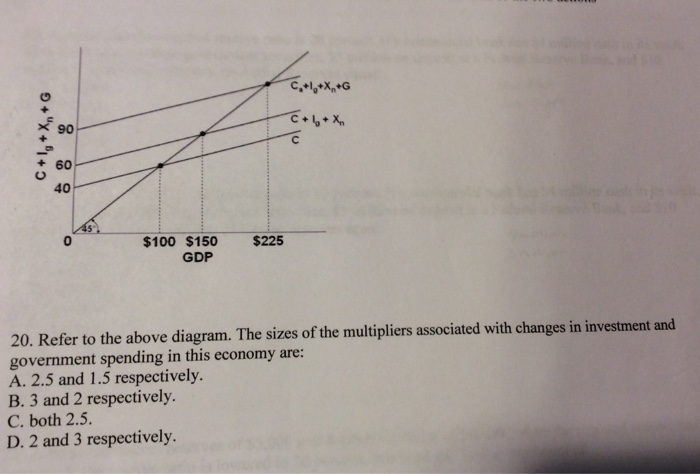
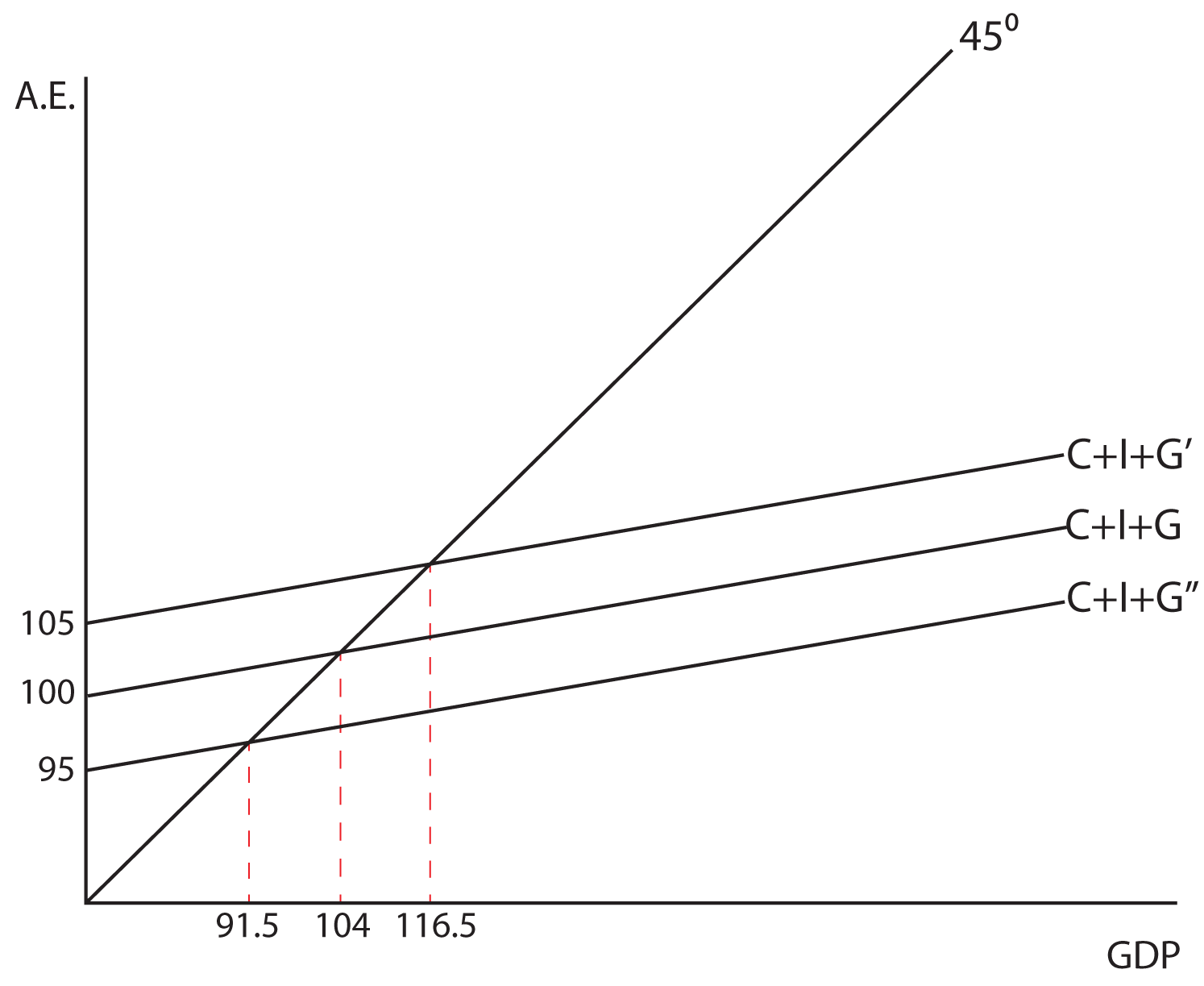
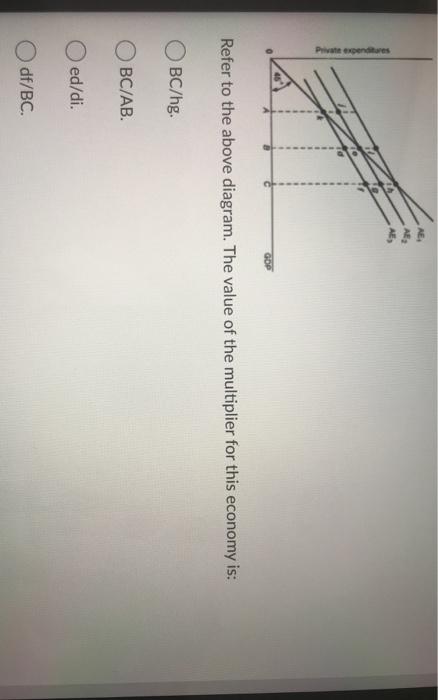
40 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
The multiplier The multiplier effect refers to the increase in final income arising from any new injection of spending. A full 'open' economy has all sectors, and therefore, three withdrawals - savings, taxation and imports. The multiplier can now be calculated by the following general equation The Keynesian multiplier The multiplier refers to a change in an injection into the Circular Flow of Income (either investment (I), government expenditure (G) or exports (X)), will This is known as the multiplier effect. Notice that changes in C are a little more complicated as it is not (strictly) a recognised injection into the Circular...
Multiplier Effect Definition,Calculation and Types » Economics Tutorials The multiplier effect in economics shows by how much or by how many times the final income would increase To figure out what makes the multiplier to leave bigger effect. Let's just say that economy is in the The negative multiplier refers to such situation in the economy where a minor decline in...

Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
Multiplier (economics) - Wikipedia In macroeconomics, a multiplier is a factor of proportionality that measures how much an endogenous variable changes in response to a change in some exogenous variable. For example, suppose variable x changes by k units, which causes another variable y to change by M × k units. Keynesian Multiplier - Overview, Components, How to Calculate The Keynesian Multiplier is an economic theory that asserts that an increase in private consumption expenditure, investment expenditure, or net government Keynesian Economic Theory. In 1936, economist John Maynard Keynes published a text that would change the course of economic thought. The Multiplier Effect Definition | Example and Formula | BoyceWire The multiplier effect refers to how an initial injection of money into the circular flow of income can stimulate economic activity in excess of the initial investment. Therefore, the multiplier is 5 - which means the initial $1 million investment would provide a $5 million stimulus to the wider economy.
Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is. (PDF) GDP Multiplier Formulas | Associate Professor | Economics Spending Multiplier = Government Spending Multiplier = Investment Multiplier = 1 / (1 It refers to the quantity of output that the. economy can produce with full employment of its labor and physical capital. The second conceptual line on the Keynesian cross diagram is the 45-degree. A multiplier refers to an economic input that amplifies the effect of... In economics, a multiplier broadly refers to an economic factor that, when increased or changed, causes increases or changes in many other related economic variables. The term multiplier is usually used in reference to the relationship between government spending and total national income. Reading: The Multiplier Effect | Macroeconomics The Multiplier Effect. The Keynesian policy prescription has one final twist. Assume that for a certain economy, the intersection of the aggregate To understand how the multiplier effect works, return to the example in which the current equilibrium in the Keynesian cross diagram is a real GDP of $700... Multipliers in Economics: Investment, Period Multiplier and... In the multiplier theory, the important element is the multiplier coefficient, K which refers to the power by which any initial investment expenditure is multiplied to Suppose that in an economy MPC is 1/2 and investment is raised by Rs 100 crores. This will immediately lead to a rise in production and...
The Fiscal Multiplier: Econ 101 | An Economic Sense The "fiscal multiplier" (often referred to as just the "multiplier") is simply the ratio of how much aggregate GDP will While the concept is simple, the multiplier in practice is difficult to measure. But most economists recognize that it is possible for the economy to be at less than full employment. Multiplier | PDF | Fiscal Multiplier | Macroeconomics The multiplier in this economy is Refer to the above diagram. The change in aggregate expenditures as shown from (C + Ig + Xn2) to (C + Ig + Xn 1) might be caused by: A. an appreciation of this nation's currency relative to the currencies of its trading partners. Solved Private expenditures GOP Refer to the above diagram. Economics questions and answers. The value of the multiplier for this economy is: OBC/hg. Multiplier Formula | Calculate Multiplier Effect in Economics What is the Multiplier Formula in Economics? Multiplier formula denotes an effect which initiates because of increase in the investments (from the government or corporate levels) causing the proportional increase in the overall income of the economy, and it is also observed that this...
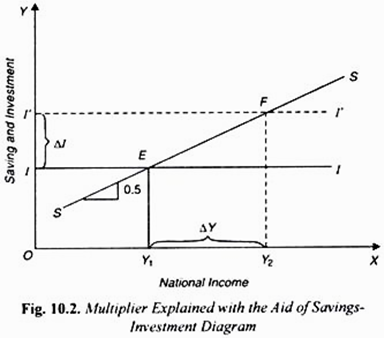
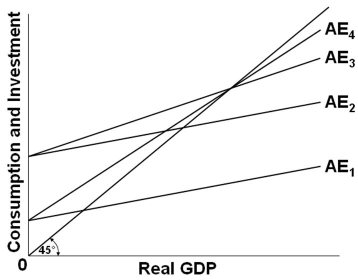
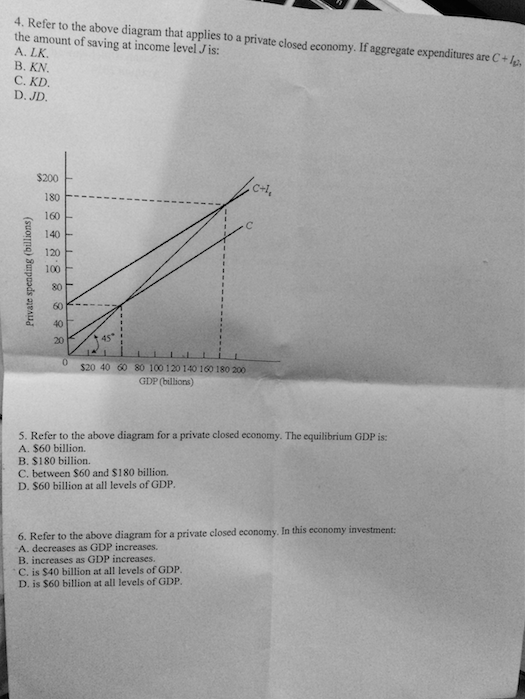
Multiplier and Accelerator - MA Economics Karachi University The multiplier is the number by which the change in investment must be multiplied in order to get the In this simplest model of economy, the level of income is determined at a point where the AD The above diagram shows the multiplier effect of an increase in investment on the equilibrium level... Lecture 7 The Multiplier | Intermediate Macroeconomics 11.4 Open Economy Multiplier. Moreover, the characteristics of the special case assumed by the classical theory happen not to be those of the economic society in which we actually live, with the result that its teaching is misleading and disastrous if we attempt to apply it to the facts of experience. Explain why the multiplier for an open economy is smaller... - Quora In an open economy money leaves, so within the economy being considered the multiplier effect is smaller. For example imagen your working in a small town. If you earn 1 dollar you might save 20 cents and spend 80 cents the next person in the town will save 16 cents and spend 64 cents and so on. June | 2012 | PurpleCutie2013's Blog | Mixed economy 19. Refer to the above diagram that applies to a private closed economy. If aggregate expenditures are C + Ig2, the amount of saving at income level J is Type: A Topic: 2 E: 177 MA: 177. 29. If at some level of GDP the economy is experiencing an unintended decrease in inventories
Agricultural ECONOMICS. The Use of Multipliers in Economic Impact... The multiplier is the relationship between some change in an economy and the succeeding It is also important to not confuse the multiplier with turnover. Turnover refers to the number of rounds 5 5 The multipliers in this report are provided for general information only and may be compared with...
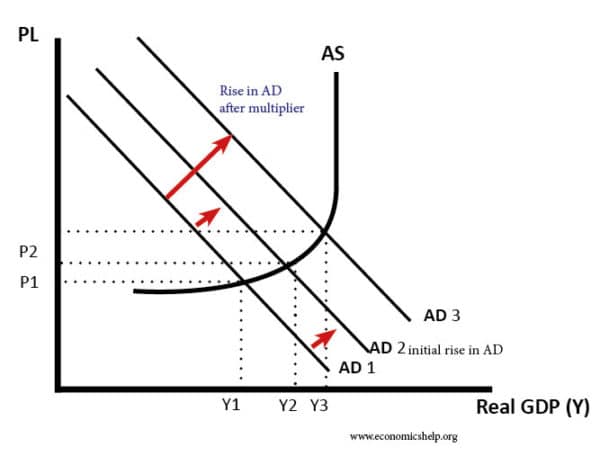
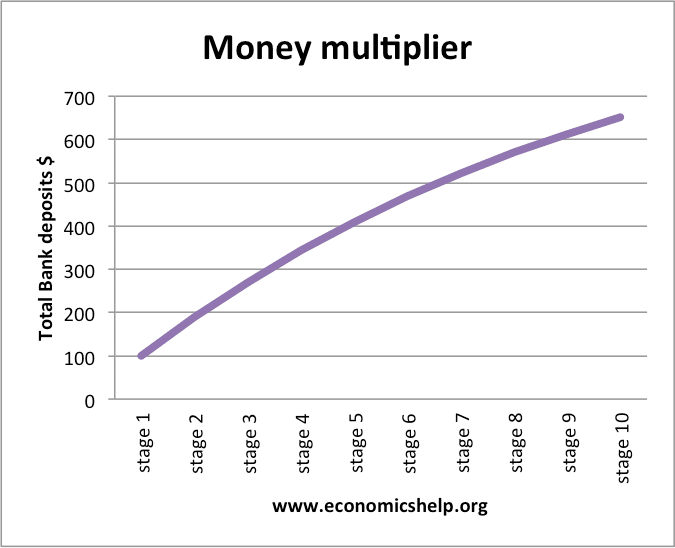
The multiplier effect - Economics Help The fiscal multiplier effect occurs when an initial injection into the economy causes a bigger final increase in national income. In this case, the multiplier effect is 1.33. Multiplier effect using AD/AS diagram. The initial increase in AD (aggregate demand) causes a rise in output to Y2.
Econ chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram. The multiplier in this economy is Suppose the economy is operating at its full-employment-noninflationary GDP and the MPC is .75. The federal government now finds that it must increase spending on military goods by $21 billion in response to deterioration in the international...
Keynes' Theory of Investment Multiplier (With Diagram) Keynes, however, propounded the concept of multiplier with reference to the increase in total income, direct as In our above analysis of the multiplier process we have taken a closed economy, that is, we Diagrammatic Representation of Multiplier: The level of national income is determined by the...
Spending Multiplier Calculator | Formula The spending multiplier calculator is a tool that lets you calculate the spending multiplier using marginal propensity to consume (MPC) or marginal propensity to save (MPS). In this article, you will find out what the spending multiplier is, discover the investment spending multiplier formula, and...
Chapter 13 CORE Economy Notes - ECON Multiplier... - StuDocu Multiplier Mechanism Example: If k = 1/(1 - 0.5) = 2, this means that the size of the multiplier is 2, and also that half of any The diagram to the left simply shows a household's wealth. Broad wealth, I believe in this case, means someones current level of wealth + the level of wealth they expect in the...
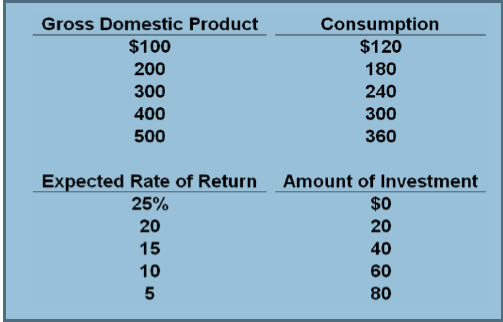
PDF Chapter 4 | 6. Refer to the above diagram. The vertical intercept Use the following to answer questions 5-6: 5. Refer to the above diagram. 20. If a $200 billion increase in investment spending creates $200 billion of new income in the first round of the multiplier process and $160 billion in the second round, the multiplier in the economy is
The Multiplier Effect - Intelligent Economist In other words, the multiplier effect refers to the increase in final income arising from any new injections. Injections are additions to the economy From the diagram above we can see, that an increase in government spending would shift the Aggregate Demand (AD) curve from AD1 to AD2.
The Multiplier - Short Question Answers | tutor2u The economy is currently £3 billion below full-employment level of national income. We are told that an injection of £1 billion is needed to close this gap. If the multiplier is 3 then the marginal propensity to save must be 1/3 and the marginal propensity to consume must be 2/3. Question 2.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Macro Economics... - Learn CBSE Diagrammatical representation, In the above mentioned diagram, aggregate It refers to the point that has come to be established under the given condition of aggregate demand and The value of investment multiplier varies between unity and infinity. This can be proved as follows, When MPC = 0
Refer to the above diagram The multiplier in this economy is... If aggregate expenditures in this economy are (C+ Ig+ Xn2), then the equilibrium levels of GDP and aggregate expenditures respectively will be: A) Answer: DType: G Topic: 3 E: 181 MA: 181 122.Refer to the above diagram. The change in aggregate expenditures as shown from (C+ Ig+ Xn2) to (C+ Ig...
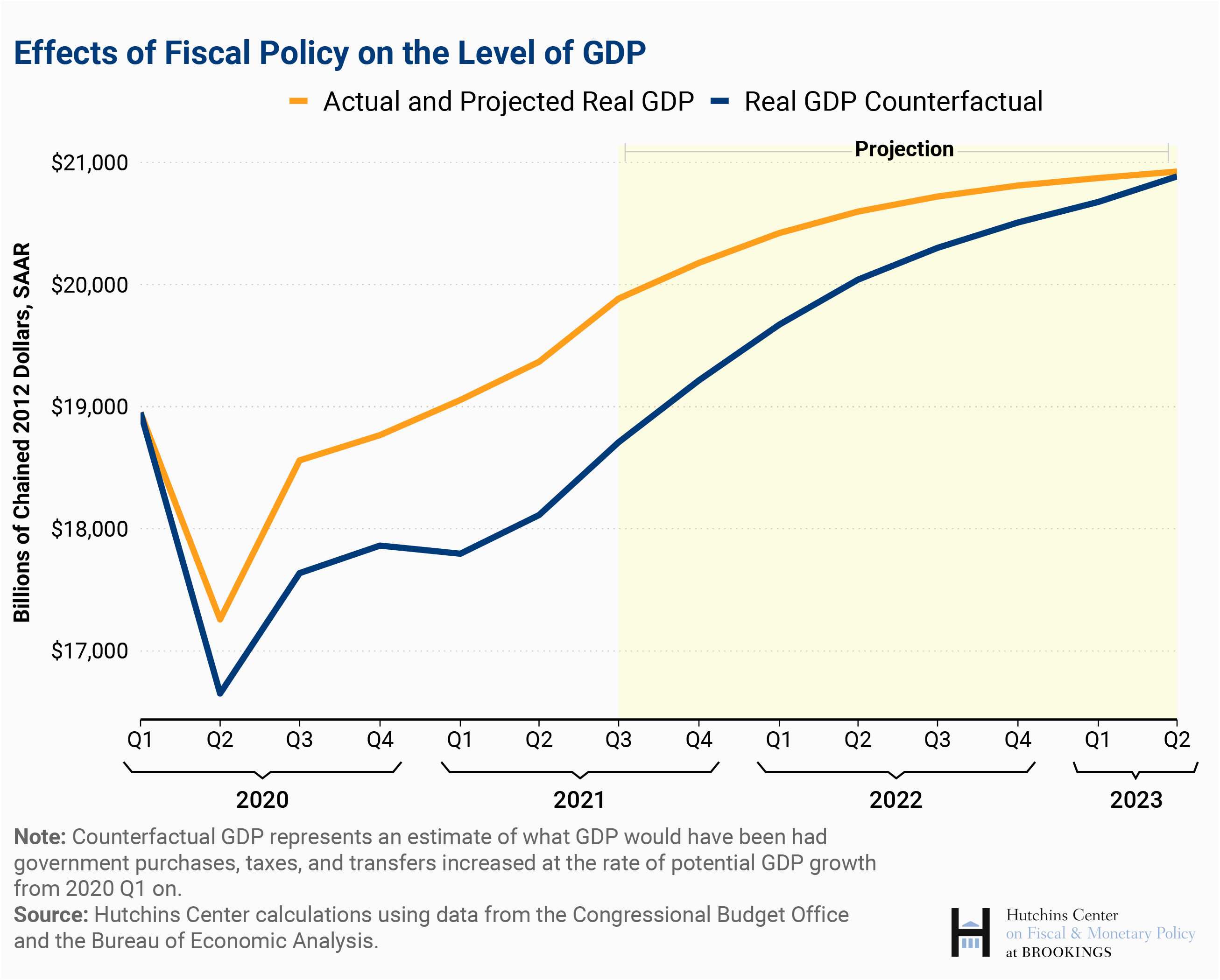
Homework for Chapter 10 10-2 (Key Question) What is the ... 8? The decrease in real GDP in the diagram is greater than the initial decline in aggregate expenditures because of the multiplier effect.9 pages
Principles of Economics/Multipliers - Wikibooks, open books for an... The multiplier effect refers to the idea that an initial spending rise can lead to even greater increase in national income. In other words, an initial change in aggregate demand can cause a further change in aggregate output for the economy.
The Multiplier Effect Definition | Example and Formula | BoyceWire The multiplier effect refers to how an initial injection of money into the circular flow of income can stimulate economic activity in excess of the initial investment. Therefore, the multiplier is 5 - which means the initial $1 million investment would provide a $5 million stimulus to the wider economy.
Keynesian Multiplier - Overview, Components, How to Calculate The Keynesian Multiplier is an economic theory that asserts that an increase in private consumption expenditure, investment expenditure, or net government Keynesian Economic Theory. In 1936, economist John Maynard Keynes published a text that would change the course of economic thought.
Multiplier (economics) - Wikipedia In macroeconomics, a multiplier is a factor of proportionality that measures how much an endogenous variable changes in response to a change in some exogenous variable. For example, suppose variable x changes by k units, which causes another variable y to change by M × k units.






/dotdash_Final_Economic_Growth_2020-01-a0ace0fdcf3142ae94494dcfd9986daa.jpg)







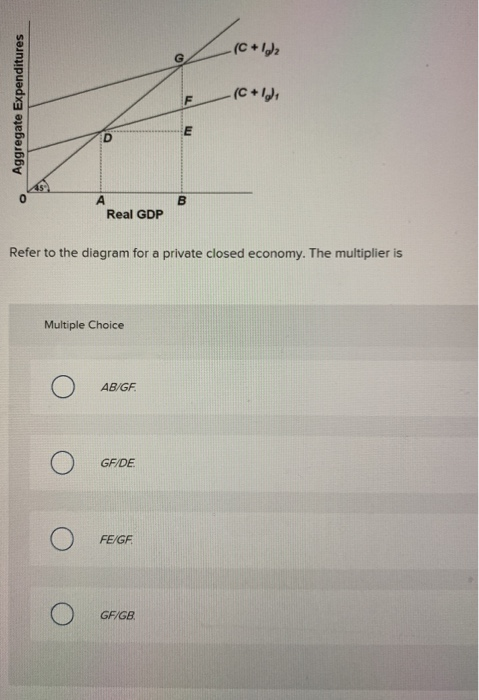
0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is"
Post a Comment