40 geology block diagram exercises
6-E1 LAB EXERCISES - RELATIVE TIME. Relative time is an important tool for geologist to quickly construct a model for a series of geologic events, especially in the field. In the following section, apply what you have learned regarding relative time to the questions below. Figure 6-E1 | Block diagram to use to answer questions 1 and 2.
Exercise Part 1 (do before lab): Visualizing Geology in 3-D with online program . tasks/questions in italics will be graded . We are going to explore the block-diagrams provided on the previous pages in 3-D by
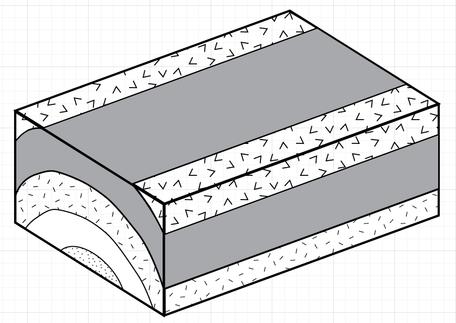
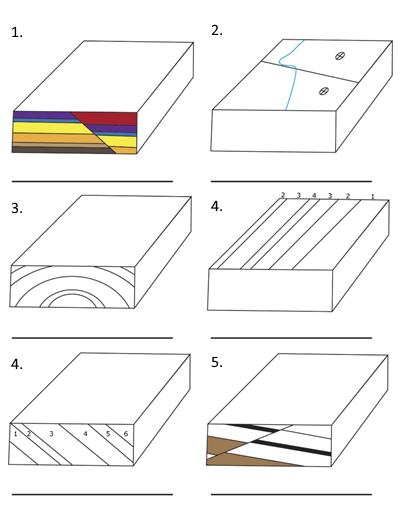
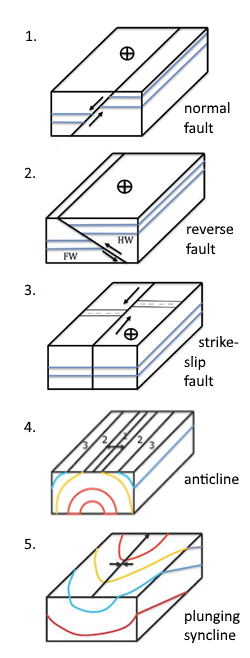
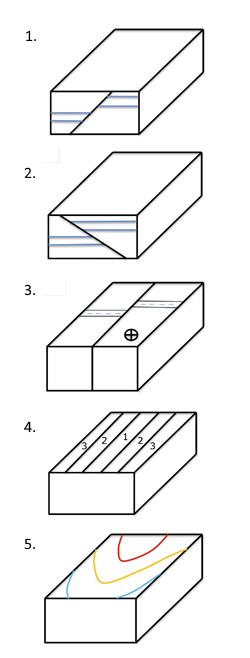
What type of unconformity is represented by Erosion A in block 1? 2. What type of unconformity is represented by Erosion N in block 2? 3. What type of fault is Fault A in block 4? 4. What type of fault is Fault S in block 5? 5. What type of fold is present in block 6? 6. In block 6, is the igneous rock a pluton or a lava flow? Or both? Explain? 7.
Geology block diagram exercises
This is a Google Earth based virtual field exercise focused on Sandy Hollow, near Block Mountain and McCartney Mountain in southwest Montana. This is a classic field locality in the Montana portion of the Sevier fold-thrust belt. For more information on the area, the reader is referred to Chapter 6: Geology of Southwest Montana in Guidebook to ...
Block models provide a useful tool for visualizing geology in three dimensions. The top surface of the block represents the surface of the Earth, and the four sides provide four cross-sectional views of the geology in the subsurface. Layers of rocks are planar Figure 9.1.1: Block diagram of horizontal strata showing four distinct planar layers.
School of Geosciences - Faculty of Science
Geology block diagram exercises.
Visible Geology is an interactive online educational tool for visualizing 3D geologic block models. You can create your own topography and show the outcrop pattern of geologic beds, folds, dykes, or faults in seconds!
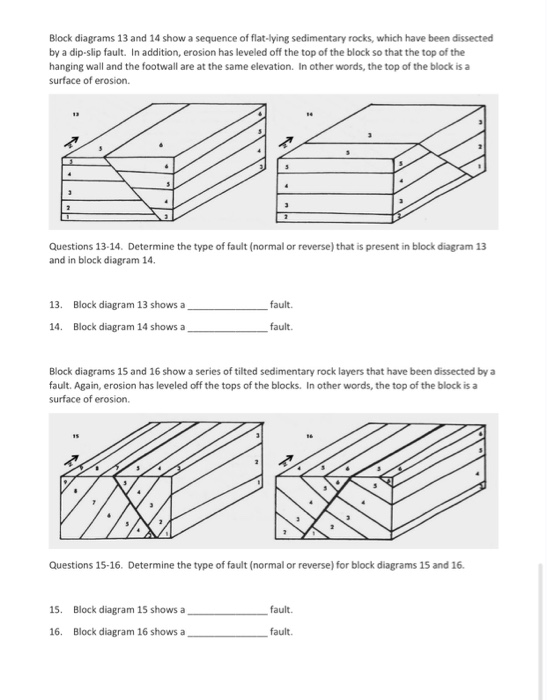
11. In a dip-slip fault, if the hanging wall block moved up relative to the footwall block, then the fault is classified as a _____ . 12. In a dip-slip fault, if the hanging wall block moved down relative to the footwall block, then the fault is classified as a _____ . 13.
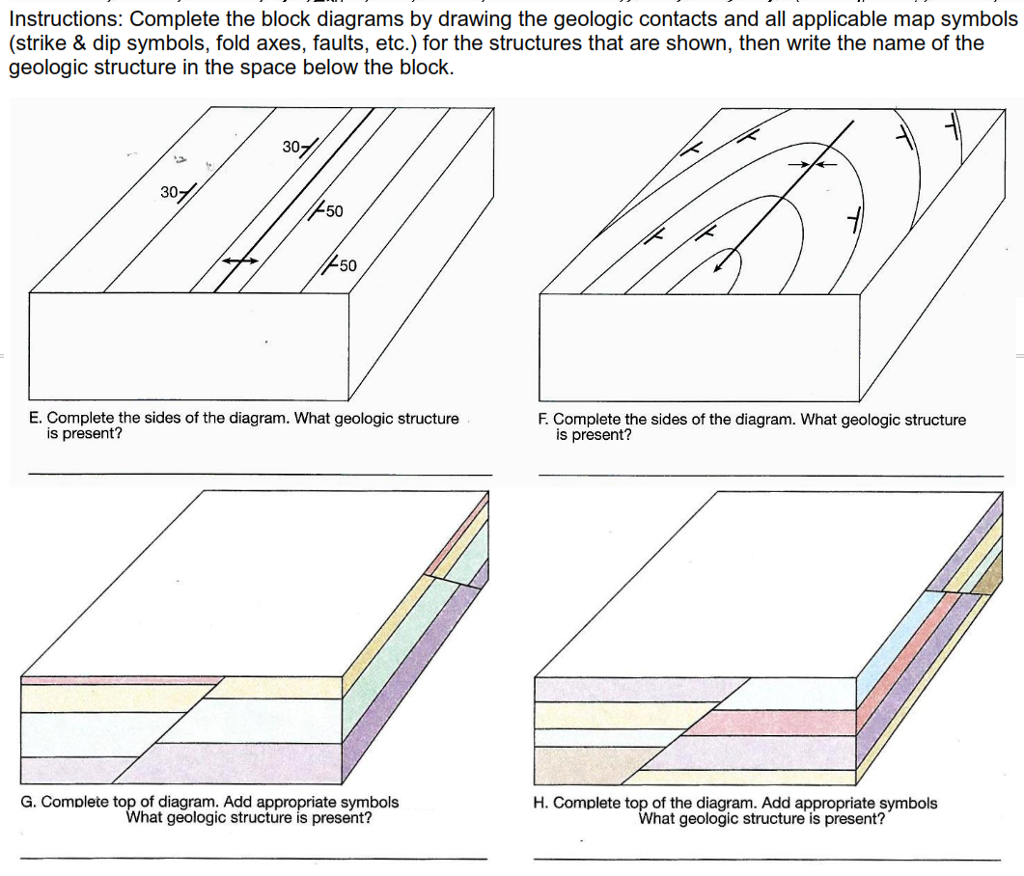
Department of Geology GEOLOGIC STRUCTURES IN THREE DIMENSIONS This exercise will develop your ability to define, describe, and interpret geological structures in three dimensions. To do this, we will use three-dimensional block diagrams that combine geologic maps with geologic cross-sections.
Geologic Structures Diagrams (Depending upon your printer, you may have to adjust your page and/or printer settings to make a print out of the following diagrams. These adjustments may include things like page orientation, page reduction (80% vs. 100%), grayscale vs. black/white, etc.
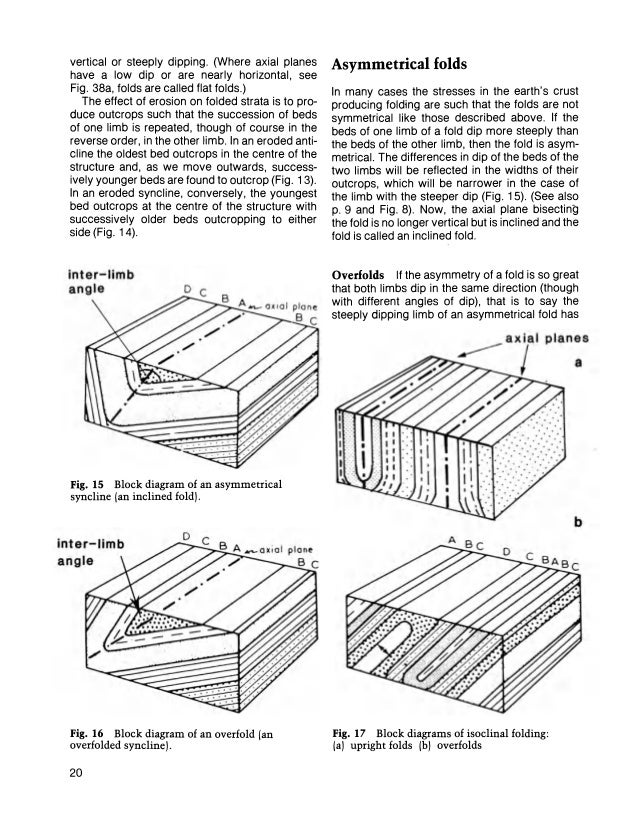
The top of a block diagram is an oblique view of the earth's surface, in other words it is a geologic map that you are viewing at an angle from above. The vertical sides of a block diagram are cross-sections, cut-away views that show how the rocks and structures extend into the earth.
In the diagrams shown in Figure 8.20, numerical labels on beds indicate the relative ages of the beds, with 1 being the oldest and 6 the youngest. Complete the block diagrams by doing the tasks listed below. Assume that the geologic units have not been overturned (flipped upside down).
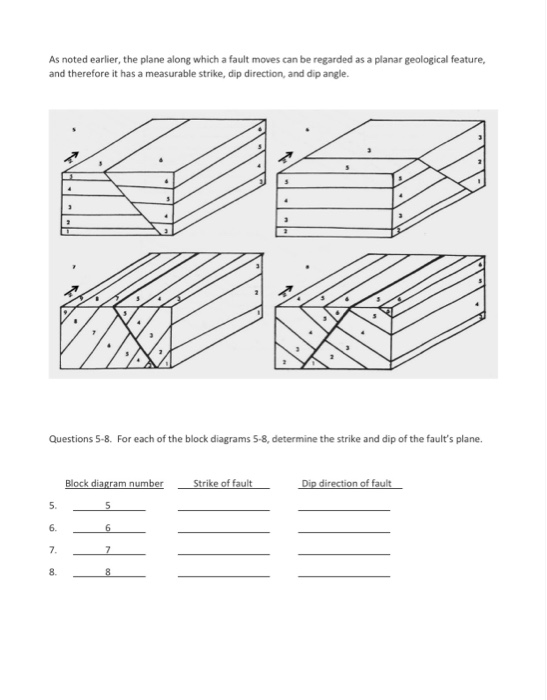
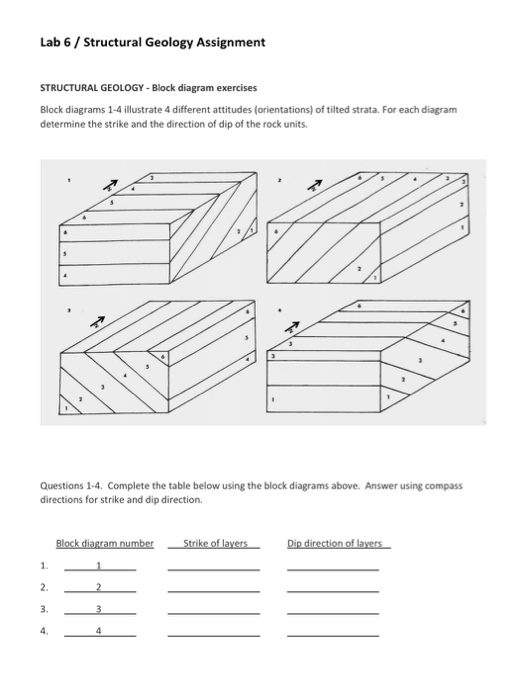
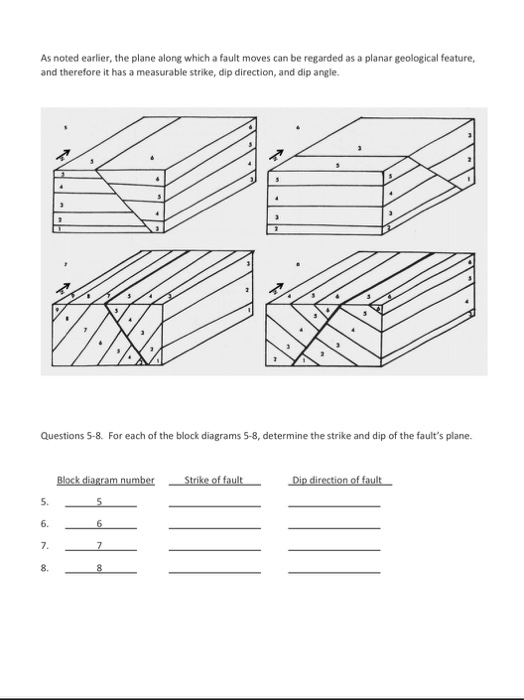
Transcribed image text: Lab 6 / Structural Geology Assignment STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY - Block diagram exercises Block diagrams 1-4 illustrate 4 different attitudes (orientations) of tilted strata. For each diagram determine the strike and the direction of dip of the rock units. 5 Questions 1-4. Complete the table below using the block diagrams above.
Transcribed image text: Lab 6/Structural Geology Assignment STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY-Block diagram exercises Block diagrams 1-4 illustrate 4 different attitudes (orientations) of tilted strata. For each diagram determine the strike and the direction of dip of the rock units Questions 1-4. Complete the table below using the block diagrams above.
A Guide to Block Diagrams. Information Given by the Block Diagram: 1) The top of the block is a HORIZONTAL PLANE - A dipping bed that intersects it forms a STRIKE LINE . 2) The sides of the block are VERTICAL walls - Will show the DIP DIRECTION of the beds - Will show the DIP angle of the beds * Up to Structural Geology Topic List *
A geological cross-section shows geologic features from the side view (the side views of the block diagrams in Figures 8.3-8.5 are cross-sections). They are similar to the topographic profiles that you created in the topographic maps chapter, but they also show the rock types and geologic structures present beneath Earth's surface.
The oldest rock in this diagram has a relative age of that is at least as old as which geologic eon/era? (a)Cenozoic (b)Proterozoic (c)Paleozoic (d) Mesozoic 8.Layer G, a siltstone from the first block diagram (page 7) has the mineral glauconite, which can be dated using Potassium 40. In G, 85% of its original Potassium 40 remains.
/,67 2) ),*85(6)ljxuh *hrorjlf wlph vfdoh )ljxuh 5xoh ri ³9´v iru frqwdfwv )ljxuh 6whhso\ glsslqj vwudwd
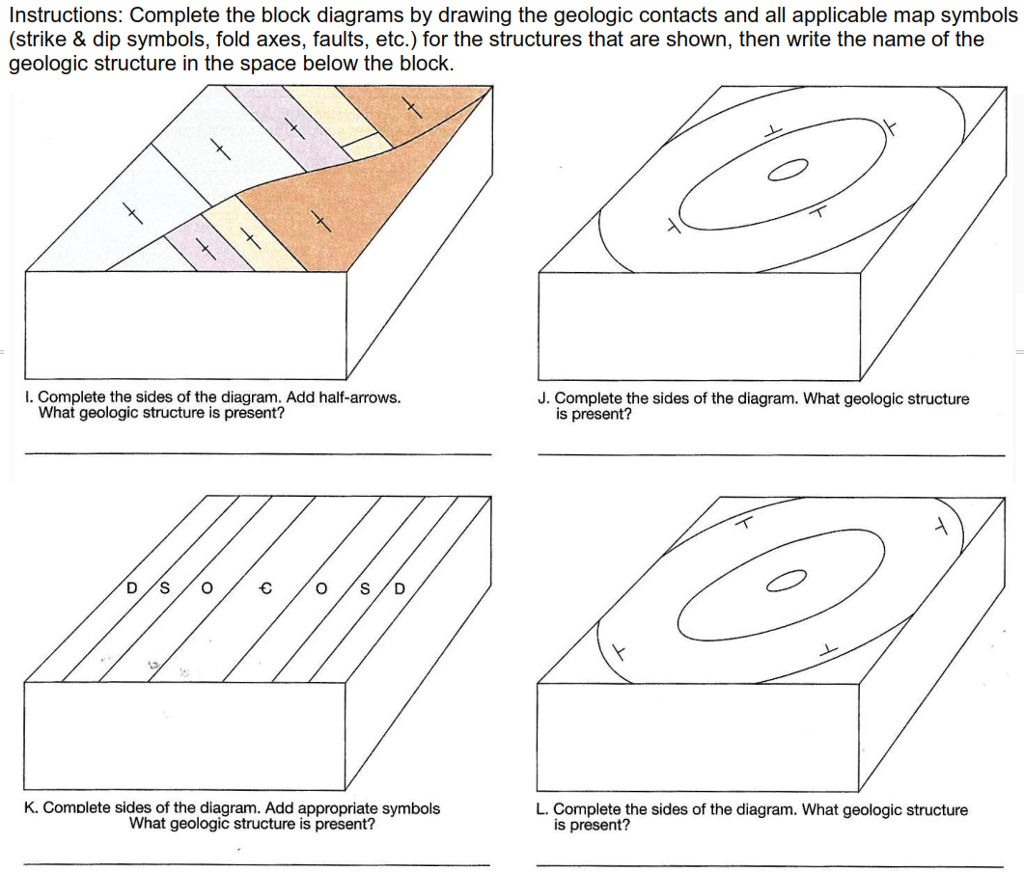
The rest of the exercises in this lab will be part of your grade for this lab. 1. (4 pts each, 24 pts total) Please complete the following block diagrams. For each block diagram: Complete the diagram drawing in the geological contacts on each side of the block
Due to the positive response to my answer of December 13th, 2014, I present here an example of a meaningful hand drawing of a block diagram with geological and morphological details by my ...
Geologic block diagrams and relative age (Based on an exercise in Tarbuck, Lutgens, Pinzke. 2006. Applications and Investigations in Earth Science, 5th edition. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.) In your reading assignments and in class, you've learned about the principles and
Physical Geology 101 Laboratory Structural Geology II - Drawing and Analyzing Geologic Block Diagrams . I. PRELAB SECTION - To be completed before labs starts: A. Introduction & Purpose: Structural geology is the study of how geologic rock units are initially arranged and later deformed. Changing spatial relations between geologic units and ...
After successfully completing this exercise, students will be able to sketch geologic block diagrams of simple structures chosen by the instructor. Context for Use This exercise is designed to be used as an early 3D sketching exercise in a Structural geology course, though it could also be used in any other course where basic structures are ...
GEOLOGY - Block diagram exercises Block diagrams 1-4 illustrate 4 different attitudes (orientations) of tilted strata. For each diagram determine the strike and the direction of dip of the rock units. Questions 1-4. Complete the table below using the block diagrams above. Answer using compass directions for strike and dip direction.
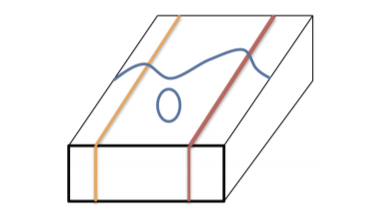
Block diagrams are a combination of geologic maps and cross-sections, illustrating both surface features and cross-sections through the earth. Structural geology is the study of the ways in which rocks or sediments are primarily arranged and secondarily deformed on the Earth.
Lab 6 / Structural Geology Assignment STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY - Block diagram exercises Block diagrams 1-4 illustrate 4 different attitudes (orientations) of tilted strata. For each diagram determine the strike and the direction of dip of the rock units. Questions 1-4. Complete the table below using the block diagrams above.
EPS 116 - Laboratory Structural Geology Lab Exercise #1 Spring 2016 Page 8 of 9 5. Think in 3 dimensions. Sketch a 3D isometric block diagram of a cube (like the example provided). Indicate the orientation of the three dimensional coordinate system that defines your reference frame (east-north-up). Within the volume of this
Lab 6 / Structural Geology Assignment STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY - Block diagram exercises Block diagrams 1-4 illustrate 4 different attitudes (orientations) of tilted strata. For each diagram determine the strike and the direction of dip of the rock units. Questions 1-4. Complete the table below using the block diagrams above.
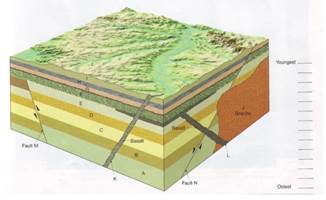
Geologic Cross Sections. Many geologic maps include geologic cross-sections, or profiles of the extrapolated geologic structures and rock units beneath the surface. The geologic structures block diagrams and topographic profiles are examples of cross-sections that we have already covered. A geologic cross-section will be labeled on the map ...














0 Response to "40 geology block diagram exercises"
Post a Comment