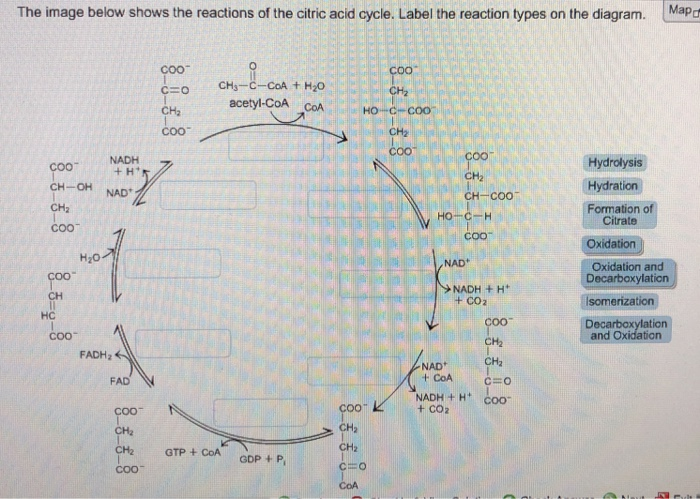
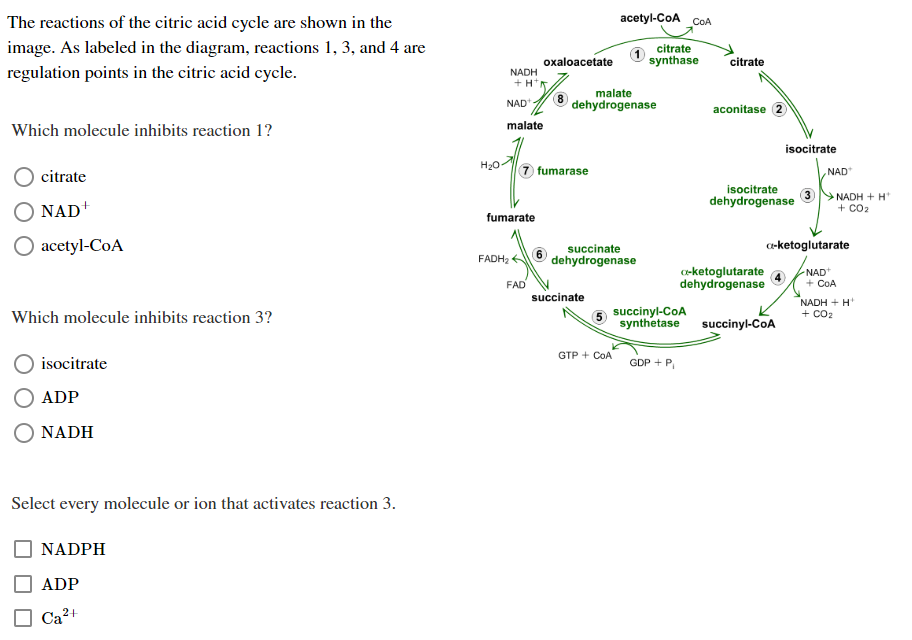
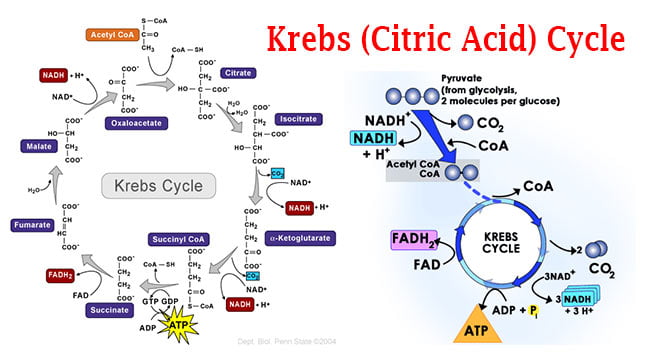
34 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.
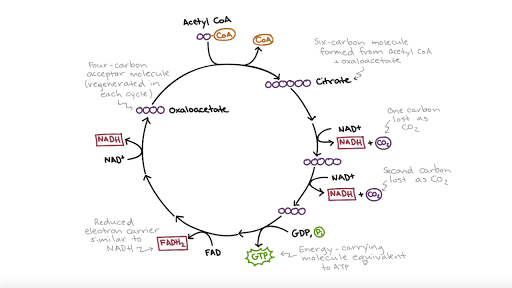
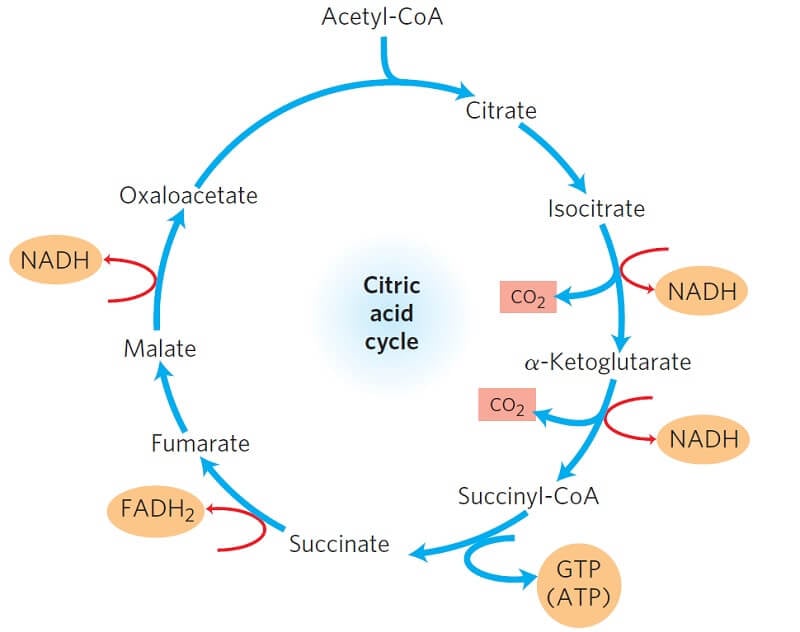
The Krebs cycle has 9 main reactions, which happen quickly in succession. The image below shows these reactions. Note that citrate is the first molecule created after acetyl CoA is added. This is why the Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle. The products of the cycle are in the image above.
Glycolysis Location images, similar and related articles aggregated throughout the Internet.
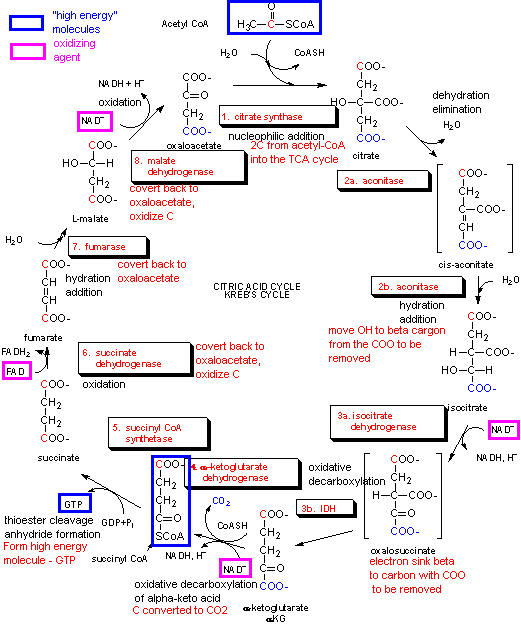
Decarboxylation which will be observed twice more in the citric acid cycle is the removal of the carboxylic acid group and subsequent conversion into CO 2 . This oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid is catalyzed by the enzyme complex - pyruvate dehydrogenase. The term complex is used because three enzymes and five coenzymes are involved.
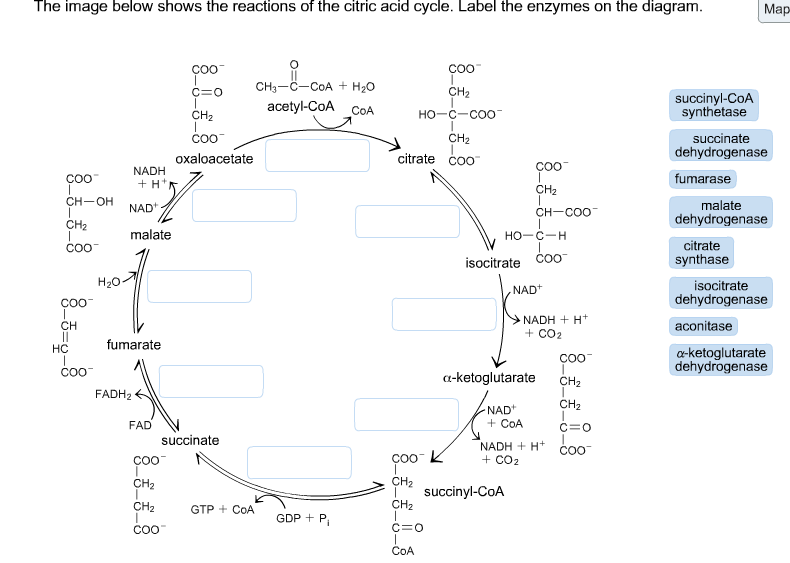
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.
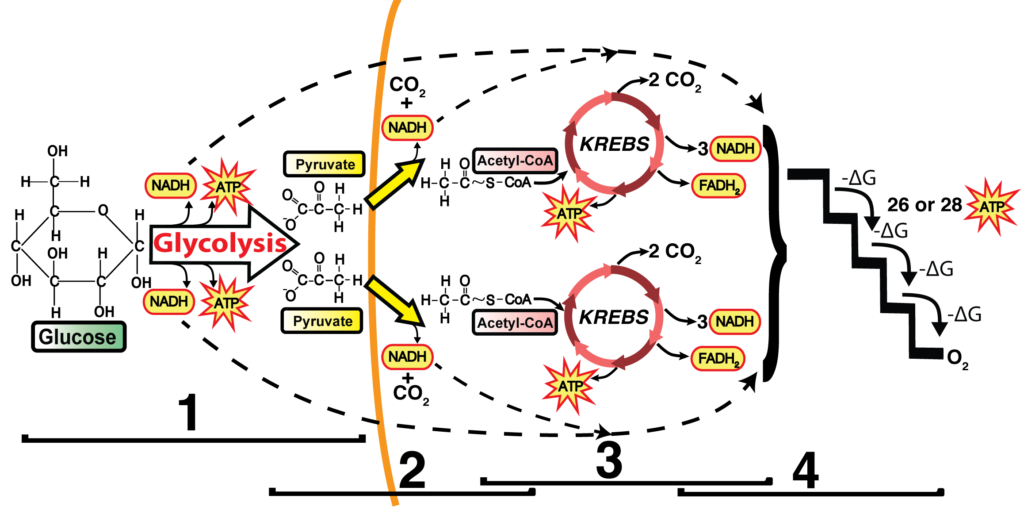
3. The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules. More than three-quarters of the original energy in glucose is still present in the two molecules of pyruvate. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where enzymes of the citric acid cycle complete the oxidation of the organic fuel to carbon ...
This complex acts on the succinate produced by the citric acid cycle, and converts it to fumarate. This reaction is driven by the reduction and oxidation of FAD (Flavin adenine dinucleotide) along with the help of a series of Fe-S clusters. These reactions also drive the redox reactions of quinone.
2. Krebs's Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle/TCA Cycle: Citric acid cycle also known as tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is named after the scientist Sir Hans Krebs (1900-1981) who discovered it. He proposed the key elements of this pathway in 1937 and was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for the discovery in 1953.
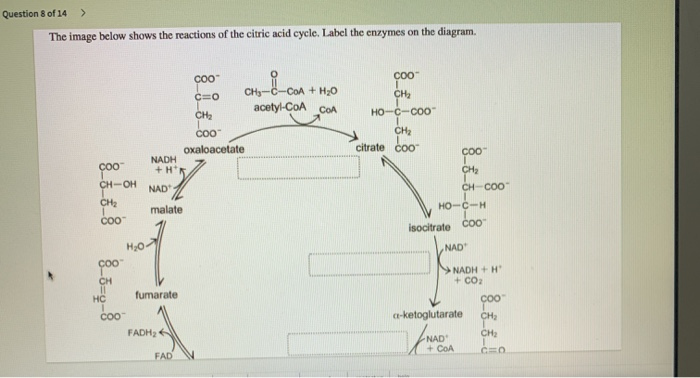
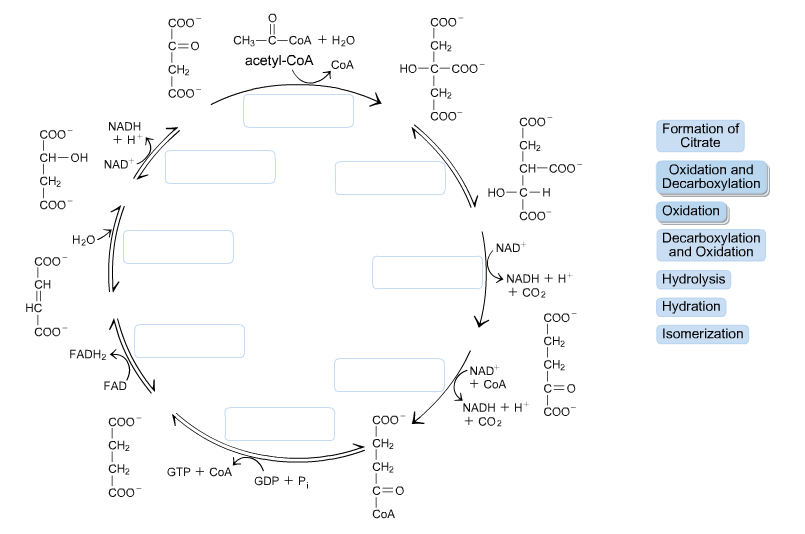
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram..
The 4 steps of cellular respiration can be seen in the image below. The first step occurs outside of the mitochondria. This involves the breakdown of glucose, lipids, or amino acids. This step is symbolized here with "Glycolysis" only. Remember that there are other ways to generate pyruvate and intermediates the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle).
Krebs cycle Definition. The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the mitochondria resulting in oxidation of acetyl CoA to release carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms that later lead to the formation of water.
The net reactions for glycolysis (Equation 5) and the citric-acid cycle (Equation 7) are shown below. (Note: In the equations below, glucose and the carbon compounds into which glucose is broken are shown in red; energy-currency molecules are shown in green, and reducing agents used in the synthesis of ATP are shown in blue.)
NAD participates in many redox reactions in cells, including those in glycolysis and most of the reactions in the citric acid cycle of cellular respiration. This site shows three examples of oxidoreductase enzymes (an oxidase that uses molecular oxygen as the electron acceptor) that use NAD as a cofactor to catalyze a dehydration reaction.
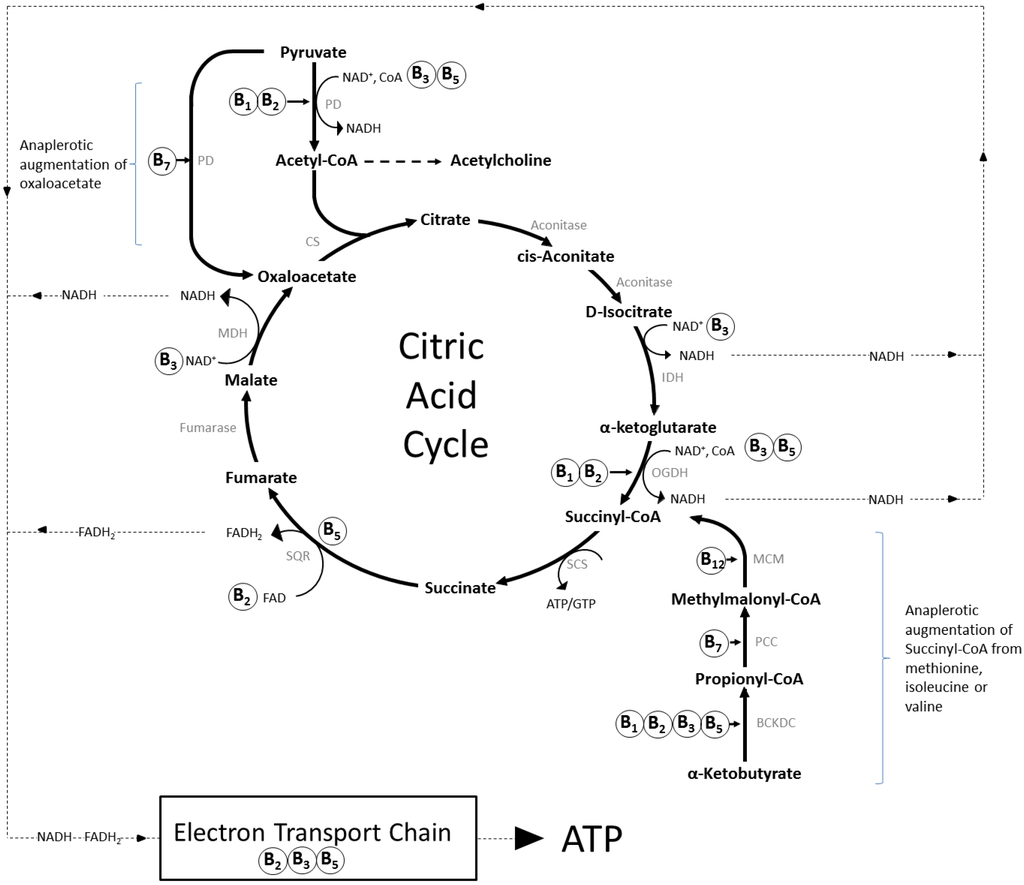
In aerobic glucose metabolism, the oxidation of citric acid uses ADP and Mg²+, which will increase the speed of reaction: Iso-citric acid + NADP (NAD) — isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) = alpha-ketoglutaric acid. In the Krebs cycle (the citric cycle), IDH1 and IDH2 are NADP+-dependent enzymes that normally catalyze the inter-conversion of D ...
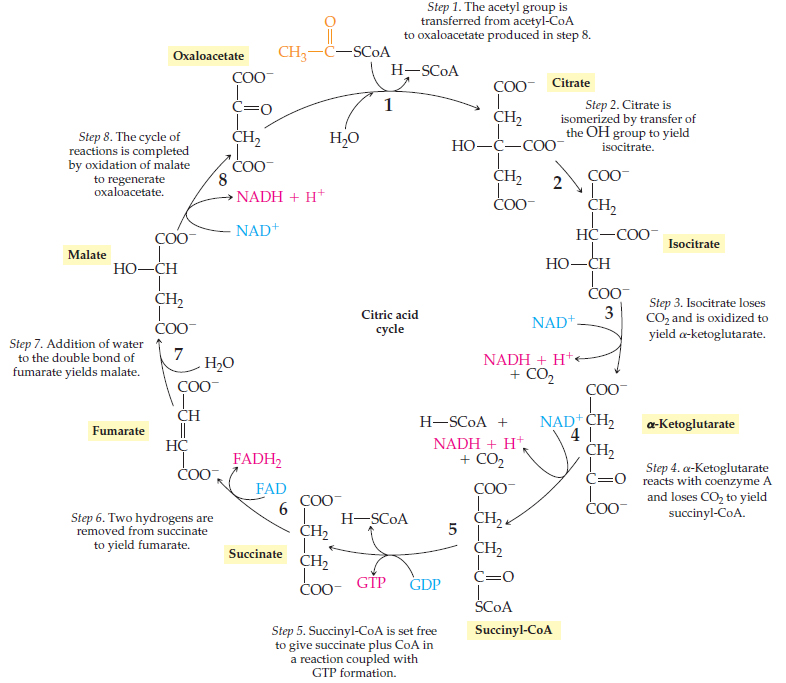
Step 1. In the first step of the citric acid cycle, acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Step 2. In the second step, citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate.
The acetyl group enters a cyclic sequence of reactions known collectively as the citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid [TCA] cycle). The cyclical design of this complex series of reactions, which bring about the oxidation of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide and water, was first proposed by Hans Krebs in 1937.
Below is an image of a worksheet I use in my Biology classes to help students learn the ATP Cycle to mastery. Right click the image below to download the worksheet. Fill it out as you watch the YouTube video "ATP and ADP: Chemical Energy for Cells" and explain what is happening in each step.
C) the citric acid cycle D) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA E) the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP Answer: B Topic: Concept 9.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 9) Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O 2) is present or absent? A) electron transport B) glycolysis C) the citric acid cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the Tricarboxylic Acid or Citric Acid Cycle, was discovered by Dr H. A. Krebs. The TCA cycle is the central component of the cellular respiration. The starting material is acetyl CoA (produced by pyruvate oxidation) and energy is harvested in the form of NADH, FADH2, and ATP.
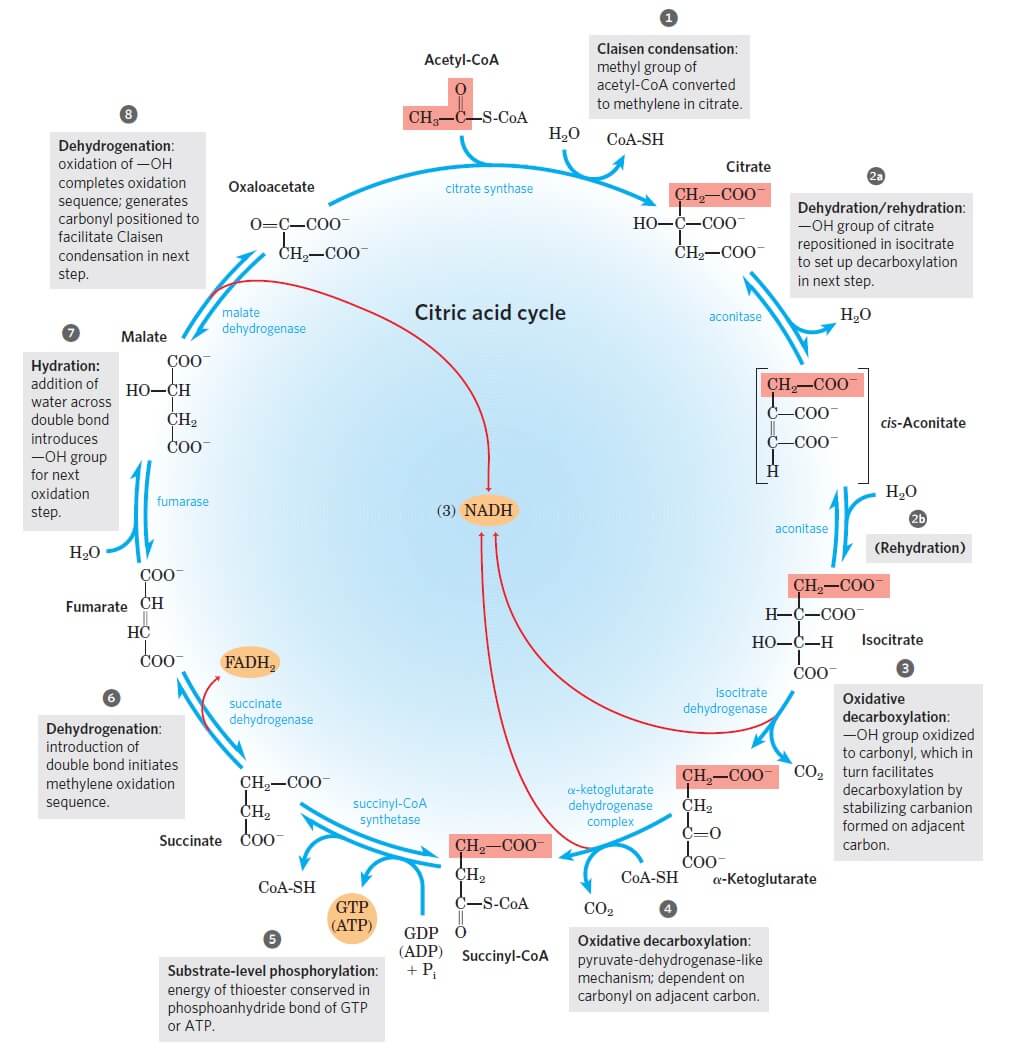
Reaction 2: Acontinase. The next reaction of the citric acid cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme acontinase. In this reaction, a water molecule is removed from the citric acid and then put back on in another location. The overall effect of this conversion is that the -OH group is moved from the 3' to the 4' position on the molecule.
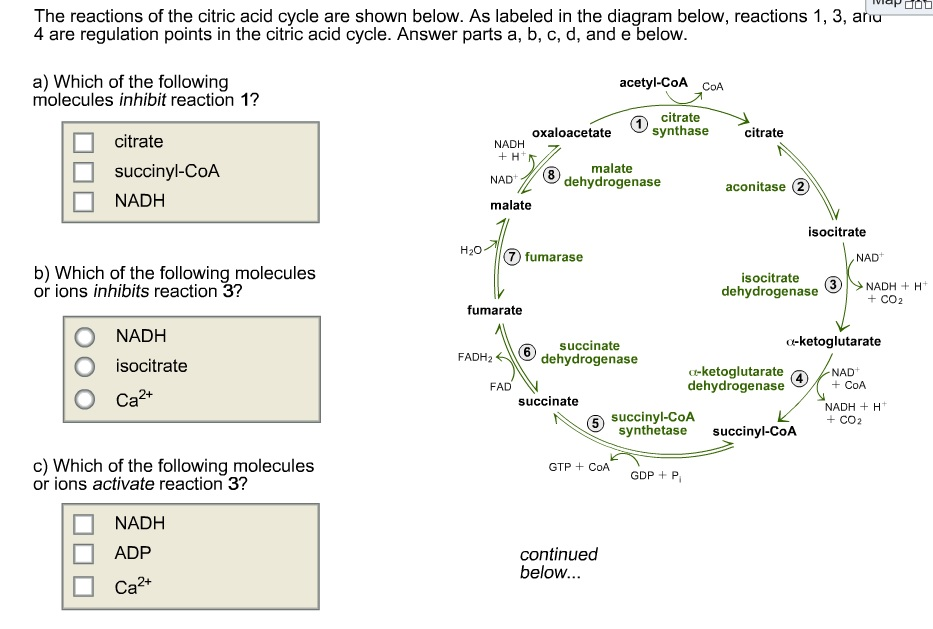
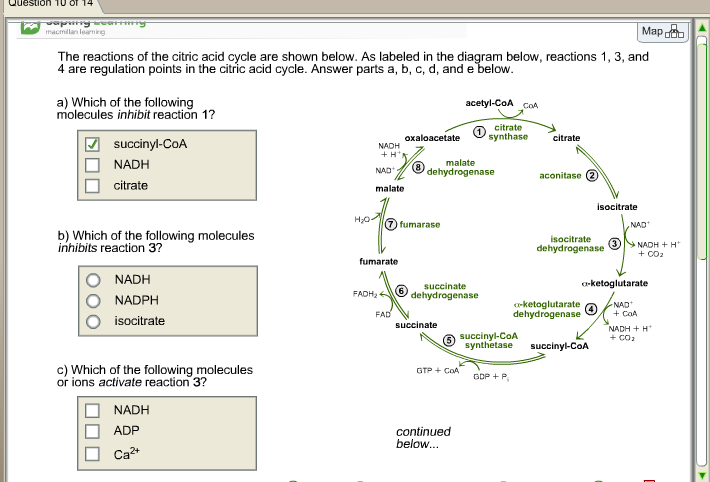
The reaction of the citric acid cycle that produces an ATP equivalent (in the form of GTP) by substrate level phosphorylation is the conversion of: succinyl-CoA to succinate. Citrate synthase and the NAD+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase are two key regulatory enzymes of the citric acid cycle.
The PDC and citric acid cycle reaction occur in the mitochondrial matrix. ... some of the enzymes in the citric acid cycle have both cytoplasmic and mitochondrial variants. ... This is a key catalytic residue which act as a general base that accepts a proton from succinate in the reaction. The top image below show a very general and abbreviated ...
16. Reactions of the citric acid cycle Page: 610 Difficulty: 2 Ans: E The reaction of the citric acid cycle that is most similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex-catalyzed conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA is the conversion of: A) citrate to isocitrate. B) fumarate to malate. C) malate to oxaloacetate. D) succinyl-CoA to succinate.
The net effect of the eight steps of the citric acid cycle is to _____ ... The image below shows the reactions of the beta-oxidation pathway. Label the reaction types on the diagram. Oxidation, Hydration, Oxidation, Cleavage.
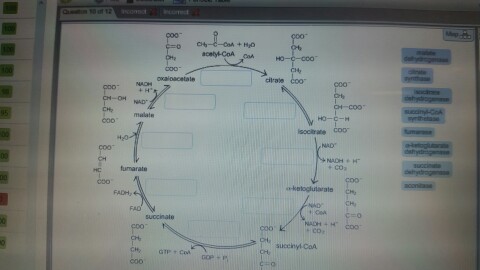
As labeled in the diagram below reaction. Label the enzymes on the diagram. Reactions of the citric acid cycle page. Figure 15 10 each turn of the citric acid cycle produces three nadh and one fadh2 as well as one gtp or atp. The reactions of the citric acid cycle are shown below. The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle.
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. As labeled in the diagram below reaction. View Question 188 chapter 16 the citric acid cycle 13. The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle label the enzymes on the diagram. Keep in mind that most of the reactions are actually reversible as shown in fig.
Similar to the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram., Amino acids would be the developing blocks of proteins, and proteins make up tissues, muscle mass, glands, organs, tendons, enzymes, nails and hair. This places amino acids in a position of primary importance.
As labeled in the diagram below reaction. The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle label the enzymes on the diagram. Show transcribed image text the reactions of the citric acid cycle are shown below. B co2 production c flavin reduction d lipoic acid present in some of the enzyme systems. Detailed diagram of the citric acid ...
Related to the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram., A new discovery has revealed, even so, that women, being a entire, are obtaining enough Folate to prevent NTDs, nonetheless they are still NOT acquiring adequate to help with other health and fitness difficulties, most notably Cervical ...
Home › The Image Below Shows The Reactions Of The Citric Acid Cycle. Label The Enzymes On The Diagram. The Image Below Shows The Reactions Of The Citric Acid Cycle. Label The Enzymes On The Diagram Written By White Thaparme Sunday, October 31, 2021 Add Comment Edit. Abstract.
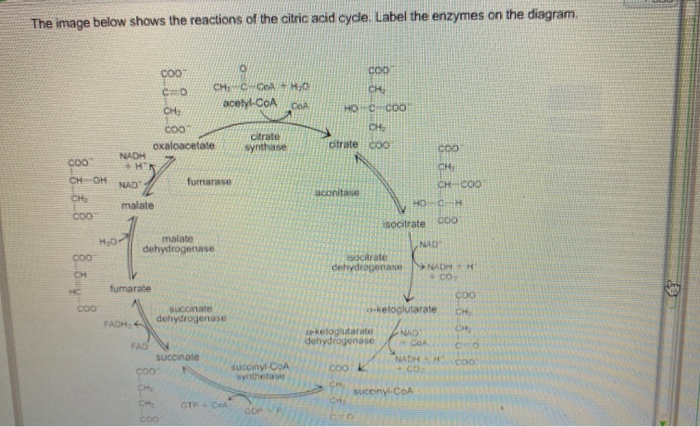
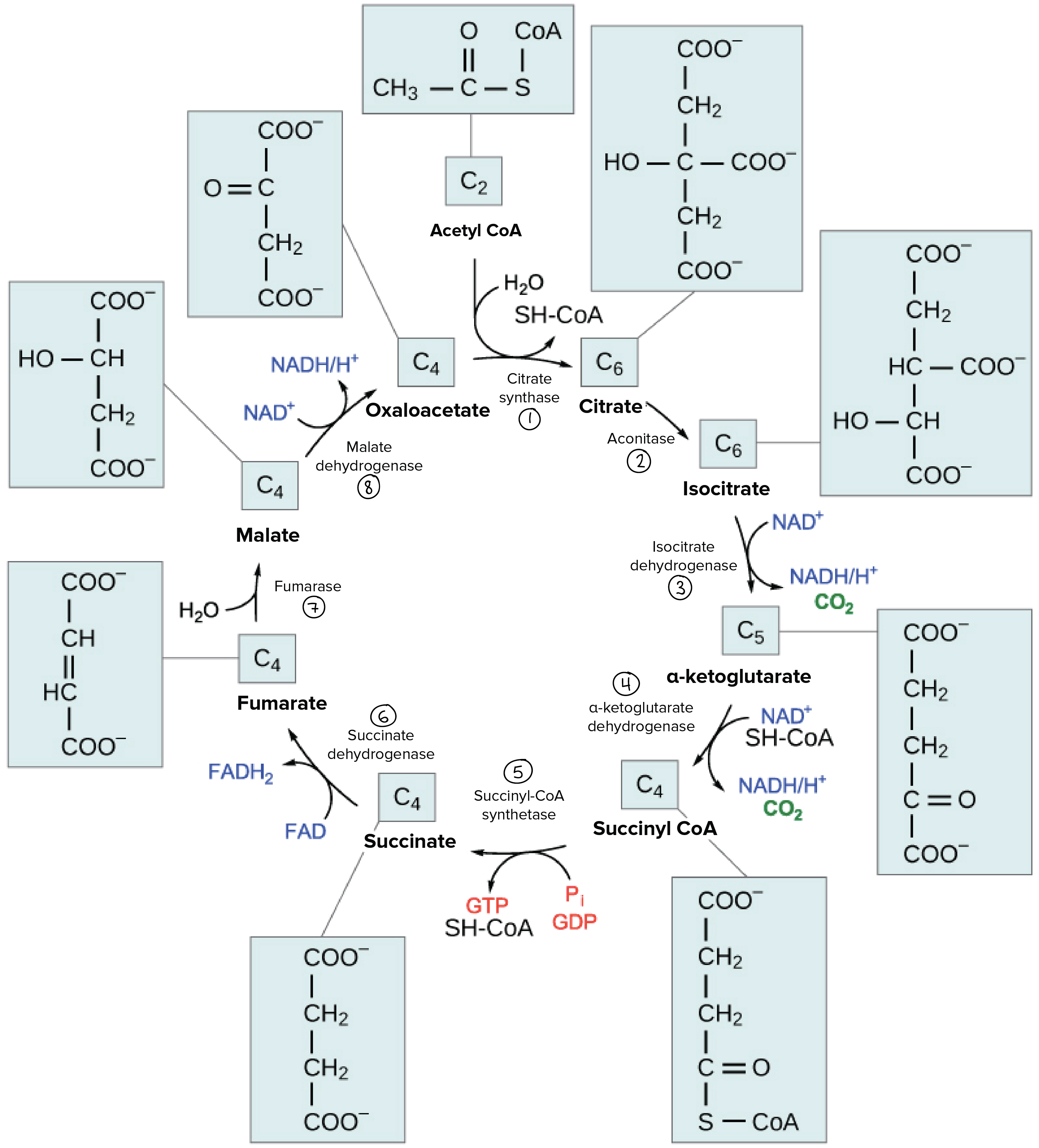
Transcribed image text: The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram, Coo CHECCO HO acetyl-CoA COA coo CH Hoo-coo CH citrate oxaloacetate citrate coo NADH CHOHAD coo CHA CH-coo HOOH fumarase malate COO socitrate coo malate dehydrogenase NAD socitrate hydrogenas NAOH CO fumarate соо -ketoglutarate CH SUCC dehydrogenase FADH NAD kelogiar tu ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 97% (61 ratings) Transcribed image text: The image below shows she reactions of the cltric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram dehydragars coo.









0 Response to "34 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram."
Post a Comment