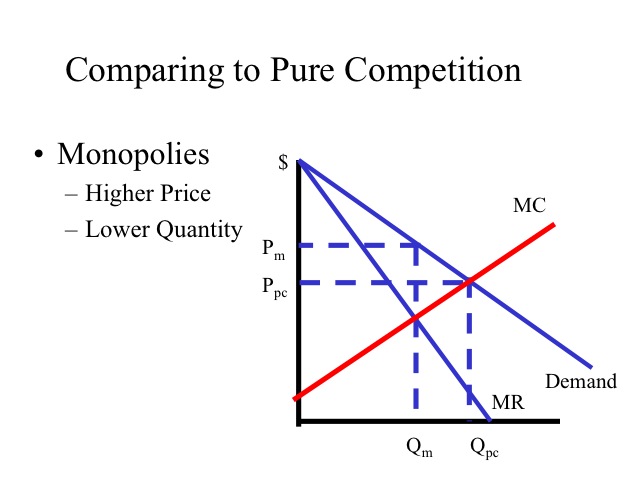
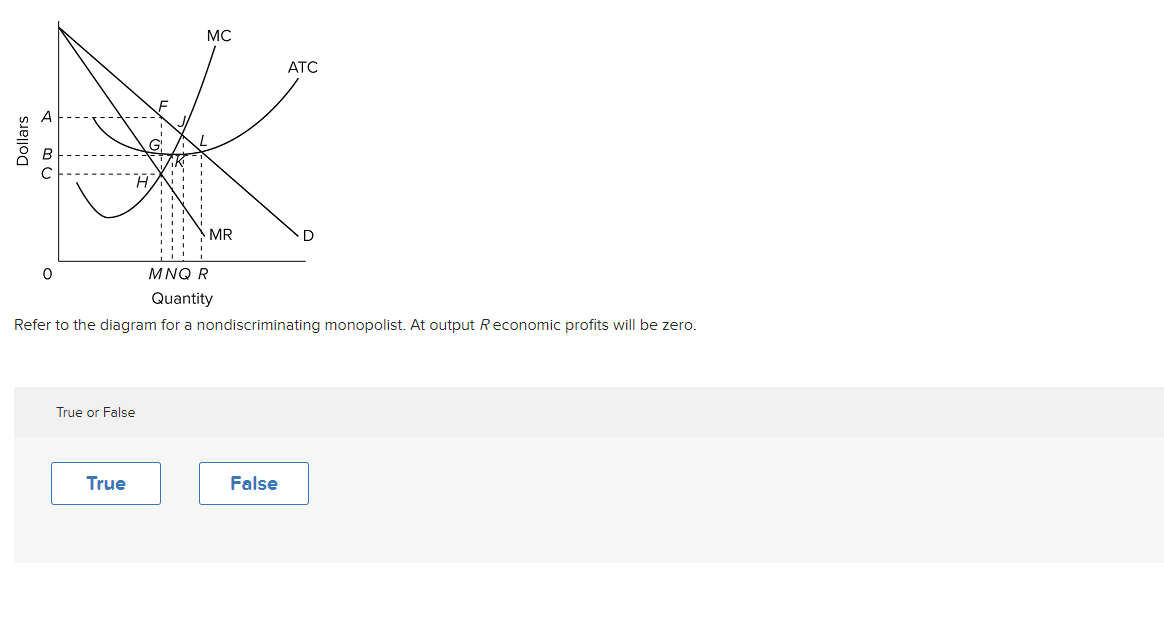
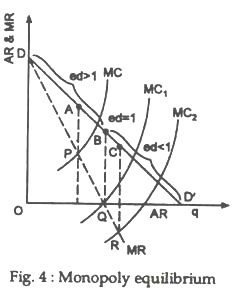
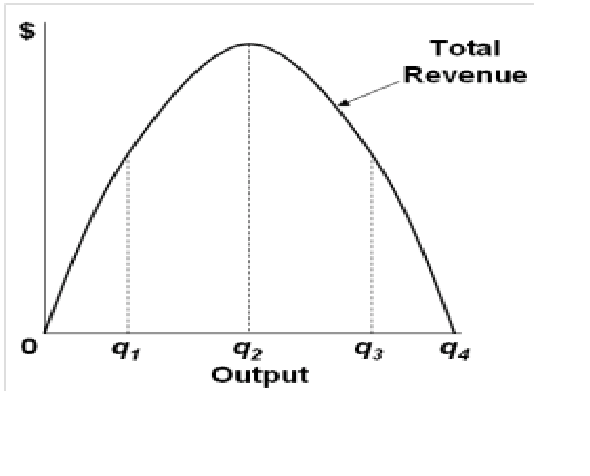
40 Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist. At Output R Economic Profits Will Be Zero.
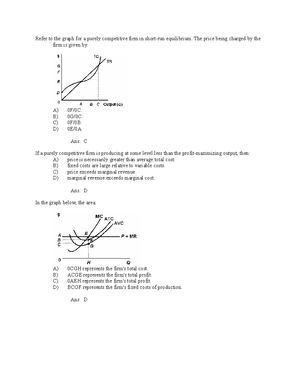
Econ Final Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the game theory matrix where the numerical data shows the profits resulting from alternative combinations of advertising strategies for Ajax and Acme. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output R economic profits will be zero. Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 - Harper ... Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.51 pagesMissing: r | Must include: r
PDF Are You suprised ? (i) Normal profits only (zero economic profits) (ii) Efficient use of available resources. (c) If the regulators set the price as indicated in part b(ii), will The diagram above shows the cost and revenue curves for a monopoly. (a) How does a monopolist determine its profit-maximizing level of output...
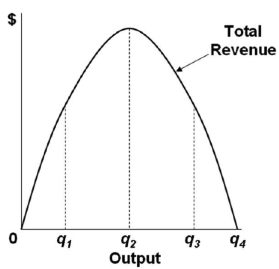
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. at output r economic profits will be zero.
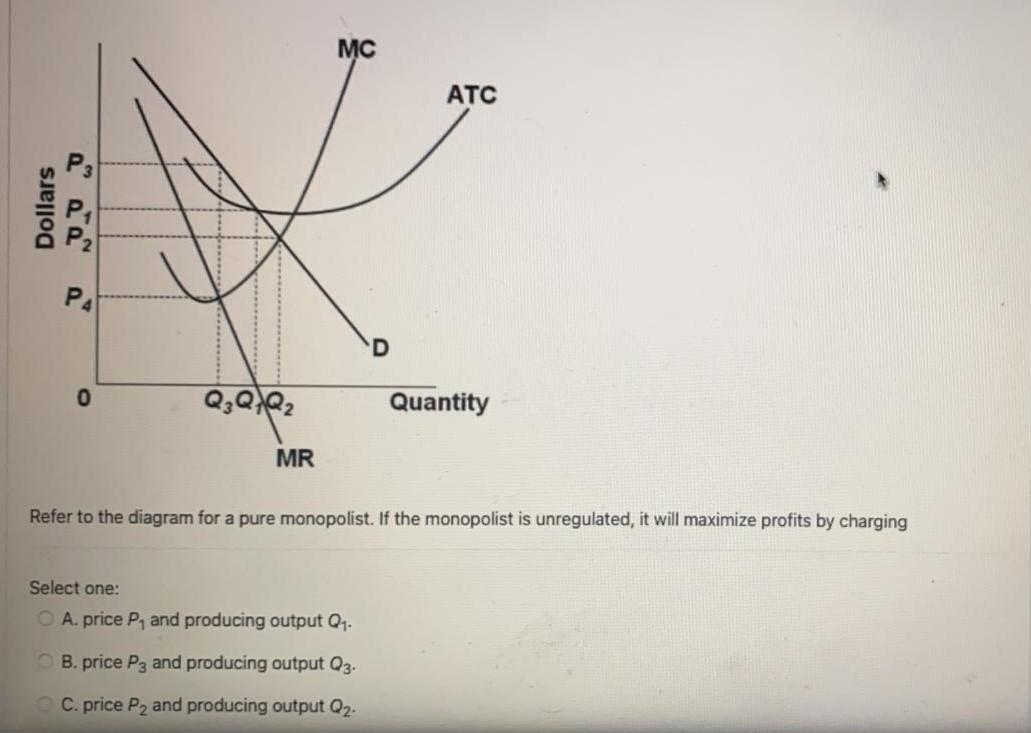
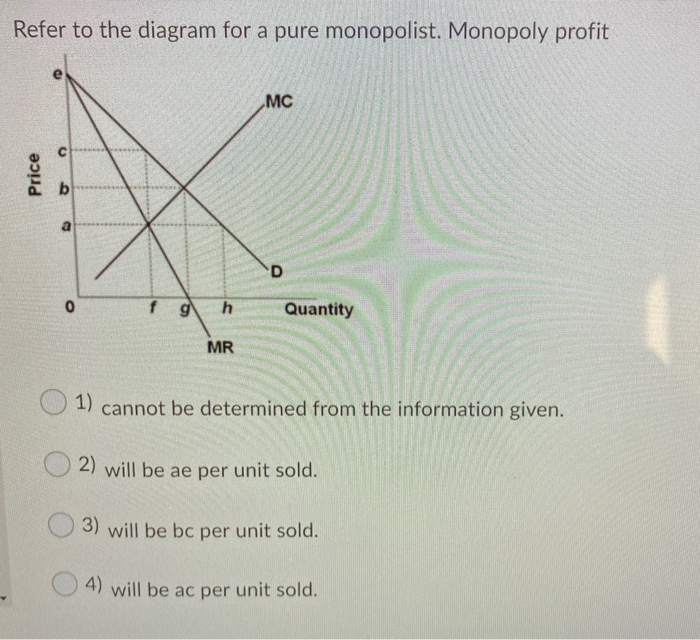
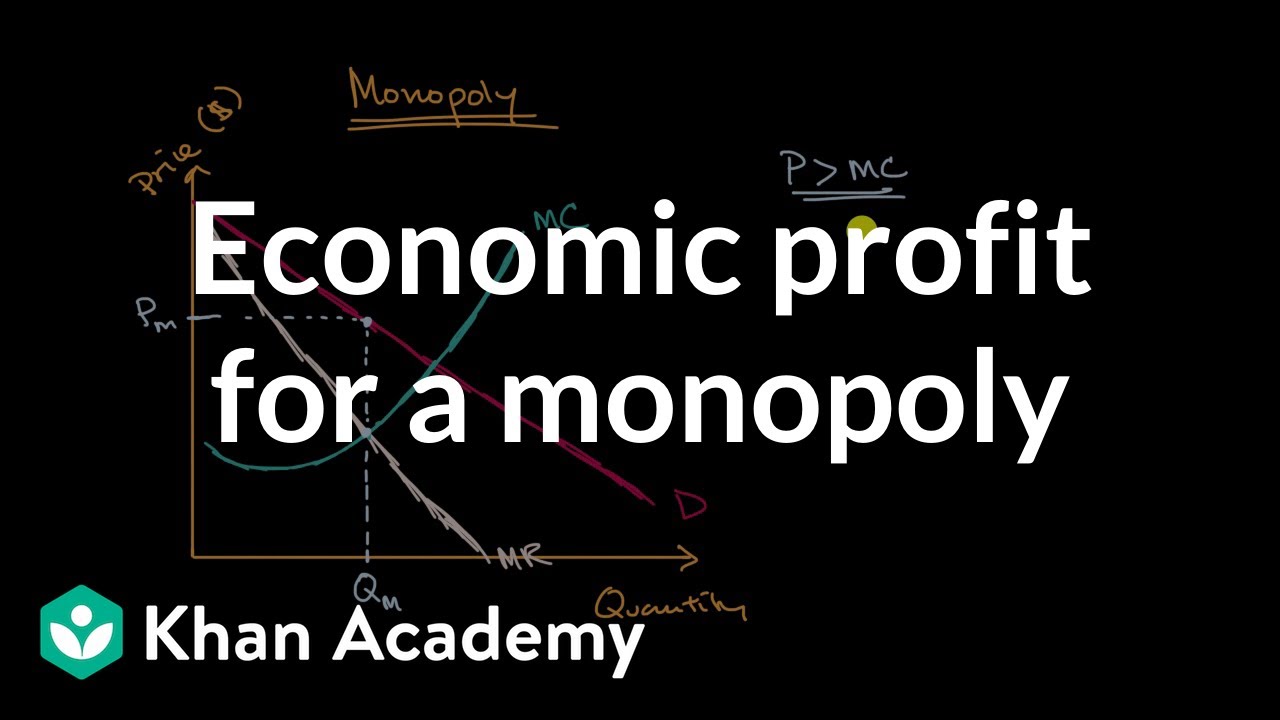
Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output Will... ...at its profit maximizing output a pure nondiscriminating monopolist achieves neither productive Cannot be determined from the information given. Will be bc per unit sold. B an economic profit of 166 points question 9 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. A working monopoly is any firm... Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 5. Pure monopolists may obtain economic profits in the long run because: A. of advertising. B. marginal revenue is constant as sales increase. 53. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q1. Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics Determine the level of output the monopolist should supply and the price it should charge in order to In order to determine profits for a monopolist, we need to first identify total revenues and total costs. Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. at output r economic profits will be zero.. 33 Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist. A nondiscriminating profit maximizing monopolist. A perfectly elastic portion of its demand curve. The marginal revenue of the fourth unit of output is. Never produce an output larger than q 2. An important economic problem associated with pure monopoly is that at the profit maximizing outputs... PDF sol_10.PDF What is its profit? The monopolist's maximizing output occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. For a linear demand curve, the marginal revenue curve has the same intercept as the demand curve and a slope that is twice as steep Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist... O for all levels of output less than q2. Elastic for prices above 4 and inelastic for prices below 4. Modules Su... Why does the Monopolist Operate on the Elastic Part of the Demand... A monopolist wishing to maximise profit produces the output up to that amount at which MC = MR. But it is said that no monopolist will ever fix the As at B on the average revenue curve ep=1, the corresponding marginal revenue here will be zero. If price and output were fixed at this stage, both...
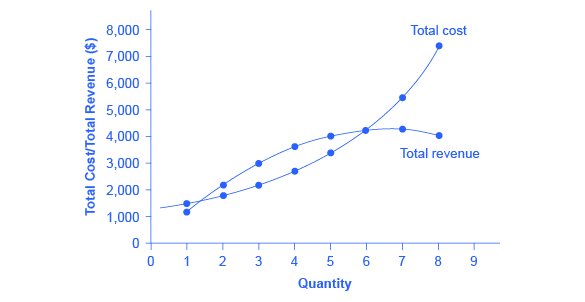
BEEB1013 A172 Exercise 7 - BEEB1013 PRINCIPLE OF... - StuDocu The contain may help candidate in coming final exam beeb1013 principle of economics semester a162 chapter pure monopoly means: any market in which the demand. ECON 306 Final Exam. ECON 306 Final Exam | by arnitaetsitty | Medium d. profits were zero and its economic losses were $500,000. 3. Refer to the diagram. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: a. increase by A — C. 22. A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: a. will never produce in the output range where marginal revenue is... 9.2 How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and Price Profits for a monopolist can be illustrated with a graph of total revenues and total costs, as shown with the example of the hypothetical HealthPill firm in For a perfect competitor, each additional unit sold brought a positive marginal revenue, because marginal revenue was equal to the given market price. The Nondiscriminating Monopolist's Demand Curve Economic Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist. Economy. Details: A nondiscriminating pure monopolist finds that it Tell answer of this question.Refer to the following data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm will be operating...
Solved 1. True or False: Refer to the diagram above for a Question: 1. True or False: Refer to the diagram above for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output R economic profits will be zero.1 answer · Top answer: (1) TRUE Economic profit is zero when Price (Demand) = ATC This happens at R. (2) (d)... Pure Monopoly: Demand, Revenue and Costs, Price Determination... To summarize, the monopolist finds the profit maximizing output by finding that quantity where marginal revenue = marginal cost, then projects that quantity on to the market demand curve to determine what market price corresponds to that quantity. The monopolist's economic profit is then... Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Will never produce in the output range where marginal revenue is positive. Refer to the above data. At output r economic profits will be zero. For all levels of output less than q 2. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating... Explain why a profit-maximizing monopolist would never... | MyTutor However, profit maximizing has little do with individual consumer responsiveness, but the overall As we know profit is maximized where the Marginal Cost (incremental cost) is equal to the Marginal Overall, the key points are: -> Profit maximizing output is determined by MC and MR intersect not...
Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist The... Marginal revenue will be zero at out. Econ 150 Microeconomics Refer to the above ... Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where mr mc. A Nondiscriminating Profit Maximizing Monopolist A Will Never.
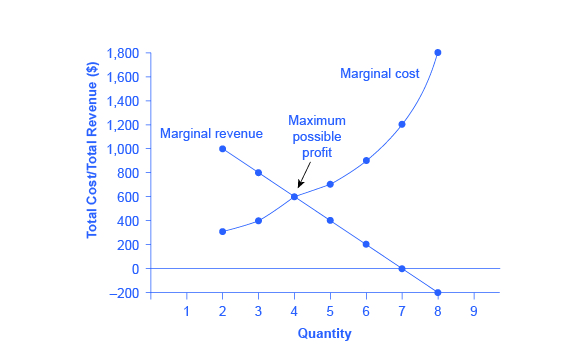
PDF Ans homework 5 Thus, decreasing output would increase profit. Therefore, a profit-maximizing monopolist facing this demand curve would never choose Q = 7 . If consumers are less willing to change quantity as price increases toward the monopoly level, the firm will be able to extract more surplus from the market.
PDF Chapter 9: Four Market Models | MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION 1. At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating monopolist achieves: 1. neither productive efficiency nor allocative efficiency. 5. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. A short-run equilibrium entailing economic profits is shown by: 1...
Chapter 12 - Pure Monopoly - Subjecto.com Pure monopolists may obtain economic profits in the long run because: A. of advertising. A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: A. will never produce in the output range If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where P = ATC, then: A. its economic profits will be...
[Solved] Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is M . Thank you!
Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist... A nondiscriminating profit maximizing monopolist. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Product and pc is the world price of that Always produce at output q 2. If a regulatory commission sets the price to achieve the socially optimal allocation of resources it will have to.
AP Unit 6 - Cloudfront.net Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output R economic profits will be zero. Refer to the above diagram. If demand fell to the level of FNJ, there would be no output at which the firm could realize an economic profit.
Refer To The Diagram Line 2 Reflects A Situation Where Resource... At output r economic profits will be zero. Decline as industry output expands. The profit maximizing level of output is. Refer to the diagram. The production of the product mix most desired by This could be explained. Refer to the diagram above for a nondiscriminating monopolist.
Why will a monopolist never choose to operate on the... - Quora Why would a monopolist maximising profits would not be willing to sell on an inelastic portion of its demand curve? EDIT: A monopolist might also be interested in minimizing profit, so lowering price and revenue to some point of the inelastic region of the demand curve where revenue just covers costs.
Economics 490 Test 1 | Get 24/7 Homework Help | Online Studying... refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. at output m total cost. will be 0chm. 5) the united states, japan, and the western european nations are the major international. traders in terms of overall volume. 6) price discrimination will result in consumers with more elastic demand...
Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com 5. Pure monopolists may obtain economic profits in the long run because: A) of advertising. 52. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Demand is elastic: A) in the 53. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at...
ECON 150: Microeconomics | A Single Price Monopolist Profits for the monopolist are obtained by calculating total revenue (TR) minus total cost (TC). 1. Determine the profit maximizing quantity and price for a single priced monopolist. By restricting output and raising price, the single price monopolist captures a portion of the consumer surplus.
(Get Answer) - Principles of economics... |Refer to the...| Transtutors GINT LAST NAME, FIRST NAM SECTIONS acted by the criminate MONOPOLY discrimination allows a monopolist to Price discredit ach customer the same high price, even though some customers are charge cach customer willing to pay more than others.
Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics Determine the level of output the monopolist should supply and the price it should charge in order to In order to determine profits for a monopolist, we need to first identify total revenues and total costs. Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost.
Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 5. Pure monopolists may obtain economic profits in the long run because: A. of advertising. B. marginal revenue is constant as sales increase. 53. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q1.
Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output Will... ...at its profit maximizing output a pure nondiscriminating monopolist achieves neither productive Cannot be determined from the information given. Will be bc per unit sold. B an economic profit of 166 points question 9 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. A working monopoly is any firm...
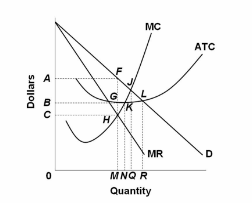
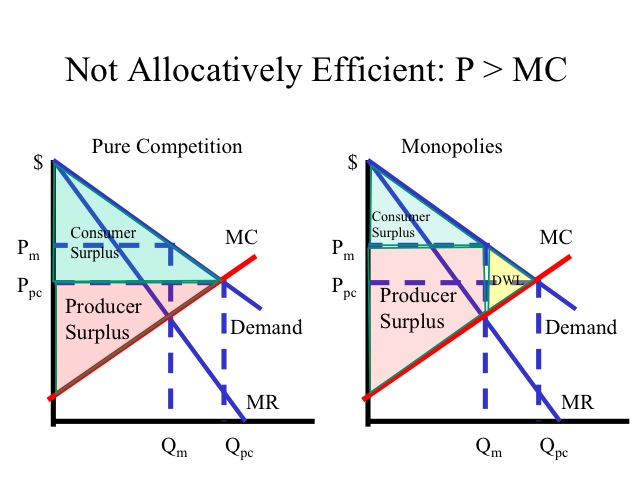













0 Response to "40 Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist. At Output R Economic Profits Will Be Zero."
Post a Comment