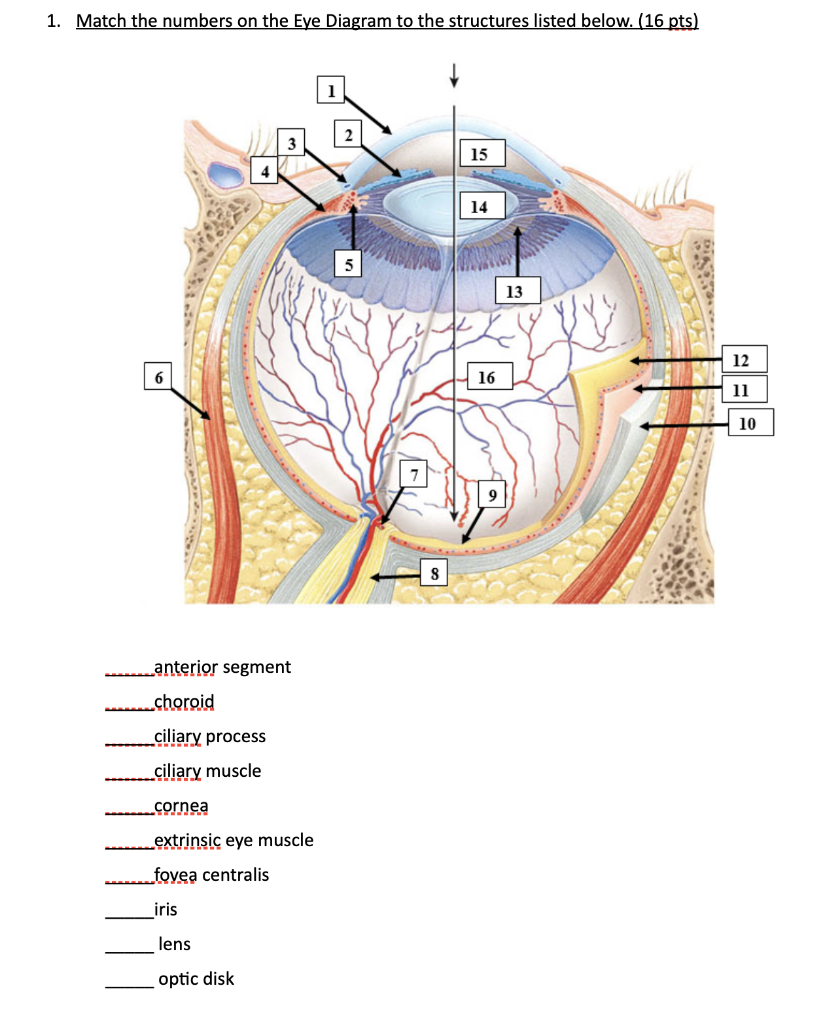
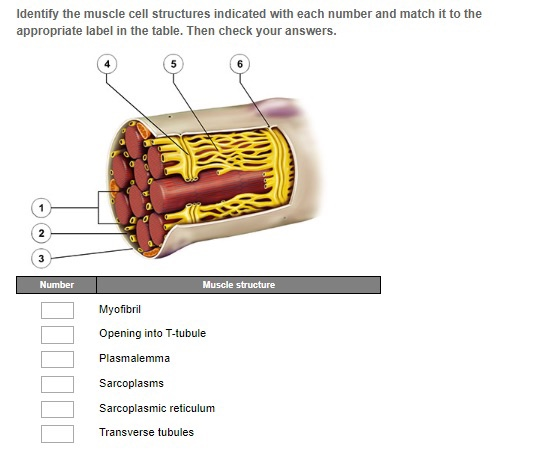
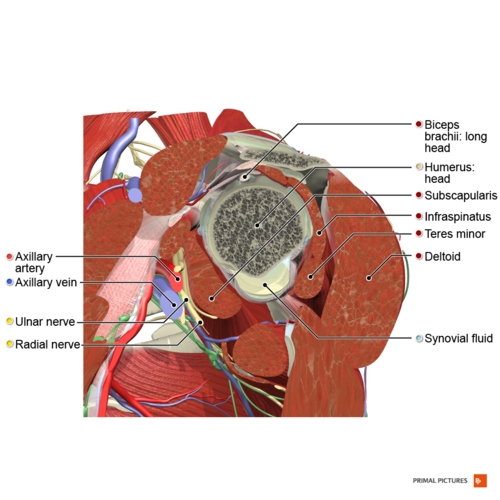
39 which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown?
Figure 4.4.1 - Muscle Tissue: (a) Skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. (b) Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) Cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. From top, LM × 1600, LM × 1600, LM × 1600. Which correctly matches the biological molecules in the food samples with the colour for a ... Three proteins that have a quaternary structure are listed.
Labeled Sarcomere Diagram. Their observations led to the discovery of sarcomere zones. Sarcomere The figure depicts the structure of a Sarcomere. (Each zone is labeled). They first. Start studying Sarcomere Labeling. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
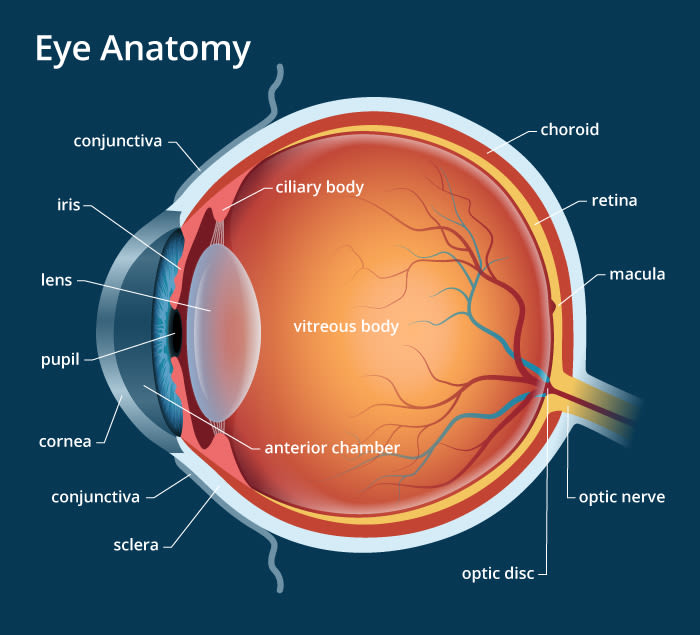
Which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown?
Transcribed image text: EXERCISE Anatomy OT the Heart Name Lab Time/Date Gross Anatomy of the Human Heart 1. An anterior view of the heart is shown here. Match each structure listed on the left with the correct letter in the figure 1. right atrium 8. brachiocephalic trunk 14. left pulmonary veins 2. right ventricle 15. right coronary artery 9. left common carotid artery 3 left atrium 16. ((The Lewis structure has a double bond between phosphorus and one of the fluorine atoms.)) The Lewis structure has 26 valence electrons. The Lewis structure is not an exception to the octet rule. No resonance structures can be drawn. The molecule has a lone pair (nonbonding pair) on the central atom. The Shape and Structure of Proteins. From a chemical point of view, proteins are by far the most structurally complex and functionally sophisticated molecules known. This is perhaps not surprising, once one realizes that the structure and chemistry of each protein has been developed and fine-tuned over billions of years of evolutionary history.
Which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown?. Match the structures on the right with the letter that identifies their location on the figure from the column on the left A- Goblet cell B- cilia C- pseudostratified ciliated epithelium Which is the location of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium lining of trachea A. Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: B. Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: 1. 2. 1. 2. Simple epithelium Stratified epithelium Found in areas where protection is a major function, e.g., skin, anal canal, and vagina. Found in organs where the principal functions are diffusion, 1 The diagram shows cells from a plant leaf. Which structure contains a high concentration of magnesium? D A B C 2 Which statements about diffusion are correct? 1 Molecules move at random. 2 Molecules move down a concentration gradient. 3 Molecules may move through a partially permeable membrane. Which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown? 1 = single muscle cell; 2 = filaments; 3 = sarcomere; 4 = myofibril 1 = sarcomere; 2 = single muscle cell; 3 = filaments; 4 = myofibril
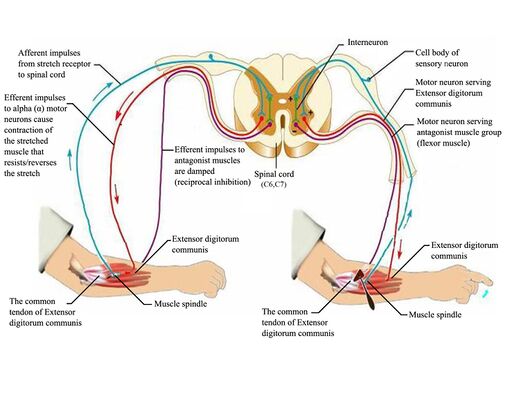
Within a muscle fiber, proteins are organized into structures called myofibrils that run the length of the cell and contain sarcomeres connected in series. Because myofibrils are only approximately 1.2 μm in diameter, hundreds to thousands (each with thousands of sarcomeres) can be found inside one muscle fiber. or agonist is used to describe a muscle or group of muscles that directly performs a specific movement. The movement produced by a muscle acting as a prime mover is described as the "action"or "function"of that muscle. For example, the bi-ceps brachii shown in Figure 10-5 is acting as a prime mover during flexion of the forearm. internal cellular network of rodlike structures Differences and Similarities in Cell Structure 3. Choose the specimen observed In Activity S (squamous epithelium, sperm. cells, smooth_muscle. or human red blood cells) that fits the description below. cell has flagellum for movement cells have an elongated shape (tapered at each end) 4. 6. u" Muscle Types. In the body, there are three types of muscle: skeletal (striated), smooth, and cardiac.. Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal muscle, attached to bones, is responsible for skeletal movements.The peripheral portion of the central nervous system controls the skeletal muscles.Thus, these muscles are under conscious, or voluntary, control.
Muscle Structure and Function CHAPTER 5 Studying Human Movement and Health 57 ANSWERS 5.1.3 Bundle of Muscle Label the components of skeletal muscle below, and explain how its structure is similar to an electrical cord. The cylinder-shaped muscle cells (fibres) are each made up of a number of myofibrils, and 3 Which eyepiece and objective lens combination of a light microscope allows the greatest number of cells in a field of view to be seen? eyepiece lens objective lens A ×5 ×10 B ×5 ×40 C ×10 ×10 D ×10 ×40 4 Which row correctly matches each cell structure with its function? microtubules rough endoplasmic reticulum Which correctly matches the biological molecules in the food samples with the colour for a ... Three proteins that have a quaternary structure are listed. 2. The diagram shows the stages in one cycle that results in movement of an actin filament in a muscle myofibril (a) Describe how stimulation of a muscle by a nerve impulse starts the cycle shown Calcium ions bind to and move tropomyosin to reveal the actin binding site so myosin heads can bind to the exposed binding sites to form
1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy are both commonly used to determine the structure of an organic compound. Match each type of spectroscopy with the information it can provide. 1H NMR =Choice, number and type of the specific nucleus detected number and type of the specific nucleus detected 13C NMR = Choice, type of the specific nucleus detected
Of body muscle is smooth and cardiac muscles, which farm the bulk of the walls Of hollow organs and the heart. Smooth and cardiac muscles are involved. in the transport of materials within the body. Study activities in this chapter deal with microscopic and gross structure Of muscle, identification of voluntary muscles, body movements, and ...
Question 5. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Report an issue. Q. The differences between two molecules include the type of sugar that forms a section of the molecules and the identity of one of the four nitrogenous bases that make up another section of the molecules. These two molecules are -. answer choices. proteins.
Cell Structure and Plasma Membrane Function Practice Questions Name: Date: 1. Use this diagram to answer the question. What is the main purpose of the mitochondria shown by the arrow? A. cell reproduction B. cellular digestion C. energy production D. protein manufacture 2. Which statement about plant and animal cells is true? A.
The skeletal muscles consist of a bundle of muscle fibres namely fascicule. These fascicules are cylindrical in shape as shown in the figure. These muscle fibres are surrounded by blood vessels and a number of layers of other tissues enclosing it. Each muscle fibre is lined by plasma membrane namely sarcolemma reticulum.
Which of the following statements correctly describe the bonding in the structure shown? (Select all that apply.) The bond between O and C is formed by the overlap of an sp3 orbital from each atom. The O lone pairs are both in sp3 orbitals. The O-H bond is formed by the overlap of an sp3 orbital from O with an sp3 orbital from H.
Identify the structure indicated. Skeletal Muscle MultiplePeripherally Located Nuclei Identify the structure indicated. Neuron Cell Body Identify the structure indicated. Compact Bone (Osseous Tissue) Central Canal Identify the tissue type and a location where it is found. Elastic Cartilage •External Ear •Epiglottis
Anatomy and Physiology Q&;A Library A F B E Match the labelled synapse structure with the correct structure or function. Place the correct number in each blank. Use each letter only once. : Synaptic vesicle containing the neurotransmitters • Postsynaptic membrane of the dendrite • Synaptic cleft • Receptor site for the neurotransmitter on the dendrite Axon terminal • Mitochondria, which ...
General. Question #99126. Which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown? General. 672 students attemted this question.
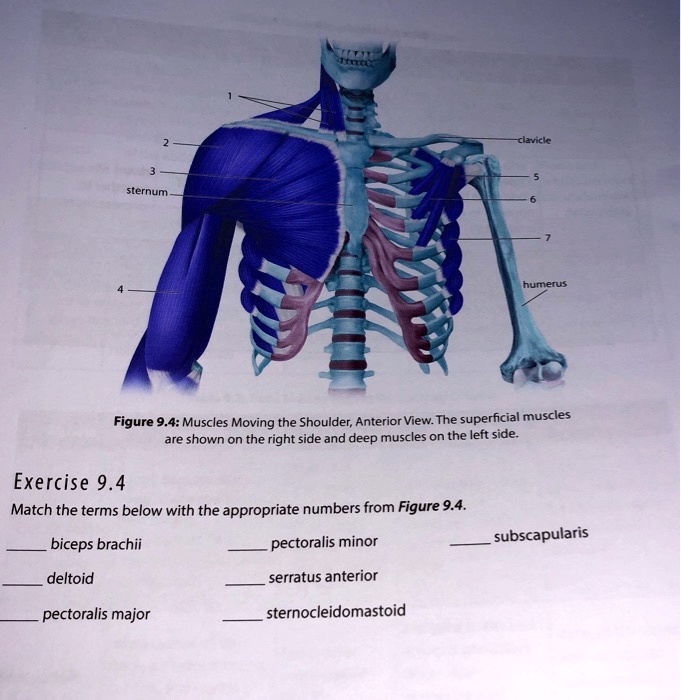
Anatomists name the skeletal muscles according to a number of criteria, each of which describes the muscle in some way. These include naming the muscle after its shape, its size compared to other muscles in the area, its location in the body or the location of its attachments to the skeleton, how many origins it has, or its action.
Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function How are Substances Transported Across Membranes? Answer: Concentration Gradients Concentration = Number of molecules in a given unit of volume (e.g. grams / liter; moles / liter) Gradient = Difference between two regions of space such that molecules move from one region to the other
27 Sep 2016 — Which of the labeled structures on the diagram holds muscles with ... Show transcribed image text match the structure with the correct ...
Tour of an Animal Cell: Part A. Drag the labels on the left onto the diagram of the animal cell to correctly identify the function performed by each cellular structure. a. smooth ER- synthesizes lipids. b. nucleolus- assembles ribosomes. c. defines cell shape. d. rough ER- produces secretory proteins.
Match the type of muscle tissue with its description. Organs are composed of more than one tissue type working together to perform a specific set of functions. The small intestine shown here is lined with a mucous membrane, contains neurons that control muscle contraction, and has an abundance of blood vessels.
D= Electron transport chain. Match the name of the muscle cell component with its function. Muscle Fiber: a. regulates entry and exit materials. b. metabolic activities; contraction. c. site of metabolic processes for normal muscle fiber activities. d. stores calcium ions needed for muscle contraction. e.
14. Relative to general terminology concerning muscle activity, first label the following structures on Figure 6—5: insertion, origin, tendon, resting muscle, and contracting muscle. Next, identify the two structures named below by choosing different colors for the coding circles and the corresponding structures in the figure. Movable bone
Figure 1.4.2 - Directional Terms Applied to the Human Body: Paired directional terms are shown as applied to the human body. Body Planes. A section is a two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut. Modern medical imaging devices enable clinicians to obtain "virtual sections" of living bodies.
Chapter 7. The mixing of purified microtubules with transport vesicles and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) does not result in movement of the vesicles. Why? Kinesin is missing. A large carbohydrate is tagged with a fluorescent marker and placed in the extracellular environment surrounding a eukaryotic cell. The cell ingests the carbohydrate via ...
Which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown? Which composition of transformations below will map figure k onto figure s and then onto figure u? Logic structures are also called ____ structures. True/false: decision structures are also known as selection structures. Which of these correctly illustrates the ...
Dec 19, 2017 · A diagram of a plant cell is shown below. Insertion origin tendon resting muscle and contracting muscle. 20 1 Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Endomysium surrounds each muscle fiber match the following area of a muscle fiber with its description. Which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown ...
34 Questions Show answers. Question 1. SURVEY. 120 seconds. Report an issue. Q. Students use a microscope to look for structures present in four different cells. The students placed an X for each structure that was viewed for each cell on the table shown. Which cell that was viewed is most likely a prokaryote.
The Shape and Structure of Proteins. From a chemical point of view, proteins are by far the most structurally complex and functionally sophisticated molecules known. This is perhaps not surprising, once one realizes that the structure and chemistry of each protein has been developed and fine-tuned over billions of years of evolutionary history.
((The Lewis structure has a double bond between phosphorus and one of the fluorine atoms.)) The Lewis structure has 26 valence electrons. The Lewis structure is not an exception to the octet rule. No resonance structures can be drawn. The molecule has a lone pair (nonbonding pair) on the central atom.
Transcribed image text: EXERCISE Anatomy OT the Heart Name Lab Time/Date Gross Anatomy of the Human Heart 1. An anterior view of the heart is shown here. Match each structure listed on the left with the correct letter in the figure 1. right atrium 8. brachiocephalic trunk 14. left pulmonary veins 2. right ventricle 15. right coronary artery 9. left common carotid artery 3 left atrium 16.


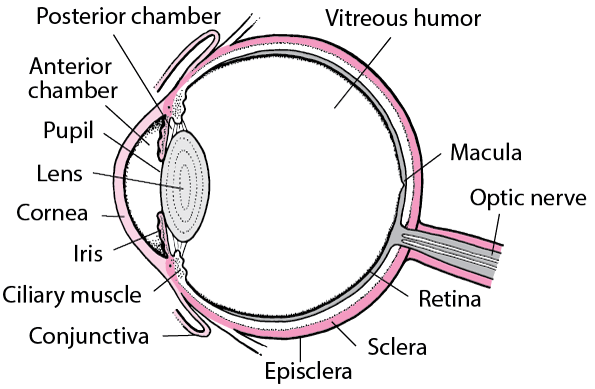


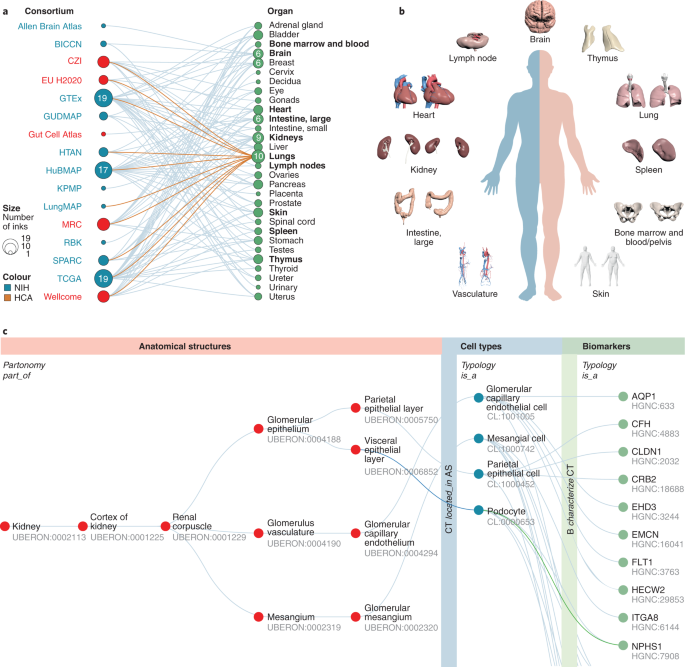
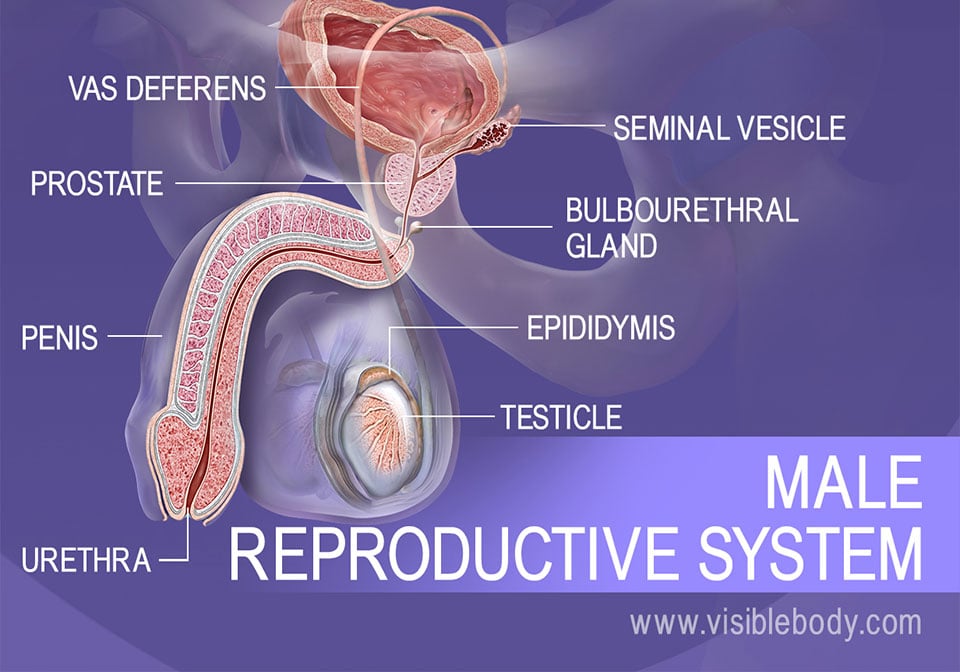


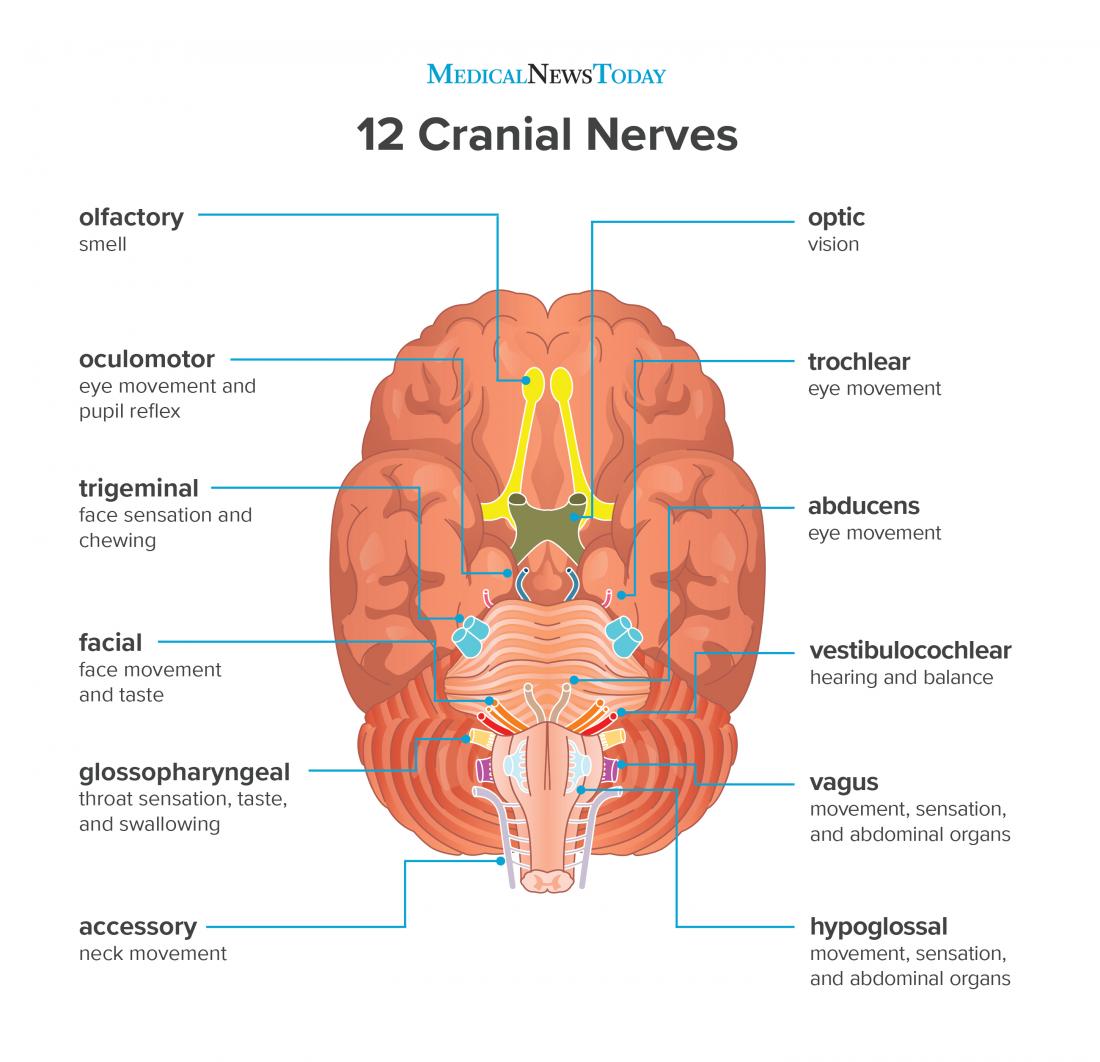







/what-are-alveoli-2249043-01-94dfddd4dfe9488b8056d586824c7c36.png)







0 Response to "39 which correctly matches numbers with structures in the diagram of a muscle shown?"
Post a Comment