35 solid liquid phase diagram
Solid-Liquid Phase Diagram in a Two-Component System 1 Introduction The substances we encounter everyday are commonly mixtures of two or more components. For example, brass is a mixture of copper and zinc, and dish-washing detergent is a mixture of many chemicals. The components may interact with each other in a variety of different manners. If it is decreasing, the liquid phase is denser, if it is increasing, the solid phase is denser. For example, the phase diagram of water has a negative solid-liquid line; the liquid phase of water is denser. The densest phase exists at the highest pressure and lowest temperature. This comes back to looking at the top left corner of the graph. Share
• Phase Diagram for Cu-Ni system Adapted from Fig. 9.3(a), Callister 7e. (Fig. 9.3(a) is adapted from Phase Diagrams of Binary Nickel Alloys , P. Nash (Ed.), ASM International, Materials Park, OH (1991). • 2 phases: L (liquid) α (FCC solid solution) • 3 phase fields: L L + α α 0 20 40 60 80 100 wt% Ni 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 ...
Solid liquid phase diagram
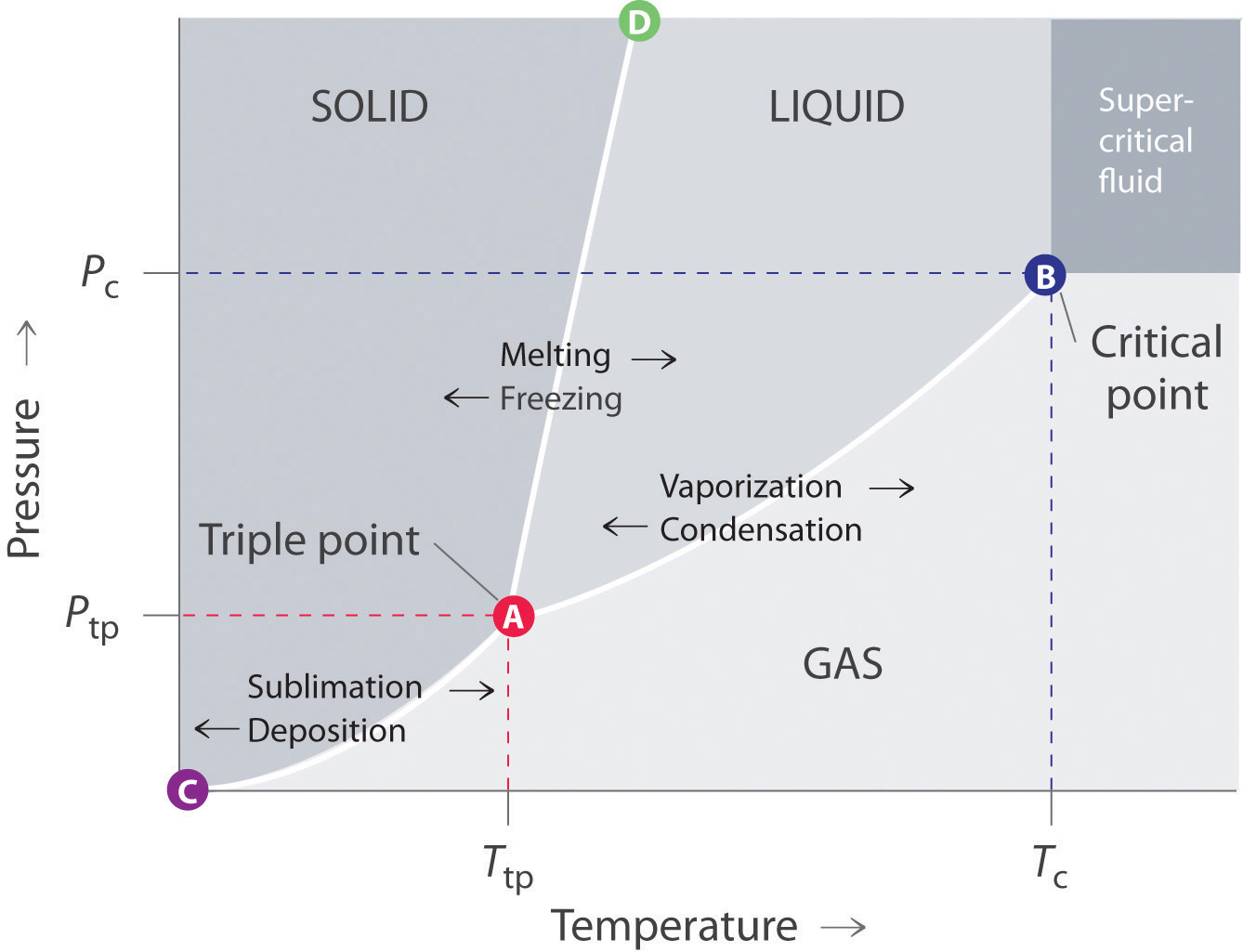
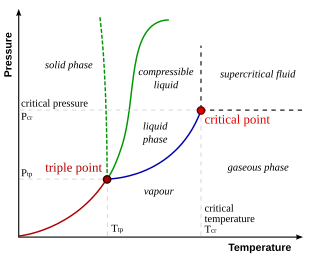
Overview: This module uses screencasts and interactive simulations to explain phase changes on a solid-solid-liquid phase diagram and utilizes the lever rule to determine the relative fraction of each component in each phase. It then provides example problems to allow the user to test themselves. Your retention of material in this module will ... Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 11.5.5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a ... Phase Diagrams. The figure below shows an example of a phase diagram, which summarizes the effect of temperature and pressure on a substance in a closed container. Every point in this diagram represents a possible combination of temperature and pressure for the system. The diagram is divided into three areas, which represent the solid, liquid ...
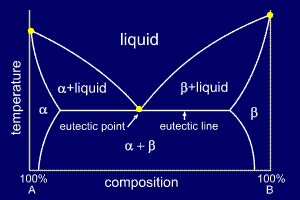
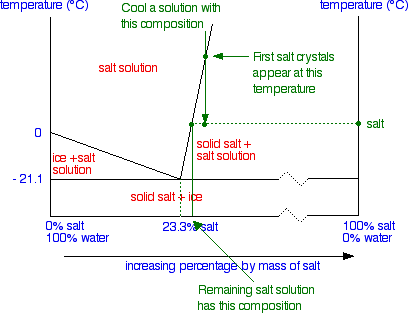
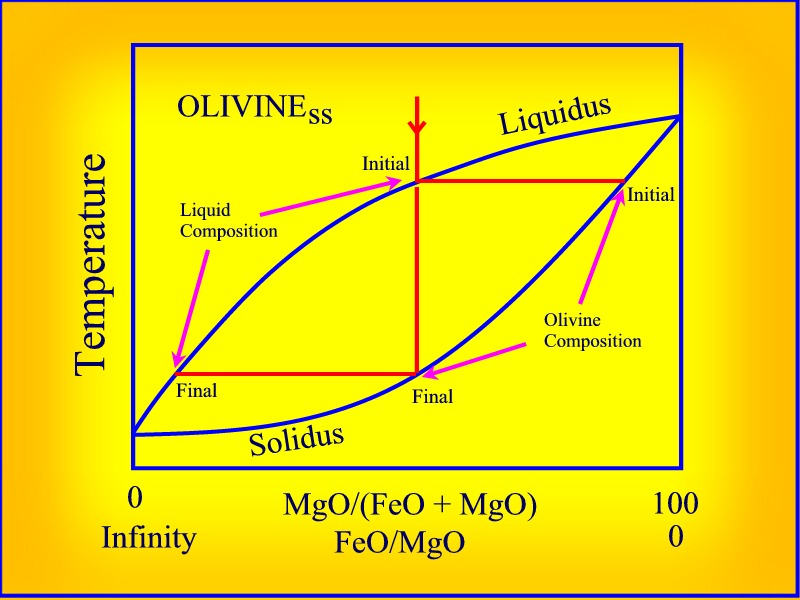
Solid liquid phase diagram. Phase diagrams give the state of a substance (solid, liquid, gas) given a specific set of conditions such as temperature and pressure. Below is an example of a simple phase diagram for water. 1 It is well known that water exists as a solid at or below its freezing point of 0 °C. SOLID-LIQUID PHASE DIAGRAMS: TIN AND LEAD This page explains the relationship between the cooling curves for liquid mixtures of tin and lead, and the resulting phase diagram. It also offers a simple introduction to the idea of a eutectic mixture. Solid-liquid phase diagrams The solid solution phase diagram explains the behavior of chemical solid solution series, such as the transition from high temperature, calcium-rich plagioclase to low temperature sodium-rich plagioclase, or the transition from high temperature magnesium-rich to low temperature iron-rich crystals in ferromagnesium minerals (e.g. olivine, pyroxene).
#4 A fundamental problem of interest in Materials Science is the calculation of solid - liquid phase diagrams. Many systems of similar compounds form simple eutectic solutions. The phase diagram for such a system and the equations that describe the phase transition lines are shown in our class notes. The temperature and pressure conditions at which a substance exists in solid, liquid, and gaseous states are summarized in a phase diagram for that substance. Phase diagrams are combined plots of three pressure-temperature equilibrium curves: solid-liquid, liquid-gas, and solid-gas. • Phase Diagrams Phase diagrams are graphs that give information on the equilibrium temperature and pressure for a particular compound. The equilibria occur for the solid- liquid plateau, liquid-vapor plateau and solid-vapor plateau. In this experiment, the phase diagram is shown for the solid-liquid equilibrium point, and varies from 100% ... Describes an interactive simulation that shows the phase diagram (temperature versus mole fraction) for two solids that form a solid compound. Heat can be ad...
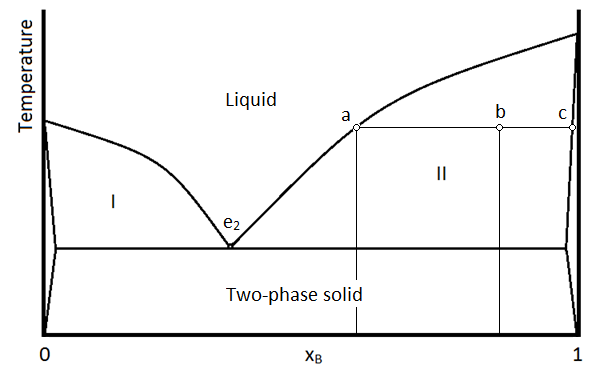
Isomorphous system -complete solid solubility of the two components (both in the liquid and solid phases). Binary Isomorphous Systems (I) Three phase region can be identified on the phase diagram: Liquid (L) , solid + liquid (α +L), solid (α ) Liquidus line separates liquid from liquid + solid Solidusline separates solid from liquid + solid α+ L α 8.6 Liquid-solid phase diagram Consider the two-component liquid of composition a1 in the diagram above. The changes can be described as follows: (1) a1®a2. The system enters the two phase region labeled 'liquid + B'. Pure solid B begins to come out of solution and the remaining liquid becomes richer in A. (2) a2®a3. by LJBM Kollau · 2019 · Cited by 13 — mixtures are liquids is set by the location of the solid–liquid phase boundary. Here we present experimen- tal phase diagrams of various recent and new DESs ...9 pages remaining liquid solution. In the salt water analogy, the solid ice (pure H2O) is in equilibrium with the liquid H2O that remains in the unfrozen salt water. Mixtures of naphthalene and diphenylamine, both solids in the pure state at room temperature, will be prepared and their phase transitions studied by means of a thermal analysis.
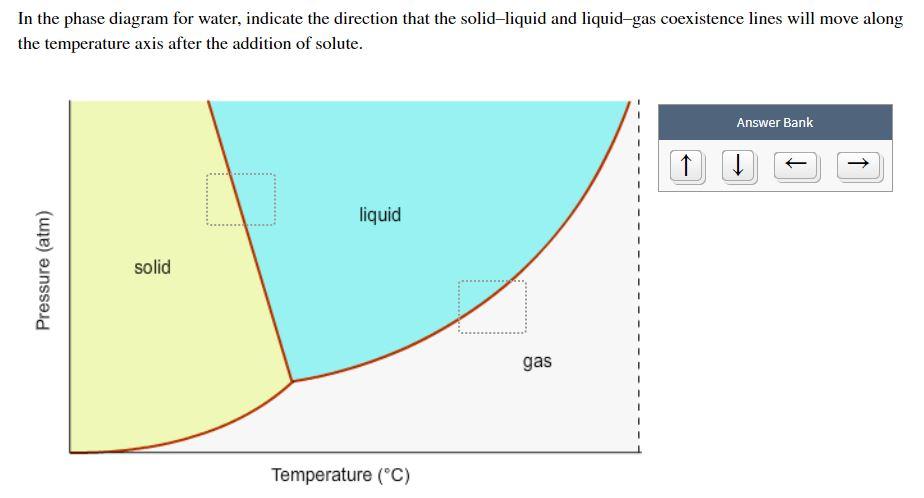
A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid-gas, solid-liquid, and solid-gas phase-transition equilibria of a substance.
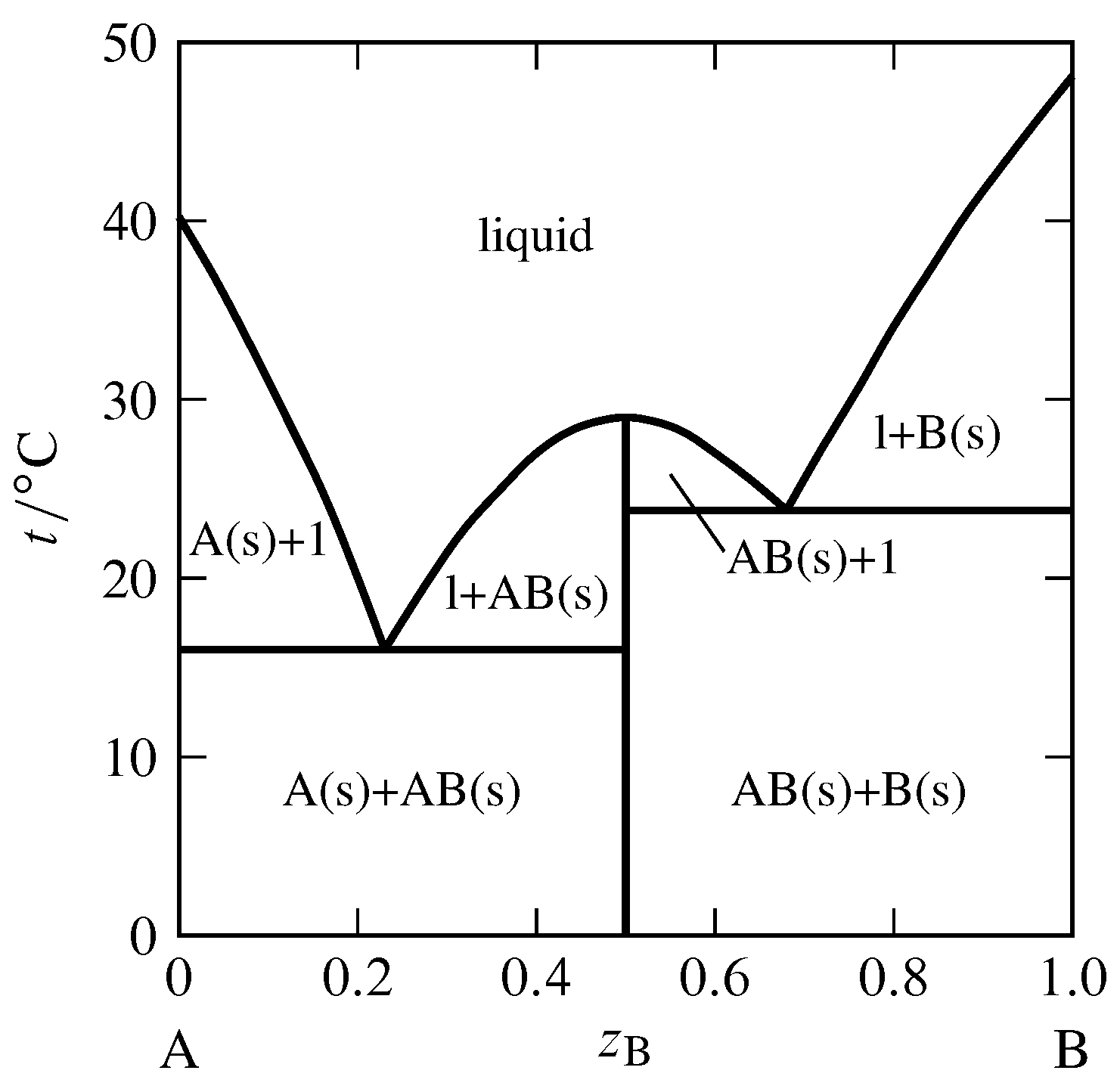
5.9 Liquid-solid phase diagrams Key points 1. At the eutectic composition the liquid phase solidifies without change of composition 2. The phase equilibria of binary systems in which the components react may also be summarized by a phase diagram 3. In some cases, a solid compound does not survive melting
3. Solid-Liquid phase diagrams measurements. Binary mixtures between sugar alcohols, or between [Ch]Cl and sugar alcohols, were prepared in different proportions covering the full compositions range (at mole fraction intervals of 0.1) by weighting the proper amounts of each pure substance using an analytic balance Mettler Toledo XP205 (repeatability of 0.015 mg).
Introduction Solid-liquid phase diagrams show the phase relationships in mixtures of two or more components and are very important in understanding the behavior of mixtures in metallurgy, material science and geology.
The simplest phase diagrams are pressure-temperature diagrams of a single simple substance, such as water.The axes correspond to the pressure and temperature.The phase diagram shows, in pressure-temperature space, the lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries between the three phases of solid, liquid, and gas.. The curves on the phase diagram show the points where the free energy (and other ...
The phase diagram for water is shown below. The solid lines identify the temperatures and pressures at which an equilibrium exist between phases. The point at which the lines intersect represents the triple point. At the pressure and temperature of the triple point, all three phases (solid, liquid and gas) exist in equilibrium.
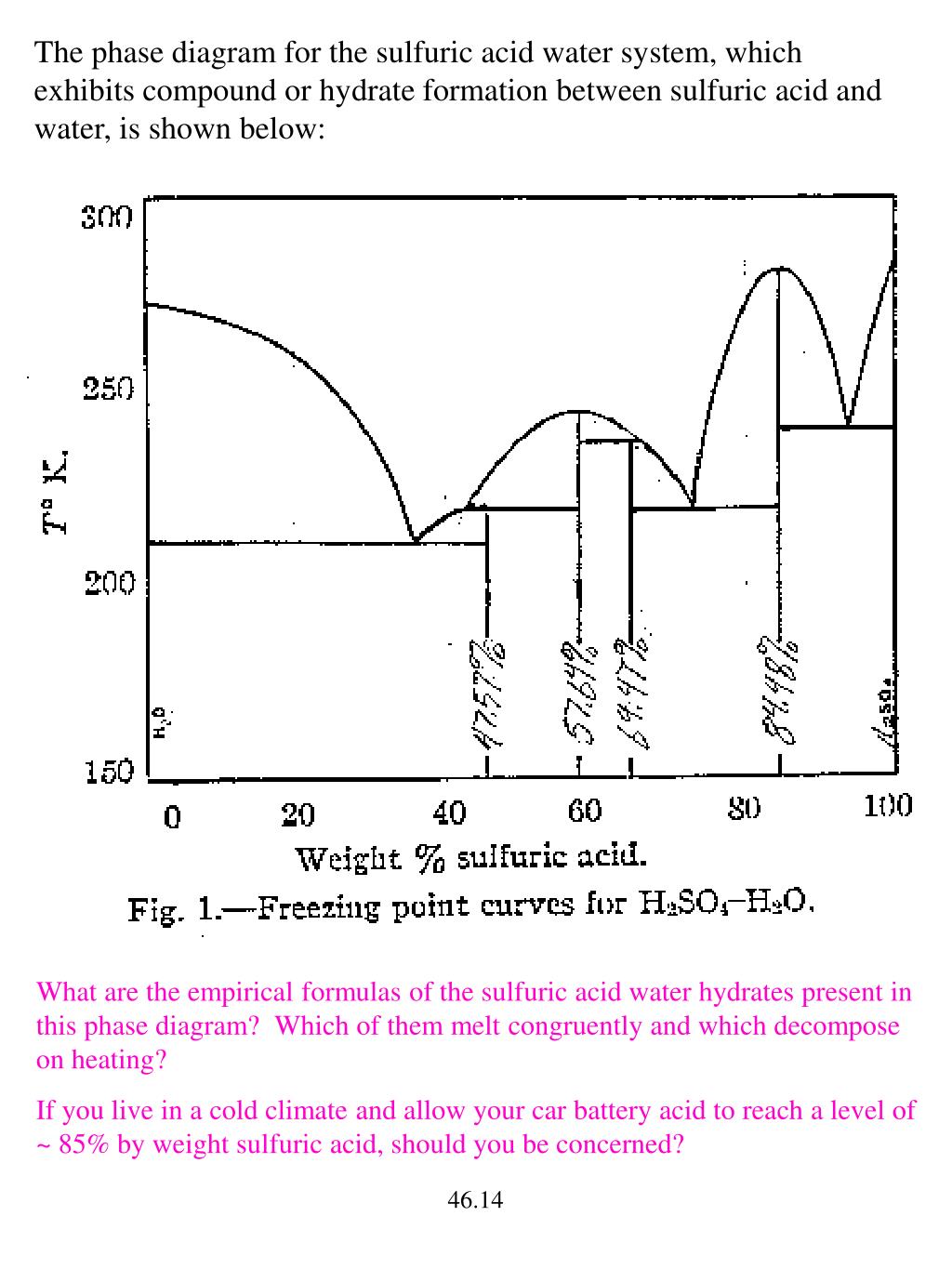
Solid-liquid Phase Diagram . Ref: P.A. Giguere. "Complements au Nouveau Traite de C. himie Minerale - No. 4 - Peroxyde d'Hydrogene et Polyoxydes d'Hydrogene" Paris, Masson 1975 (181 p).
Phase Diagrams: composition of phases At TA= 1320°C: Only Liquid (L) present CL= C0 ( = 35 wt% Ni) At TB= 1250°C: Both and L present At TD= 1190°C: Only Solid ( ) present C = C0( = 35 wt% Ni) C L = C liquidus ( = 32 wt% Ni) C = C solidus ( = 43 wt% Ni) 18 • Rule 3:If we know T and Co, then we know: --the amount of each phase (given in wt%).
Solid-liquid phase diagram for a binary mixture. Consider a mixture at point F as shown in Fig. 12.3 b. As this liquid mixture is cooled at constant pressure, pure solid 1 forms when the temperature drops to T ∗ (point G) and the relationship between T ∗ and x 2 ∗ is given by Eqn (12.1-17), i.e.
Liquid-Solid Phase Diagrams: Salt Solutions Non-Ideal Mixtures of Liquids Donate Contributed by Jim Clark Former Head of Chemistry and Head of Science at Truro School in Cornwall This page explains the relationship between the cooling curves for liquid mixtures of tin and lead, and the resulting phase diagram.
Solid - Liquid Phase Diagram of a Binary Mixture: The Question of Fatty Acids Dimers in the Liquid Phase Gary L. Bertrand University of Missouri-Rolla Overview Two components will be assigned for this experiment. One will be a carboxylic acid, and the other will be a relatively non-polar material.

SAKURAI / Introduction to M-Theory and SuperStrings / The Final Visualization In Twenty Six Dimensions
The temperature and pressure conditions at which a substance exists in solid, liquid, and gaseous states are summarized in a phase diagram for that substance. Phase diagrams are combined plots of three pressure-temperature equilibrium curves: solid-liquid, liquid-gas, and solid-gas.
Phase Diagrams. The figure below shows an example of a phase diagram, which summarizes the effect of temperature and pressure on a substance in a closed container. Every point in this diagram represents a possible combination of temperature and pressure for the system. The diagram is divided into three areas, which represent the solid, liquid ...
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 11.5.5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a ...
Overview: This module uses screencasts and interactive simulations to explain phase changes on a solid-solid-liquid phase diagram and utilizes the lever rule to determine the relative fraction of each component in each phase. It then provides example problems to allow the user to test themselves. Your retention of material in this module will ...


















0 Response to "35 solid liquid phase diagram"
Post a Comment