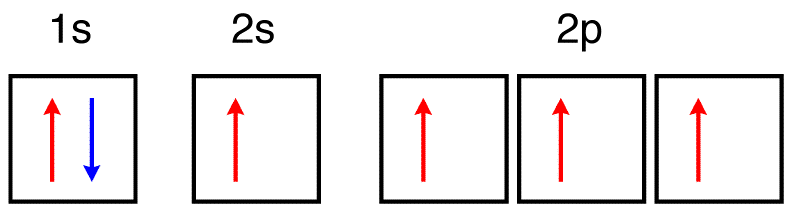
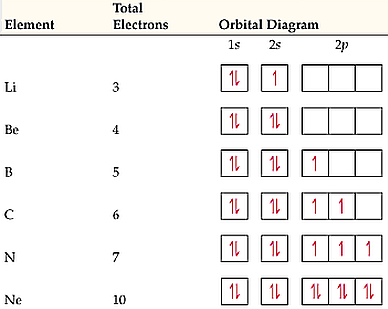
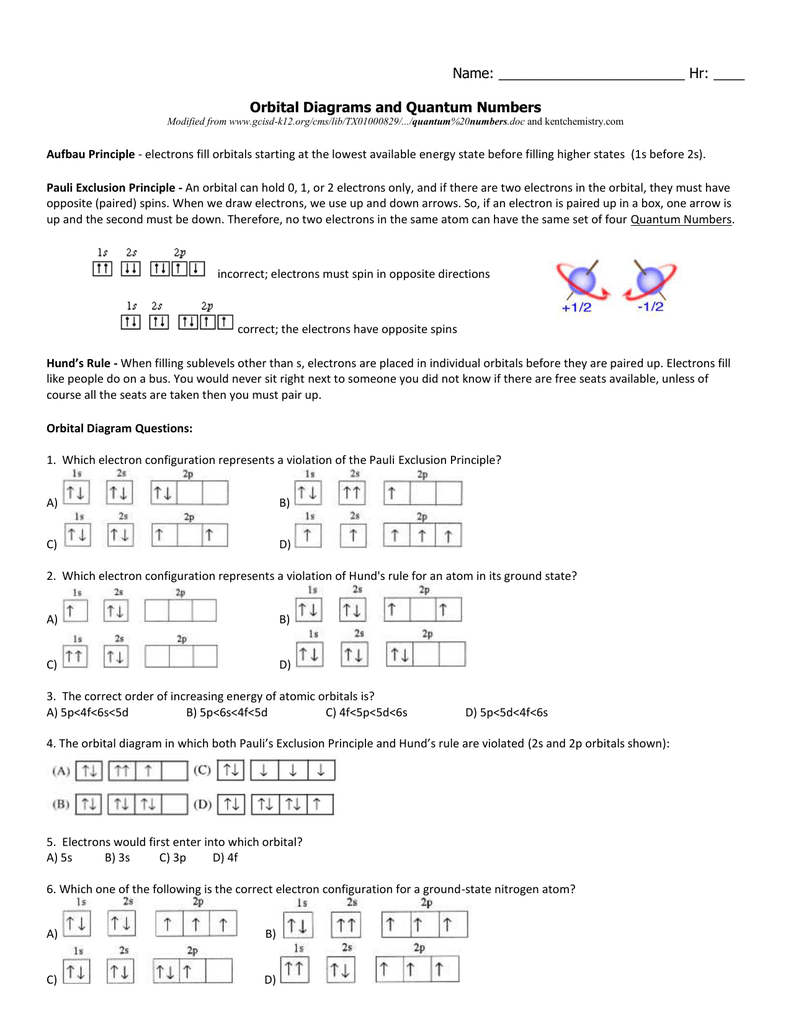
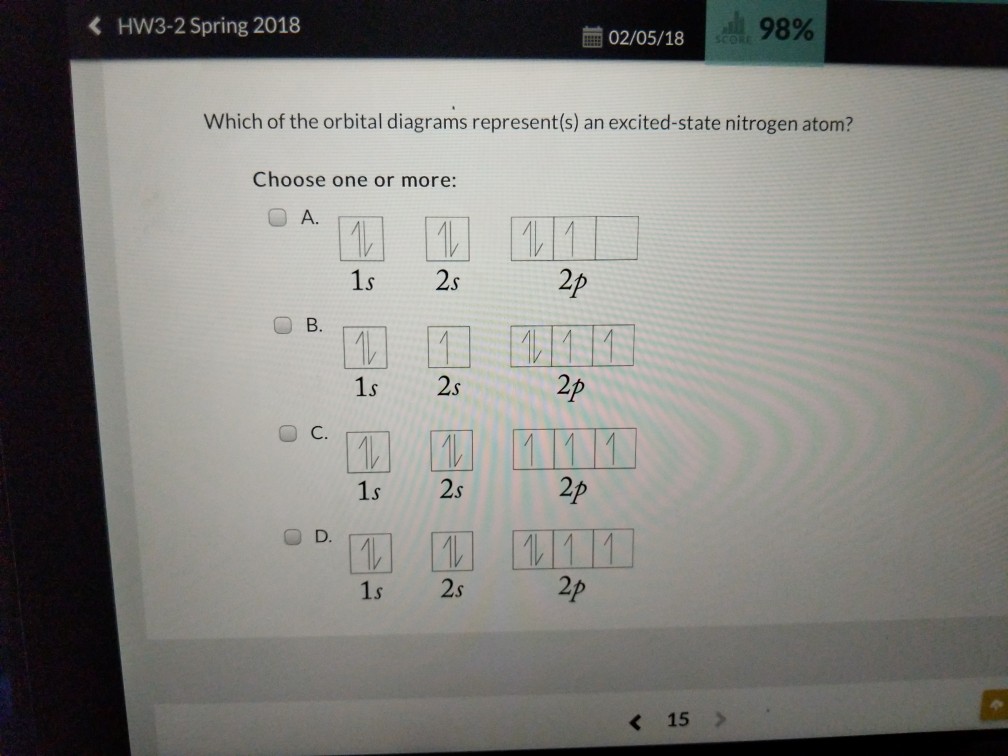
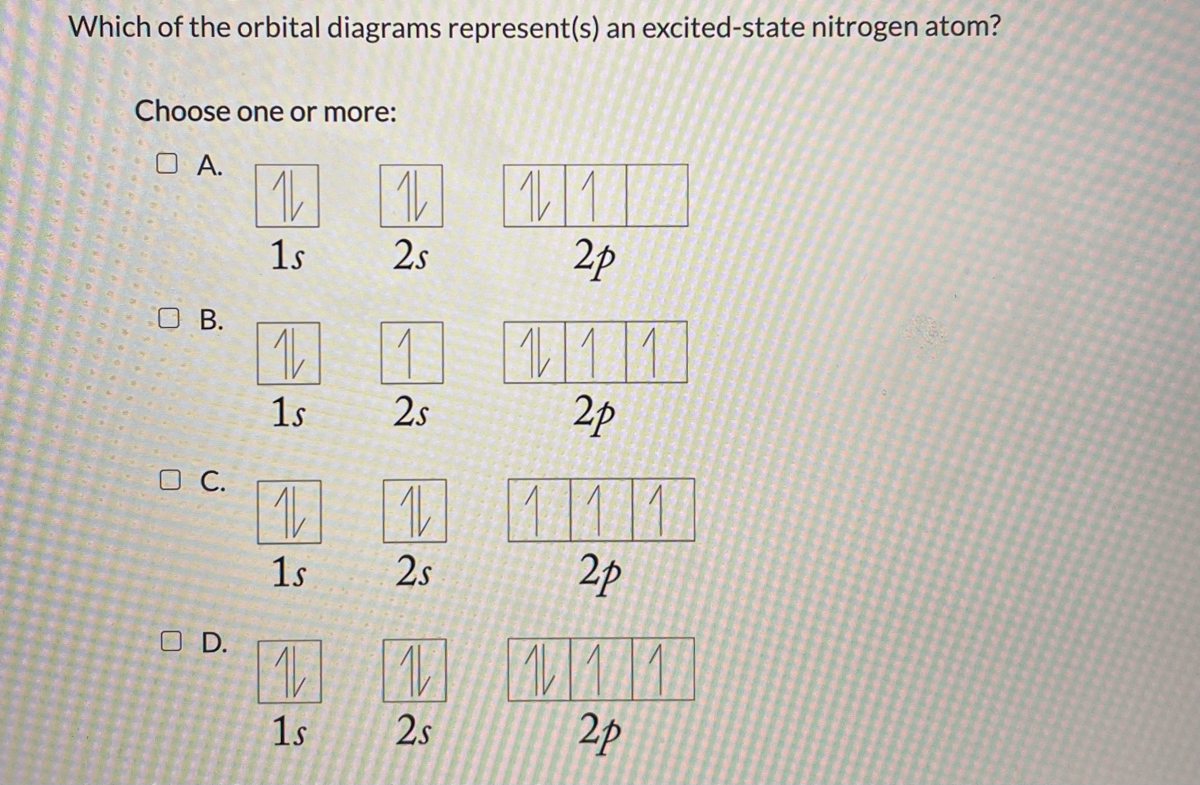
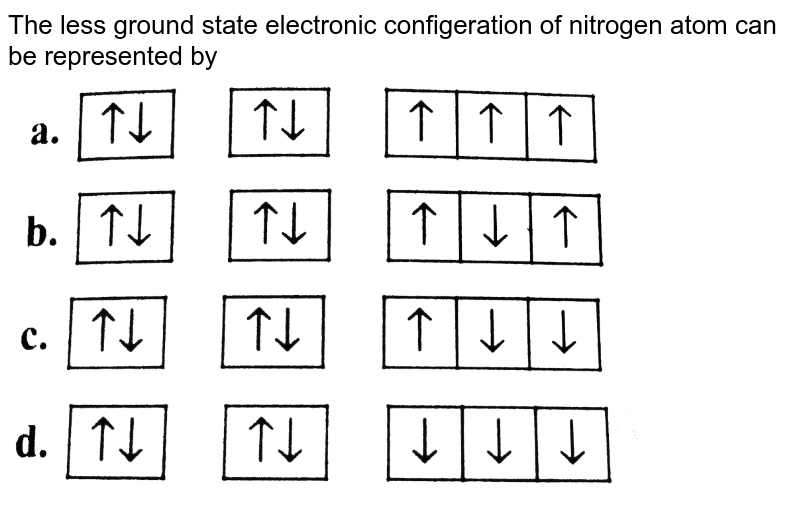
37 the orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is
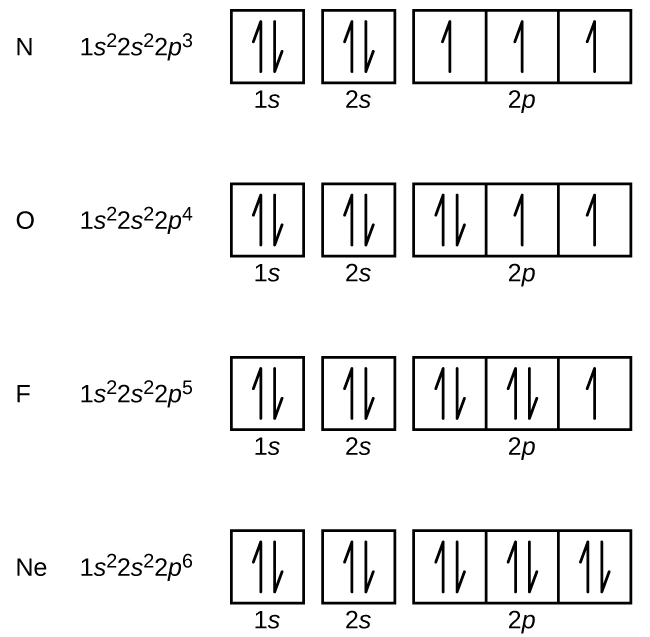
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is 1s 2s 2p A: 5. The number of orbitals in a d subshell is A: 5 6. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy an energy level described by the principal quantum number, n, is A: 2n^2 7. A ground-state atom of manganese has ___ unpaired electrons and is _____. A: 5, paramagnetic 8. A nitrogen atom has 3 orbitals; the 1s orbital, the 2s orbital, and the 2p orbital. In this case, the 2s and 2p orbitals are the valence orbitals, as they have the electrons with the most energy.
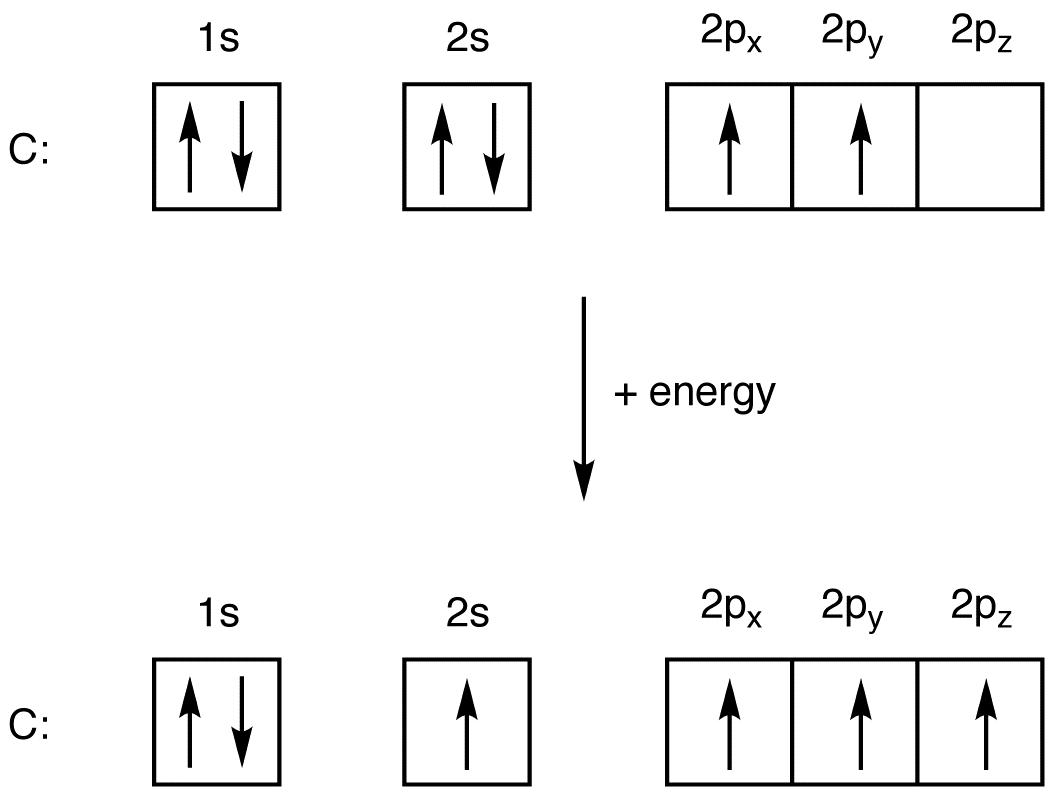
Orbital Diagram Fluorine (F) Fluorine(F) excited state electron configuration. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital by excited state. This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of fluorine is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. The p-orbital has three sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are p x, p y, and p z. Each sub-orbital can ...

The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is
A diagram illustrating the order in which atomic orbitals are filled is provided below. Here, ‘n’ refers to the principal quantum number and ‘l’ is the azimuthal quantum number. The Aufbau principle can be used to understand the location of electrons in … We can formalize this procedure as follows, where q is the total pi electron density at atom i , Q i is the charge density at atom i (1-q i), N i is the number of electrons in a given orbital (the occupancy number), a ij is the coefficient of atom i in the jth MO, and the summation is over all singly or double occupied orbitals (since each ... The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is 1s- up down 2s- up down, up 2p- up up Calculate the wavelength, in nanometers, of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron falls from the n = 7 to the n = 4 principal energy level.
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is. Orbital Diagram for Oxygen (O) Oxide ion(O 2–) electron configuration. Ground state electron configuration of oxygen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 2 2p y 1 2p z 1. This electron configuration shows that the last shell of oxygen has six electrons. In this case, the valence electrons of oxygen are six. The elements that have 5, 6, or 7 electrons in the ... Answer Electronic configuration of nitrogen in ground state is 1s2 2s2 2p3 or 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1. Hence, in excited state one of the 2s electron will jump to 2p orbital,so the excited state electronic configuration should be 1s2 2s1 2px2 2py1 2pz1. I BEG you A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine … In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one …
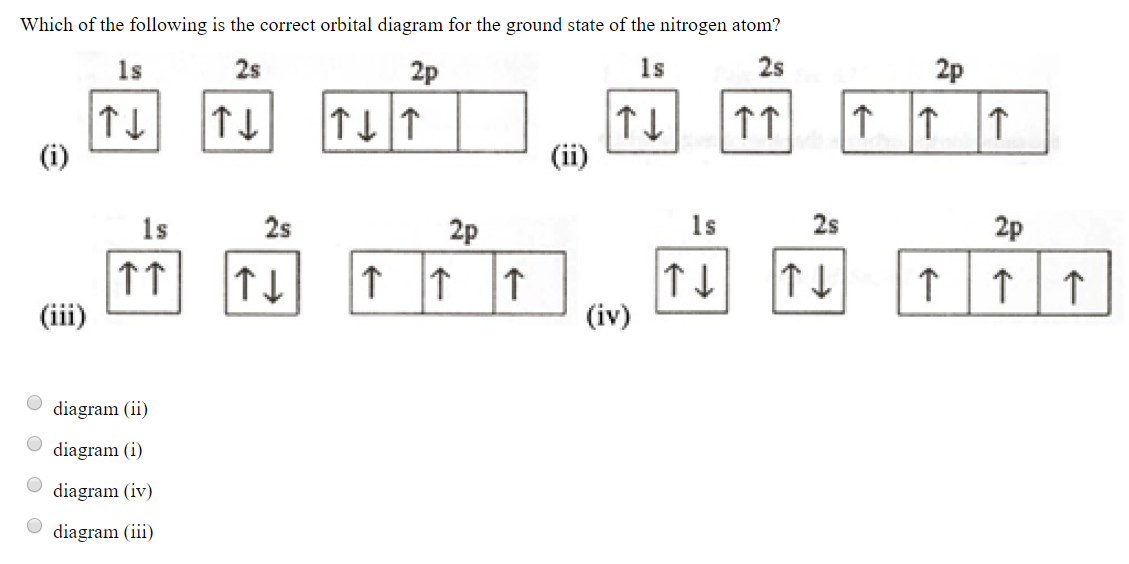
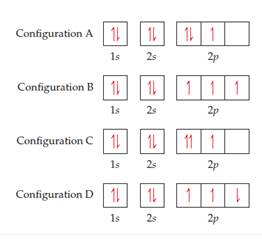
The orbital diagram for nitrogen is drawn with 3 orbitals. The orbitals are 1s, 2s, and 2p. The nitrogen orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in 1s orbital, 2 electrons in 2s orbital, and the rest three electrons in 2p orbital. Orbital diagram for a ground-state electron configuration of nitrogen atom is shown below-. In compounds of type E C l 3 , where E = B, P, A s o r B i, the angles Cl-E-Cl is in order. 4. The ground state electronic configuration of nitrogen atom can be represented by. Structure of Atom. 5. The correct order of increasing C- O bond length of. C O, C O 3 2 −, C O 2 is. 6. Feb 15, 2021 · Ground State Electron Configuration For Nitrogen. When we talk about the electronic configuration, then the ground state Nitrogen Electron Configuration is written as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.Below you can get the full image representation which will help you to understand the topic more easily. The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is A) A B) B C) C D) D ... The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is A) A B) B C) C D) D. D. section 7.9 A possible set of quantum numbers for the last electron added to complete an atom of gallium (Ga) in its ground state is A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E.
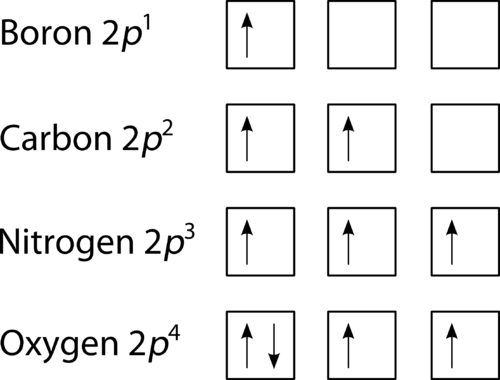
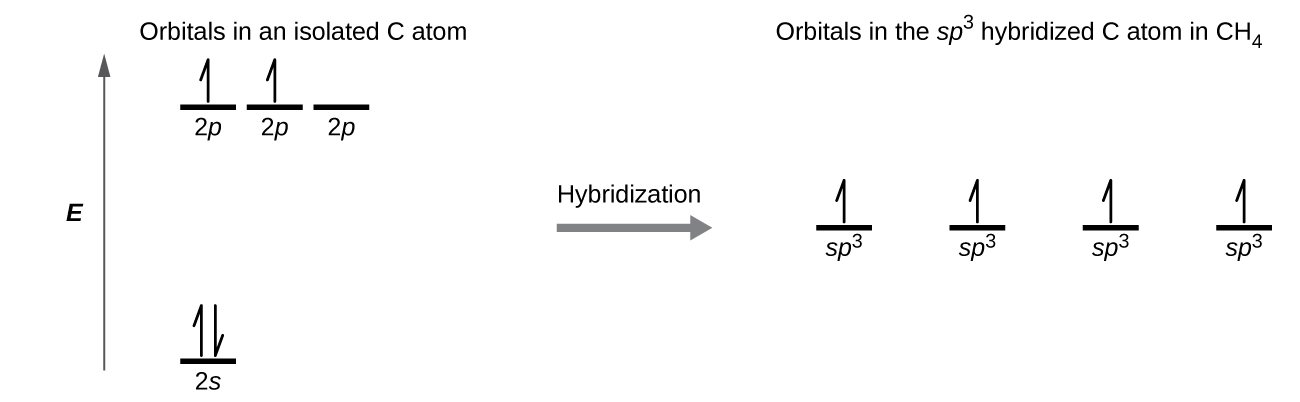
What is the orbital diagram for the valence electrons in a ground state atom of nitrogen? Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Ans :- The orbital dia …. Solved The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is | 1s 25 A.TV C. | | 치서 cm 0 e o000 치어 리 리 리 기 기tmuo | 소. Boron configuration diagram: One of the three boron electrons is unpaired in its ground state. The atomic s- and p-orbitals in boron’s outer shell mix to form three equivalent hybrid orbitals. These particular orbitals are called sp 2 hybrids, meaning that this set of orbitals derives from one s- orbital and two p-orbitals of the free atom. (Recall from Section 5.3B that two electrons in an orbital spin in opposite directions on their axes.) Therefore, if an orbital contains two electrons, its box will contain two arrows, one pointing up and the other down. Using a box diagram, we show the electron configuration of nitrogen as: Notice that the 2p electrons are shown as
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is 1s- up down 2s- up down, up 2p- up up Calculate the wavelength, in nanometers, of the light emitted by a hydrogen atom when its electron falls from the n = 7 to the n = 4 principal energy level.
We can formalize this procedure as follows, where q is the total pi electron density at atom i , Q i is the charge density at atom i (1-q i), N i is the number of electrons in a given orbital (the occupancy number), a ij is the coefficient of atom i in the jth MO, and the summation is over all singly or double occupied orbitals (since each ...
A diagram illustrating the order in which atomic orbitals are filled is provided below. Here, ‘n’ refers to the principal quantum number and ‘l’ is the azimuthal quantum number. The Aufbau principle can be used to understand the location of electrons in …















0 Response to "37 the orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is"
Post a Comment