37 orbital diagram for xenon
... Abundance, Physical Properties, Thermal Properties, Crystal Structure, Atomic & Orbital Properties, electron configuration, Chemical Properties xenon, ... Orbital Diagram. 1s. ↿⇂. 2s. ↿⇂. Orbital Diagram for Elements with Xenon as a Base. Name and Date. Element Name. 5s. 5d. (Xe). 5p. 5f. 6p. Black 5s and 5p orbitals are included in xenon and. TL;DR Xenon hexafluoride has a fluxional structure in the gas phase, with . the best explanation is given by qualitative molecular orbital theory.
Xenon Electron Configuration - 9 images - titanium electron configuration ti with orbital diagram, webelements periodic table tin properties of free atoms,

Orbital diagram for xenon
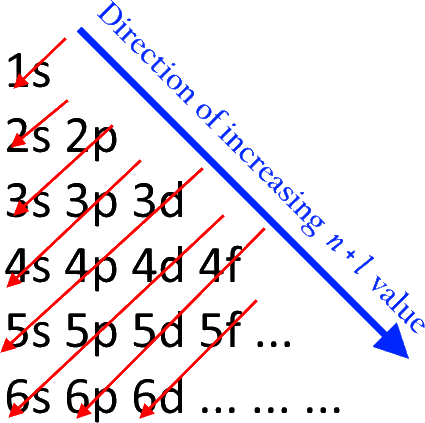
Principal quantum number, angular momentum quantum number and the number of electrons on the orbital specified by n and l. [Xe]6s1 means that you have the closed shell structure of Xenon and one electron in the n=6, l=0 state or in other words Cesium. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atomic nucleus. In other words, it's the sum of the number of nucleons in an atom. The ratio of the average mass per atom of an isotope to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Relative atomic mass is also known as atomic weight (symbol: A r ). Xenon Tetrafluoride consists of the central atom xenon, which is the epicenter where the hybridization takes place. The valence shell of the atom contains 6 electrons in the 5p orbital whereas the 5s orbital entails 2 electrons. There are no electrons present in the f and d orbital of the 5th shell.
Orbital diagram for xenon. Xe (Xenon) is an element with position number 54 in the periodic table. Located in the V period. Melting point: -111.9 ℃. Density: 0.00449 g/cm 3 . Electronic configuration of the Xenon atom in ascending order of orbital energies: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6. Electronic configuration of the Xenon atom in ascending ... Xenon. Full electron configuration of xenon: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6. iodine ← xenon → cesium. Orbital diagram of Xenon (Xe) 55: Orbital diagram of Caesium (Cs) 56: Orbital diagram of Barium (Ba) 57: Orbital diagram of Lanthanum (La) 58: Orbital diagram of Cerium (Ce) 59: Orbital diagram of Praseodymium (Pr) 60: Orbital diagram of Neodymium (Nd) 61: Orbital diagram of Promethium (Pm) 62: For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron shells are shown, moving outward from the nucleus. The final ring or shell of electrons contains the typical number of valence electrons for an atom of that element. The element atomic number and name are listed in the upper left.
Xenon atoms have 54 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.18.8. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral xenon is [Kr].4d10 ... Neon (Ne) electron configuration with full orbital diagram. Neon (Ne) is the tenth element in the periodic table and the 2nd element in group-18. The atomic number of neon is 10 and its symbol is 'Ne'. The standard atomic mass of neon is 20.1797 and it is an inert element. #MOT Molecular Orbital Diagram Of #XeF2 #Xenon Di FluoRide In English#NobleGases#InertGases#Chemistry#XenonDiFluoride#Bonding#MolecularOrbitalDiagram#Jee #Neet Xenon (Xe). Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of xenon-131 (atomic number: 54), an isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 54 protons (red) and 77 neutrons (orange). 54 electrons (white) occupy shells (rings); eight fill the outer (fifth) electron shell in what is a very stable configuration.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF 2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds.Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. An orbital diagram naturally leads to the writing of an electron configuration. V5+ Cr3+ Ni2+ Fe3+ Explore each Elements orbitals and electron configuration. Xenon; Mercury (use the periodic table included at the bottom of this to determine the order of the sublevels) 9. What is wrong with the following electron orbital diagram? What is the name of the rule that allows you to identify the error? 10. How many unpaired electrons does cobalt have? An MO diagram is a descriptive instrument that is particularly used to explain the formation of chemical bonds in molecules with the help of molecular orbital theory. Dear Student, a) b)In,XeF4,the central atom,Xe,has eight electrons in its outermost shell. Determine whether each is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Fluorine(F) is the 9th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'F'. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of fluorine and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of fluorine, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.Hopefully, after reading this article you will know in detail about this.
Orbital Diagram For Xenon Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of xenon (atomic number: 54), an isotope of this. Sep 8, TL;DR Xenon hexafluoride has a fluxional structure in the gas phase, with . the best explanation is given by qualitative molecular orbital theory.
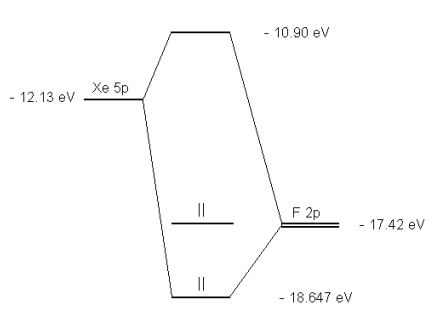
Orbital diagrams of the predicted energy schemes using valence bond theory (a) and molecular orbitalScheme 1. theory Resonance structures of PF (b). ... are delocalized in a single bonding orbital between the xenon and two fluorine atoms, and another orbital in which the electrons belong exclusively to the fluorine atoms.
Which is the correct electron configuration for xenon? — What are the 3 rules for orbital diagrams? How do you write orbitals? What is the orbital diagram ...
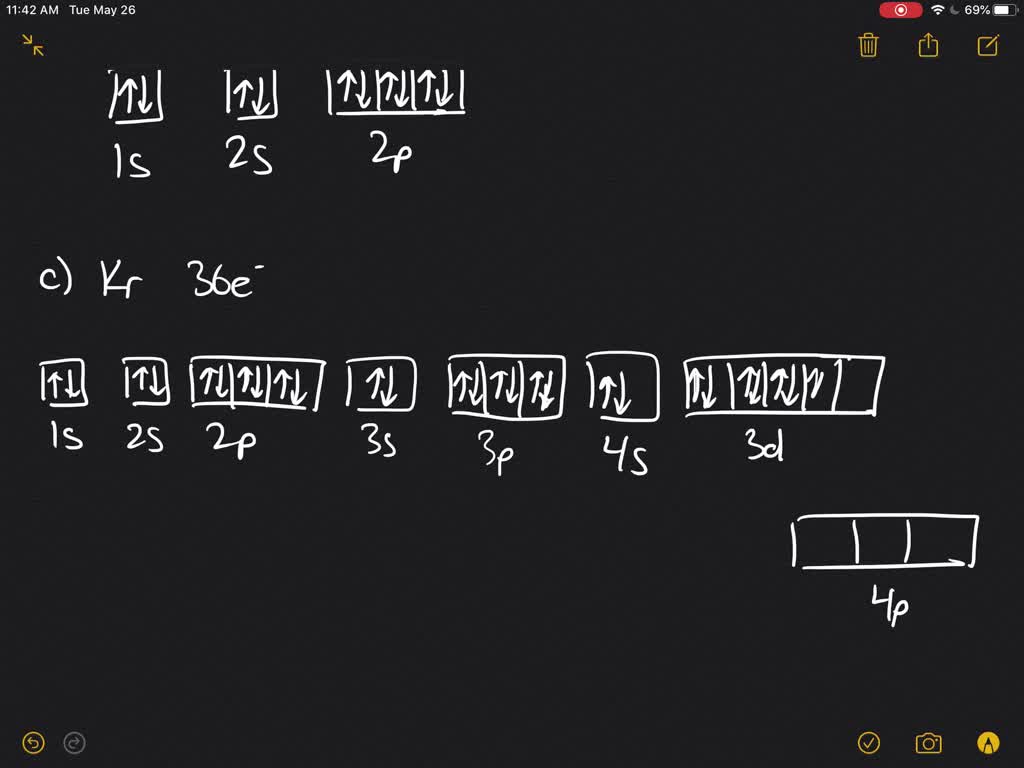
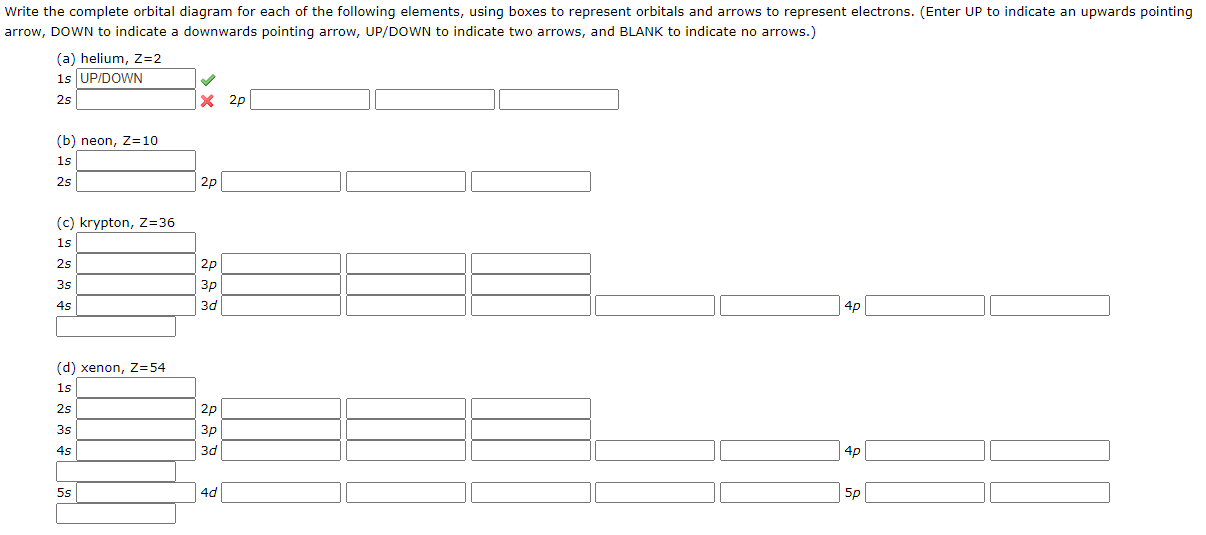
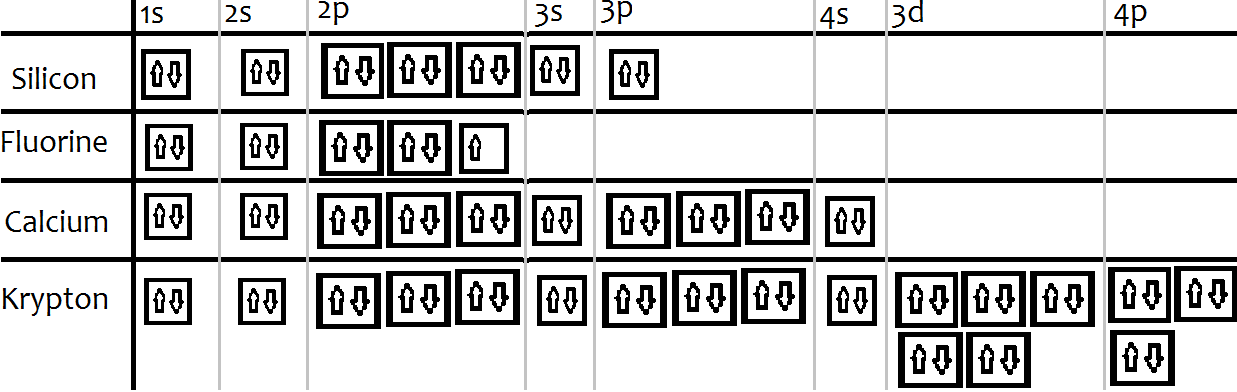
write the complete orbital diagram for each of the following elements using boxes to represent orb 2
In xenon tetrafluoride, the hybridization takes place in the central atom which is Xenon (Xe). If we look at the valence shell of Xe there are a total of six electrons in the 5p orbital and two electrons in the 5s orbital. If we observe the 5th shell then there are the d orbital and f orbital in which no electrons are present.
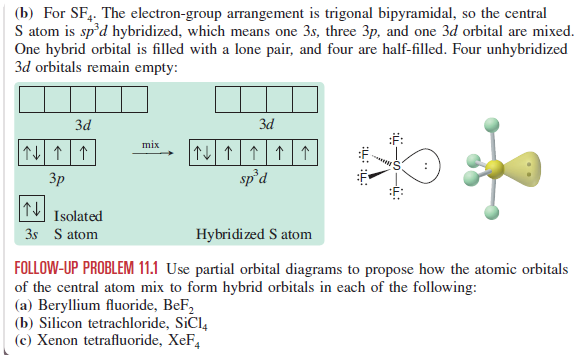
Use partial orbital diagrams to show how the atomic orbitals of the central atom mix to form hybrid orbitals in (a) nitrogen dioxide, NO2; (b) silicon tetrachloride, SICI4; (c) xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4. Q.2. Use and molecular orbital (MO) diagram and the bond order you obtain from
Now, here xenon has more than eight electrons in its valence shell( unpaired) as per Lewis Structure. So, this makes the atom excited and the configuration now has 5s2 5p5 5d1. So, the hybridization here is sp3d. Two hybrid orbitals are used for sigma bond formation( single bond) in XeF2 (F-Xe-F). Molecular Orbital Diagram
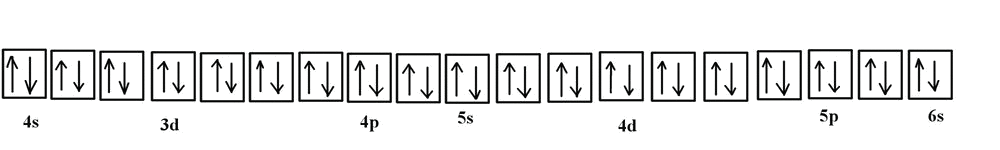
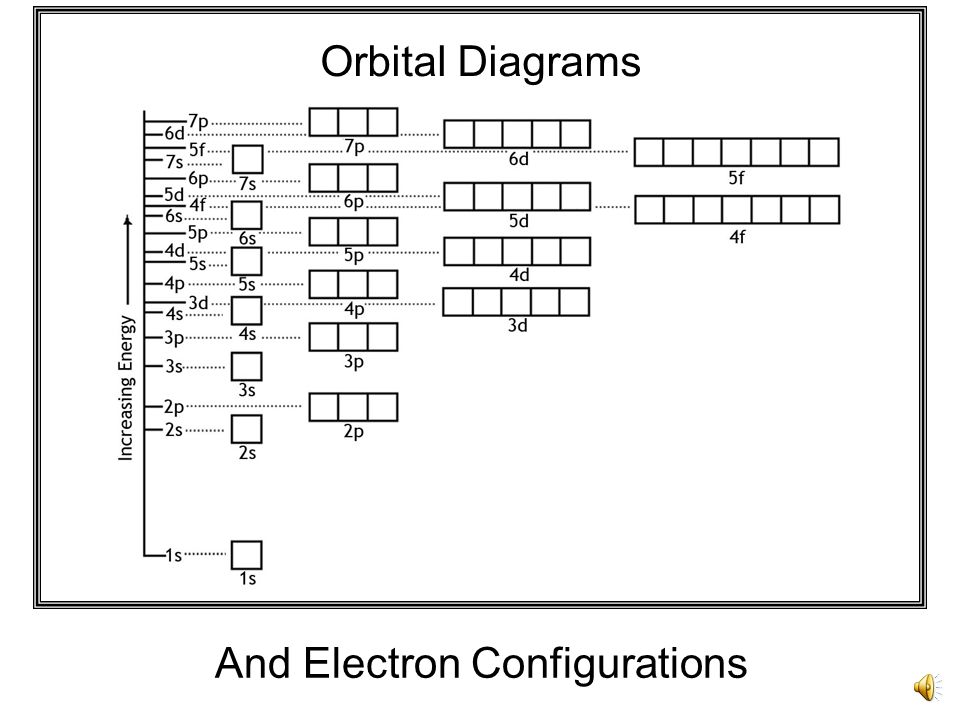
The electron configuration for chromium is: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4 The orbital diagram above is formatted in such a manner as to place the various orbital types at different energy levels. Orbital Diagrams. Many times it is necessary to see all the quantum numbers in an electron configuration, this the purpose of the orbital diagram.
Krypton Orbital Diagram. Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of krypton (atomic number: 36), the most common . Box spin diagram of outer electron orbitals for the electron configuration of the atom . 36 Krypton, Kr, [Ar]3ds24p6 = [Kr] (), [Ar]3d 4s 4p v. stable, Kr .
The electron dot, or Lewis dot diagram for xenon is the symbol Xe surrounded by four pairs of dots, representing eight valence Refer to the related link for an illustration. What is the orbital...
The 4d subshell in the ground state of atomic xenon contains [al 2 [b] 6 22. Which electron orbital diagram represents a violation of the Aufbau principle? electrons. [c] 8 d] 10 e] 36 ls 2s 2s Ib] 2s ls 2s 1s 2s 2p Te] 23. The complete electron configuration of vanadium, element 23, is [c] 1s' 2s 2p 3s 3p [d] 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 24. Which is the ...
Download Clker's Xenon Orbital Diagram clip art and related images now. Multiple sizes and related images are all free on Clker.com.
Xenon Tetrafluoride consists of the central atom xenon, which is the epicenter where the hybridization takes place. The valence shell of the atom contains 6 electrons in the 5p orbital whereas the 5s orbital entails 2 electrons. There are no electrons present in the f and d orbital of the 5th shell.
The sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atomic nucleus. In other words, it's the sum of the number of nucleons in an atom. The ratio of the average mass per atom of an isotope to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Relative atomic mass is also known as atomic weight (symbol: A r ).
Principal quantum number, angular momentum quantum number and the number of electrons on the orbital specified by n and l. [Xe]6s1 means that you have the closed shell structure of Xenon and one electron in the n=6, l=0 state or in other words Cesium.

/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


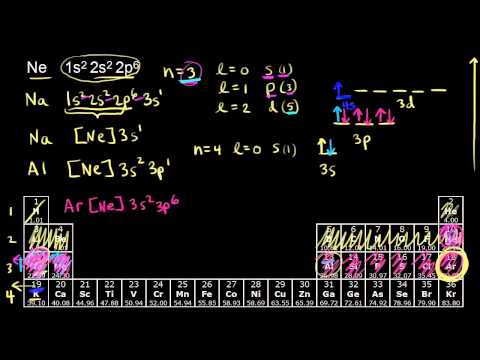








![Solved The correct orbital diagram for Pb [Xe] a) [Xe ...](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media%2Fa91%2Fa9100cd2-e53a-44f2-b0ef-c4e0a304bbc2%2Fimage)





0 Response to "37 orbital diagram for xenon"
Post a Comment