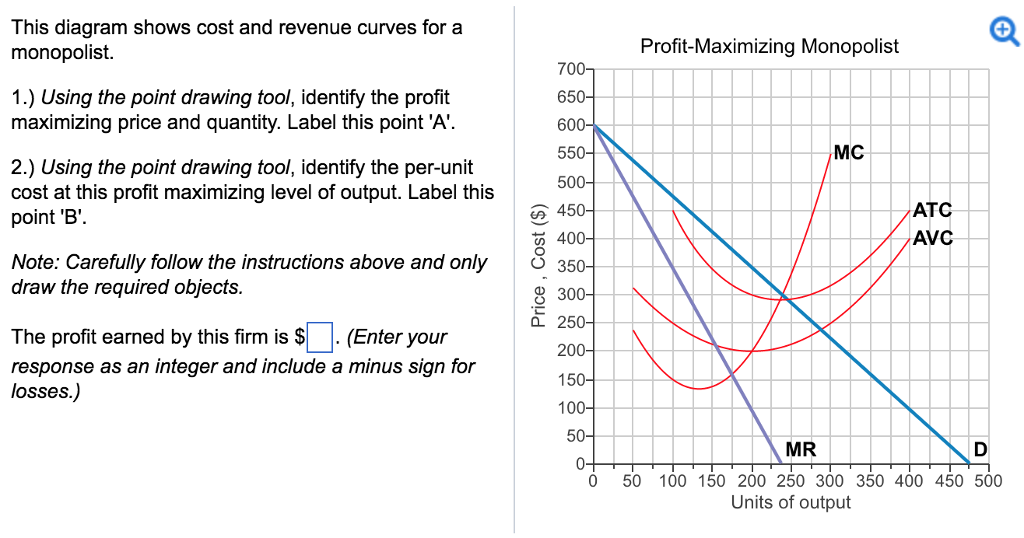
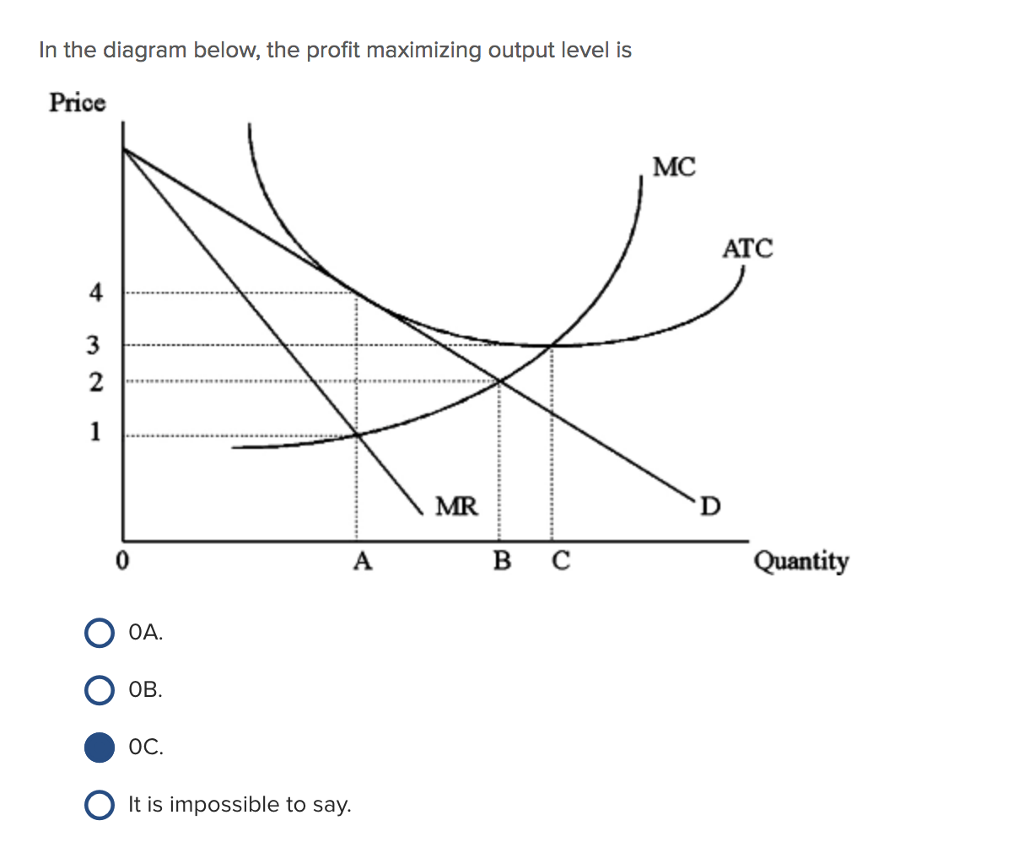
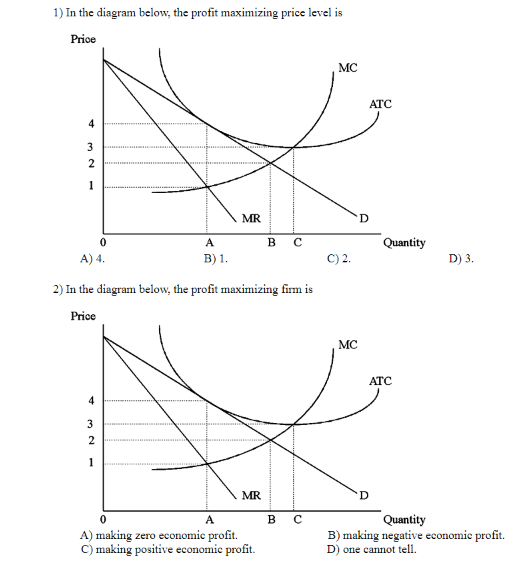
36 refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
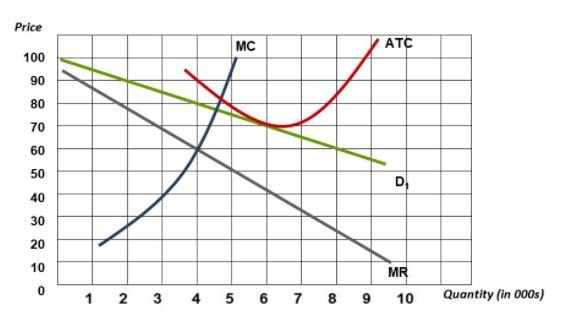
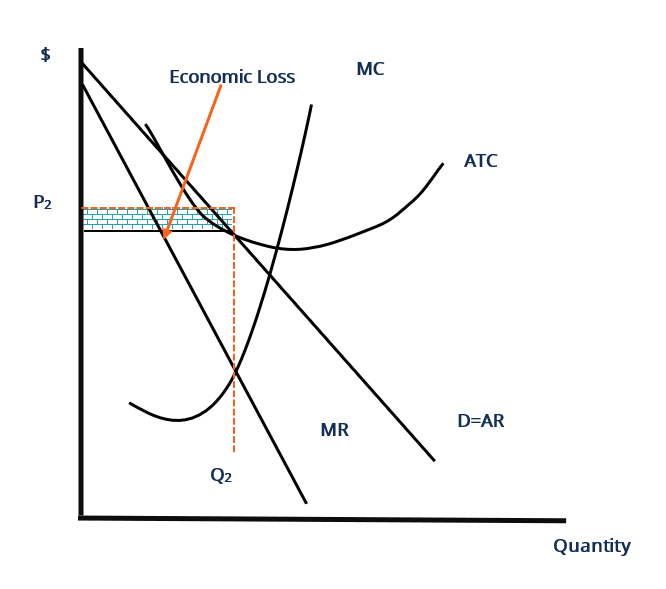
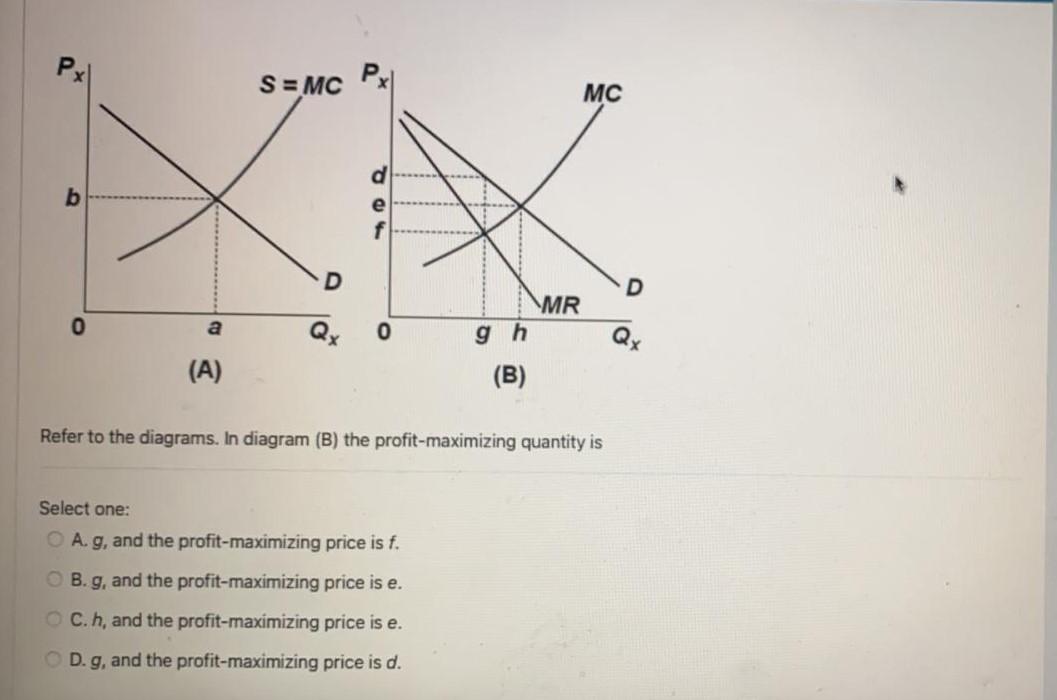
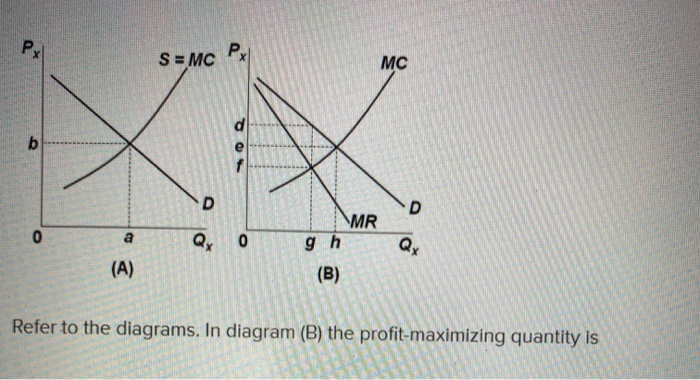
Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is g, and the profit-maximizing price is d. At the point where 3 units are being sold, the coefficient of price elasticity of demand is greater than unity (one). Confronted with the same unit (average) cost data, a monopolistic producer will charge In diagram B the profit maximizing quantity is:-g and the profit-maximizing price is d. In which one of the following market models is X-inefficiency most likely to be the greatest? ... Refer to the diagrams. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize:-an economic profit of ABHJ.
Refer to the diagrams. Diagram (A) represents: ... In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g, and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram: (A), there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.

Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
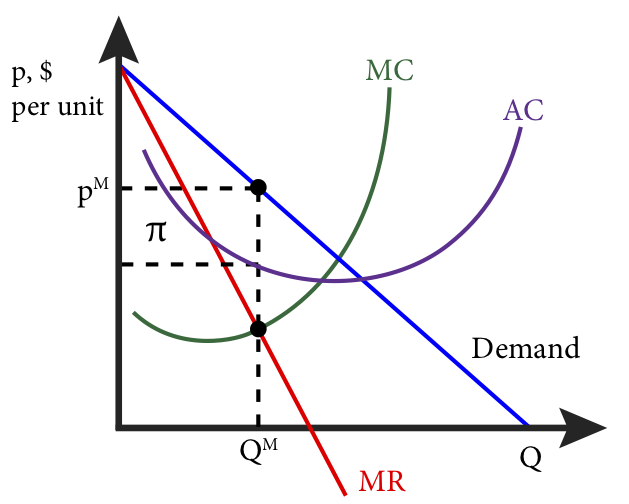
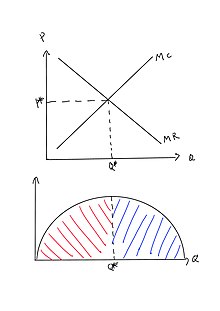
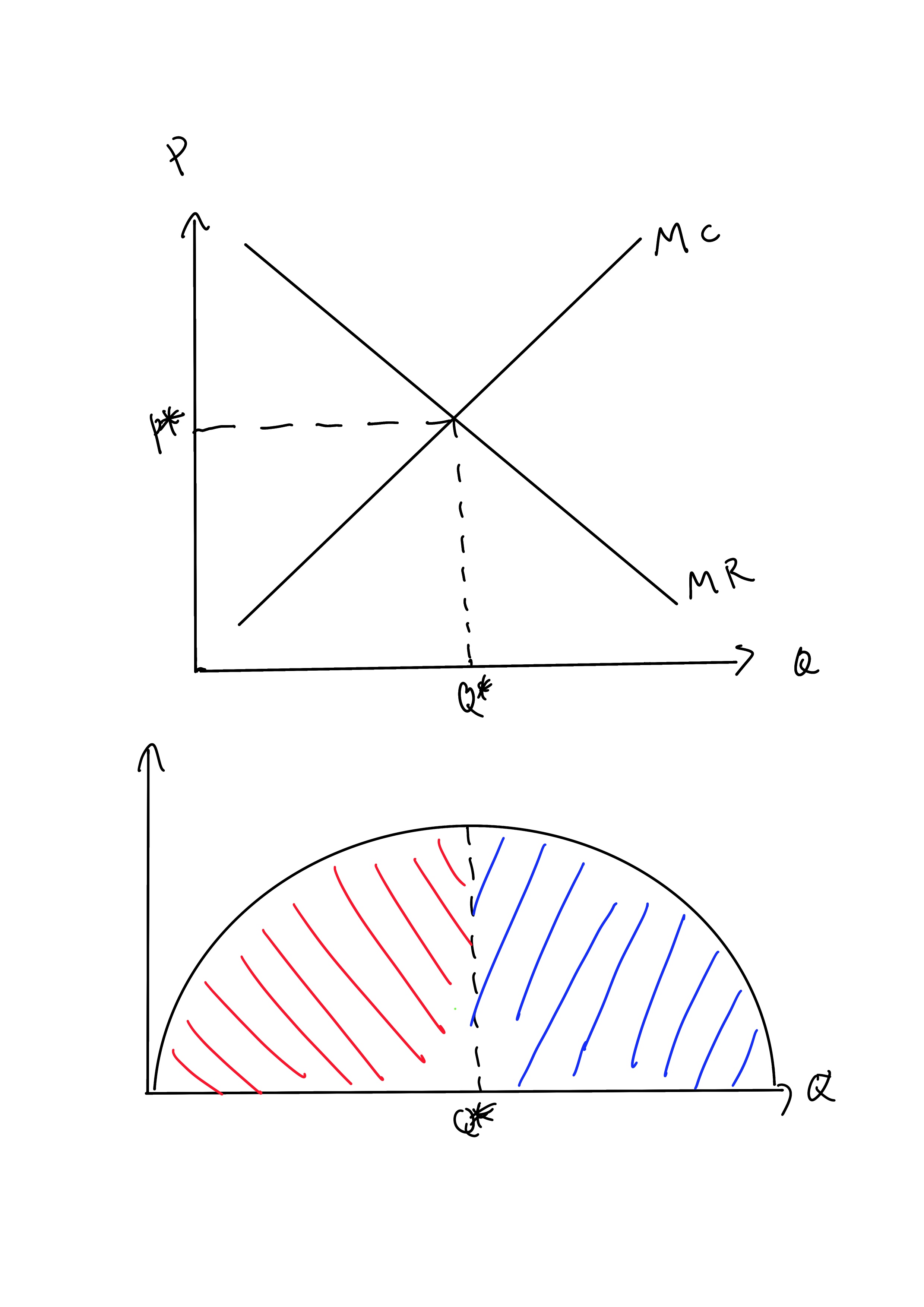
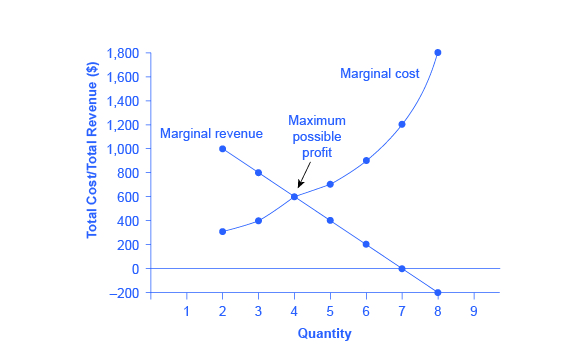
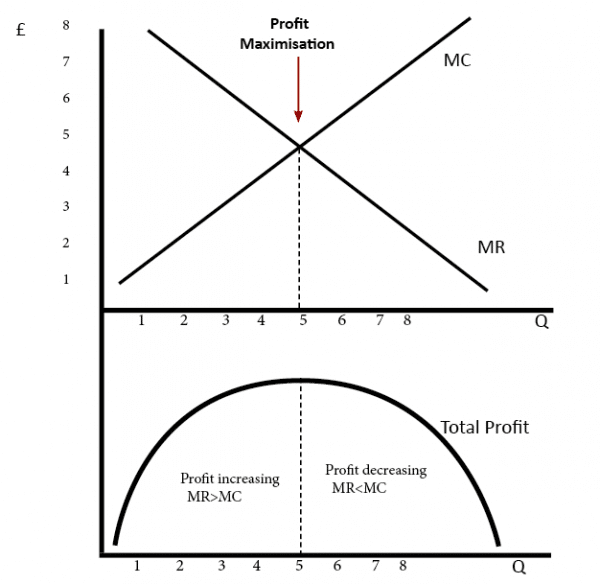
The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 9.7. 100 2q 3 8q 0 dq d (q) 100q q2 420 3q 4q2 = = − − − = Π In a picture, this all looks like: A graph showing a profit curve that has an inverted U-shape and has a peak at the profit maximizing quantity. Profit is maximized at the quantity q* and is lower at all other quantities. The curvature 10. Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is A. g, and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g, and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g, and the profit-maximizing price is d. Economists use the term imperfect competition to describe: 1. all industries which produce standardized products. 2. any industry in which there is no nonprice competition. 3. a pure monopoly only. 4. those markets which are not purely competitive. 5. In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult?
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is g , and the profit-maximizing price is d .. Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram (A), there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is Multiple Choice o 9. and the profit-maximizing price is f 0 g, and the profit maximizing price is e. h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. 0 0 g. and the profit maximizing price is < Prev 6 of 25 Next > MacBook Air on Previous question Next question by drcollinsapeconomics , Apr. 2014 Subjects: Morgan Hughes Click to Rate "Hated It" Click to Rate "Didn't Like It" Click to Rate "Liked It" Click to Rate "Really Liked It" Click to Rate "Loved It" Favorite Add to folder [?] Flag Flashcards Memorize Test Games Tweet Related Essays Card Range To Study through Click or Press Spacebar to Begin » Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.
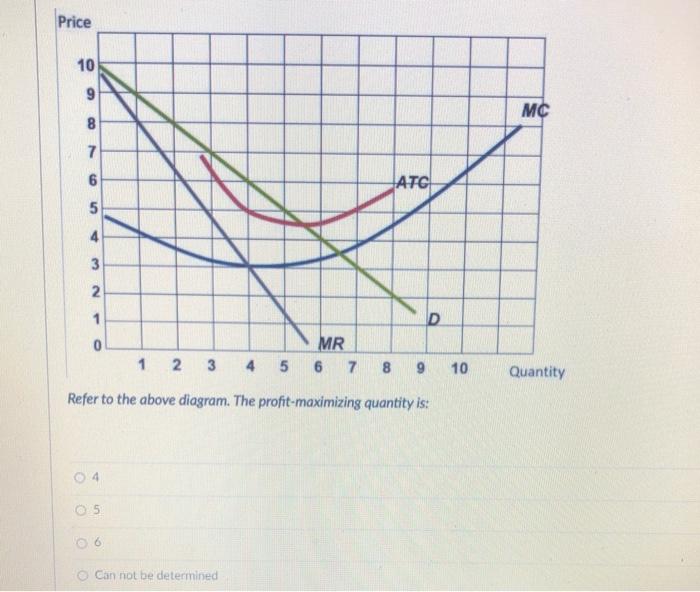
79. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: A. g and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g and the profit-maximizing price is d. View Homework Help - ECONHW13Sols41.pdf from ECON 4103 at University of New South Wales. 117. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the prot-maximizing quantity is g, and the Economists use the term imperfect competition to describe: 1. all industries which produce standardized products. 2. any industry in which there is no nonprice competition. 3. a pure monopoly only. 4. those markets which are not purely competitive. 5. In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult? 10. Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is A. g, and the profit-maximizing price is e. B. h, and the profit-maximizing price is e. C. g, and the profit-maximizing price is f. D. g, and the profit-maximizing price is d.
The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 9.7. 100 2q 3 8q 0 dq d (q) 100q q2 420 3q 4q2 = = − − − = Π In a picture, this all looks like: A graph showing a profit curve that has an inverted U-shape and has a peak at the profit maximizing quantity. Profit is maximized at the quantity q* and is lower at all other quantities. The curvature












0 Response to "36 refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is"
Post a Comment