36 reflection of light diagram
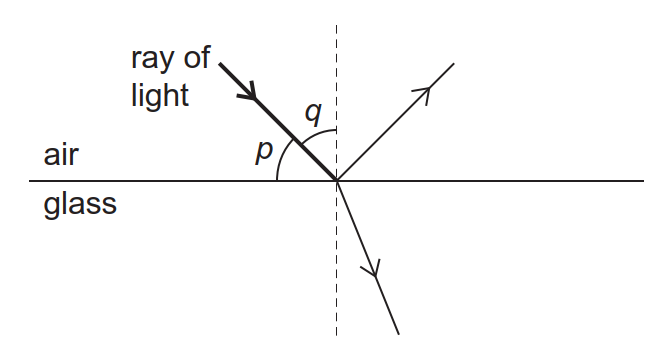
We use the diagram shown below to answer the questions. a) angle of incidence: i = 90 - 56 = 34 °. b) angle of reflection r = i = 34 ° (by the law of reflection) c) q = 90 - r = 90 - 34 = 56 °. d) i + r = 34 + 34 = 68 °. Example 2: A ray of light is reflected by two parallel mirrors (1) and (2) at points A and B.
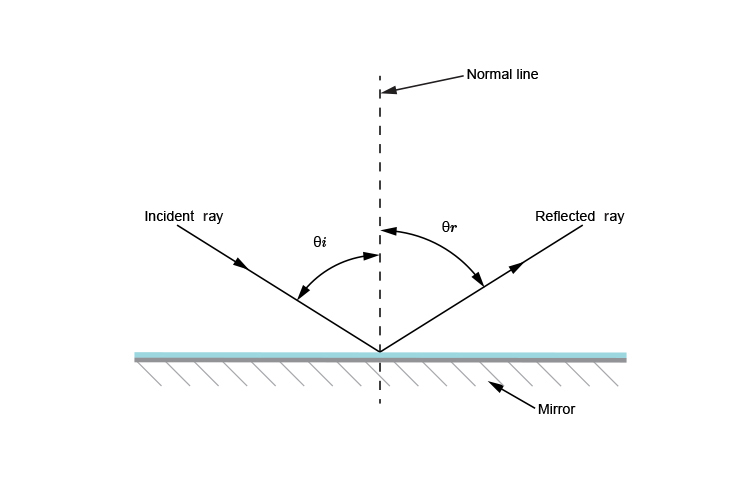
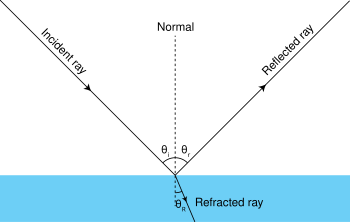
Reflection is the abrupt change in the direction of propagation of a wave that strikes the boundary between two different media. At least some part of the incoming wave remains in the same medium. Assume the incoming light ray makes an angle θiwith the normal of a plane tangent to the boundary. Then the reflected ray
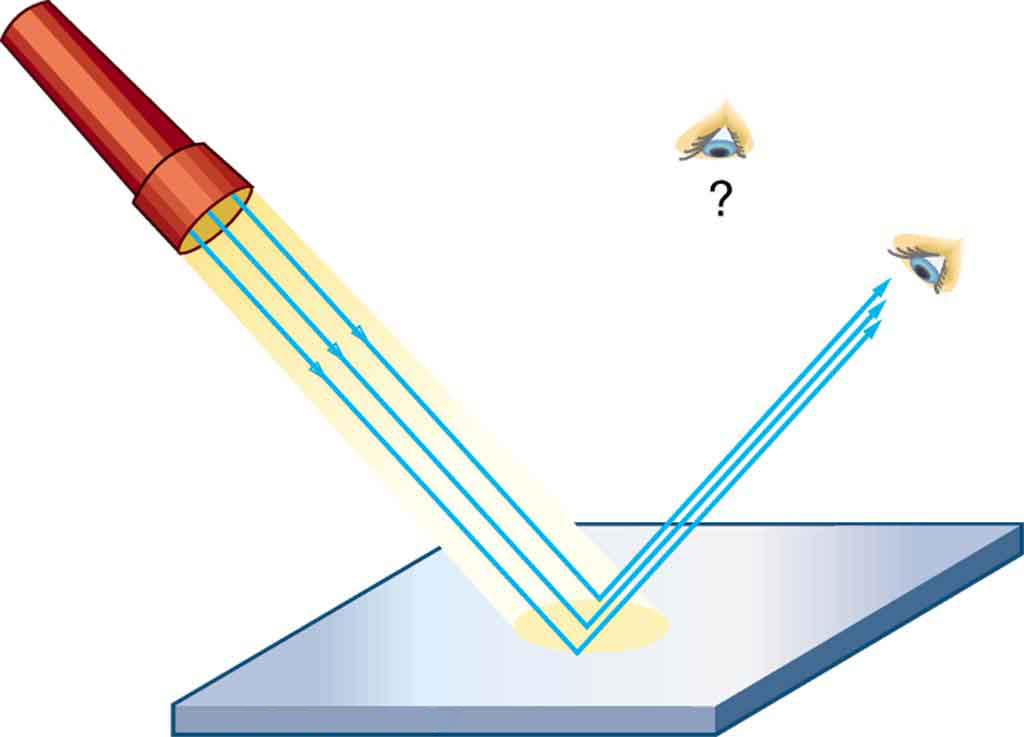
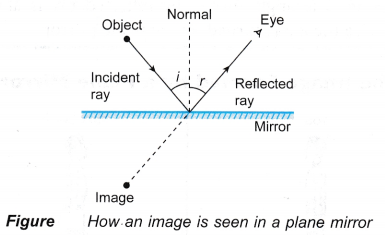
Figure 6: A ray diagram showing the reflection of several rays of light, and the corresponding virtual image. Quick Q1 Construct a ray diagram to show the path of rays that reflect off a plane mirror from the top and bottom of an object to an eye.

Reflection of light diagram
Reflection is enhanced in metals by suppression of wave propagation beyond their skin depths. Reflection also occurs at the surface of transparent media, such as water or glass . Diagram of specular reflection In the diagram, a light ray PO strikes a vertical mirror at point O, and the reflected ray is OQ.
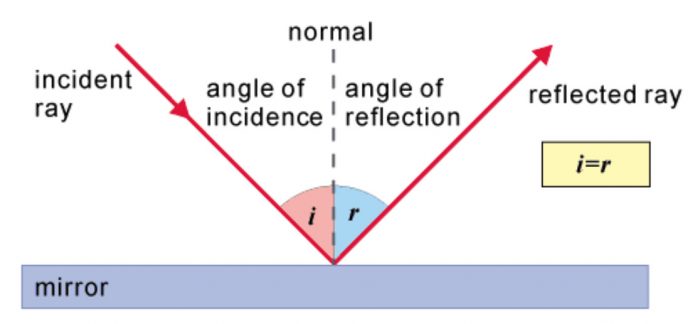
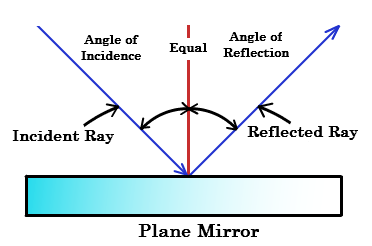
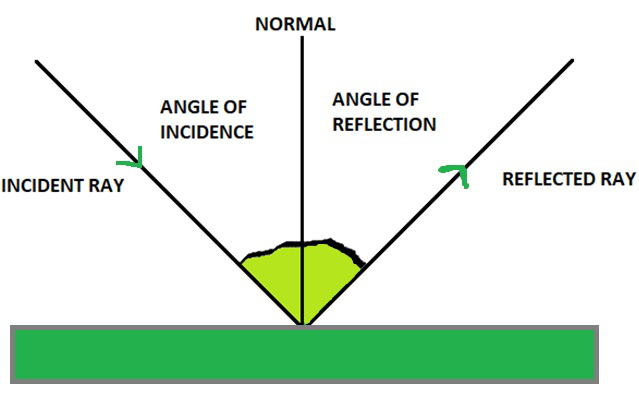
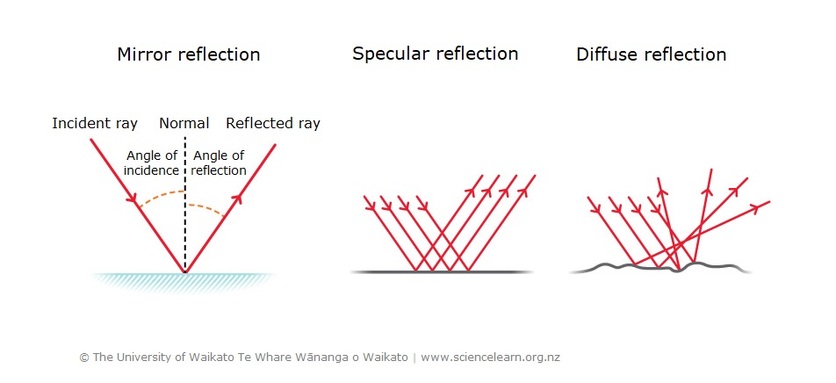
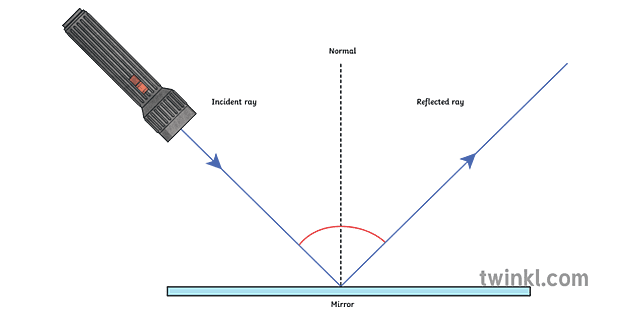
Light is a form of energy Light helps us see objects What is reflection of light? When a ray of light strikes a mirror, it is reflected in a different direction Laws of Reflection There are 2 laws of Reflection The Incident ray, Reflected ray and the Normal, all lie in the same plane The Angle of Incidence is always equal to Angle of Reflection
Reflection of Light Multiple Choice Quiz. Try this as often as you like. You will get a different set of questions each time you attempt this quiz. <= => The diagram shows a ray of light being reflected by a plane mirror. The angle of reflection is: ? 55 o ? 20 o ? 110 o ? 70 ...
Reflection of light diagram.
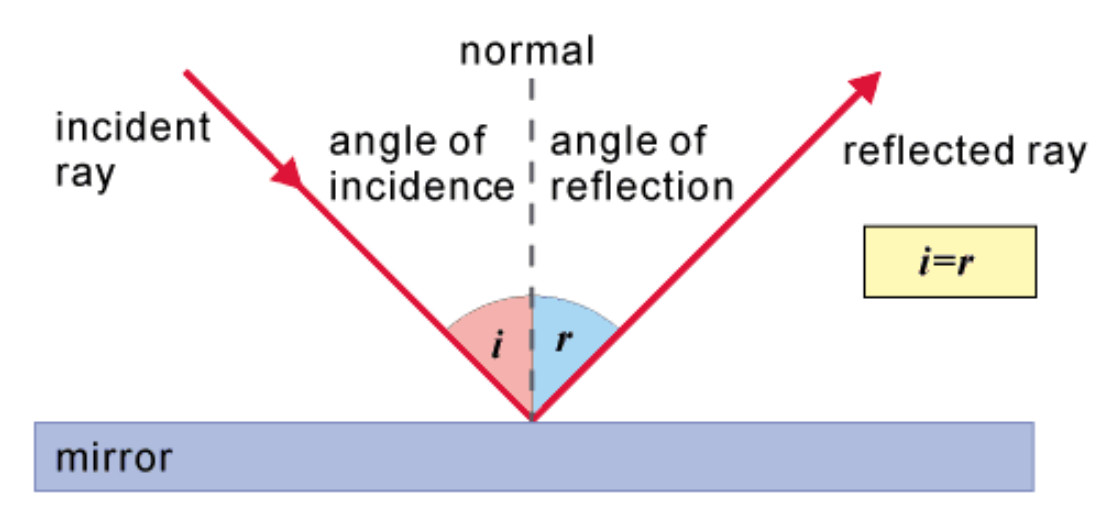
5. Ask students to refer back to their diagrams, and use these to explain the use of a ray diagram that shows the direction of a moving light ray. Students should be able to define and label the normal ray, the incident ray, the reflected ray, the angle of incidence, and the angle of reflection.
The reflection and refraction of light 7-27-99 Rays and wave fronts. Light is a very complex phenomenon, but in many situations its behavior can be understood with a simple model based on rays and wave fronts. A ray is a thin beam of light that travels in a straight line.
Reflection of light is the simple phenomenon of the light bouncing back after falling on an object. The most common example of this is not being able to see anything on entering a dark room but once you switch on the lights, everything will be visible.
Reflection of Light. The process of sending back light rays which fall on the surface of an object, is called reflection of light. A plane mirror reflects almost all the light which falls on it. In order to study the reflection of light, we need an apparatus which can produce a thin beam of light.
Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface. Refraction is the bending of light when it travels from one media to another. Diffraction is the spreading of light when it passes through a narrow opening or around an object. A change of media is required for refraction to take place.
When a ray of light falls on any object (polished, smooth, shiny object), light from that object bounces back those rays of light to our eyes and this is known as "Reflection" or "Reflection of Light". This phenomenon is what enables us to look at the world around us based. Before, after and during reflection light travels in a straight line.
The reflection of visible light is a property of the behavior of light that is fundamental in the function of all modern microscopes. Light is often reflected by one or more plane (or flat) mirrors within the microscope to direct the light path through lenses that form the virtual images we see in the oculars (eyepieces).
Diffused/Irregular reflection is a non-mirror-like reflection of light. In this type of reflection rays of light that hit an irregular object with a rough surface, are reflected back in all directions. Here, the incident ray which is reflected along with reflected ray doesn't have the same angle to the normal as the incident ray.
Reflection of light. Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the surface. This is called specular reflection. Light reflects from a smooth surface at the same angle as it hits the surface.
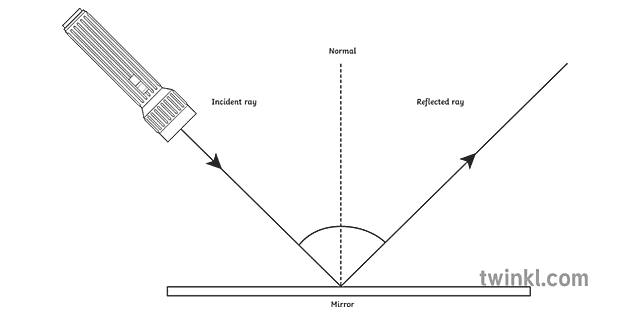
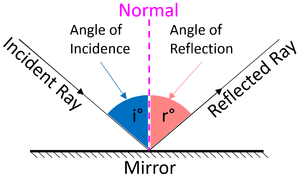
Laws of Reflection. In the diagram given above, the ray of light that approaches the mirror is known as "Incident Ray". The ray that leaves the mirror is known as "Reflected Ray". At the point of incidence where the incident ray strikes the mirror, a perpendicular line is drawn known as the "Normal". This normal is what divides the ...
Check out our video on "How To Draw Ray Diagrams | Reflection Of Light| Physics | Science | LetsTute" In This Session of Light Reflection in Plane Mirror and...
Reflection A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line with an arrowhead pointing in the...
In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line; with an arrowhead pointing in the direction that the light travels. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Investigating the law of...
The regular reflection or specular reflection is a type of reflection when light rays fall on a very smooth surface and reflected in one direction. Reflection happens uniformly and almost all the incident lights got reflected. Reflection on the mirror is an example of regular or specular or uniform reflection.
Jun 09, 2019 · What is Reflection of Light? When a ray of light approaches a smooth polished surface and the light ray bounces back, it is called the reflection of light. The incident light ray which lands upon the surface is said to be reflected off the surface. The ray that bounces back is called the reflected ray. If a perpendicular were to be drawn on a ...
Reflection by a concave mirror and a convex mirror has many uses as listed above. Reflection helps in medical diagnosis and optical communications. Light and Sound both follow the law of reflection, both being waves. Using the law of reflection for sound and light, we can measure the distances accurately to objects.
The light reflection is the returning back of light waves in the same medium on meeting a reflecting surface, and the surface at which the reflection takes place is called the reflecting surface, The light reflection is classified according to the nature of the reflecting surface into the regular (uniform) reflection, and the irregular (non-uniform) reflection.
What is reflection of light? Draw a labelled diagram showing reflection of light by a plane mirror.NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Physics Chapter 10 Light Re...
The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram).
Hello!Refraction of Light Diagram || How To Draw Refraction of Light Through Glass Slabrefraction of light diagram, refraction of light, reflection and refra...
The diagram below depicts several rays from the object reflecting from the mirror and converging at the image location. The reflected light rays then begin to diverge, with each one being capable of assisting an individual in viewing the image of the object. If the light bulb is located at a different location, the same principles apply.
69. List the sign conventions for reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions in the determination of focal length of a spherical mirror which forms a three times magnified real image of an object placed 16 cm in front of it. [Delhi ] Answer. Sign conventions for reflection of light by spherical mirror are:
The reflection of light 7-25-00 Sections 23.1 - 23.3 Rays and wave fronts. Light is a very complex phenomenon, but in many situations its behavior can be understood with a simple model based on rays and wave fronts. A ray is a thin beam of light that travels in a straight line.
A ray of light is the straight line that the light travels along and a series of light rays is considered a light beam. Laws of Reflection of Light. The angle of incidence at the point of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection and the incident radius, the reflected radius and the normal mirror at the point of incidence.


















0 Response to "36 reflection of light diagram"
Post a Comment