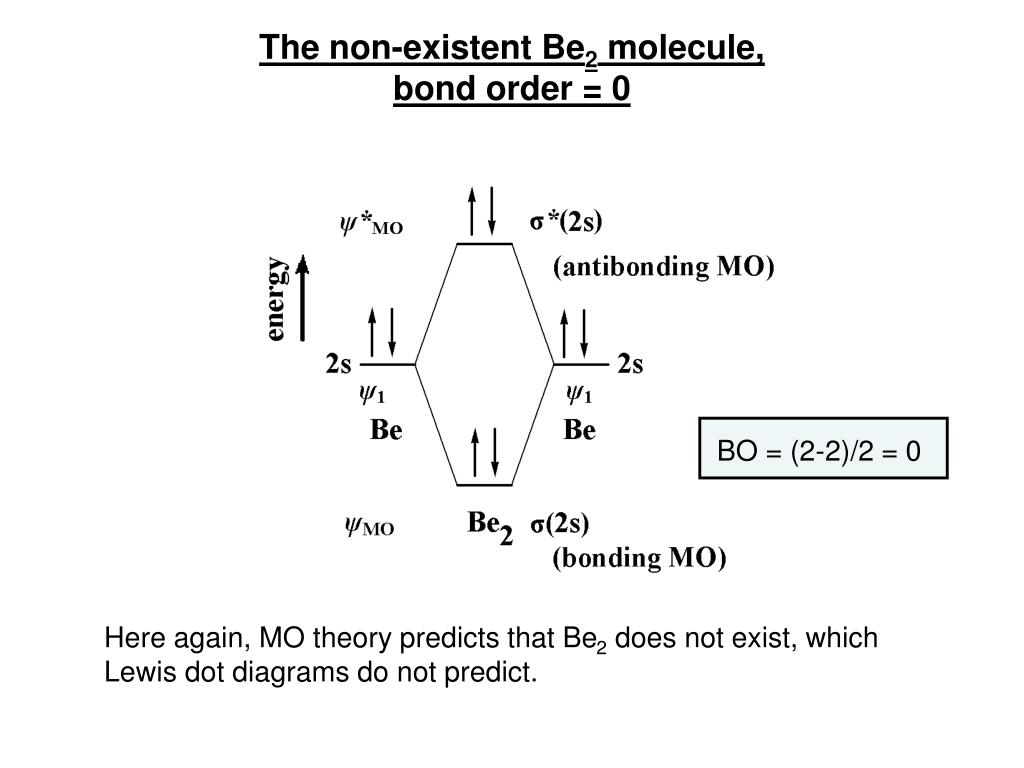
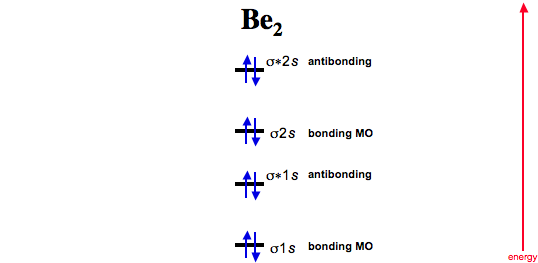
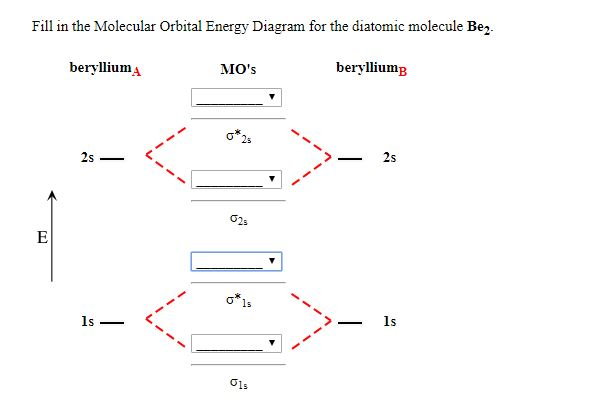
37 molecular orbital diagram for be2
PDF Microsoft Word - Handin8s2017ans.docx 1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. Assume the valence 5s-orbitals of Xe are sufficiently Determine the primary MOs that determine the bond order. Compare the general features of your MO diagram to the MO diagram for [F-H-F]... Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram of Be2 - YouTube Molecular Orbital Diagram for Beryllium Dimer (Be2)Fill from the bottom up, with 4 electrons total.Bonding Order is 0, meaning it does not bond, and it is...
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory... Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. • When bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their • Symmetry properties and degeneracy of orbitals and bonds can be learned from corresponding character tables by their inspection holding in mind the...

Molecular orbital diagram for be2
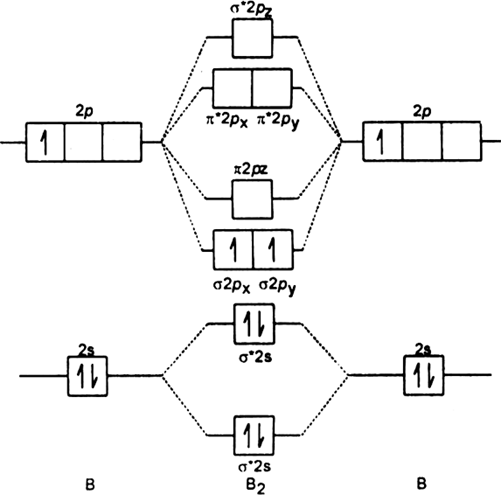
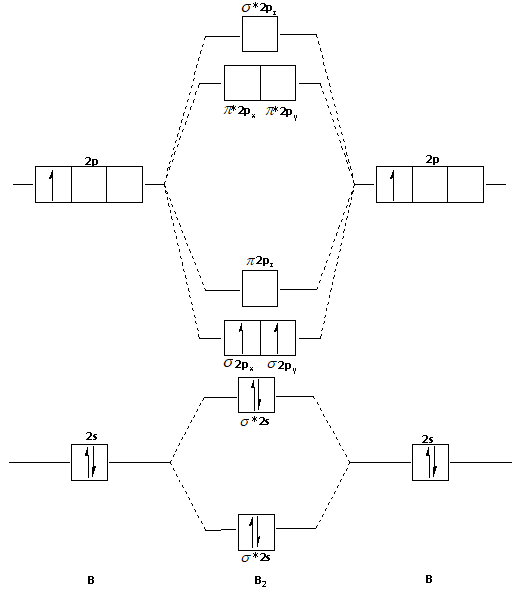
What is the molecular orbital diagram for B_2? | Socratic Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. 7. The Full Molecular Orbital Diagram For The Butadienyl System (n=4) The second-lowest-energy molecular orbital in butadiene will have 1 node. The trick is knowing where to put it. As we saw with the allyl system, the node cannot just be placed anywhere; the A molecular orbital diagram without electrons is like an apartment building without people. Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Molecular orbital diagram for be2. molecular orbital energy-level diagram | Britannica Figure 8: Molecular orbital energy-level diagrams for (A) beryllium hydride, BeH2, with linear shape, and (B) water, H2O, with bent shape. The molecular orbitals are labeled to reflect the atomic orbitals from which they are composed as well as their symmetry properties. PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. The solid lines represent the relative energies of the indicated atomic and molecular orbitals. (a) The diagram for H2, He2, Li2, Be2, B2, C2, and N2... CHAPTER 5: MOLECULAR ORBITALS energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons.29 pages Using the molecular orbital theory, why does a Be2 molecule not exist? The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels According to molecular orbital theory,molecular orbital diagram for helium molecule can be given as. From molecular orbital configuration,bond...
SOLVED:Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond ... VIDEO ANSWER: Let's first draw the molecular orbital energy diagram where we have ... Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2-.12 Jul 2021 The molecular electronic configuration of Be2 is: - Toppr Electronic configuration according to molecular orbital theory: ... Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:- ...1 answer · Top answer: Total no. of electrons in Be2 = 8 .Electronic configuration according to molecular orbital theory: σ1s^2 , σ^*1s^2 , σ2s^2 , σ^*2s^2 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. Figure 8. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical Bonding and... The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow 3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. Be2 does not exist.
Paramagnetic vs Diamagnetic | Forum For a molecule to be paramagnetic, there has to be at least one unpaired electron in a molecular orbital. Quick question regarding this answer, for the MO diagram we use to determine if a molecule is diamagnetic or paramagnetic, are we supposed to use the MO... PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... - MO diagrams for Inorganic complexes. • It is a waste of both the lecturers and students time if the tutorial to ends up being a lecture covering questions. 5. An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory. electronic configuration - Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and... Will the MO diagram be the same as that of $\ce{N2}$ or not? Now note that even in this advanced molecular orbital theory a bunch of approximations is introduced, and the answer in general depends on at which level of theory calculations are done. Introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory There are two molecular orbitals for hydrogen, the lower energy orbital has its greater electron density between the two nuclei. The energy levels in a hydrogen molecule can be represented in a diagram - showing how the two 1s atomic orbitals combine to form two molecular orbitals, one bonding (s)...
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the There are two types of molecular orbitals that can form from the overlap of two atomic s orbitals on adjacent Figure 8.34 This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic. Be. 2.
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Asked for: "skewed" molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bonding... When we draw a molecular orbital diagram for a molecule, there are four key points to remember It so happens that the molecular orbital description of this molecule provided an explanation for a long-standing puzzle that could not be explained using other bonding models.
PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for For the interaction to be strong, the energies of the two orbitals must be approximately equal and the overlap must be large. Bond Order. 3. For remainin g elements, molecular orbitals must also be formed usin g p orbitals. Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for.
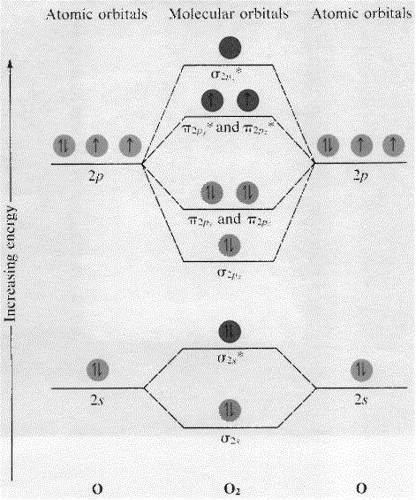
Molecular Orbital Theory This molecular orbital model can be used to explain why He2 molecules don't exist. Combining a pair of helium atoms with 1s2 electron configurations would The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified | by Megan A. Lim | Medium Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. On the other hand, Molecular Orbital Theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule.
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center.
MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis In its full development, molecular orbital theory involves a lot of complicated mathematics, but the fundamental ideas behind it are quite easily understood, and this is all we will try...
Molecular orbital diagram — Wikipedia Republished // WIKI 2 Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital Often even for simple molecules, AO and MO levels of inner orbitals and their electrons may be omitted from a diagram for simplicity.
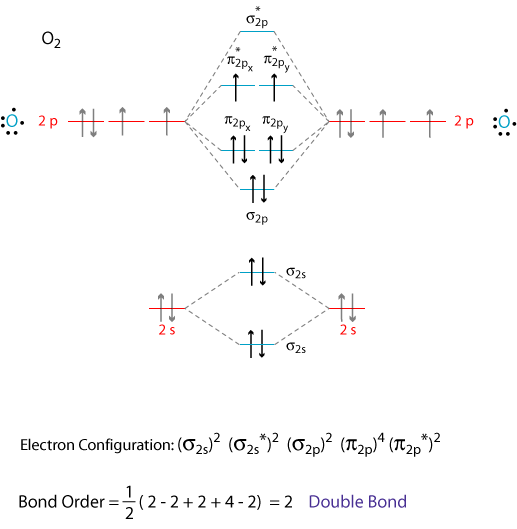
Molecular Orbital Theory: Explanation, Illustrations and... - Embibe Molecular Orbital Theory: It is used to define the bonding in molecules which cannot be explained with the The molecular orbital energy level diagram for dioxygen molecule is shown below However, if electrons singly occupy one or more molecular orbitals, it is said to be paramagnetic.
Why does the molecular orbital diagram for Be2+ consist of... Why is it that for Be, though, you look at the atomic number instead of the number of valence electrons it has? I apologize if this is a stupid question, but I For (Be_2)+, each beryllium atom has 4 electrons, and there are 2 of them. The plus charge removes one. This is considering all electrons, not just the...
Molecular orbital diagrams - Overleaf, Online LaTeX Editor Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in LaTeX by means of the package MOdiagram. For information about the more traditional molecular structure...
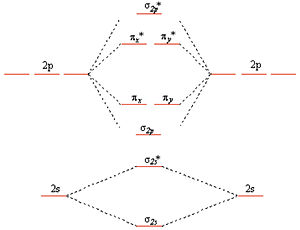
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Chemistry Study... | eMedicalPrep For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like Li2, Be2, B2 , C2, N2 , the σ 2pz MOs is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py MOs. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if...
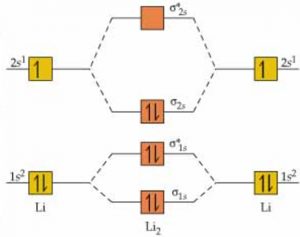
Explain Energy Level Diagram for Molecular Orbitals The relative energies of molecular orbitals depend upon the following two factors: (i) Atomic orbitals energies for the combination to form For molecules Li2, Be2, B2, C2 and N2 the molecular orbital energy level diagram. In the diagram, the molecular orbitals are place at the center and the atomic...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
7. The Full Molecular Orbital Diagram For The Butadienyl System (n=4) The second-lowest-energy molecular orbital in butadiene will have 1 node. The trick is knowing where to put it. As we saw with the allyl system, the node cannot just be placed anywhere; the A molecular orbital diagram without electrons is like an apartment building without people.
What is the molecular orbital diagram for B_2? | Socratic Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals.
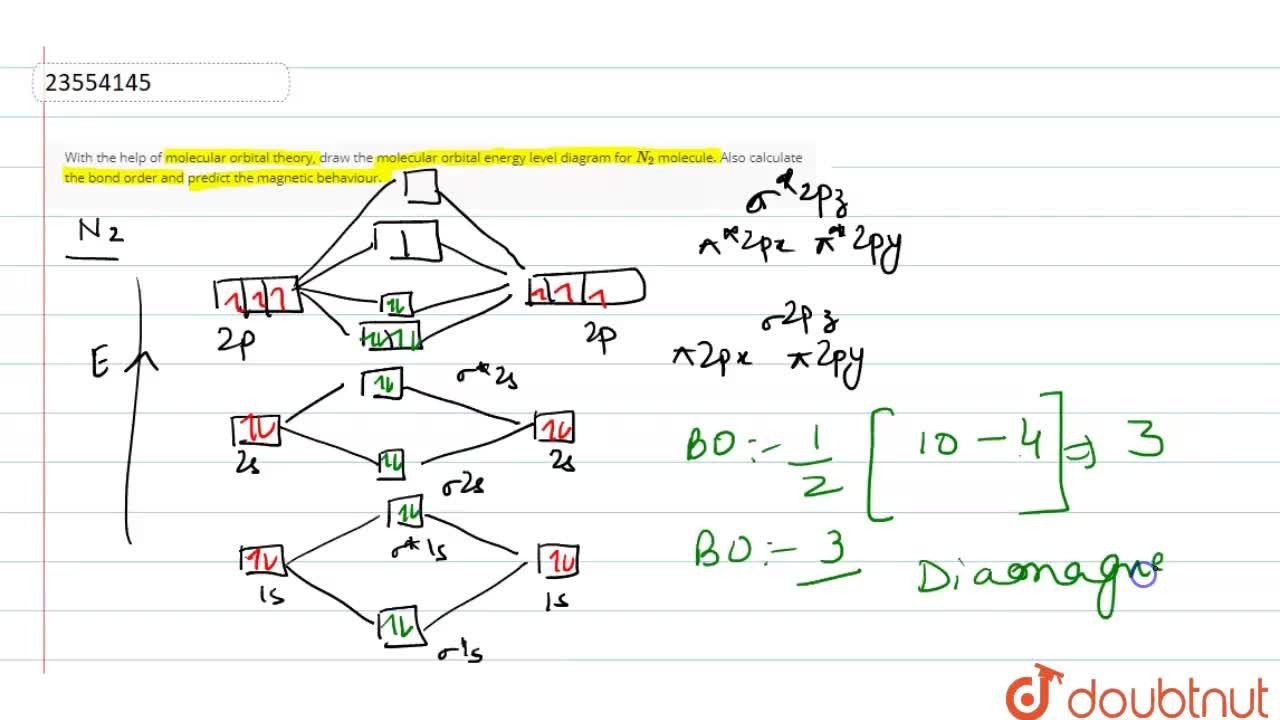
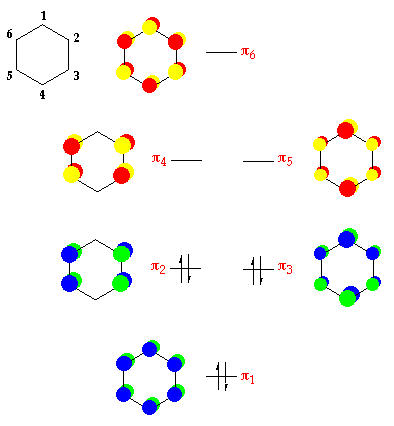



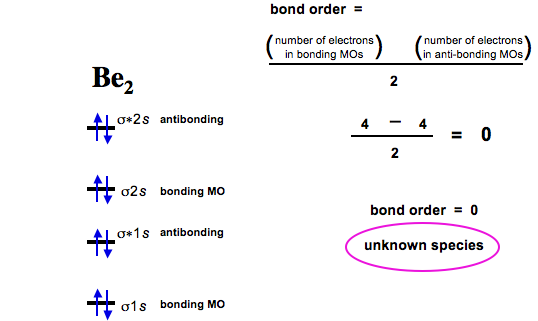


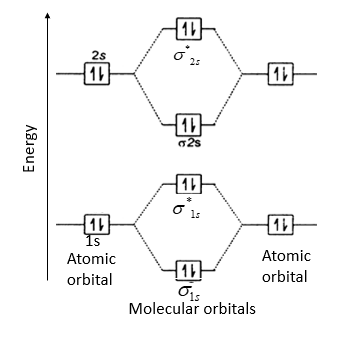



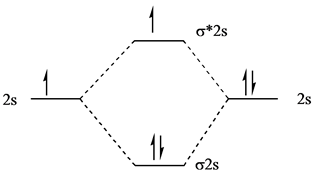









0 Response to "37 molecular orbital diagram for be2"
Post a Comment