37 flat mirror ray diagram
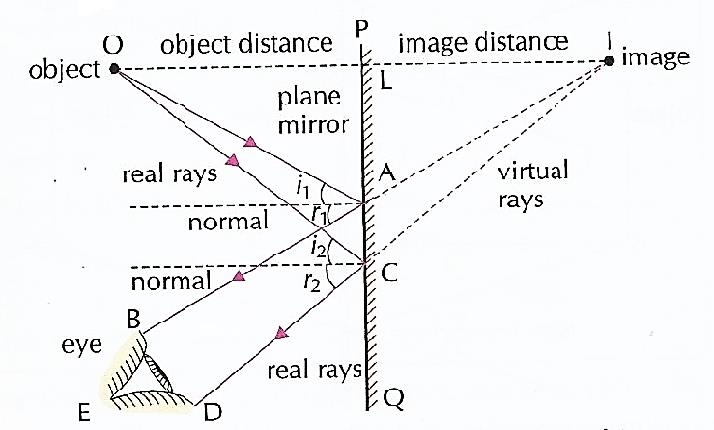
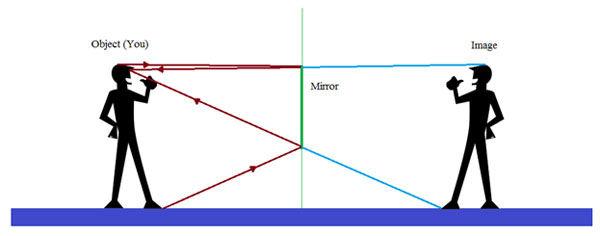
Uses of Ray Diagrams. Ray diagrams can be particularly useful for determining and explaining why only a portion of the image of an object can be seen from a given location. The ray diagram at the right shows the lines of sight used by the eye in order to see a portion of the image in the mirror. Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. This is the currently selected item. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Cartesian sign conventions mirrors. Practice: Sign convention. Solved example: Mirror formula. Practice: Using the mirror formula.
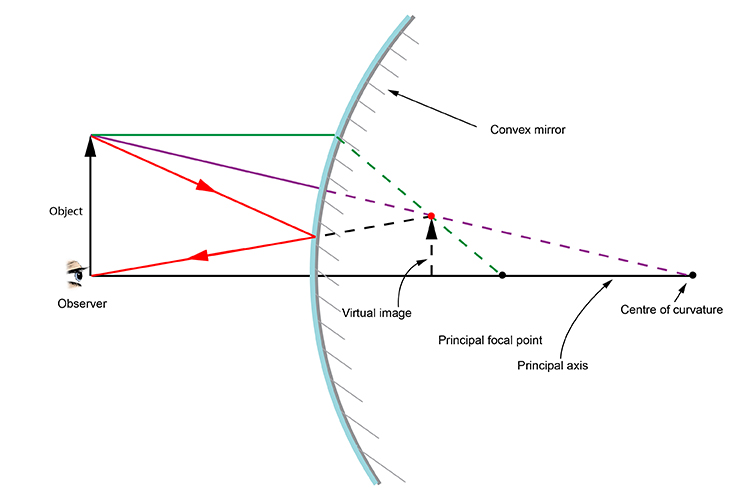
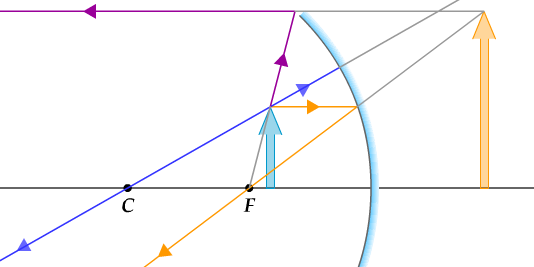
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.
Flat mirror ray diagram
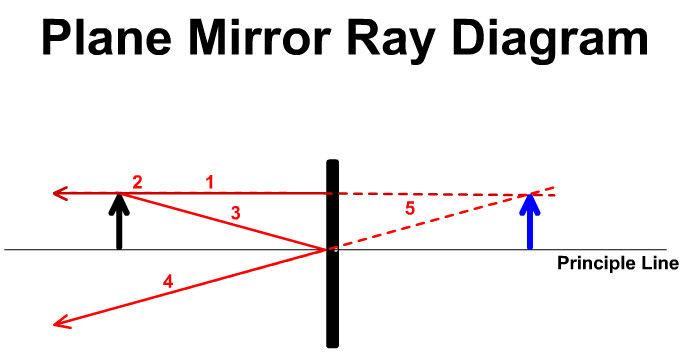
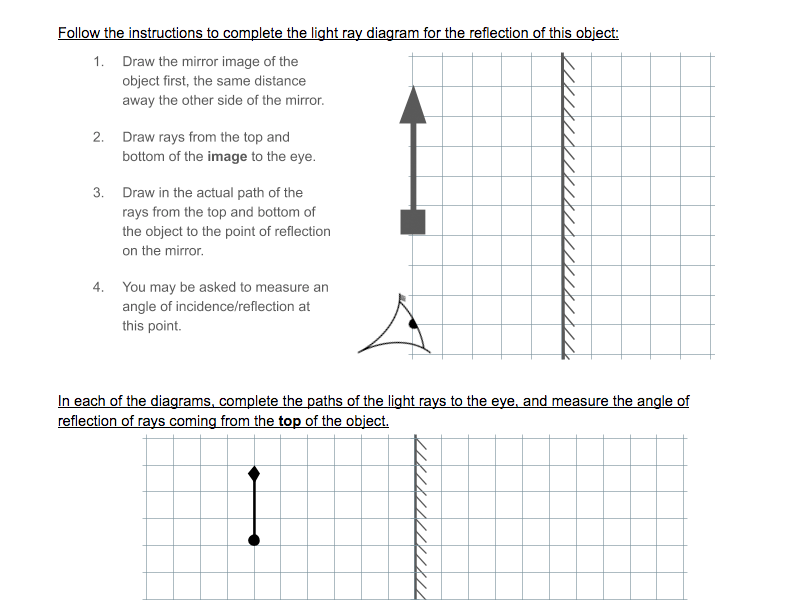
Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat mirror in which a person 5' 10" in height can see his or her full image. (A ray diagram would be helpful). A. 2' 11" B. 3' 9" C. 5' 10" D. Depends on distance to mirror. Answer klm In what location will the image form? 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Answer klm Which ray is correct? ray A ray B ray C ray D ... How to draw a ray diagram for a plane (flat) mirror.Please visit www.studyphysics.ca Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.
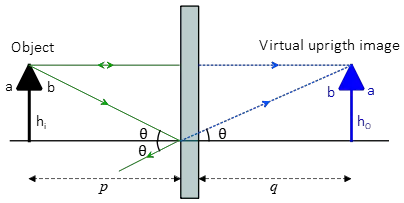
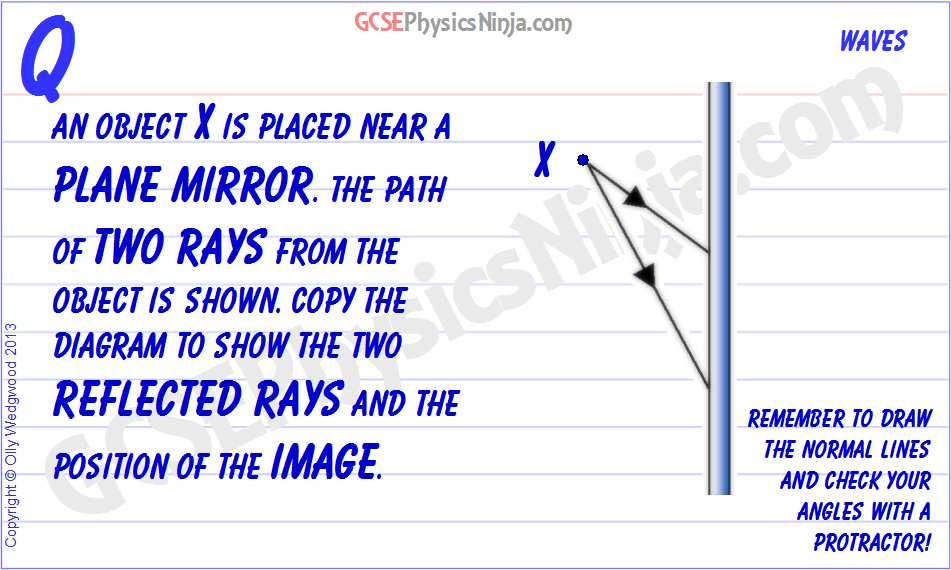
Flat mirror ray diagram. • Ray diagrams are based on the premise that to view an object in a mirror, one must sight along a line at the image of the object. When one does, light travels along that line to your eye. • Ray diagrams can be drawn for all types of mirrors. This video focuses on plane mirrors. Proceure for Drawing Ray Diagram Step 1 Locate the Image: Using flat mirrors ray diagram rules How do we draw the ray diagram for a flat mirror, an object and an observer using flat mirror ray diagram rules? See below: The first stage is to draw an image on the other side of the mirror perpendicular (at 90°) to the mirror. Behind the mirror Equal distance The same size Ray Diagrams The example ray diagram above shows three imaginary "rays" of light being reflected off a mirror and then going through a lens. You can see where the focus is by looking where the "rays" cross each other. It is the lens that is making the light focus. If you want to use a mirror to focus light, then it needs to have a curved surface. The way to draw the ray diagram for this situation is to carry out the three stages as we have previously learnt as follows: The first stage is to draw an image behind the mirror by marking either end of the image as being equal-distance and perpendicular (at 90°) from the mirror. Behind the mirror Equal distance The same size
Flat Mirror Diagrams . Overall Information In this diagram you can see how an image is formed. 1. Light leaves the object and hits the mirror ... Drawing Ray Diagrams •For our ray diagrams you will need to determine the location of the top of the object and the location of the bottom of the object. Use the following steps to do that. Step 1 ... Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p. oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. This is a simulation to illustrate the processes involved in the formation of images in plane mirrors. When the control points are visible, you can move the object (the blue arrow), the four points where the (blue) incident rays strike the mirror, as well as the two ends of the mirror itself. We've got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. Start exploring! Science Physics Q&A Library Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat mirror in which a person 178 cm tall can see their full image. (Hint: draw a ray diagram!).
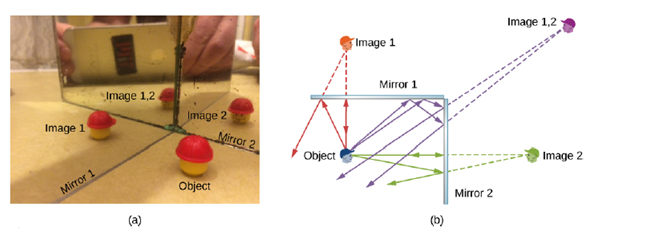
A mirror is an optical element that reflects the light incident on it. This chapter deals with various mirrors (flat, concave, and convex) and their properties. The focus of this chapter is understanding images formed by mirrors. You will use ray diagrams, explore the focal length and focal point of mirrors, and learn about real and virtual ... How to draw a ray diagram that shows the formation of a virtual image in a plane mirror. How to draw a ray diagram that shows the formation of a virtual image in a plane mirror. Infinite reflections may terminate. For instance, two mirrors at right angles form three images, as shown in part (a) of . Images 1 and 2 result from rays that reflect from only a single mirror, but image 1,2 is formed by rays that reflect from both mirrors. This is shown in the ray-tracing diagram in part (b) of . To find image 1,2, you have ... Mirror details. A flat mirror. Let us trace a ray across a singe, flat reflecting surface at the origin. Let the index of refraction of the surrounding material be n = 1. For a flat mirror R = infinite and . Let the ray leave position (x 1, z 1) = (1 cm, -4 cm) making an angle θ 1 = 0.1 radians with the z axis.
How to draw a light ray diagram for a flat mirror and locate the looking glass' virtual image. Locating Flat Mirror Virtual Images Top » Consulting » Tutorials » Flat Mirror Images: Flat Mirror Ray Diagram. Translatable page. Shop for neat science stuff. ...
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror ¥ The object is in front of a convex mirror ¥ The image is Ðvirtual Ðupright Ðsmaller than the object (reduced) Notes on Images ¥With a concave mirror, the image may be either real or virtual ¥With a convex mirror, the image is always virtual and upright ¥An image is real when the rays are passing through,
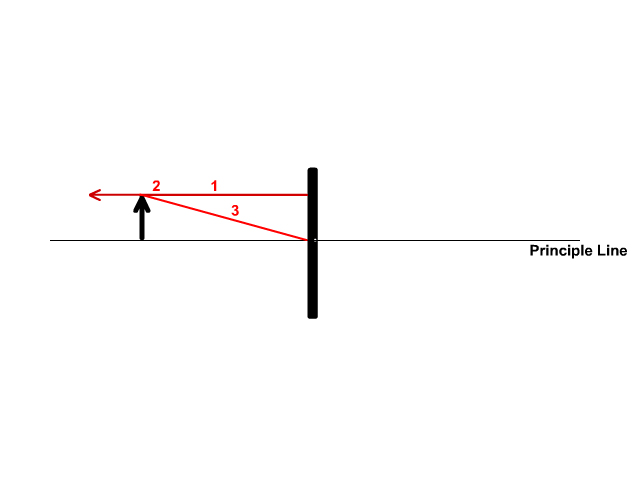
The simple ray diagram maker shows one principal ray leaving a candle of height h and striking a flat mirror. This ray strikes the mirror a distance h below the flame. The angle between the reflected ray and the surface normal is the same as that between the incident ray and the normal in accord with the principles of geometric optics.
Ray Diagrams J.M. Gabrielse Outline • Reflection • Mirrors • Plane mirrors • Spherical mirrors • Concave mirrors • Convex mirrors • Refraction • Lenses • Concave lenses • Convex lenses J.M. Gabrielse A ray of light is an extremely narrow beam of light.
The simple ray diagram maker shows one principal ray leaving a candle of height h and striking a flat mirror. This ray strikes the mirror a distance h below the flame. The angle between the reflected ray and the surface normal is the same as that between the incident ray and the normal in accord with the principles of geometric optics. Drag the ...
Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror. Mirrors: 1 of 4 An interactive demonstration of the principal ray diagram of a flat mirror. link: view. type: simulation. system reqs: Flash player. author: Dr. Barbara Hoeling. design credits: Erick Zelaya, Developer
Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror
Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors Process of drawing ray diagrams is the same no matter where the object is located. 1. IR parallel to the principal axis, RR through the focal point upon reflection. 2. IR through the focal point F, RR parallel to the principal axis upon reflection. 3. IR through C, RR reflects through C. 4.
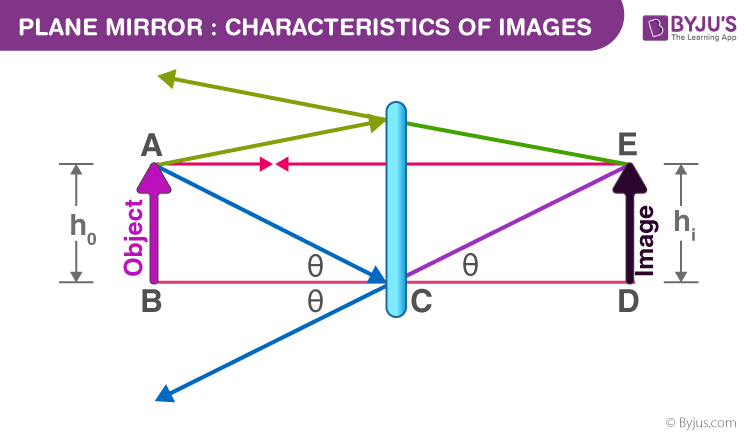
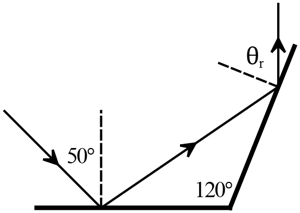
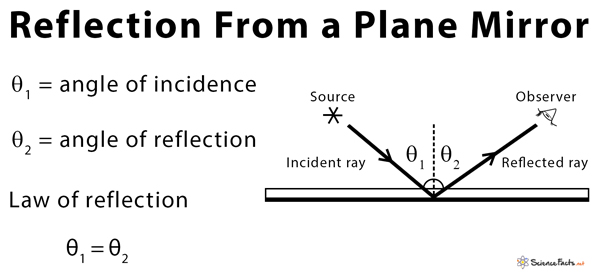
Figure 1 presents a diagram of light being reflected on a flat mirror. Figure 1: Reflection of light and its geometric elements. The elements labeled from 1 to 6 in figure 1 are described in the ...
The ray diagram below uses three reflected rays to illustrate how the image can appear to be enlarged and upright. The image formed is a virtual image. Figure 6 .
Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram. Mirrors are defined as one side-polished surface that can reflect the light rays. Plane mirrors in physics are the ones that have a flat reflecting surface and produce always a virtual image. In this tutorial, we review the most important topics in the plane (flat) mirrors in physics ...
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.
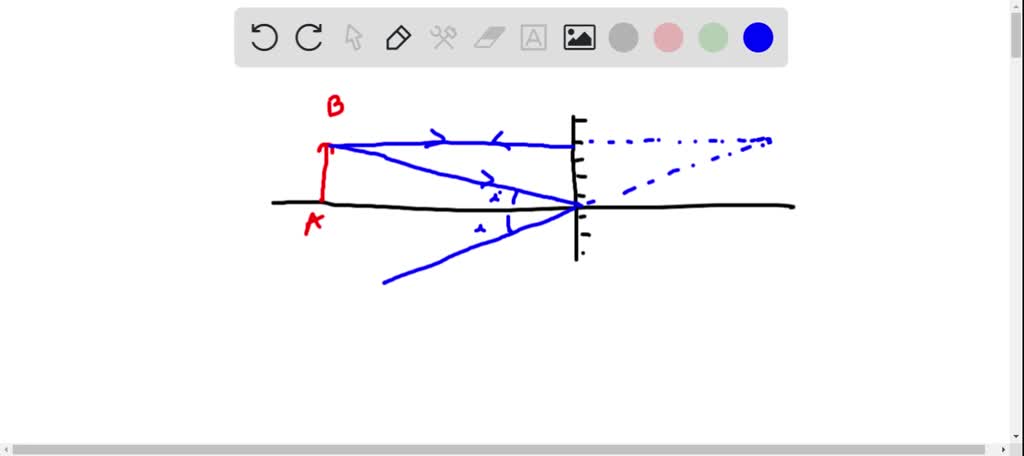
a pencil is placed in front of a plane mirror and is oriented parallel to the plane of the mirror fi
How to draw a ray diagram for a plane (flat) mirror.Please visit www.studyphysics.ca
Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat mirror in which a person 5' 10" in height can see his or her full image. (A ray diagram would be helpful). A. 2' 11" B. 3' 9" C. 5' 10" D. Depends on distance to mirror. Answer klm In what location will the image form? 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Answer klm Which ray is correct? ray A ray B ray C ray D ...












0 Response to "37 flat mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment