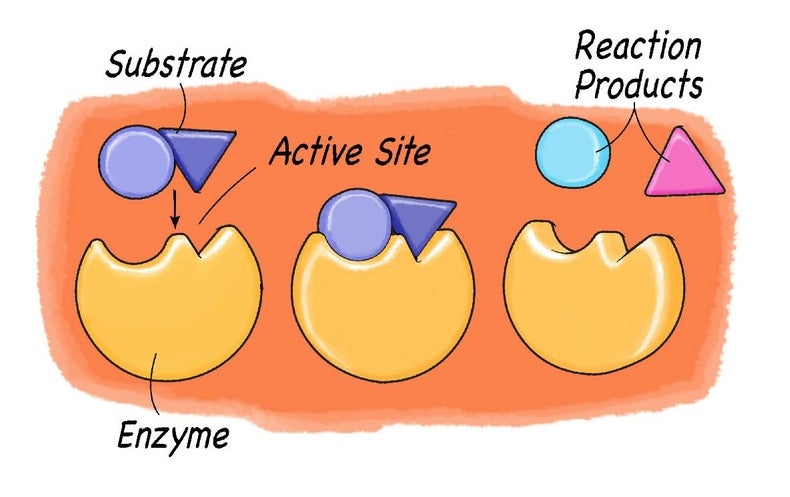
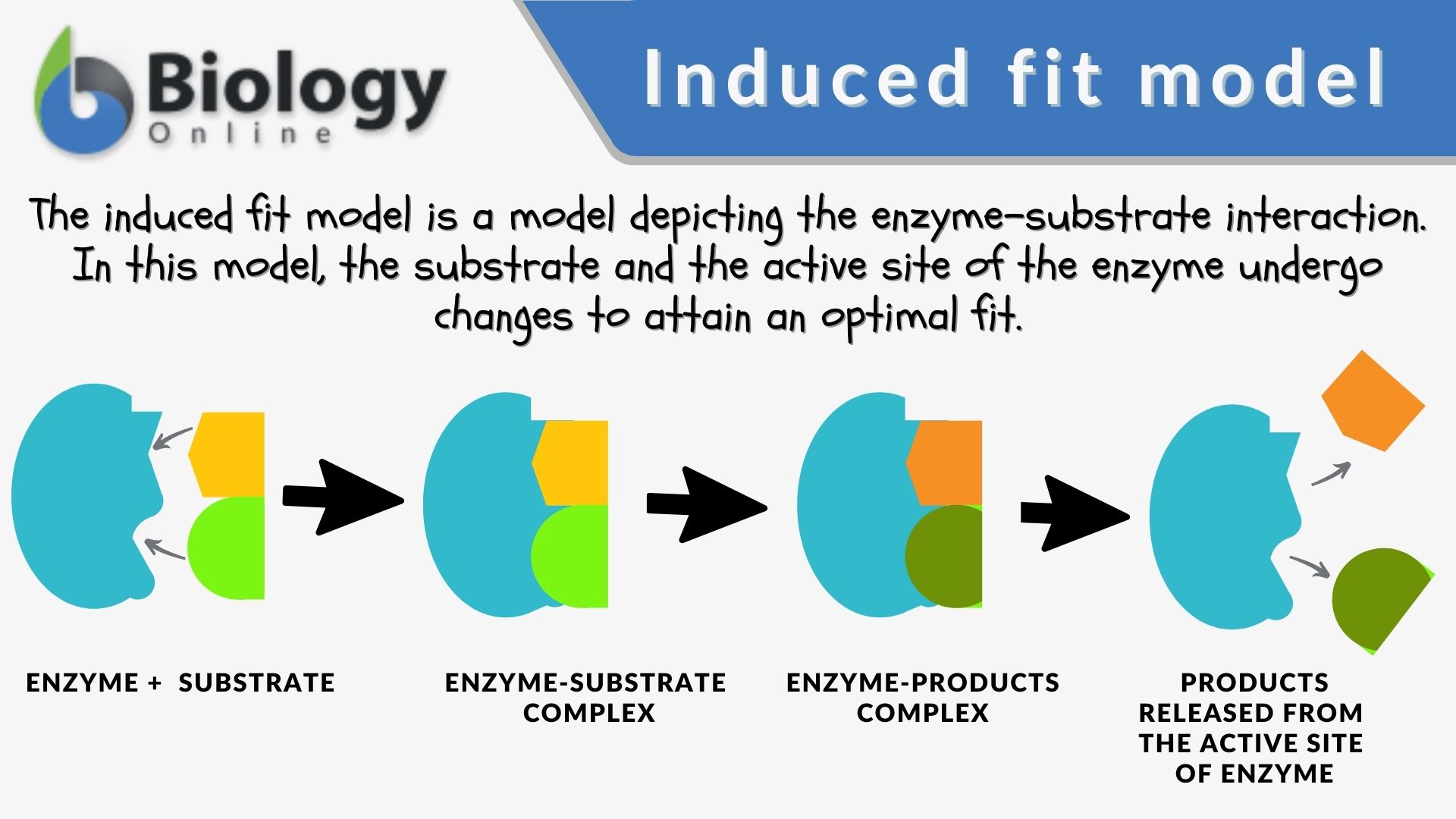
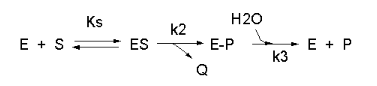
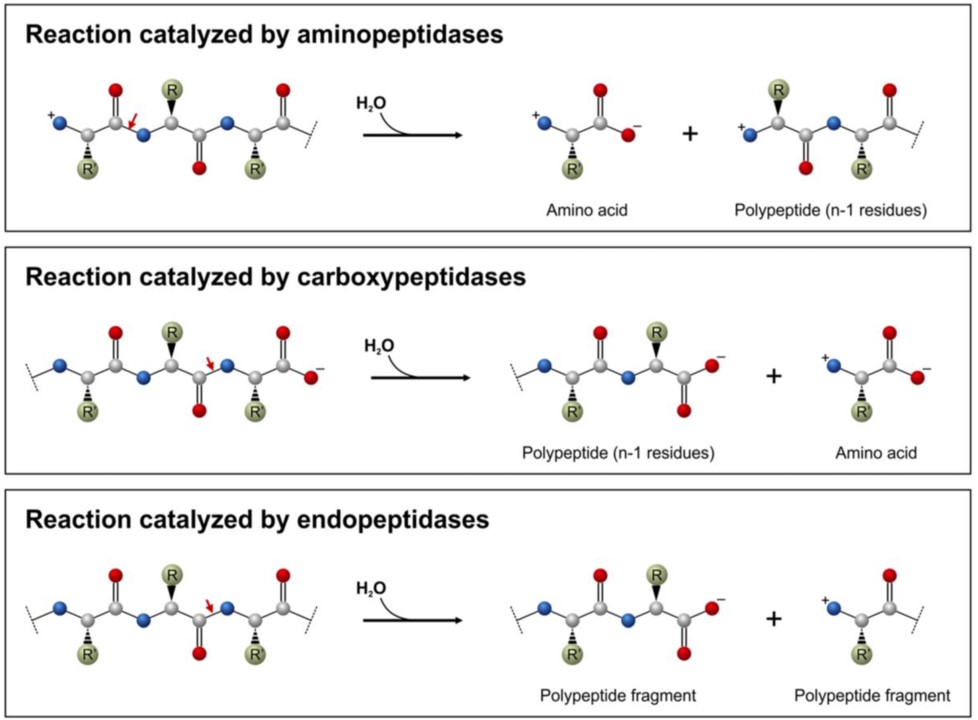
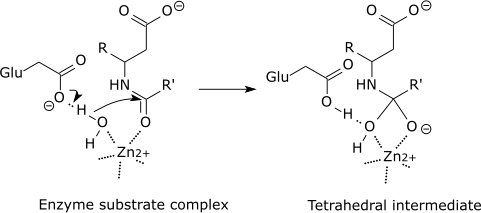
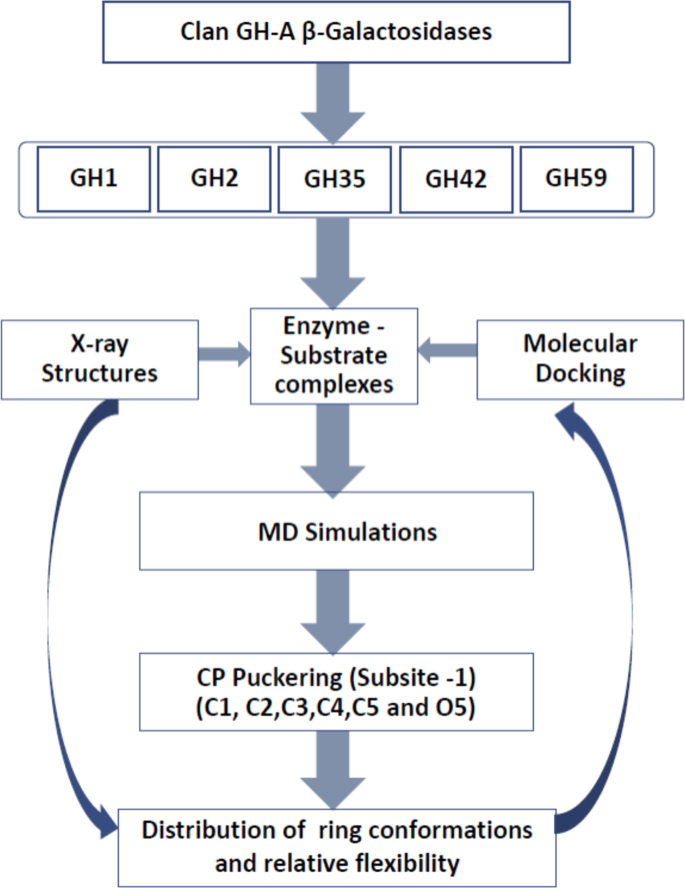
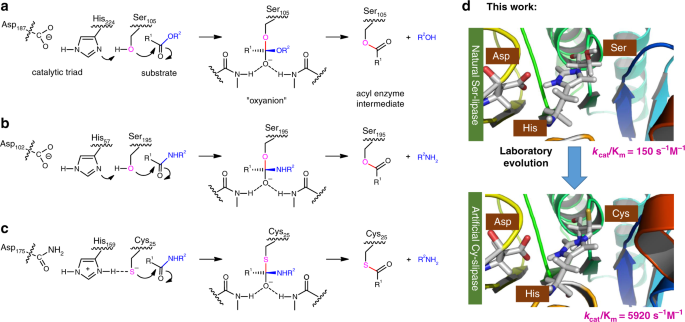
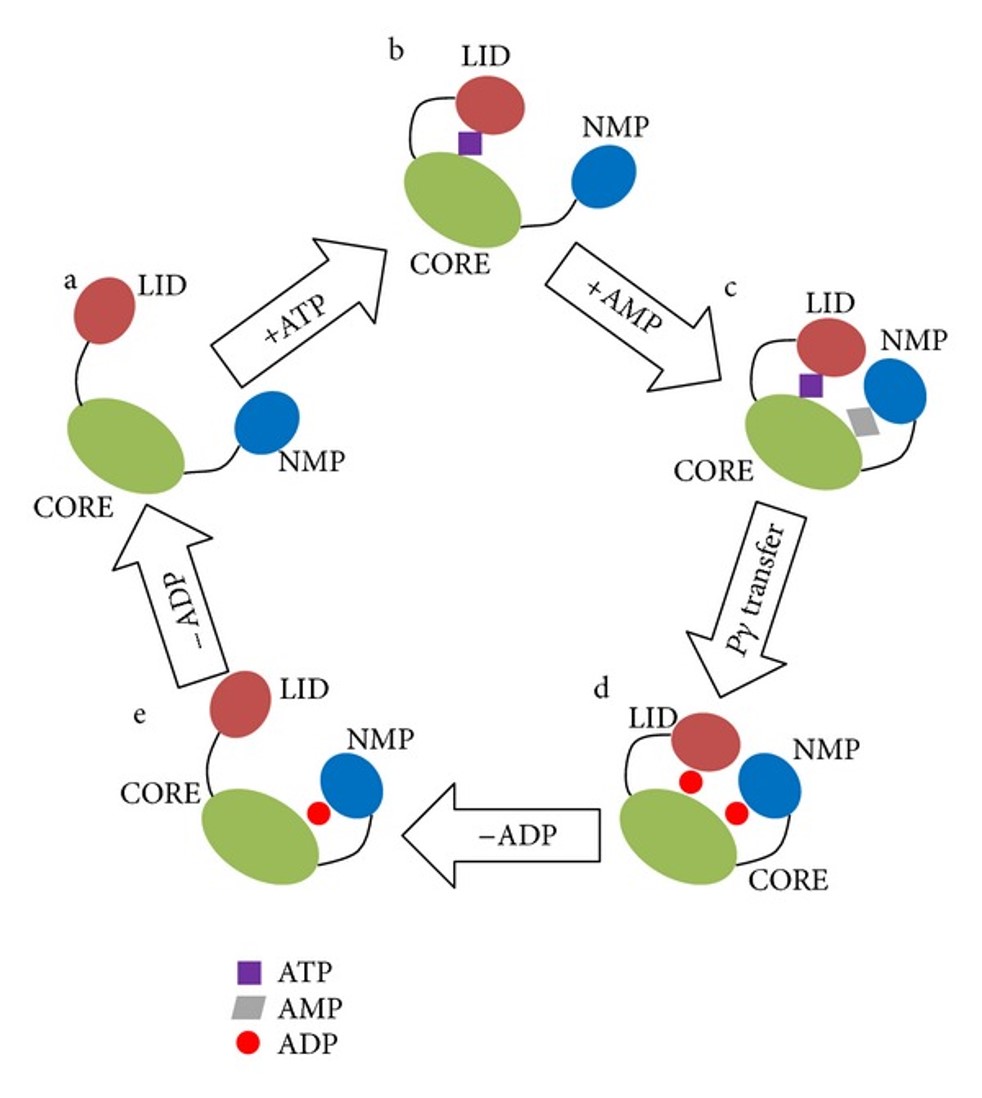
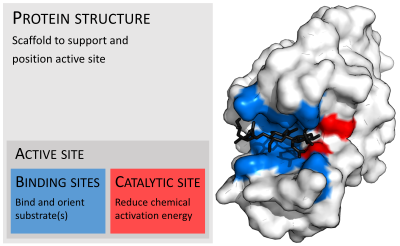
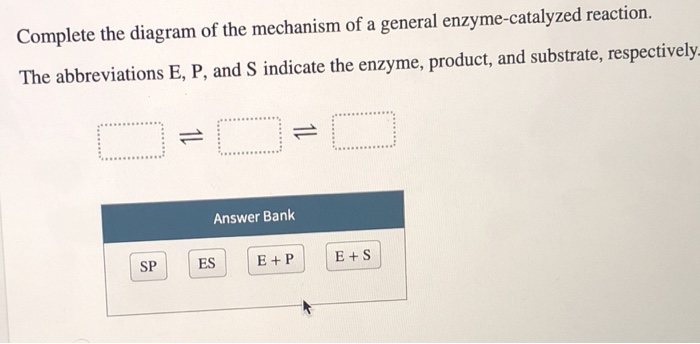
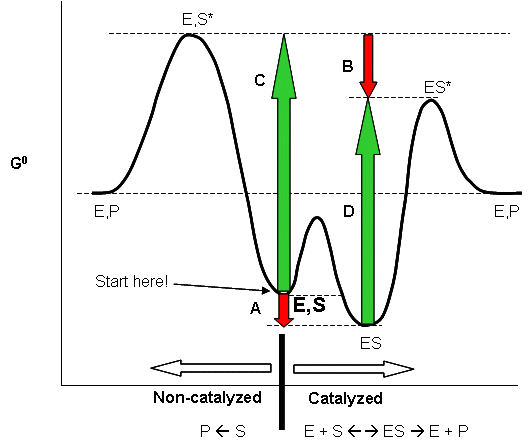
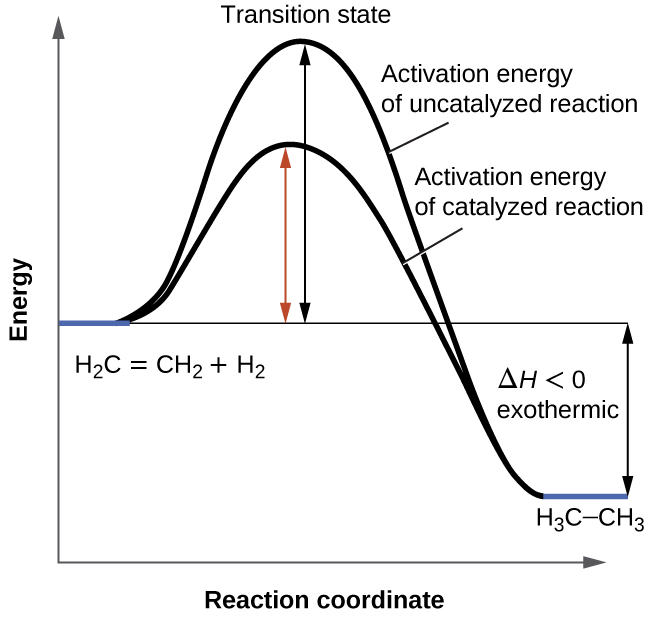
36 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
answered: read the instruction 1. Read the whole article ... 2. Write a speech transcript which should focus on the Biomolecular Networks part (Pg. 12-14). 3. You should write a brief introduction and explanation for the Biomolecular Networks Root-TRAPR: a modular plant growth device to visualize ... The Root-TRAPR system comprises of two major components—an internal root growth chamber (Fig. 2c) and an external structural frame (Fig. 2d). The internal root growth chamber has a transparent viewing configuration from either top or bottom sides through a transparent acrylic sheet and microscope slide, respectively, to facilitate plant root structure observation.
EOF
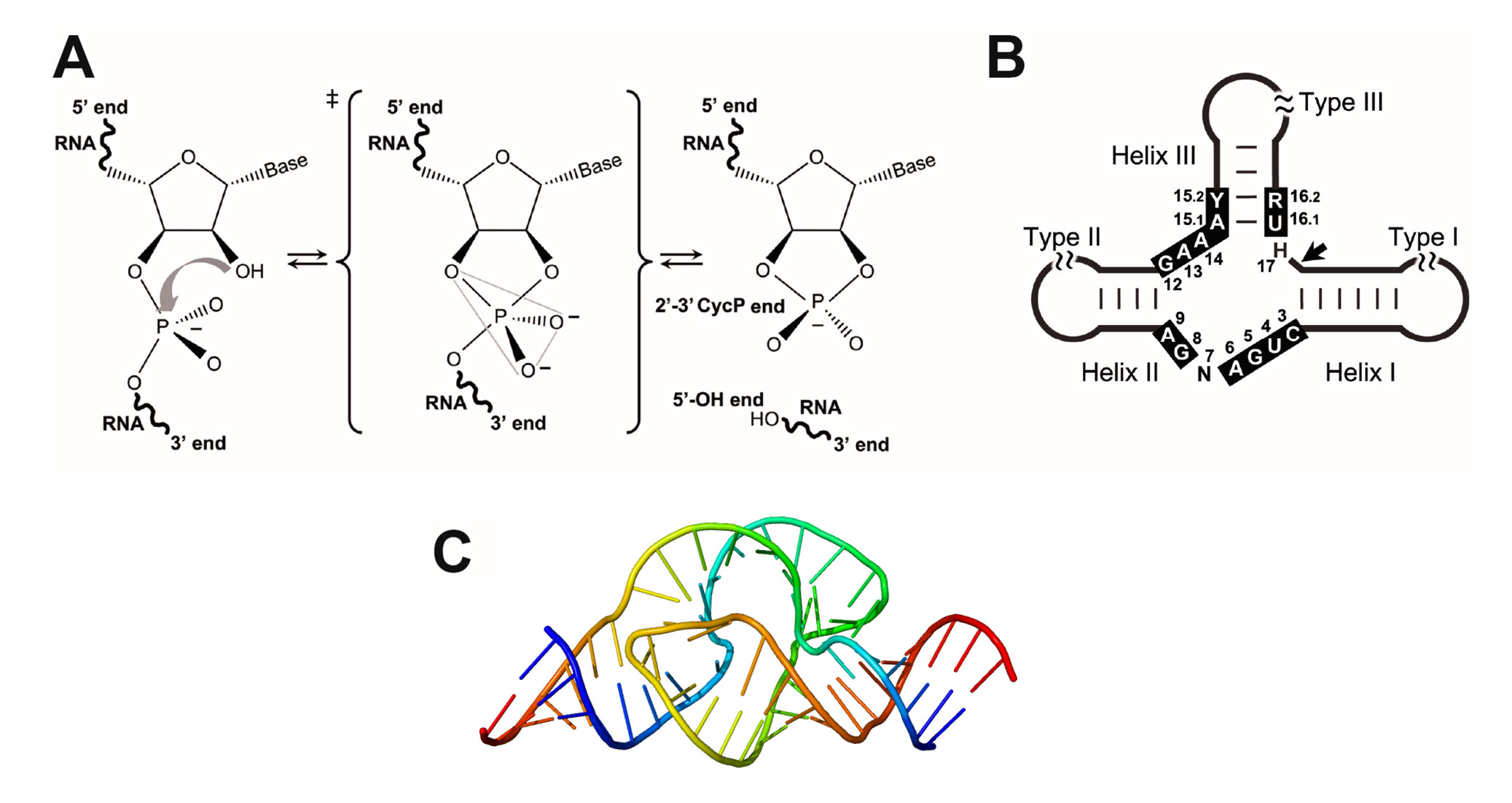
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Amino acid - Wikipedia Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−NH + 3) and carboxylate −CO − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N); in addition sulfur (S) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (Se) in the less common ... Photosynthesis - Wikipedia Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities.Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water - hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek ...
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Photosynthesis - Wikipedia Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities.Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water - hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek ... Amino acid - Wikipedia Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−NH + 3) and carboxylate −CO − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N); in addition sulfur (S) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (Se) in the less common ...
















0 Response to "36 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment