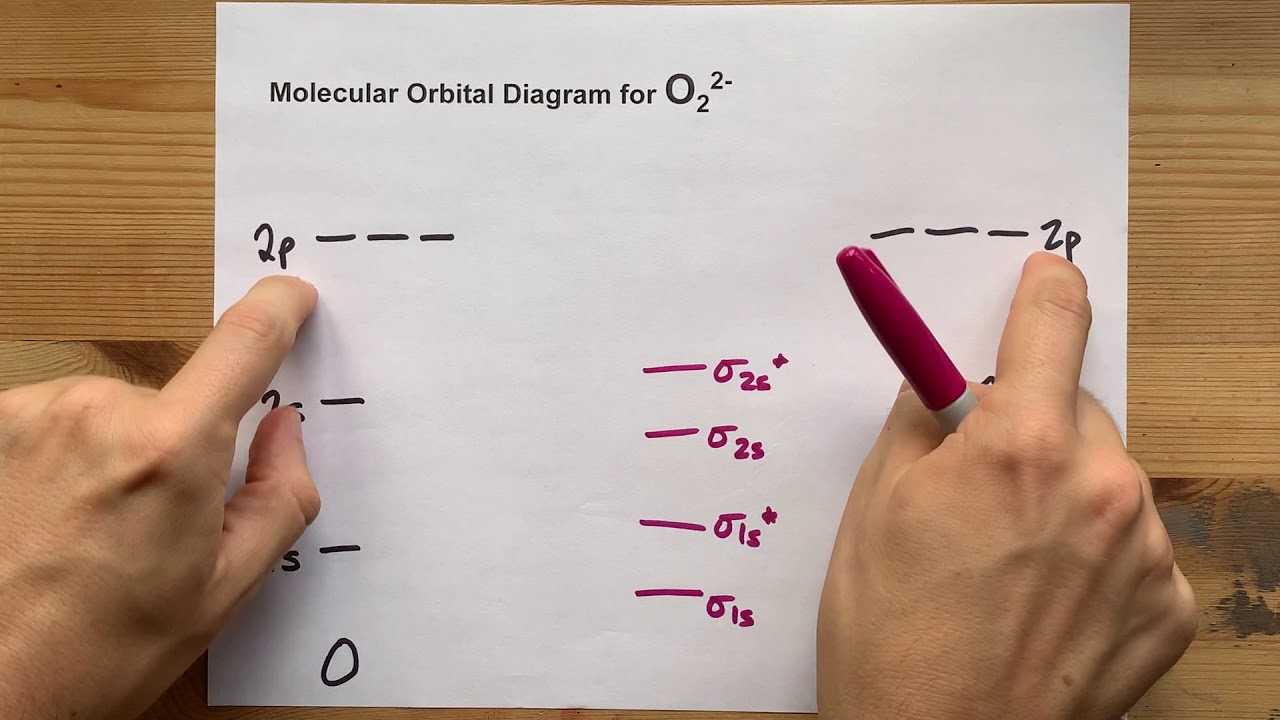
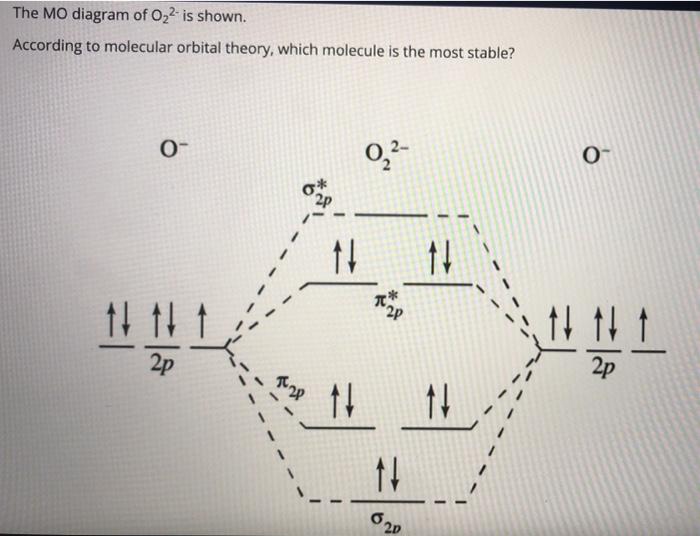
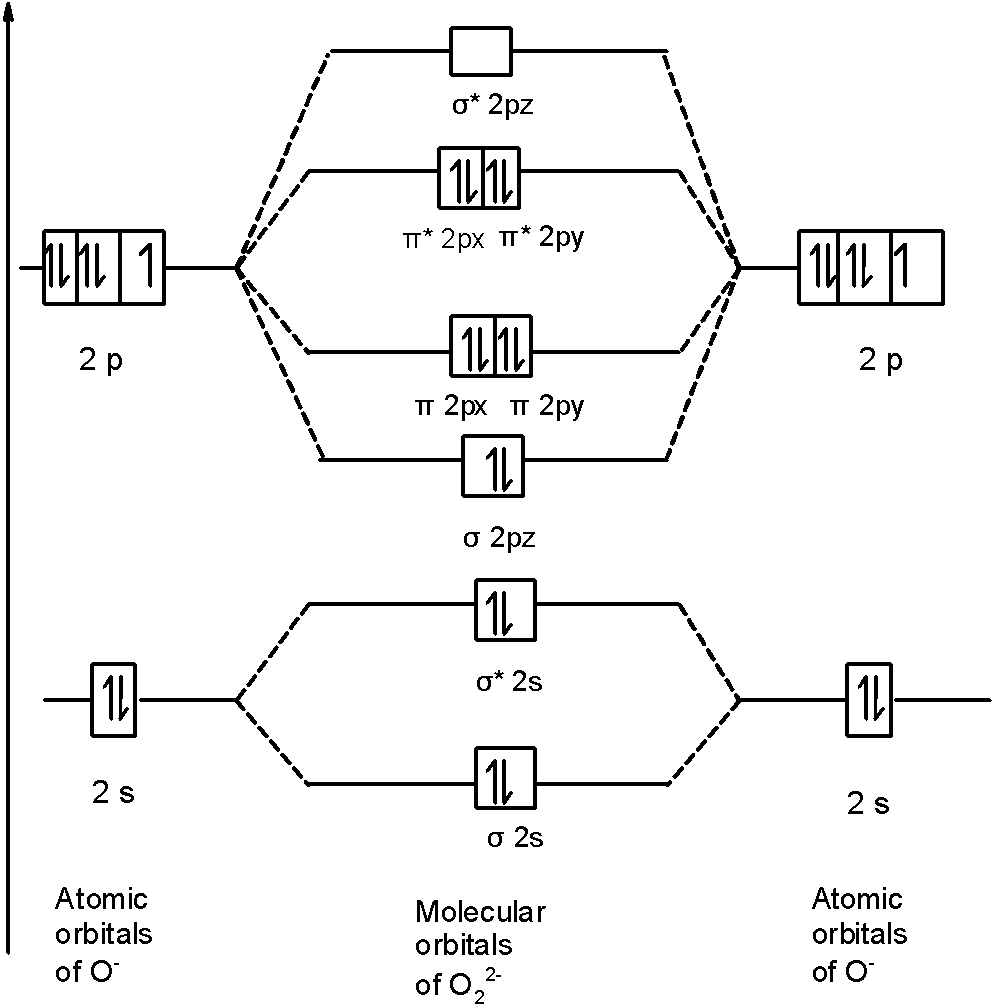
40 molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-
To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O 2, we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1 . We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
Well, s-p mixing doesn't occur with diatomic oxygen, creating a molecular orbital diagram like the first in this article. This is because, as more electrons are added to a system, the higher the energy becomes, due to their electrostatic repulsion. If the energy of the 2s and 2p orbitals are too far apart, mixing won't occur.
Molecular orbital theory Features of Molecular orbital theory 1) The atomic orbitals overlap to form new orbitals called molecular orbitals. When two atomic orbitals overlap or combine ,they lose their identity and form new orbitals. The new orbitals thus formed are called molecular orbitals. 2) Molecular orbitals are the energy states of a molecule in […]

Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-
Bond Order Of O2 2. O22 means it loses 2 e-there are 4 e- in p_orbitalsAccording to MOT molecular orbital theory 6 e- are in bonding molecular orbitals BMO and 2 e- are in antibonding molecular orbitals ABMO Formula to find bond order is Noof e in BMO NO. Bond order in Oxygen molecule O 2-2 ½ Number of bonding electrons number of anti-bonding ...
Oxygen's 6 valence electrons sit in hybridized sp³ orbitals, giving us 2 paired electrons and 2 free electrons. Since water's oxygen is sp³ hybridized, the electronic geometry still looks like carbon (for example, methane). But the model kit shows just 2 H atoms attached, giving water the Bent Molecular Geometry. Sp² Hybridization
The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.
Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-.
When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
Write the Electronic configuration, Energy level diagram for the molecular orbitals of Oxygen molecule `(O_(2))`. Calculate its bond order and given reason as to why `O_(2)` is paramagnetic. Valence Bond Theory (VBT) and Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) are the two important theories of chemical bonding <br> Write the molecular orbital electronic ...
38 molecular orbital diagram of h2. Written By Chelsea P. Mariano Monday, November 8, 2021 Add Comment. Edit. 3 Feb 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2 has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ...
Significance of Bond Order. Example for Calculation of Bond Order. Hydrogen Molecular Positive Ion (H2+) Bond Order of Oxygen Molecule (O2) Bond Order of Superoxide Ion ( O 2 -) Bond Order of Peroxide Ion ( O 2 2 -) Bond Order of O 2 + Ion. Bond Order of Polyatomic Molecules and Ions. Bond Order Formula Based On Lewis Structure.
Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Consider the h 2 molecule for example. Sp mixing causes the σ g and σ u mos to be pushed apart in energy. Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o this problem has been solved. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule.
There are 10 bonding electrons (including molecular orbitals formed by the $\text{1s}$ orbitals.) and 7 nonbonding electrons. ... Therefore, the bond order $O_{2} ...
Aug 25, 2017 — In normal O2, there are 6 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, making the bond order 2. By removing the 2 highest electrons, which reside in ...3 answers · 6 votes: In O2 2+, there is 14 electrons. So, it’s MOT is comparable to N[code ]2[/code] & the MOT ...What is the electronic configuration O2^-2 molecule ...4 answersOct 6, 2015What is the molecular orbital diagram for O2- and ...5 answersMar 27, 2017What is the bond order of o2^+2? - Quora4 answersOct 1, 2018What is the bond order of O2+? - Quora6 answersJan 31, 2018More results from www.quora.com
The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n (2px) 2 n (2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. Molecular orbital diagram for c2 2-. The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
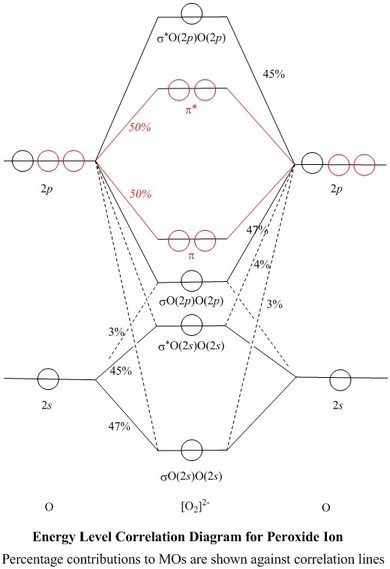
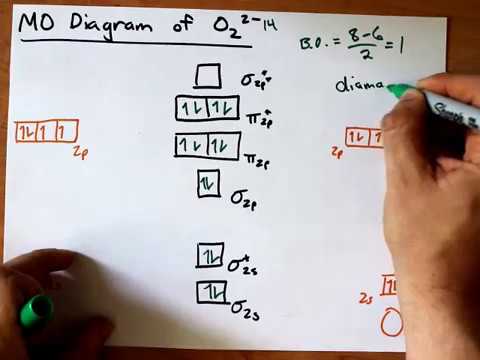
Hey there! We will begin by drawing the molecular orbital diagram for the peroxide ion (O22-). O22- ion is a homonuclear diatomic ion made up of 2 O atoms.1 answer · Top answer: [readmore]Hey there! We will begin by drawing the molecular orbital diagram for the peroxide ion (O22-).O22- ion is a homonuclear diatomic ion made up ...
The molecule is diamagnetic with zero unpaired electrons.. In order to determine the magnetism of the O2^2+ ion, we must have to write the molecular orbital configuration and fill its electrons into molecular orbitals.There are 14 electrons in the molecule. Its molecular orbital configuration is; σ1s2, σ*1s2, σ2s2, σ*2s2, σ2px2 π2py2 π2pz2. We can see from the molecular orbital ...
In the molecular orbital diagram for O 2 + ion, the highest occupied orbital is (a) σ MO orbital (b) π MO orbital (c) π* MO orbital (d) σ* MO orbital. Answer. C. Question. The theory capable of explaining paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen is (a) resonance theory (b) V.S.E.P.R. theory (c) molecular orbital theory (d) valence bond energy ...
The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2. 2s. I know ill need a 2p orbital but theres orbital mixing going on so i have 2 choices.
The Lewis structures have an unpaired electron and an average bond order of 1.5. O2 has two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals, and a bond order of 2.29 pages
ATOMIC ORBITAL DIAGRAM FOR OXYGEN ATOM Oxygen atom is on period 2, so it has access to its #1s#, #2s#, and #2p# AOs. Their relative energies are #\mathbf (2p > 2s)# #\mathbf (">>")# #\mathbf (1s)#. (The #1s# is much, much lower in energy than the #2s#, and usually is not even on the MO diagram if done to-scale).
OF2 Molecular Geometry We have already found the 2D Lewis Structure diagram of the Oxygen Difluoride molecule. Now, we are going to decipher the 3D molecular shape. Via Lewis Structure, we have realized the type of bond formed and the number of lone or unbonded pairs of valence electrons present in an OF2 molecule.
How to draw molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen molecule (O 2) ? Oxygen (O 2) molecule: Oxygen atom has electronic configuration 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 . Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each oxygen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px.
1 answerSolution · As it can be seen from the MOT of O2, The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
O2 2- molecular orbital diagram. O2 molecular orbital diagram oxygen has a similar setup to h 2 but now we consider 2s and 2p orbital s. This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbital s. Beyard 3.
To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for (ce {O2}), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure (PageIndex {1}). We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
The molecular geometry of sulphur dioxide is a curved shape. Sulphur to the Oxygen ratio in Sulfur dioxide is 1:2. Sulphur dioxide molecule has two double bonds between the Sulfur atom and also Oxygen atoms. There are five only sets of electrons in the molecule of sulphur dioxide. Molar mass of SO2 = 64.066 g/mol.
Oct 28, 2014 — Ans: The stabilities of these can be best explained using Molecular orbital theory. ... Atomic orbitals of oxygen combine to form molecular ...
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion Shapes of s, p and d - orbital s, electron spin and spin quantum number. Rules for filling electrons in orbital s - Aufbau principle, Pauli exclus ion principle and Hund's rule, electronic configurat ion of elements, the extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbital s.
The Molecular orbital diagram for O2 O 2 is like this: As you can see the oxygen molecule has two unpaired electrons in the lower π π * ant-bonding states. For O2+2 O 22 + basically remove the two unpaired electrons in the π π * anti-bonding states, as they are the most easily removed. 26K views View upvotes Sponsored by Elite Side Lines
How do you calculate bond order for O2 Plus? Bond order is defined as the number of covalent bonds in a covalent molecule.It is equal to one half of the difference between the number of electrons in the bonding & antibonding molecular orbitals. Hence, the bond order of oxygen molecule is 2. Thus, the bond order of O 2 + is 2.5.
O 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Bond Orders and Stability of Molecules. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. The molecular orbital theory explains how there are no unpaired electrons in the bonds between the two N atoms. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules.
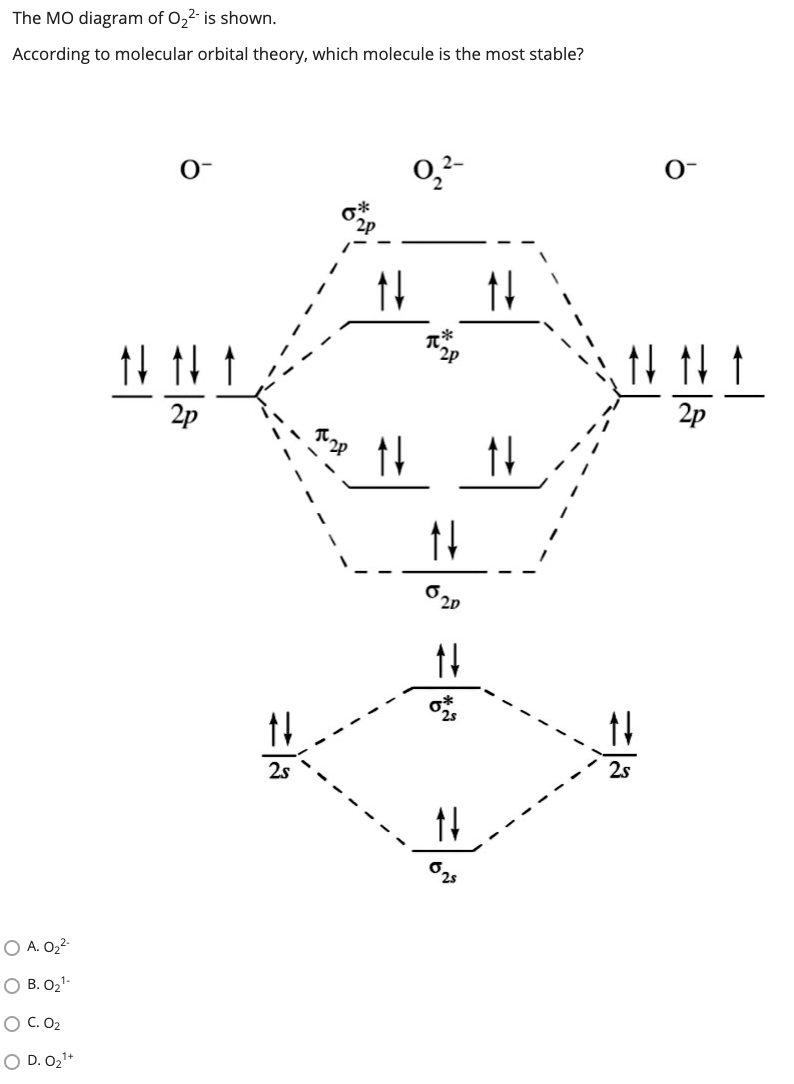
Transcribed image text: Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O2-, O22-, and O2. Which has the highest bond order? Which would be paramagnetic, and which ...
The electron filling in these molecular orbitals follow aufbau, pauli exclusion principle and hund's rule. All six electrons go to bonding molecular orbitals, so strong bonds will be formed. Bond order = Number of electrons in BMO - Number of electrons in ABMO = 6 - 0 = 3
We'll take a look at that problem on the next page. Exercise 5.1.2. 2. Draw an MO cartoon of a sigma bonding orbital formed by the overlap of two p orbitals between two oxygen atoms. Label the positions of the oxygen nuclei with the symbol "O". Label the O-O bond axis. Answer:
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion 1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in the book "Symbolic Logic" (1881). 1834, introduced by English physicist and chemist Michael Faraday (suggested by the Rev. William Whewell, English polymath), coined from Greek ion ...
1So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. Nov 11, 2016. What is the bond order of molecule B2?, Answer: The bond order of B 2 molecule is one.
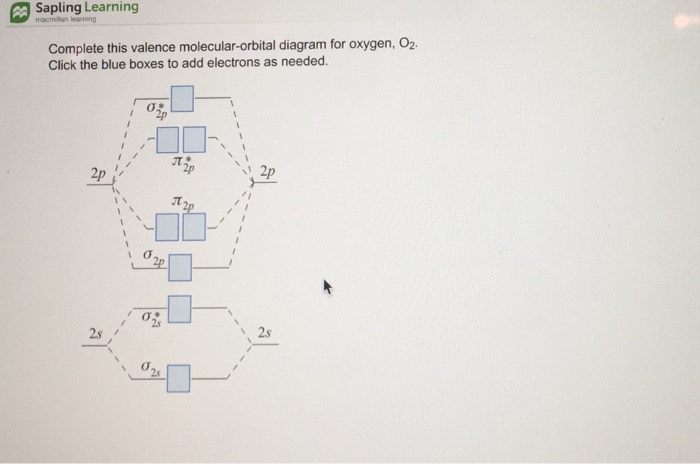
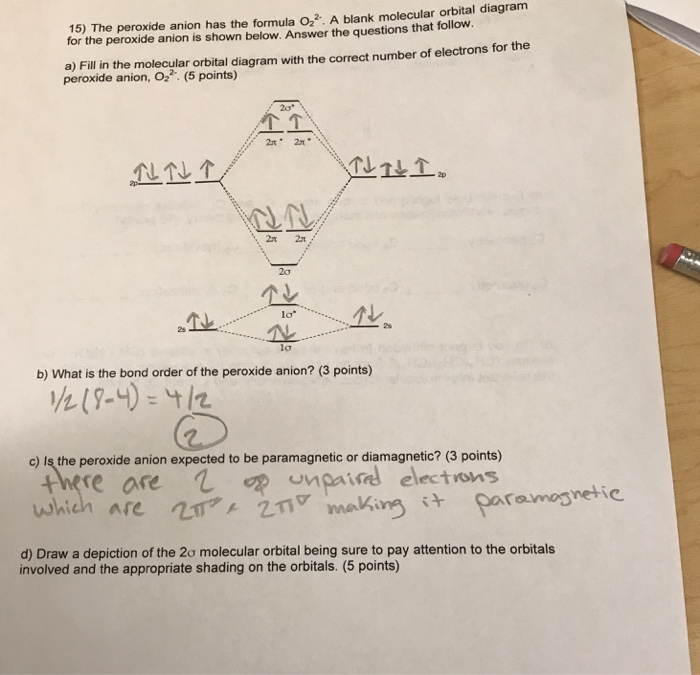
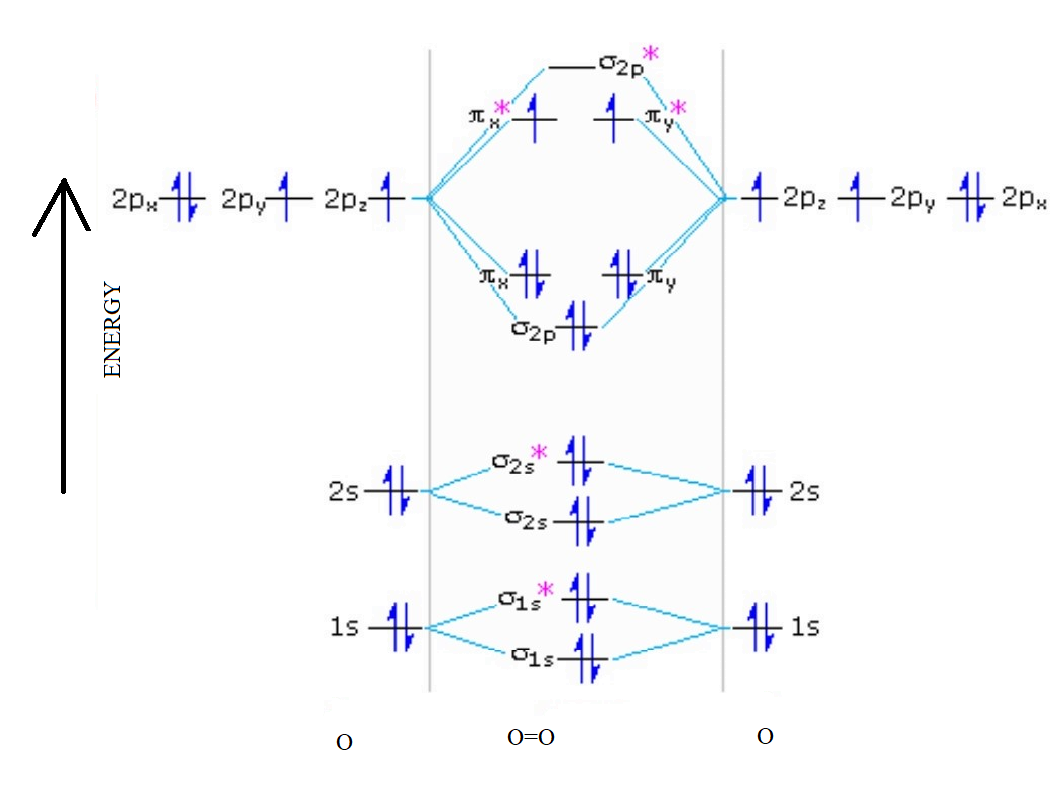
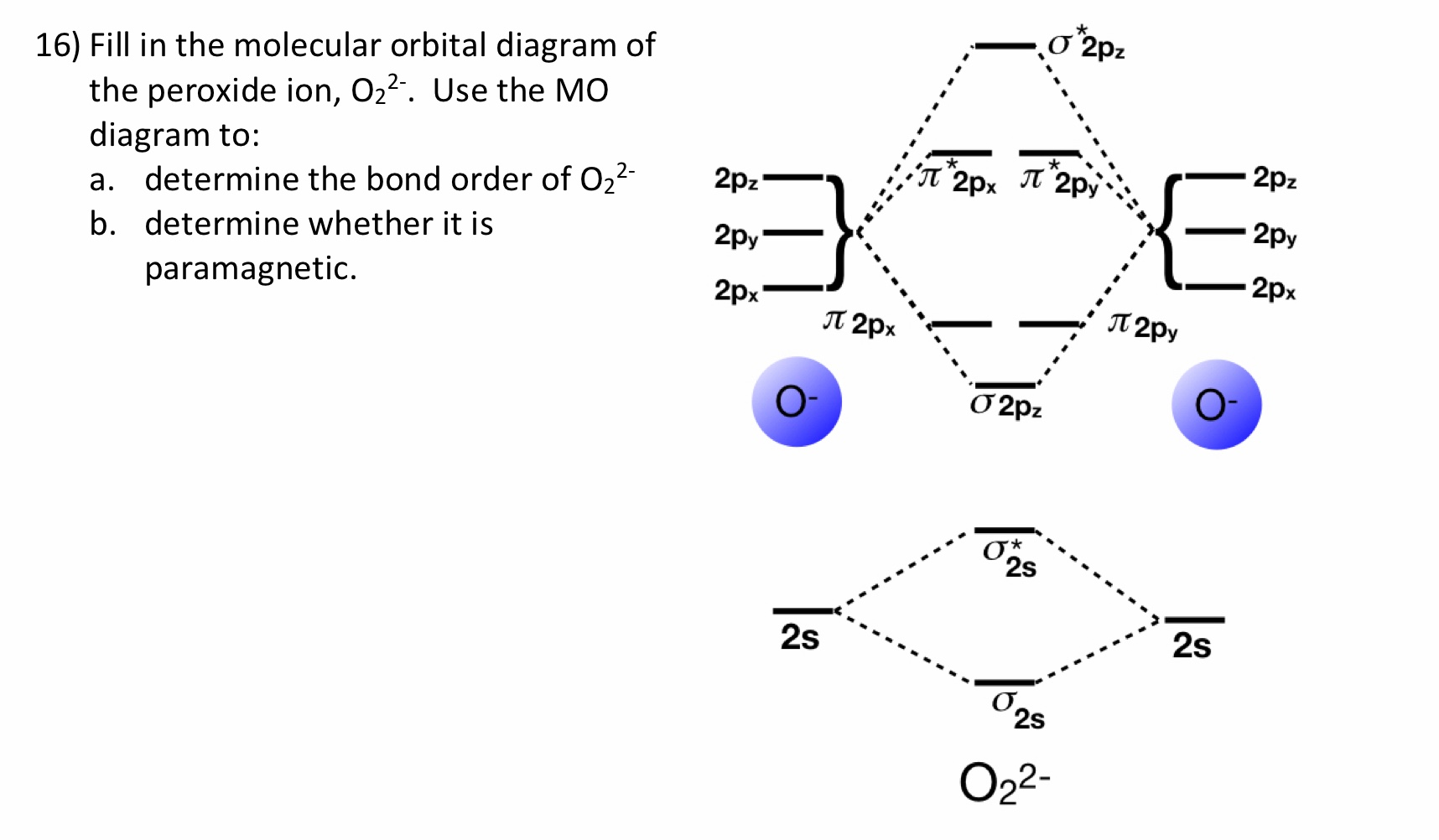



















0 Response to "40 molecular orbital diagram for o2 2-"
Post a Comment