trogen atomic orbital diagram
Atomic Orbital Diagrams: These are also known as electron-in-a-box diagrams. This is a simplified diagram of how the electrons are arranged within the orbitals for a particular atomic species.
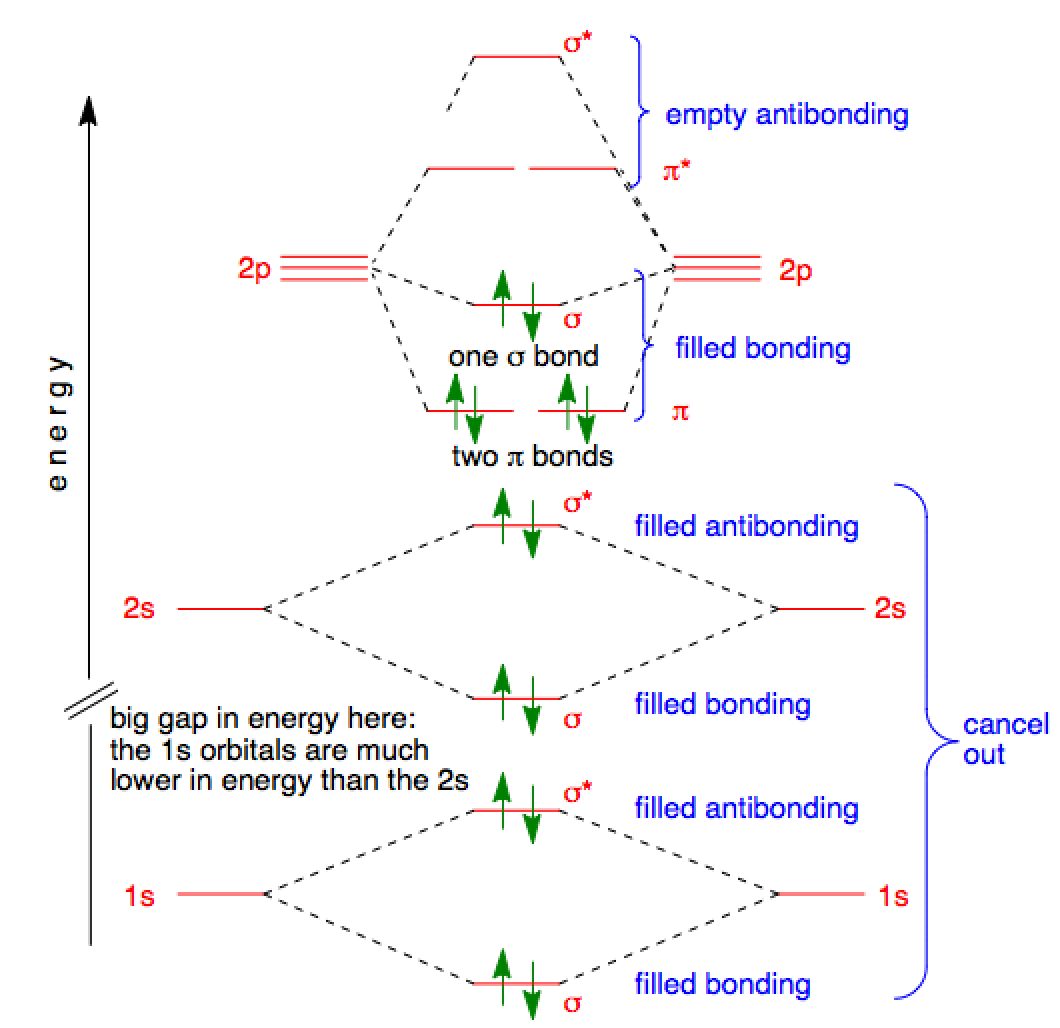
Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for N2. Now we add the 10 electrons, 5 from each nitrogen atom. Note that the bottom sigma symmetry orbital is strongly bonding, the top one is strongly antibonding, and the 2 in the middle are only weakly bonding and antibonding, respectively.
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.

Nitrogen atomic orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Atomic no. Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams; 1: Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram ...
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
Nitrogen atomic orbital diagram.
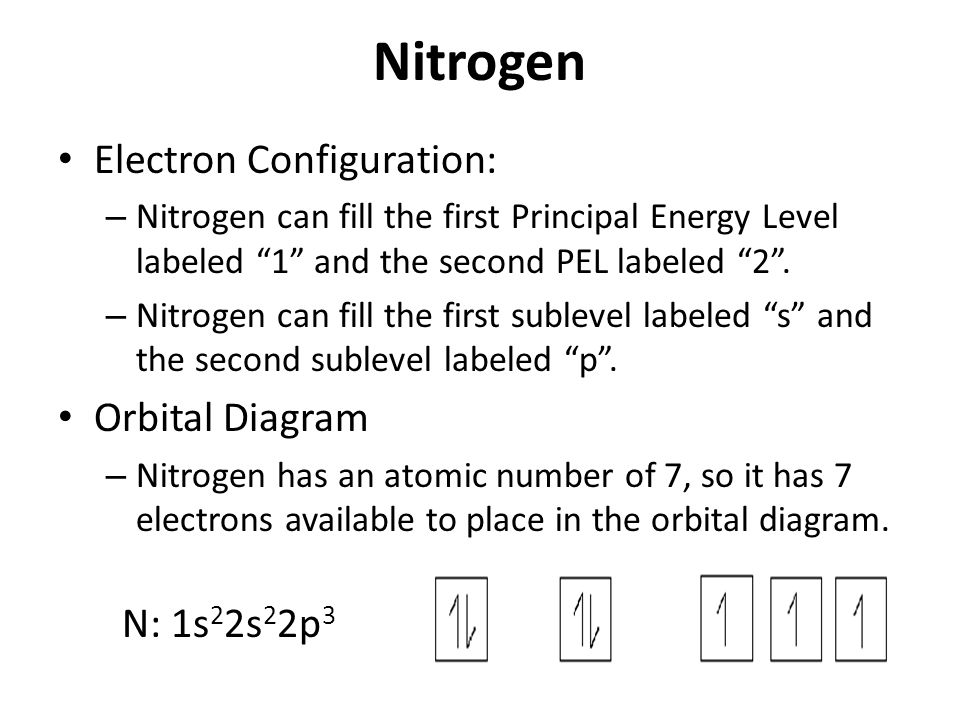
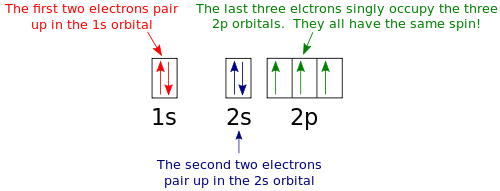
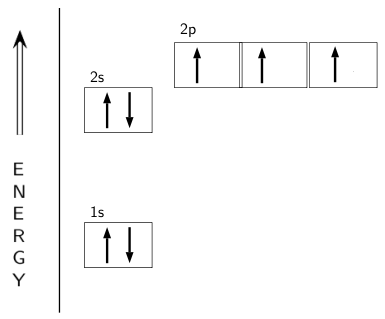
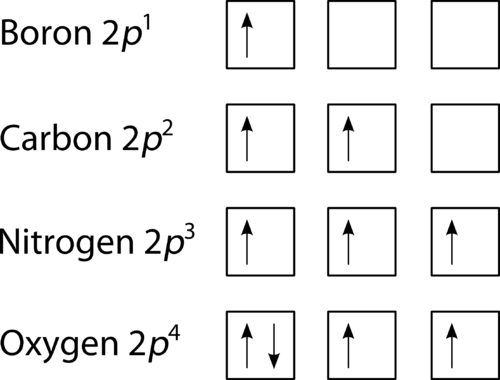
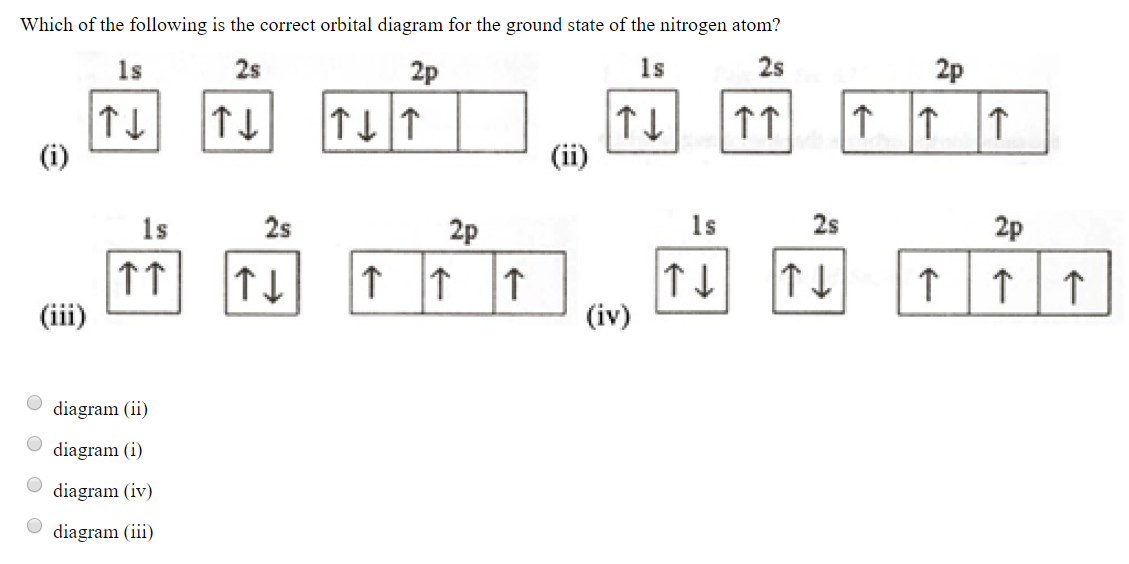
The electron configuration and orbital diagram for carbon are: Nitrogen (atomic number 7) fills the 1 s and 2 s subshells and has one electron in each of the three 2 p orbitals, in accordance with Hund's rule . These three electrons have unpaired spins.
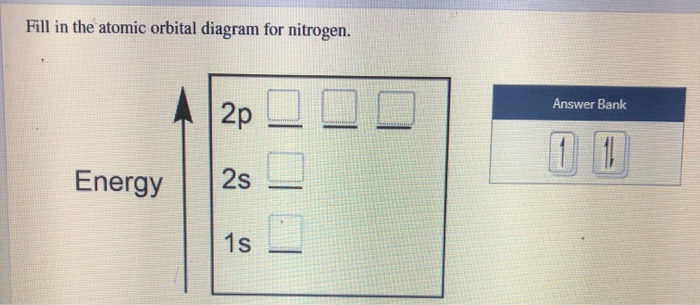
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (17 ratings) Transcribed image text: Fill in the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Answer Bank Energy Construct the orbital diagram for nickel. 1000 Answer Bank Energy 2 _ _ _.
The nitrogen atom is called the hydrogen bond The Orbital Diagram For A Ground State Nitrogen Atom Is . We can illustrate the comparison of orbitals and electron distribution in an isolated boron atom and in the bonded atom in BH 3 as shown in the orbital energy level diagram in . Nitrogen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and the total number of electrons in the oxygen atom is eight.
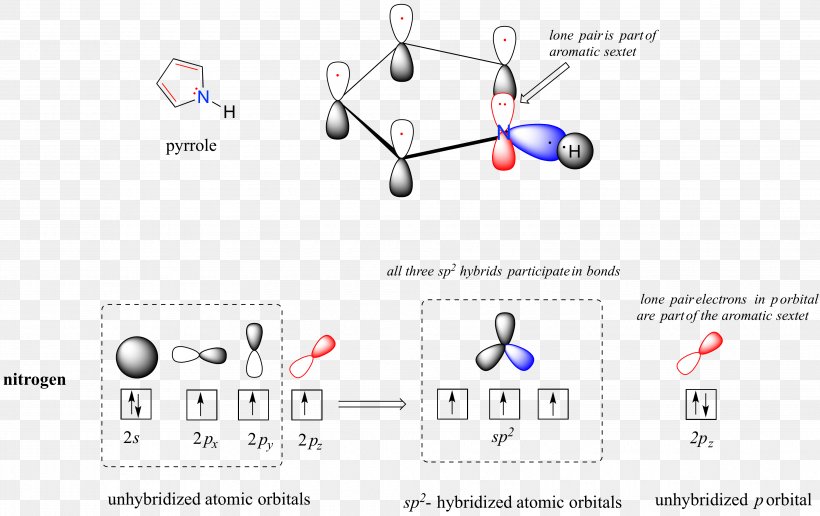
We will again need four hybrid orbitals, obtained by mixing one s and three p atomic orbitals in nitrogen. Nitrogen has five valence electrons ( ). Three hydrogen atoms with one unpaired electron apiece ( ) will overlap their 1 s orbitals with the three available sp3 orbitals on the nitrogen.
The choice A accurately specifies and illustrates the orbital diagram of a Nitrogen atom with 7 electrons. Based on the number of electrons in a Nitrogen atom, there are two energy levels, the s and p sub-levels: Nitrogen = 2, 5 The first energy level, S will take up two electrons with opposite spin.
Orbital Diagram Of Nitrogen. molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory molecular orbital theory home faculty molecular orbital theory the goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms that is in
To see this video, other videos, chemistry education text, and practice problems visit my website. Website is 100% FREE to use.http://scientifictutor.org/
Figure 8.2. 11: The four valence atomic orbitals from an isolated carbon atom all hybridize when the carbon bonds in a molecule like CH 4 with four regions of electron density. This creates four equivalent sp 3 hybridized orbitals. Overlap of each of the hybrid orbitals with a hydrogen orbital creates a C-H σ bond.
For those users who are not aware of the symbol of the element nitrogen, then it is represented by "N". Electron Configuration For Nitrogen Ion The atomic number of nitrogen is 7, the element nitrogen was discovered by a Scottish physician, Danial Rutherford.
Atomic Orbital Diagram: The simplified pictorial notation of the arrangement of the electrons within the different energy levels or orbitals of an atom is known as an atomic orbital diagram.
2s. 20.3. N. 2p. 14.5. Transformation of the valence atomic orbitals in C3v symmetry. The following table summarizes how the nitrogen and hydrogen atomic orbitals transform. Additional discussion follows regarding the assignment of characters for the 2px and 2py orbitals which transform together as a pair. C 3v.
Create the atomic orbital Diagram for Nitrogen. solved create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen st answer to create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen start by adding the appropriate subshells for example boron is in the create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen in some cases we may need to slightly alter the design color or even accessories we want a new thought for it then ...
Create the atomic orbital diagram for nitrogen. Start by adding the appropriate subshells. For example, boron is in the 2p block of the periodic table, and so you need to show the 2p subshell and everything below it. Next, click the orbitals to add electrons (represented as arrows). For boron, you would need to show a total of five electrons.
Nitrogen (N) electron configuration with full orbital diagram Nitrogen (N) is the 7th element in the periodic table and the first element in group-15. The atomic number of nitrogen is 7 and its symbol is 'N'. The standard atomic mass of nitrogen is 14.006. The period of nitrogen is 2 and nitrogen is a p-block element.
In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the N electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.
In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s. Use orbital filling diagrams to describe the locations of electrons in an atom.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
S-p mixing is the primary cause of the difference in the molecular orbitals of nitrogen and oxygen, which is influenced by the initial atomic orbital energies. The lighter second period elements (prior to oxygen) have a relatively small difference in energy between the 2s and 2p orbitals.
Molecular orbitals in Nitrogen. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. There are four molecular orbitals derived from the 1s and 2s orbitals. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma and two ...
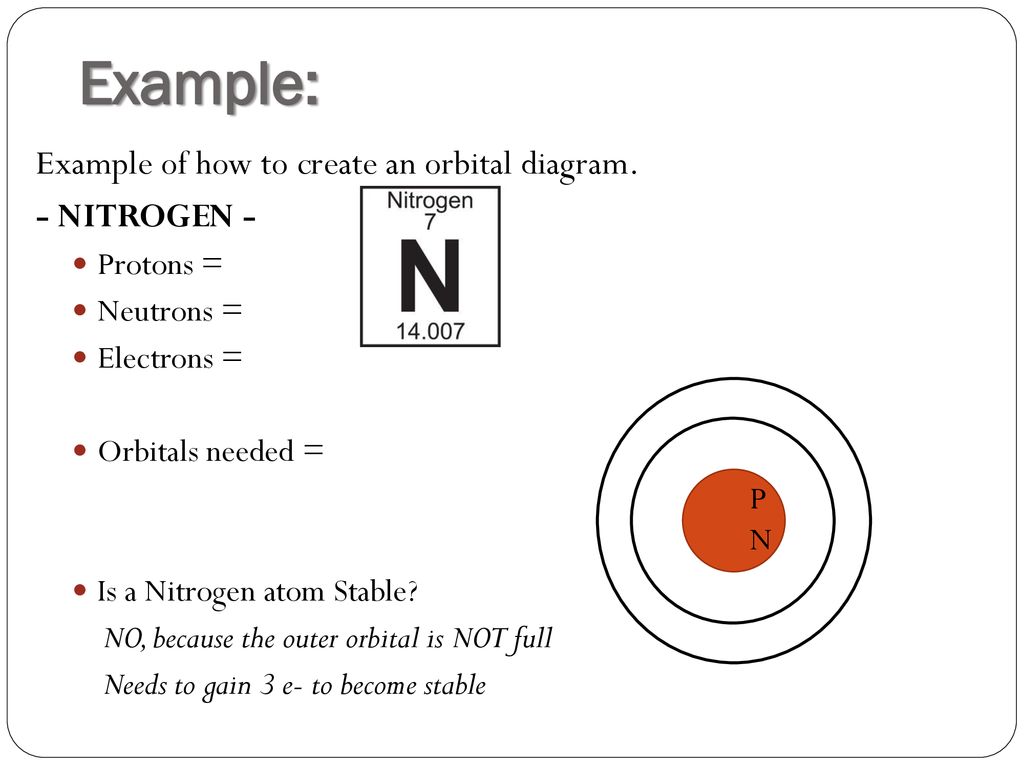
Summary. The Bohr model of Nitrogen is drawn with only two electron shells, the first shell contains 2 electrons and the second shell contains 5 electrons. Nitrogen is neutral and its atomic number is 7, hence, the number of protons and electrons available for its Bohr diagram is also 7. The number of neutrons for the Bohr diagram of Nitrogen ...
The electron configuration and orbital diagram for carbon are: Nitrogen (atomic number 7) fills the 1s and 2s subshells and has one electron in each of the three 2p orbitals, in accordance with Hund's rule. These three electrons have unpaired spins.


















0 Response to "trogen atomic orbital diagram"
Post a Comment