38 curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. A purely competitive firm’s short-run supply curve is: a. perfectly elastic at the minimum average total cost. b. upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve. c. upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average total cost curve.
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
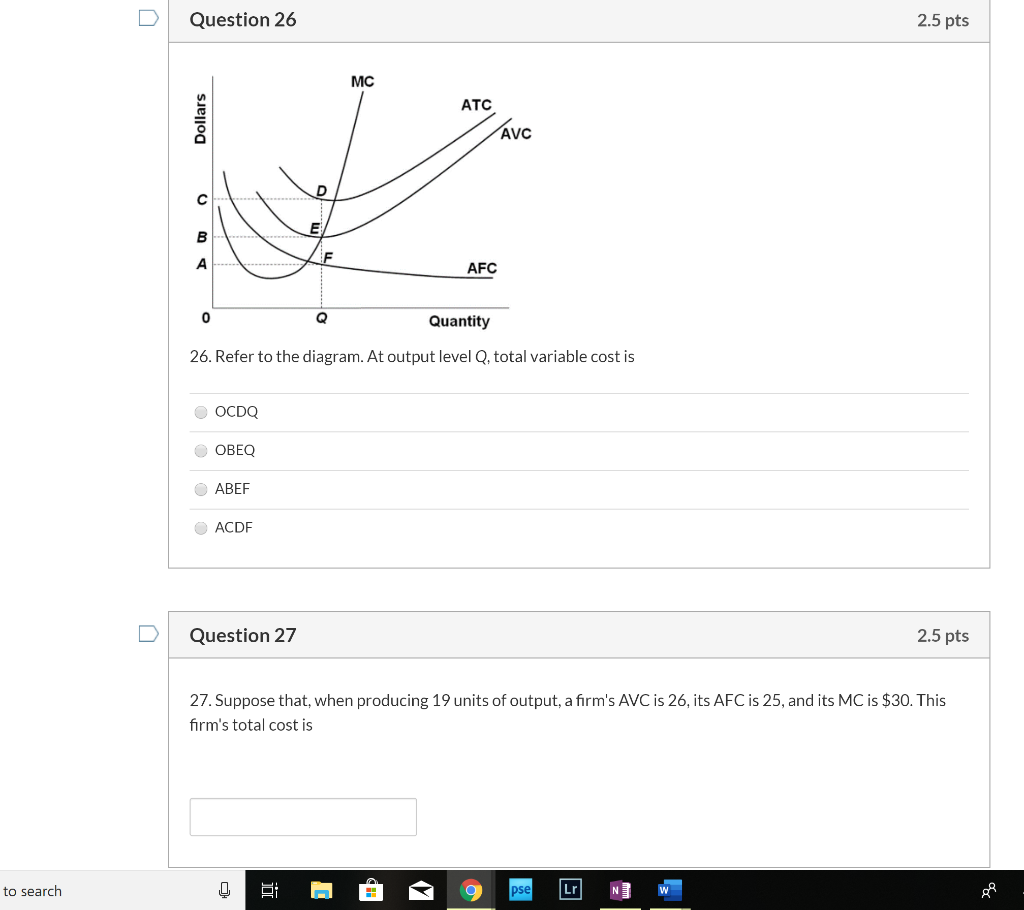
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
46. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. B) total revenue curve. C) marginal revenue curve. D) total profit curve. Answer: A. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 418 MI: 174 47. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as: Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Bloom's: Level 3 Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 08-03 Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose this firm is maximizing its total profit and the market price is $15. The firm's per unit profit is:
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total profit curve. 17. Refer to the above diagram. Curve 4 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve B total from BUSINESS 1111 at University of Texas, Dallas. 73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A) the abcd segment of the MC curve. C) the cd segment of the MC curve. B) the bcd segment of the MC curve. D) not shown. Answer: B. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 74. The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based on ... Curve (4)in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. A)total cost curve. B)total revenue curve. C)marginal revenue curve. D)total economic profit curve.
ECON CH 12. TestNew stuff! A single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. T or F: A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." Nice work! Figure 6.21 "The Supply Curve of an Individual Firm" reveals something remarkable: the individual supply curve How much output a firm in a perfectly competitive market will supply at any given price. It is the same as a firm's marginal cost curve. of the firm is the marginal cost curve. They are the same thing. A) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers." B) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price makers." C) A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." D) A purely competitive firm is a "price maker," while a monopolist is a "price taker." Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift A. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the left. B. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the right.
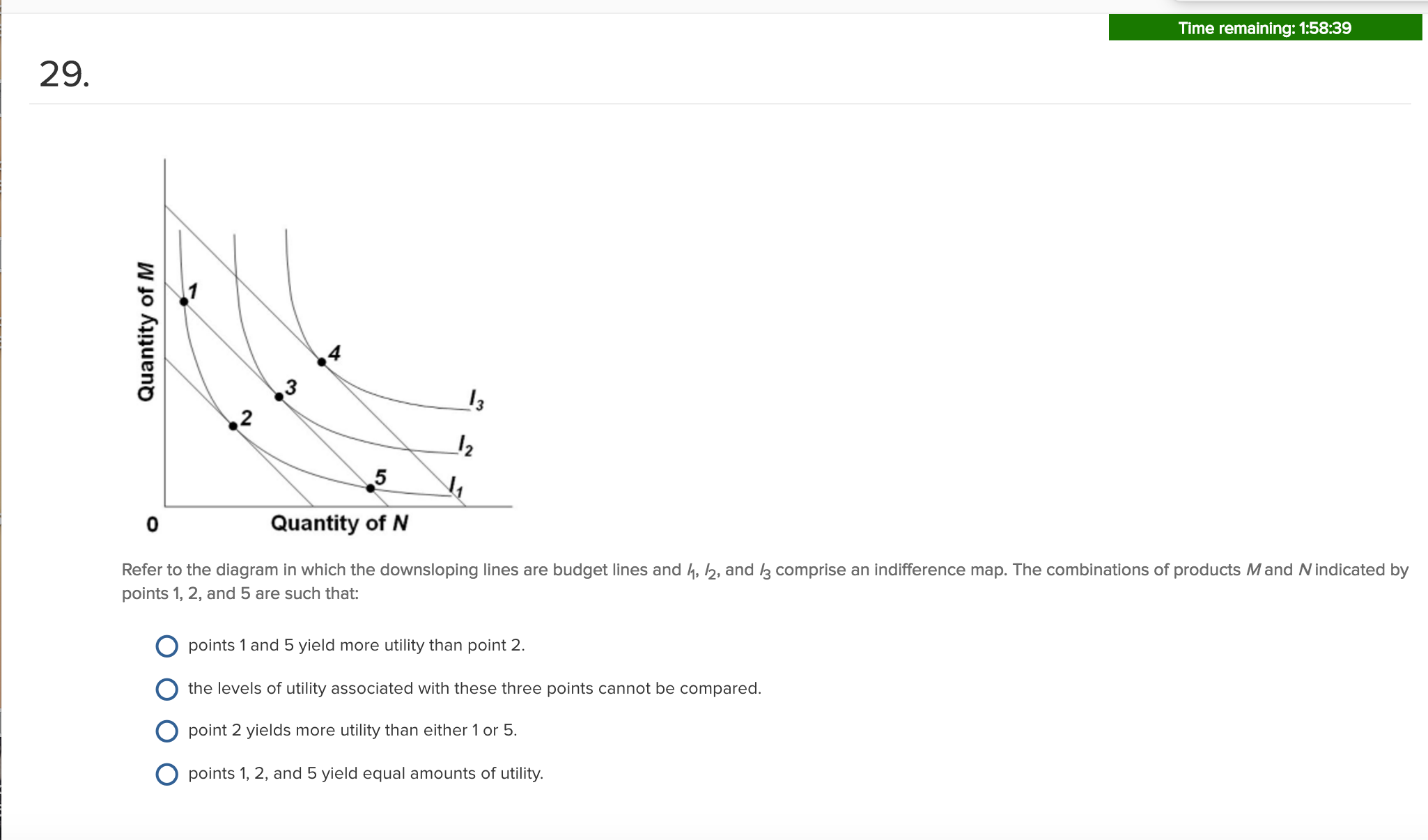
4. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is less elastic than that of a purely competitive producer. True False 5. The larger the number of firms and the less the degree of product differentiation, the greater will be the elasticity of a monopolistically competitive seller's demand curve. True False 6. Section 4: Profit Maximization Using a Purely Competitive Firm's Cost and Revenue Curves. Unit 6. ... In a graph, if the MC curve intersects the MR curve at two different quantities, the lower quantity is the profit minimizing quantity and the higher quantity is the profit maximizing quantity. The fact that a purely competitive firm's total revenue curve is linear and upsloping to the right implies that: A.product price increases as output increases. B.product price decreases as output increases. Correct C.product price is constant at all levels of output. D.marginal revenue declines as more output is produced. The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, ... The firm represented by the above diagram would maximize its profit where:.6 pages
is the same as that of a purely competitive indiLstry is its average variable cost curve does not exist because prices are not "given" to a monopolist. Use the following to answer questions 15-16: $19 100 MC ATC MR 160 180 210 Quantity 15, Refer to the above diagram for 8 monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's ...

Ein wunderbarer Blick auf die schöne Altstadt von Bautzen. A wonderful view of the beautiful old town of Bautzen. #Bautzen #Oberlausitz #Sachsen #Germany #Saxonia
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents. 11ebc1e0_a1c6_8917_8acb_d17a009a4f1f_TB8602_00 Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents A) The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry ...
Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B.total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. 40. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A.total cost curve.B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve.D. total profit curve.
Since profit maximization takes place where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, in pure competition the firm's supply curve will be it's marginal cost curve above the average variable cost. The horizontal summation of the individual firm's supply curves yields the market supply.
is more elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. 27. Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 10 units of output at $5 per unit and 11 units at $4.90 per unit.
prices for their output temporarily fall below their average variable costs of production. ... Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's:.
Difficulty: 3 Hard Bloom's: Level 4 Analyze AACSB: Reflective Thinking Type: Graph Refer To: 8_63 [Question] 66. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A. the abcd segment and above on the MC curve. B. the bcd segment and above on the MC curve. C. the cd segment and above on the MC ...
Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. McConnell/Brue: Economics, 16/e Page 695. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44.

I took the photo mainly because I couldn’t believe how smooth the road was. The roads around the area I used to live in were just terrible so I pulled over to the side of the road and tried to time it so no cars got in the frame. It’s a pretty busy road so that was more challenging than you would think. I think it’s cool how a photo of something as simple as a road can interest people. I’ve been guilty of thinking that there is nothing around me to photograph many times, so I’m trying to improve as a photographer and try to see ordinary things as extraordinary.
The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist: A. may be either more or less elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. B. is less elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. C. has the same elasticity as that faced by a single purely competitive firm. D. is more elastic than that faced by a single purely ...
If firms enter a purely competitive industry, then in the long run this change will shift the industry: A. demand curve to the left, and the market price will decrease.
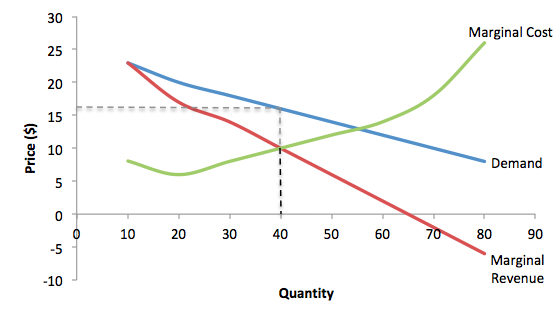
If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a rate of output for which MC ... and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.
Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total revenue curve. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total cost curve.
less elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a purely competitive seller. B. less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a purely competitive seller. ... This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. ... production for the firm shown in the diagram above is: A.
A The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, ... Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost ...
A supply curve which shows the quantity of a product a firm in a purely competitive industry will offer to sell at various prices in the short run; the portion of the firm's short-run marginal cost curve which lies above its average variable cost curve.
100% (3 ratings) 3. curve 4 is a tot …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O total revenue curve. total profit curve. total cost curve O total cost curve. O marginal revenue curve.
Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose this firm is maximizing its total profit and the market price is $15. The firm's per unit profit is:
Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Bloom's: Level 3 Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 08-03 Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run.











0 Response to "38 curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment