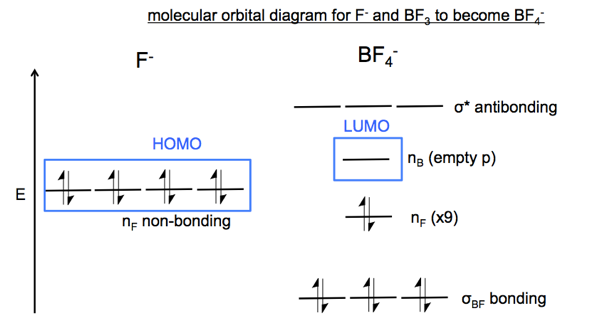
36 orbital diagram for f ion
Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are similar (as in NO or Heteronuclear Diatomic Species The following is a molecular orbital energy level diagram for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, XY, in which both... The diagrams are NOT to scale and are somewhat simplified. These are from theoretical calculations based on the probability functions of the peculiar and how to use the orbital notation to write out the full electron configuration of an element or its ion? The arrangement of electrons in the shells and...
Building Orbital Diagrams. Hund's rule specifies that when orbitals of equal energy are available, the lowest energy electron configuration has the maximum Electron Affinity (EA) is the energy change that occurs when 1 mol of electrons is added to 1 mol of gaseous atoms or ions. Atoms with a low EA...
Orbital diagram for f ion
Figure 8: Molecular orbital energy-level diagrams for (A) beryllium hydride, BeH2, with linear shape, and (B) water, H2O, with bent shape. Possible energy diagram for the dissociation of a covalent molecule, E-N, into its ions E+ and N− (see text). Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. We start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron. Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
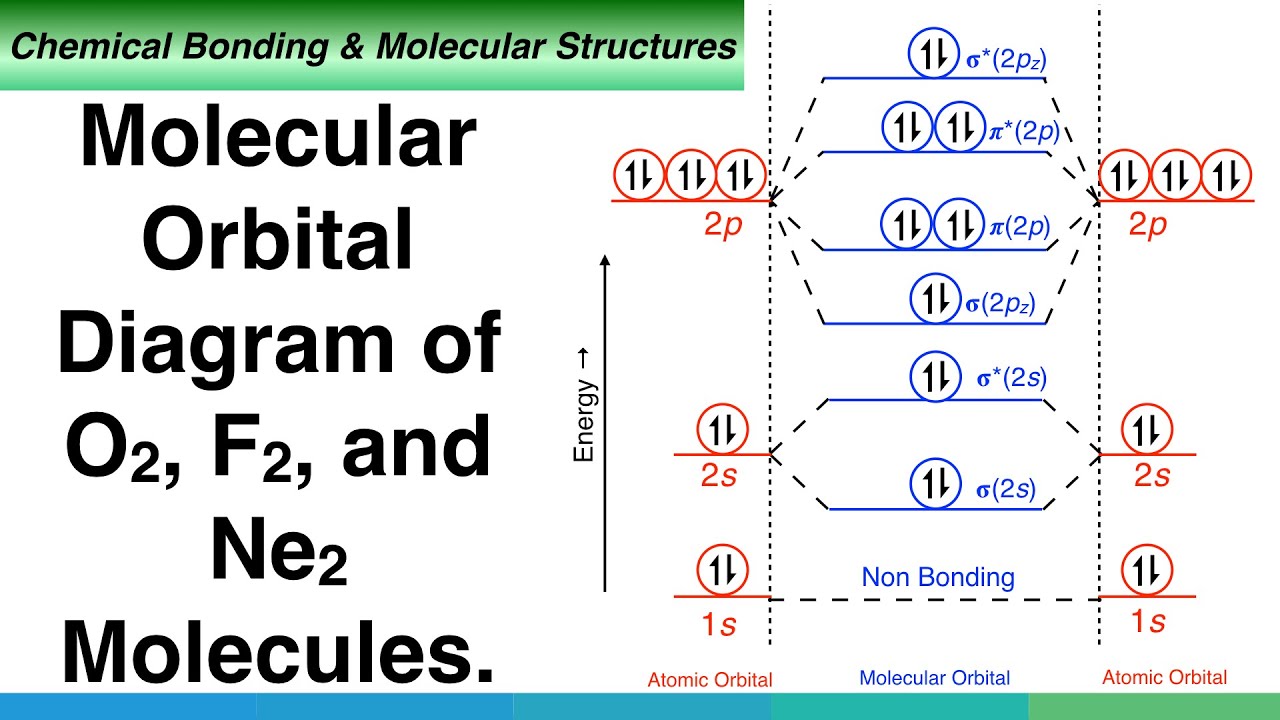
Orbital diagram for f ion. The molecular orbital diagram for dihelium (He2) is the same as that of hydrogen, with the addition of two more electrons (Figure 9.37). Chapter 9. The molecular orbital diagram for the second row homonuclear. Chapter 9. Theories of Chemical Bonding. Draw the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the system. B Determine the total number of valence electrons in the He22+ ion. We illustrate how to use these points by constructing a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for F2. Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Example 5.8. Ion Predictions with MO Diagrams. Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in. Orbital box diagrams hunds rule pauli exclusion orbital box diagrams are the electron configuration problems where you have to draw each el...
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. In which orbital does an electron in a phosphorus atom experience the greatest effective nuclear charge? a. 1s b. 2s c. 2p d. 3s e. 3p I originally thought 3p, since those are the outer electrons, but that was marked wrong. What does an orbital diagram of an iodine ion look like? Build the orbital diagram for the ion most likely formed by phosphorus? An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down arrows to represent the electrons in each orbital. Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. Ion Predictions with MO Diagrams Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in C22−. Will this ion be stable?
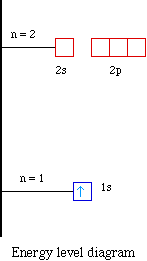
Problem: Construct the orbital diagram of the F- ion.A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. How many electrons does a F- ion have? FREE Expert Solution. We are asked to construct the orbital diagram of the F-ion. F → 9 electrons. Negative charge adds 1 electron more. F-→ 10 electrons. This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Construct the orbital diagram of the F– ion. Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (22 ratings) In this video, we create a molecular orbital diagram for peroxide and enter it into the ALEKS homework system. Orbital Diagram Fluorine (F) Fluorine(F) excited state electron configuration. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital by excited state. This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of fluorine is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. The p-orbital has three sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are p x, p y, and p z. Each sub-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons.
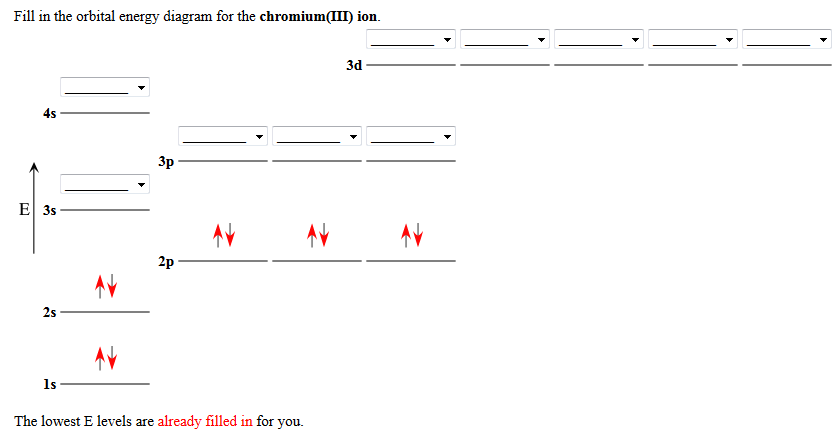
Do some orbital configurations or diagrams for some metal cat ions. So first example is going to be for chromium three plus. So as we follow the periodic table and fill the electrons properly, first row of the periodic table.
Construct the orbital diagram of the F^-ion. Question: Construct the orbital diagram of the F^-ion. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
Construct the orbital diagram of the F– ion.
F: 1s22s22p5 Now, the F− anion is formed when 1 electron is added to a neutral fluorine atom. Notice that the 2p-subshell of the neutral atom contains 5 electrons. Its maximum capacity is actually 6 electrons, two electrons for each p-orbital. This means that the extra electron will be added to one of the three 2p-orbitals, let's say to 2py.
An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals. We know how to write electron configurations for neutral atoms and ions. But, an electron configuration does not give us the full picture.
Use a qualitative molecular orbital energy-level diagram to predict the valence electron configuration, bond order, and likely existence of the Na2− ion. We illustrate how to use these points by constructing a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for F2.
Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions Orbital diagrams represent the arrangement of electrons in orbitals. • boxes or lines represent each orbital • arrows within boxes represent the electrons • max two per box • opposite direction (represents opposite spin) Section 3.5...
The orbital names s, p, d, and f describe electron configuration. These line groups are called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Each orbital is denoted by a number and a letter. The number denotes the energy level of the electron in the orbital. Thus 1 refers to the energy level closest to the...
Orbital diagrams represent the location of electrons within orbitals. Three rules must be followed when filling orbital diagrams Electron configurations can also be written for ions. First, determine the charge of the ion (like when you form ionic compounds).
Alright let's talk about orbital diagrams. Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. In order to figure out where electrons go in an atom we have to follow 3 main rules. The first one being the Auf Bau Principle, the Auf Bau Principle states that each electron occupies the lowest...
Transcribed image text: Construct the orbital diagram of the F^- ion. A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. How many electrons does a F^- ion have?
Transcribed image text: Enter the orbital diagram for the ion Cd'. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Not all group 2 targets will be filled.
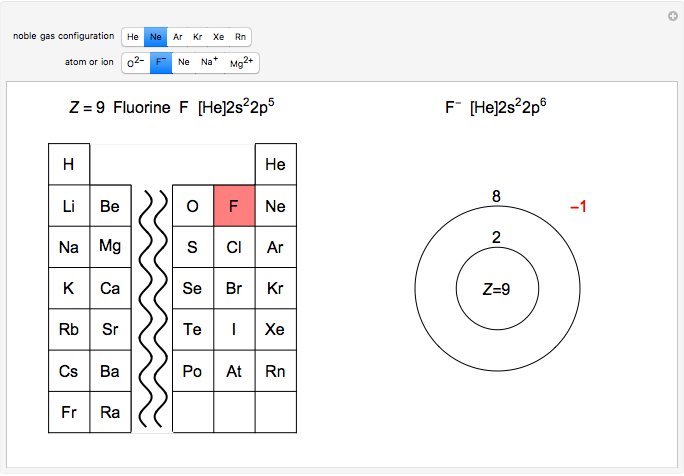
Answer: The correct ground state electron configuration of F− − ion is option c. 1s22s22p6. 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 . Explanation: The atomic...
Jan 03, 2022 · Answer. A neutral f atom has 9 electrons. The Fluoride ion formed by addition of electron to its neutral state. F + e^- rightarrow F^- Thus, F^- ion has 10 electrons. The electronic configuration of Fluoride ion is 1s^2 3s^2 2p^6. As the energy of the atomic orbital is 1s^2 < 2p^6 (2p^2_x = 2p^2_y = 2p^2_z), the orbital energy diagram is represented as shown below:
Explanation: Elemental Fluorine has an electron configuration of 1s22s22p5 and needs 1 more electron to complete its 2p orbital which it will acquire in formation of the fluoride ion . What is the electron of F? It has 5 valence electrons in the 2p level. Its electron configuration is 1s22s22p5.
Methods: Ion-pairing reversed-phase ultra-high-performance LC separation of the Pt(IV) complex anions present in aqueous solutions prior to detection by A robust reversed phase ion-pairing RP-HPLC method has been developed for the unambiguous speciation and quantification of all possible...
Therefore the f electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. Orbital box diagrams hunds rule pauli exclusion orbital box diagrams are the...
Orbital diagram for f ion. Electron configurations and orbital diagrams. Answer to construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion. Get youtube without the ads. Orbital box diagrams hunds rule pauli exclusion orbital box diagrams are the electron configuration problems where you have to draw...
9 hours ago Orbital diagram for f ion. How many electrons does a f ion. The first number is the principal quantum number n and the letter represents the value of l angular momentum quantum number.
I would like to understand how to create a molecular orbital diagram for the hydroxide ion from scratch. This includes understanding the shape of But this makes no sense. I haven't used up all the available electrons of the oxygen atom, and the diagram seems to suggest that there is a bond order...
Transition Fe3+ ions and draw the orbital box diagrams for both ions. Using this. There for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 is the electronic configration for Fe3+. half of electrons (there must be one electron in each orbital, and d has 5 orbitals). That's for filling up orbitals for ground state atoms.
Okay, so we're gonna draw some orbital diagrams. The first one is for lithium. So you want to start by writing its electron configuration but kind of spread out of it. So it's one s. 2 And then to S one. So it? S sub level has one orbital which we represent with kind of parentheses. And then we put the two electrons in One air up and one down.
Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and MO2. • In order to participate in MOs, atomic orbitals must overlap in space.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. We start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron.
Figure 8: Molecular orbital energy-level diagrams for (A) beryllium hydride, BeH2, with linear shape, and (B) water, H2O, with bent shape. Possible energy diagram for the dissociation of a covalent molecule, E-N, into its ions E+ and N− (see text).










![Electron Configuration | Chemistry [Master]](https://textimgs.s3.amazonaws.com/boundless-chemistry/gram-four-2p-hund-27s-rule.svg)














0 Response to "36 orbital diagram for f ion"
Post a Comment