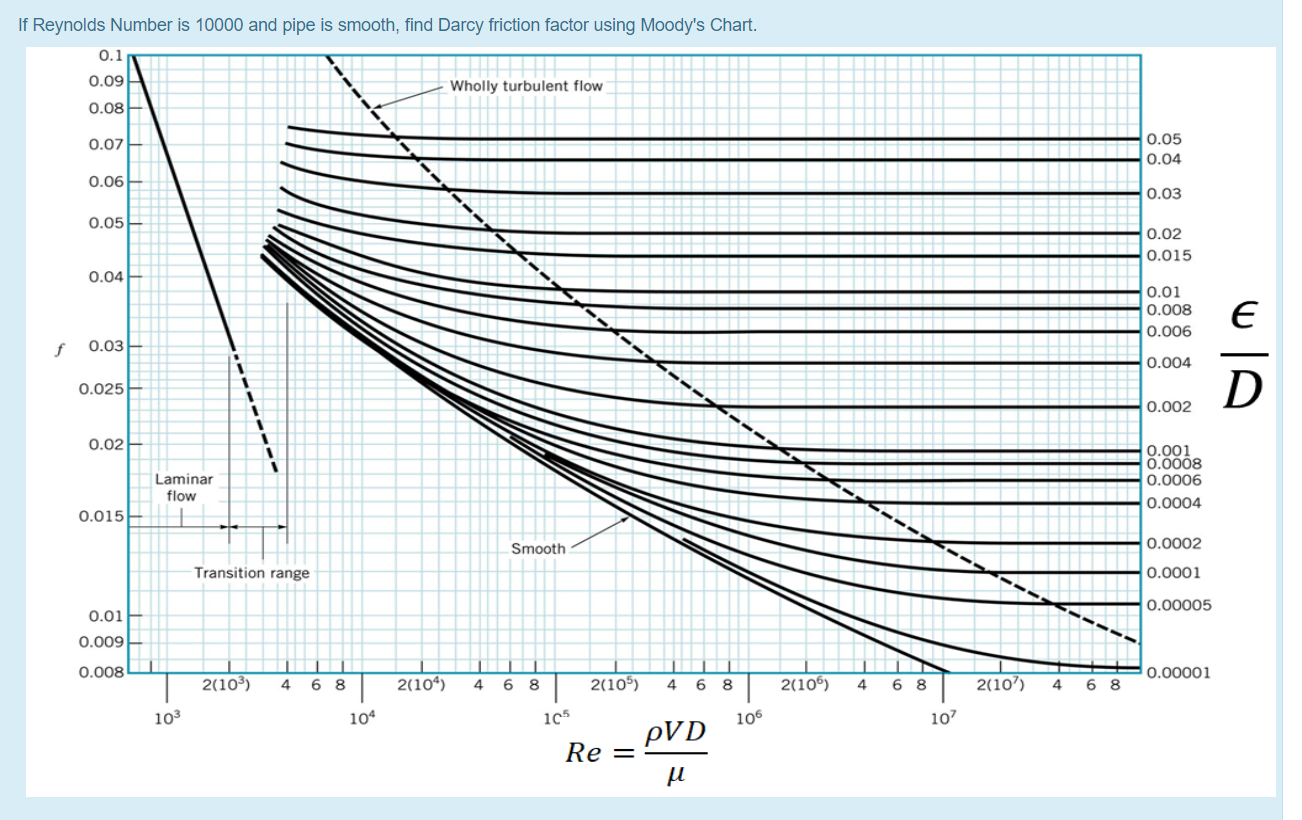
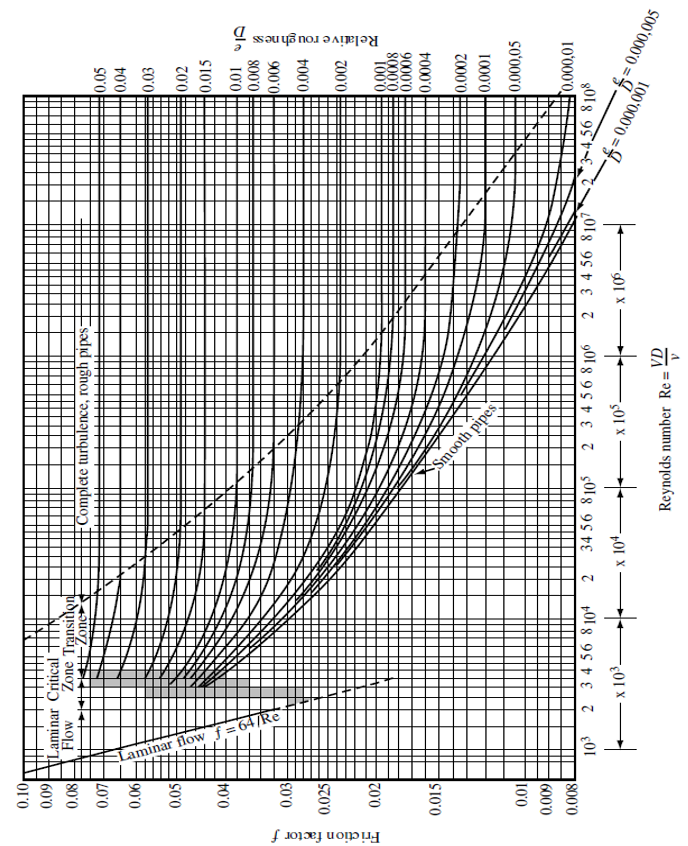
The Moody friction factor - λ (or f) - is used in the Darcy-Weisbach major loss equation. The coefficient can be estimated with the diagram below: If the flow is transient - 2300 < Re < 4000 - the flow varies between laminar and turbulent flow and the friction coefiicient is not possible to determine. The friction factor can usually be ...
The friction factor ( f) can be calculated from the Moody diagram (chart) using the Reynolds number ( Re = ρ Dv / μ) and the effective roughness ( ε / D), where μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (kg/m s) and ε is the casing roughness height or absolute roughness (mm).
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In engineering, the Moody chart or Moody diagram (also Stanton diagram) is a graph in non-dimensional form that relates the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor fD, Reynolds number Re, and surface roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe.
The blue lines plot the friction factor for flow in the wholly turbulent region of the chart, while the straight black line plots the friction factor for flow in the wholly laminar region of the chart. Friction Chart or Moody Chart The value of f, Darcy friction factor is taken from Moody Diagram.
In circular pipes this factor can be solved directly with the Swamee-Jain equation, as well as others, however most of these equations are complicated, and become cumbersome when iteration is necessary. Therefore, it is often effective to solve for this friction factor using the Moody Chart.
May 22, 2019 · The Moody chart (also known as the Moody diagram) is a graph in non-dimensional form that relates the Darcy friction factor, Reynolds number, and the relative roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe. Reynolds Number. The Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and is a convenient parameter for predicting ...
Moody factor can be calculated from Fanning factor with the following formula : fMoody = 4*fFanning f Moody = Moody's friction factor f Fanning = Fanning's friction factor Note that Moody's friction factor is sometimes called Darcy or Darcy-Weisbach friction coefficient.
Learn more about the Moody Chart Calculator here. ... D is the diameter of the pipe: Friction Factor; where, h f is the head loss f is the friction factor L is the length of the pipe D is the diameter of the pipe v is the velocity of the fluid g is gravitational acceleration: Powered by Create your own unique website with customizable templates ...
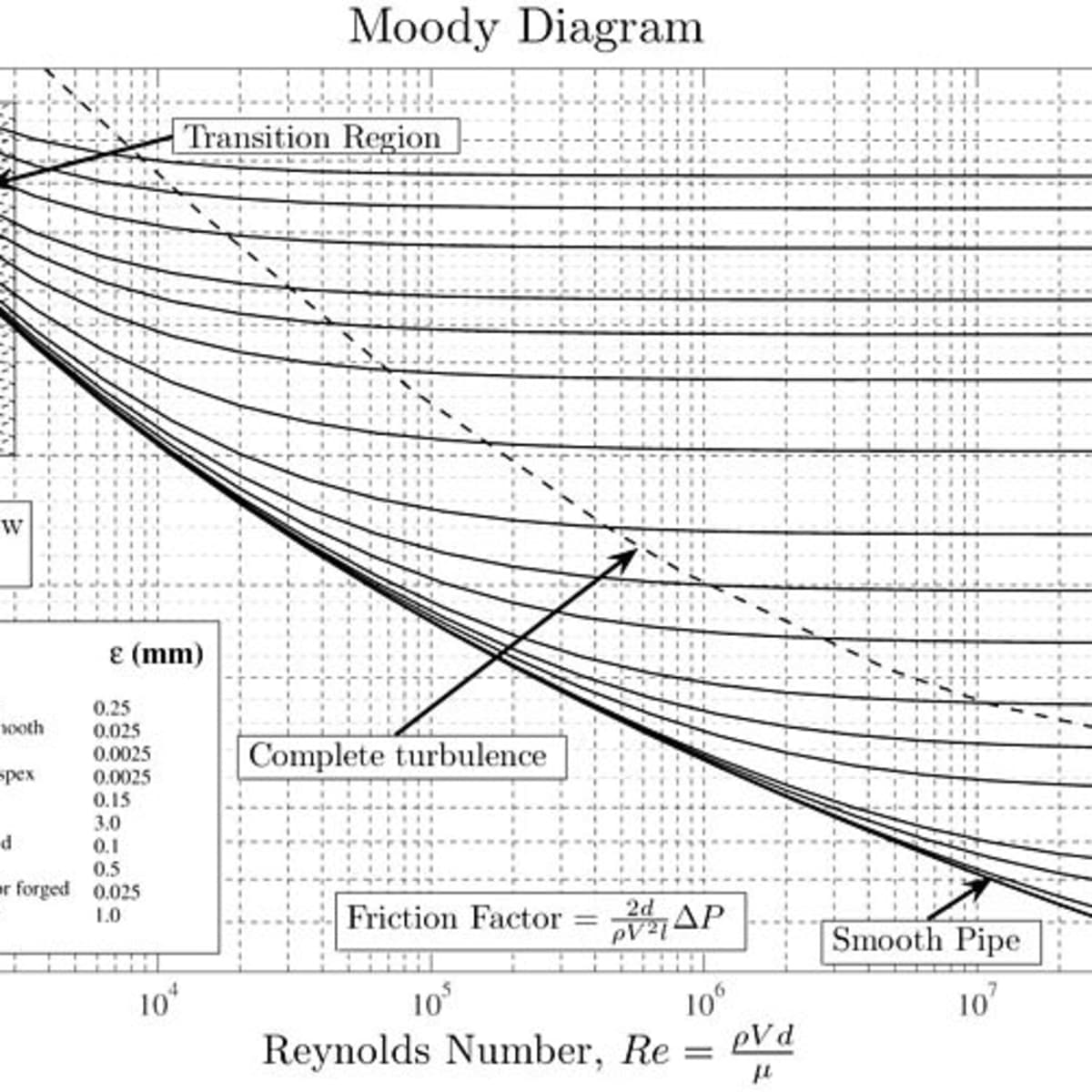
Why the Moody Diagram needs updating • Prandtl's universal friction factor relation is not universal (breaks down at higher Reynolds numbers: >3 x 106) • Transitional roughness regime is represented by Colebrook's transitional roughness function using an equivalent sandgrain roughness, which takes no account of individual roughness types
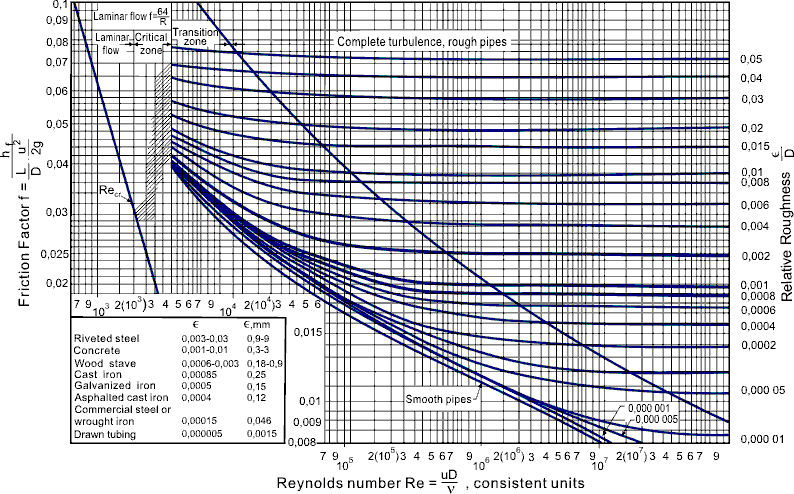
MOODY DIAGRAM Friction factors for any type and size of pipe. (From Pipe Friction Manual, 3rd ed., Hydraulic Institute, New York, 1961) O O = J uopeJ UO!IOUJ uoeqs!êM-Á0Jea S C o i. (ww u! a 'wul u! 3) = J ssauuôno' Title: Microsoft Word - Moodies diagram.doc Author: Administrator Created Date: 6/6/2008 2:04:32 PM ...
Stuart W. Churchill developed a formula that covers the friction factor for both laminar and turbulent flow. This was originally produced to describe the Moody chart, which plots the Darcy-Weisbach Friction factor against Reynolds number. The Darcy Weisbach Formula , also called Moody friction factor, is 4 times the Fanning friction factor
tion. This equation includes the Darcy friction factor. The exact solution of the Darcy friction factor in turbulent ow is got by looking at the Moody diagram [5] or by solving it from the Colebrook equation [1]. If the Darcy friction factor must be known only once, the Moody diagram is good.
The Moody diagram. The friction factor is used to calculate the pressure drop due to the flow of a fluid in a pipe. It represents the interaction in between the fluid and the pipe. There are different ways to calculate it, one can be graphical, using a Moody graph. Note that the friction factor used here is Darcy (also called Darcy-Wesibach or ...
Jul 04, 2020 · The Moody diagram is a chart showing the Darcy friction factor of a pipe as a function of the Reynolds number for selected roughnesses of the pipe wall. 1 Pressure loss. 1.1 Friction factor for laminar pipe flows. 1.2 Friction factor for turbulent pipe flows. 2 Moody chart.
Fluid Power Equipment The Moody chart or Moody diagram is a graph in non-dimensional form that relates the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor f D, Reynolds number Re, and relative roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe. It can be used for working out pressure drop or flow rate down such a pipe.
this equation. The frictional factor is estimated through Moody chart for the above calculations (Moody, 1944). The Moody chart is a graphical representation of Colebrook equation (Colebrook, 1939, Colebrook and White 1937, Lester 2002). During a computer simulation of fluid flow the direct application of Colebrook equation has advantages
Moody Chart Calculator. Reyolds number: relative roughness: friction factor: Try the Free Moody Chart Calculator app for Android at the Google play, here! Learn more about the Moody Chart Calculator, ...
Keywords: friction factor, Moody diagram, vector graphic, Darcy friction factor, Fanning friction factor, pipe ow, relative roughness, Reynolds number, monotonic roughness, in ectional roughness. Introduction. Since the mid 1940s, practicing engineers, engineering academics and stu-dents of engineering have made use of a diagram of friction ...
The friction factor or Moody chart is the plot of the relative roughness (e/D) of a pipe against the Reynold's number. The blue lines plot the friction factor for flow in the wholly turbulent region of the chart, while the straight black line plots the friction factor for flow in the wholly laminar region of the chart.
The Moody friction factor (f) is used in the Darcy-Weisbach major loss equation. Note that for laminar flow, f is independent of e. However, you must still enter an e for the program to run even though e is not used to compute f. Equations can be found in Discussion and References for Closed Conduit Flow.
In Fluid Mechanics, the Moody chart or Moody diagram is a graph which relates the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor ( fD ) , Reynolds number (Re), and surface roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe. It can be used to predict pressure drop or flow rate down such a pipe.
The Moody chart or Moody diagram is a graph in non-dimensional form that relates the Darcy friction factor, Reynolds number, and surface roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe.It is based on thousands of experiments, and the accuracy is about ±5% for smooth pipes and ±10% for rough pipes.
published "Friction Factors for Pipe Flow"1. The work of Moody, and the Moody Diagram on page 6 72 of the published transactions, has become the basis for many of the calculations on friction loss in pipes, ductwork and flues. While there are modified versions of the original Moody Diagram, I will strive to use the












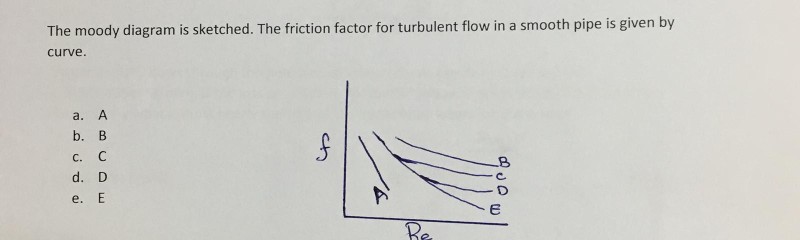




0 Response to "40 moody diagram friction factor"
Post a Comment