38 molecular orbital diagram h2-
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
Apr 12, 2018 · The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.Diatomic Species | MO theory | ChemogenesisMolecular Orbital Theory
In this video, we take a detailed look at the molecular orbitals of the H2 molecule, with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Discussed in this v...

Molecular orbital diagram h2-
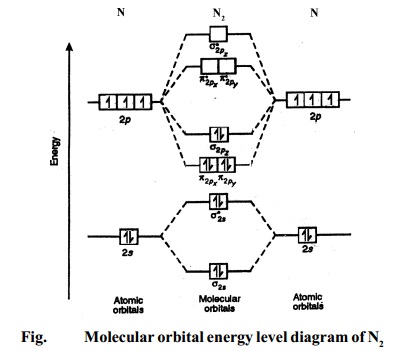
is called Molecular Orbital Theory. • MO theory assumes that the valence electrons of the atoms within a molecule become the valence electrons of the entire molecule. • Molecular orbitals are constructed by taking linear combinations of the valence orbitals of atoms within the molecule. For example, consider H2:
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
of the orbitals is specified. b. Molecular Orbital Picture We are now in a position to discuss the basic principles of the molecular orbital (MO) method, which is the foundation of the electronic structure theory of real molecules. The first step in any MO approach requires one to define an effective one electron Hamiltonian, hˆ eff. To this ...
Molecular orbital diagram h2-.
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic ... Spin‐orbitals of type 1 and 3 have the same symmetry, and therefore can “mix” (to give improved wavefunctions and energy eigenvalues): 1 ψψ αβ ...
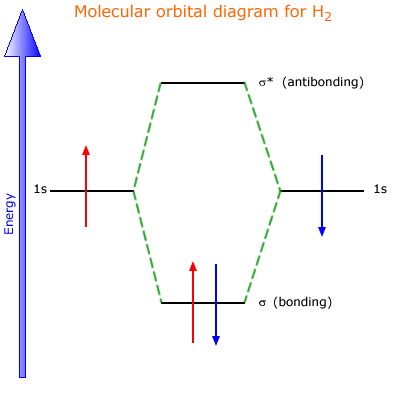
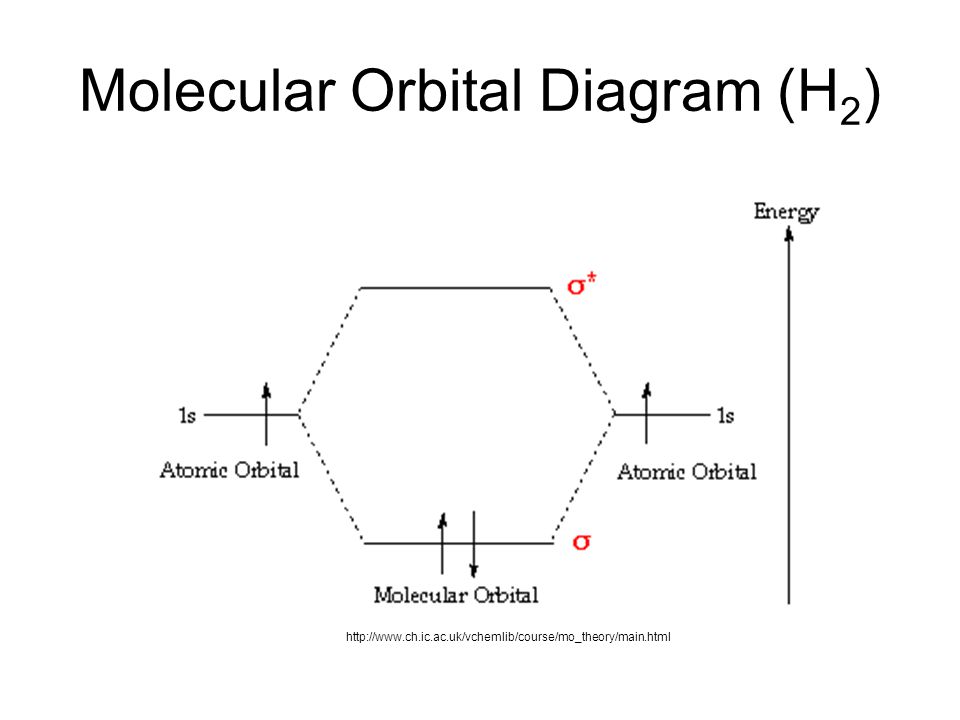
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
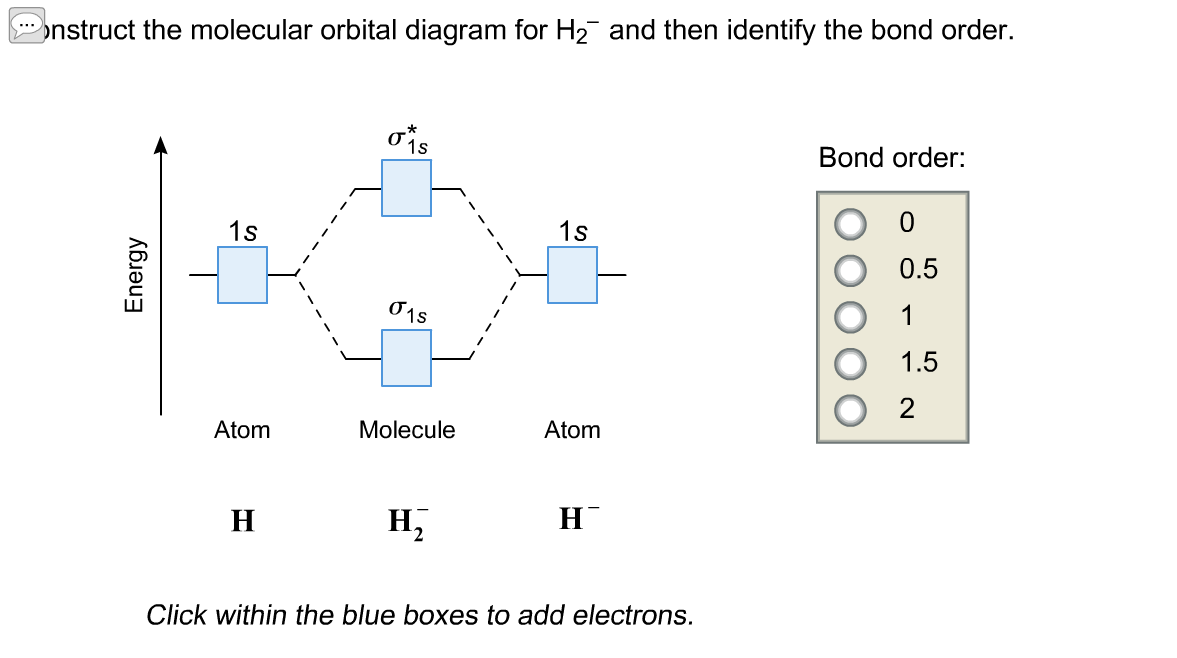
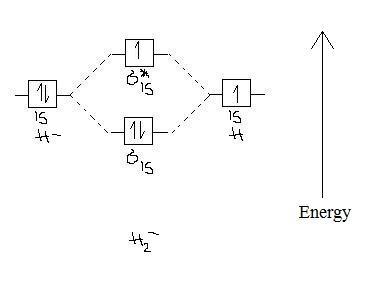
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals.
Now on adding one electron to H2, H2- is formed. So molecular orbital electronic configuration of H2- is σ1s² σ*1s¹ Bond order=1/2 [number of bonding electrons -number of antibonding electrons] bond Continue Reading Jasdeep Singh , Btech. from Lovely Professional University- LPU Answered 3 years ago Atomic no. Bond order 10 1 11. 1.5 12. 2 13 2.5
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbital s (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2 + Molecular Orbital Diagram s of Diatomic Molecules ...
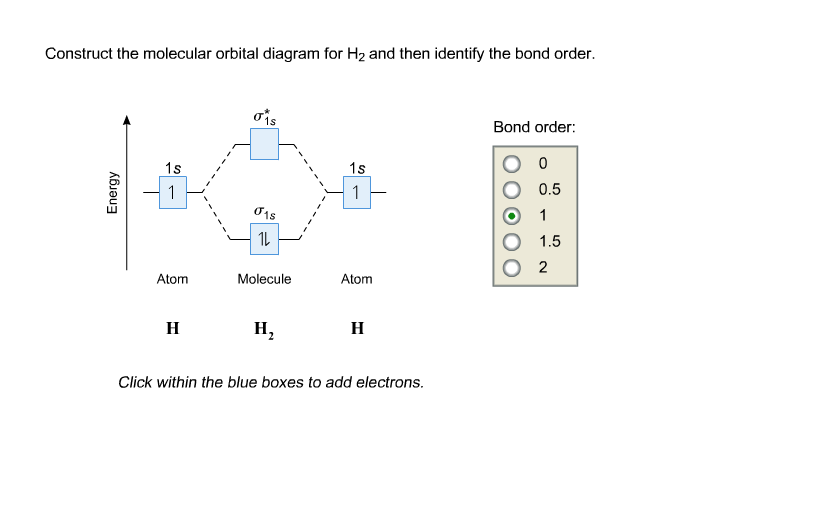
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron and thus h2 has three electrons while h2 has one. Discussed in this video are. Draw mo energy diagrams for the molecular ions h2 and h2. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2.
the molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the h 2 molecule is shown in figure on either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms a and b, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.the …
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
32846. Table of contents. Contributors and Attributions. Describe the hydrogen molecule in light of the following: H − H. H: H. Valence bond theory of H 2. Molecular orbital theory of H 2. Electron configuration of molecules.
Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
38 molecular orbital diagram of h2. Written By Chelsea P. Mariano Monday, November 8, 2021 Add Comment. Edit. 3 Feb 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2 has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
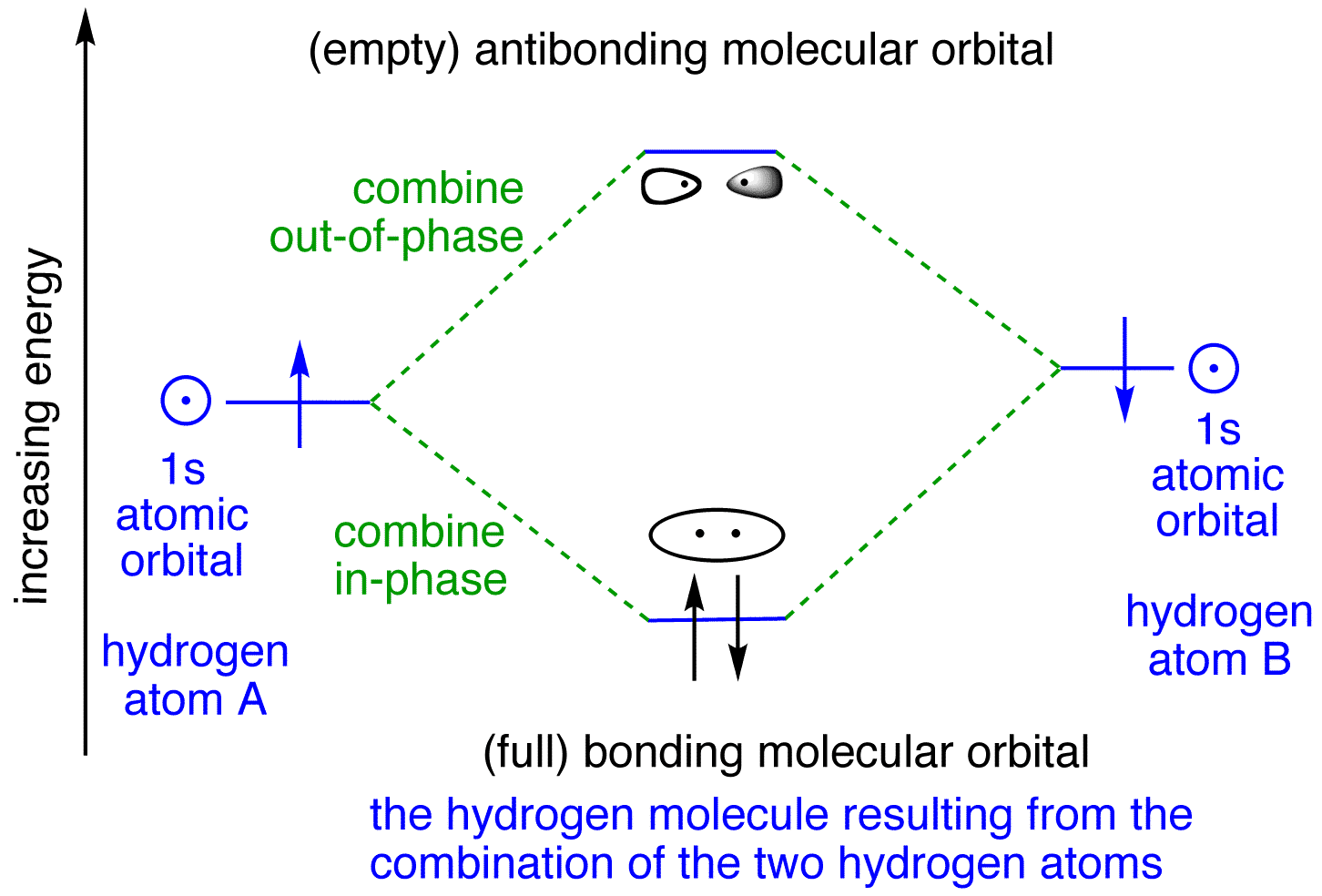
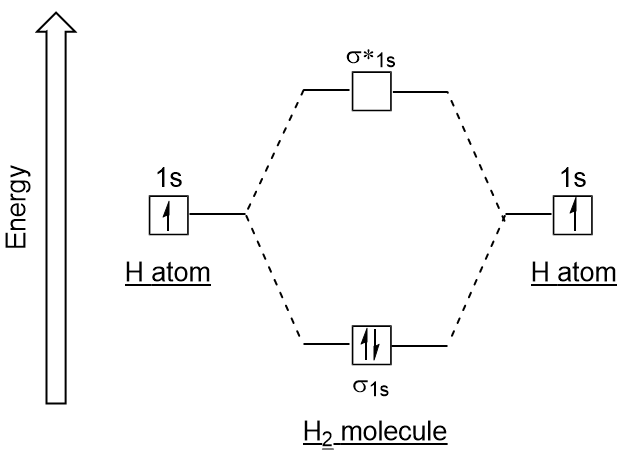
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules bond order = (number of bonding electrons) - (number of antibonding elect rons) 2 = amount of bonding 1sa hydrogen molecule = H2 LUMO HOMO σ = 1sa + 1sb = bonding MO = potential energy higher, less stable lower, more stable
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here. Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can ...
The energy curves for ψ + and ψ-reveal the following properties of the ion H 2 +. The curve for ψ + refers to the ground state of the molecule where a minimum energy is found for a nuclear distance of approximately 2a o (i.e. 100pm). Thus, H 2 + should exist as a stable molecule. The calculated bonding energy is 1.77 eV. This is a quite satisfying result; from experiments we get 2.77 eV.
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+.
Question: Each of the following five statements concerns the molecular orbital diagram for H2-. Indicate whether each statement is true or false. Indicate whether each statement is true or false. This problem has been solved!
14+ H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
The basic tenant of Molecular Orbital Theory (MO Theory) is that the number of MOs formed by a linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) is equal to the number of AOs used. The energy splitting caused by electron/electron repulsion generates two MOs due to the one #1s# orbital per hydrogen that is bonding.
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the H2(2+) molecule. The bond order of H2(2+) is calculated and the meaning of this n...
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order.
Molecular orbital diagram h2. Because of their simplicity they have been extensively studied. Two superpositions of these two orbitals can be formed one by summing the orbitals and the other by taking their difference. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order.
We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H 2+. With a bond order of only 1/2 the bond in H 2+ should be weaker than in the H 2 molecule, and the H–H bond should be longer.
Mo · Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. chemical bonding molecular orbitals of h2 and he2 as before the greater the number of these nodal planes the more the electrons that occupy the orbitals are excluded from the region between the nuclei and hence the higher the energy the resulting molecular ...
chemical bonding - chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be introduced by considering the H2 molecule. Its molecular orbitals are constructed from the valence-shell orbitals of each hydrogen atom, which are the 1s orbitals of the atoms. Two superpositions of these two orbitals can be formed, one by summing the orbitals and the other by taking their difference.

















0 Response to "38 molecular orbital diagram h2-"
Post a Comment