39 antigen antibody reaction diagram
PPT Antigen-Antibody Reactions - KSU Antigen-Antibody Reactions Antigen-antibody interactions: Are reversible specific non-covalent biochemical reactions: Hydrogen bonds (A chemical bond in which a hydrogen atom of one molecule is attracted to an electronegative atom of another molecule) Electrostatic bonds(A valence bond in which two atoms, attracted by electrostatic forces, transfer one or more electrons between atoms) Van der ... Antigen-Antibody Reactions Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Antigen-Antibody Reactions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Antigen-antibody interaction - Wikipedia Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction.The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and ...
Antigen antibody reaction diagram
Solved 4. The following diagram is an image of a dilution | Chegg.com The following diagram is an image of a dilution series of an antigen/antibody agglutination reaction. The small pellet indicates agglutination; the absence of the small pellet indicates no agglutination with the red cell hemagglutination reagents. The dilution is a 2-fold serial dilution beginning in column 1 or a 1/2. Chemiluminescent Western Blotting | Thermo Fisher ... Occasionally, an antibody to a specific antigen is unavailable or unsuitable for western blot analysis. Target protein–specific detection by blotting is possible if a corresponding binding partner is available for use as a probe. This type of application, referred to as a far-western blot, is routinely used for the discovery or confirmation of a protein–protein interaction. There are ... Factors affecting the antigen-antibody reaction - PMC The effects of antigen zygosity and red cell concentration are distinct: even when the concentration of the antigen in the reaction system is equal in both cases, and, for this reason, the concentration of the antigen-antibody complex too, the number of antibodies per cell changes and favours homozygous cells.
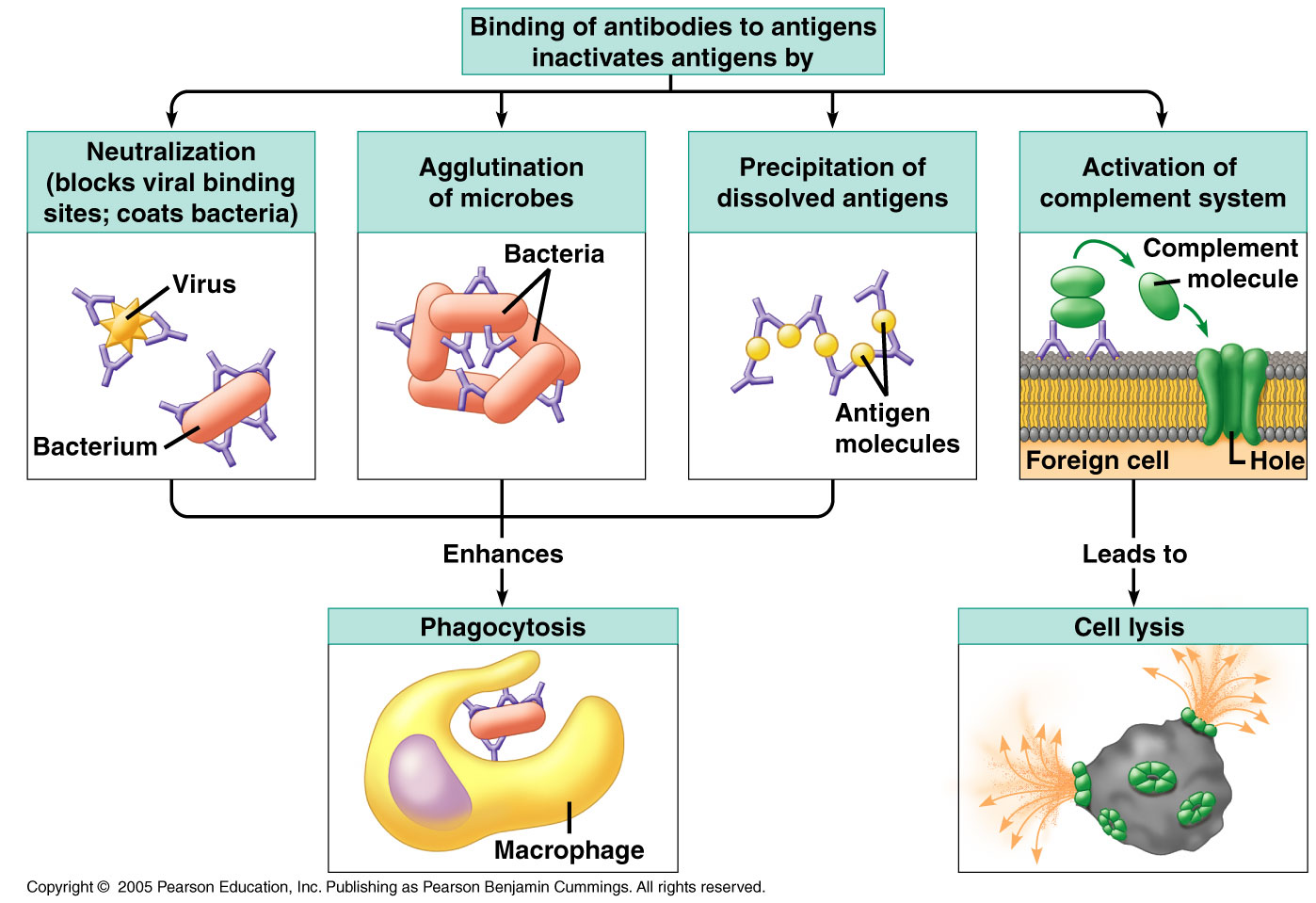
Antigen antibody reaction diagram. Antigen–antibody reactions - Armstrong - 2008 - ISBT ... 09.05.2008 · The nature of the antigen–antibody reaction determines its involvement. Complement (C′) is a large group of nine proteins present in abundance in the body, and in freshly drawn serum samples. Complement from one species is effective in antigen–antibody reactions in many other species. When activated, a cascade starts, and amplifies. One molecule of C1 … Stages Involved in Antigen-antibody Reactions The primary reaction can be detected by estimating free and bound antigen or antibody sepa-rately in the reaction mixture. Secondary stage: The secondary stage leads to demonstrable events such as pre-cipitation, agglutination, lysis of cells, killing of live antigens, neutral-ization reactions, complement fixation and enhancement of phagocy-tosis. Sandwich ELISA- Steps and Advantages - Microbe Notes 10.05.2021 · After removing any free secondary antibody by rewashing, the specific substrate is added, and the ensuing chromogenic reaction is measured. The chromogenic reaction is then compared with a standard curve to determine the exact amount of the antigen present in the test sample. In a positive test, an enzyme acts on the substrate to produce a color, and its intensity … B Cells and Antibodies - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... Antigen binding to antibody. In this highly schematized diagram, an antigenic determinant on a macromolecule is shown interacting with the antigen-binding site of two different antibody molecules, one of high affinity and one of low affinity. The antigenic . Figure 24-29. Molecules with multiple antigenic determinants. (A) A globular protein is shown with a number of different …
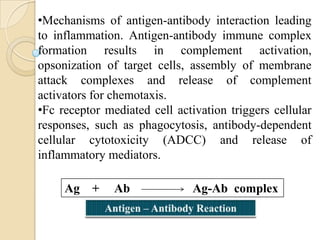
Immunoglobulins- Antigen-antibody Reactions Factors affecting measurement of antigen-antibody reactions. The only way that one knows that an antigen-antibody reaction has occurred is to have some means of directly or indirectly detecting the complexes formed between the antigen and antibody. The ease with which one can detect antigen-antibody reactions will depend on a number of factors. ELISA - Wikipedia The reaction is stopped to prevent eventual saturation of the signal. Some competitive ELISA kits include enzyme-linked antigen rather than enzyme-linked antibody. The labeled antigen competes for primary antibody binding sites with the sample antigen (unlabeled). The less antigen in the sample, the more labeled antigen is retained in the well ... PDF Antigen/ Antibody reactions Diagnostic Immunology Types of antigen-- Antibody reactions in Antibody reactions in vivo 1. Agglutination 2. Precipitation 3. Complement fixation 4. Neutralization 5. Antibody dependant cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) 6. Immobilization 12/21/13 Prof. Md. Akram, MMC 22 Antigen-antibody reaction | definition of antigen-antibody reaction by Medical dictionary antigen [an´tĭ-jen] any substance capable, under appropriate conditions, of inducing a specific immune response and reacting with the products of that response; that is, with specific antibody or specifically sensitized T lymphocytes, or both. Antigens may be soluble substances, such as toxins and foreign proteins, or particulates, such as bacteria ...
What Is an Antigen? - Verywell Health An antibody test works differently than the antigen test in the sense that it can be done after the antigens have left the body. This test is used to determine whether or not an infection had ever occurred by singling out the antibodies that were created when the immune response took place. Rapid, point‐of‐care antigen and molecular‐based tests for ... 26.08.2020 · Of 808 records selected for further assessment for inclusion in any of the four molecular, antigen or antibody test reviews, we assessed 90 full‐text reports for inclusion in this review. See Figure 1 for the PRISMA flow diagram of search and eligibility results (McInnes 2018; Moher 2009). We included 18 studies from 22 reports in this review ... Antigen-Antibody Reactions - SlideShare INTRODUCTION Antigens & antibodies combine specifically with each other. This interaction between them is called 'Antigen- Antibody reaction'. - Abbreviated as Ag - Ab reaction. - They form the basis for humoral/antibody mediated immunity. - They are used for detection of disease causing agents & some non-specific Ag's like enzymes. Overview of ELISA | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US Diagram of common ELISA formats (direct vs. sandwich assays). In the assay, the antigen of interest is immobilized by direct adsorption to the assay plate or by first attaching a capture antibody to the plate surface. Detection of the antigen can then be performed using an enzyme-conjugated primary antibody (direct detection) or a matched set of unlabeled primary and …
antigen antibody reactions Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet Lecture 5: Antigen-Antibody Reactions. antibody. immunogens. antigenicity. immunogenicity. molecules that interacts with the adaptive immune system via a…. antigens that are capable of inducing a specific antibody or c…. ability to bind to antigen recognition molecules. ability to induce an immune response.
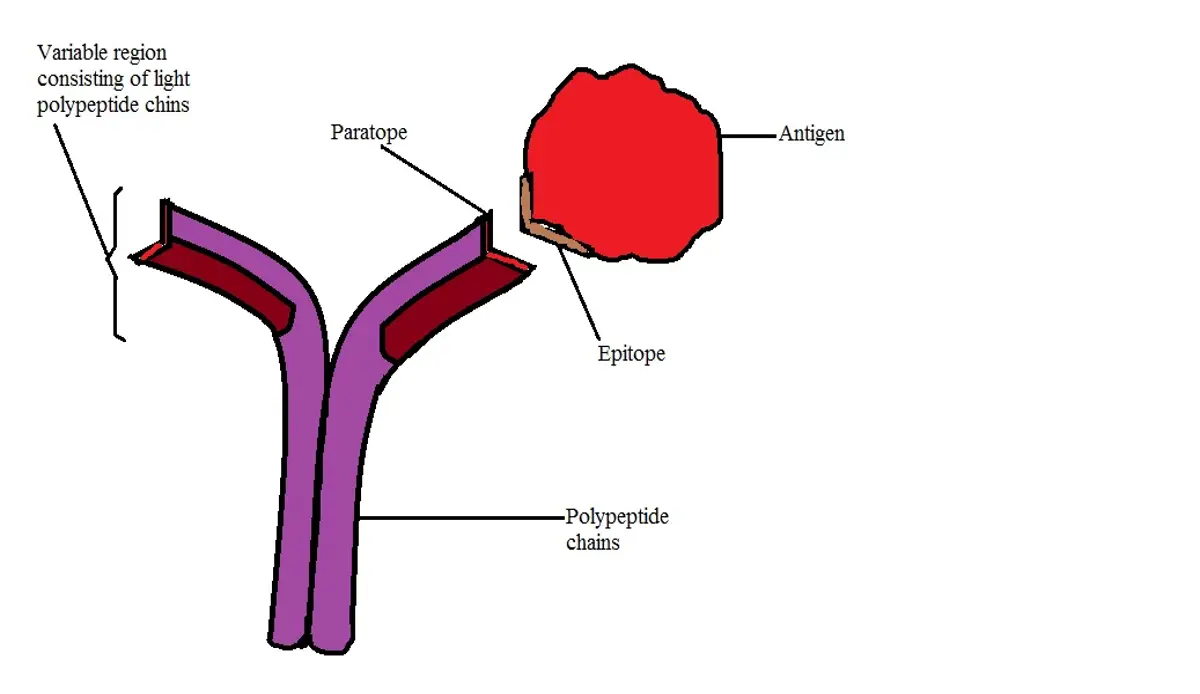
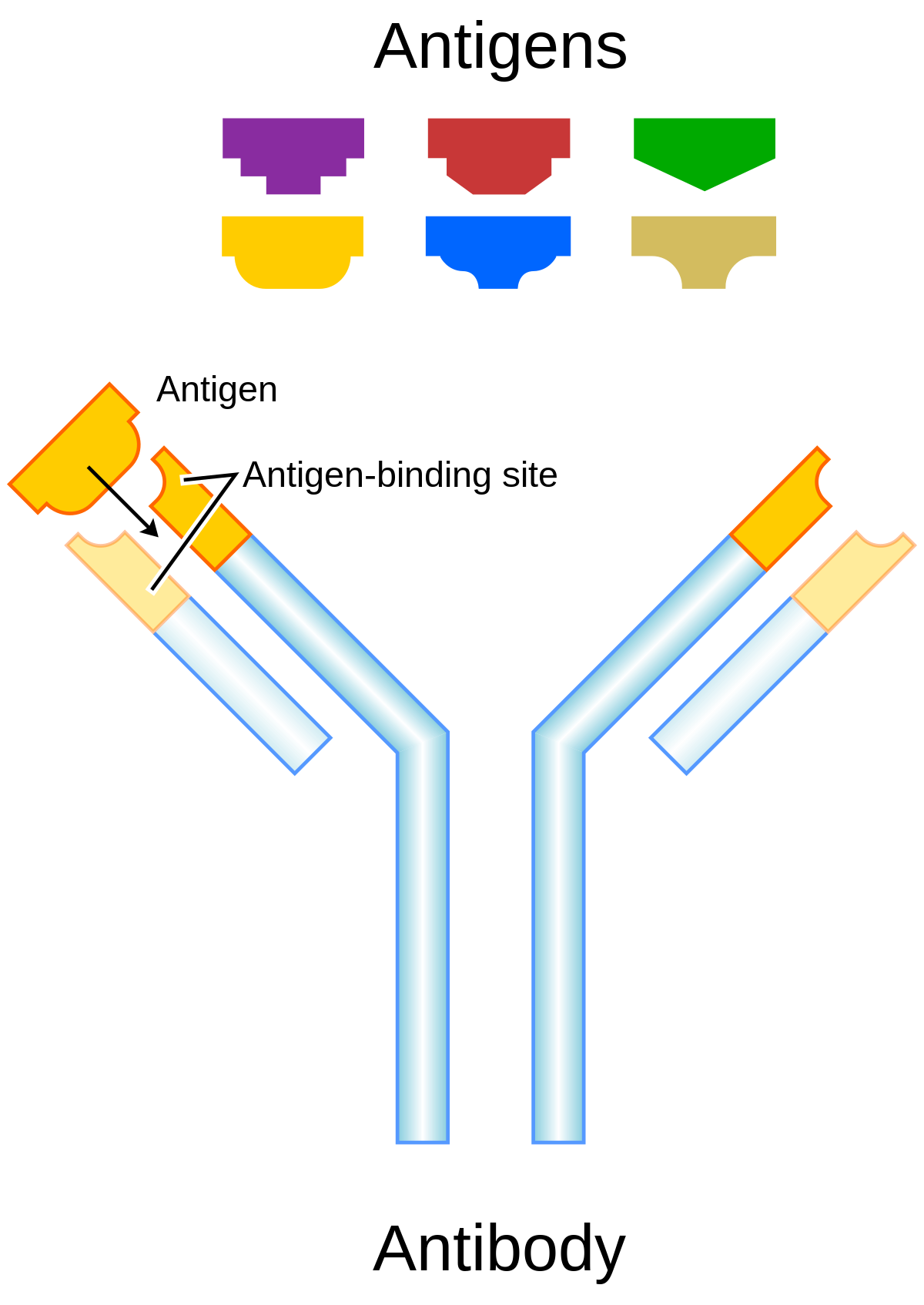
Antigen and Antibody Reaction - Jiwaji University •In antigen - antibody reaction, the antibody attaches with the antigen. •The part of antigen which combines with antibody is called Epitope. •An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or
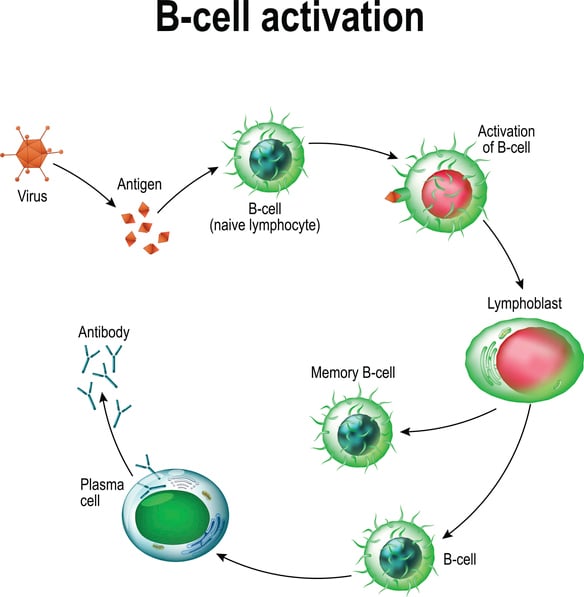
Immune response: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia 01.04.2022 · Antibodies attach to a specific antigen and make it easier for the immune cells to destroy the antigen. T lymphocytes attack antigens directly and help control the immune response. They also release chemicals, known as cytokines, which control the entire immune response. As lymphocytes develop, they normally learn to tell the difference between your …
Antigen: Meaning & Explanation - Study.com Once an antigen is detected and tagged by a B cell, an antibody is made. These antibodies stick around and wait to protect the body should the antigen decide to …
Antigen Antibody Interaction (With Reactions) | Zoology The interaction between antigen and antibody occurs in two stages: 1. Primary stage: In the primary or initial stage, non-covalent binding between the antigen and antibody produces small and soluble antigen-antibody complexes as a result of primary union. This primary reaction has no visible effect and the reaction is rapid.
9 Important Antigen-Antibody Reactions | Microbiology The following points highlight the nine important antigen-antibody reactions. They are: 1. Precipitation Reactions 2. Immunodiffusion Test 3. Counter Current Immunoelectroptioresis Test 4. Agglutination Reactions 5. Complement Fixation Reactions 6. Neutralization Reactions 7. Radioimmunoassay 8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay 9.
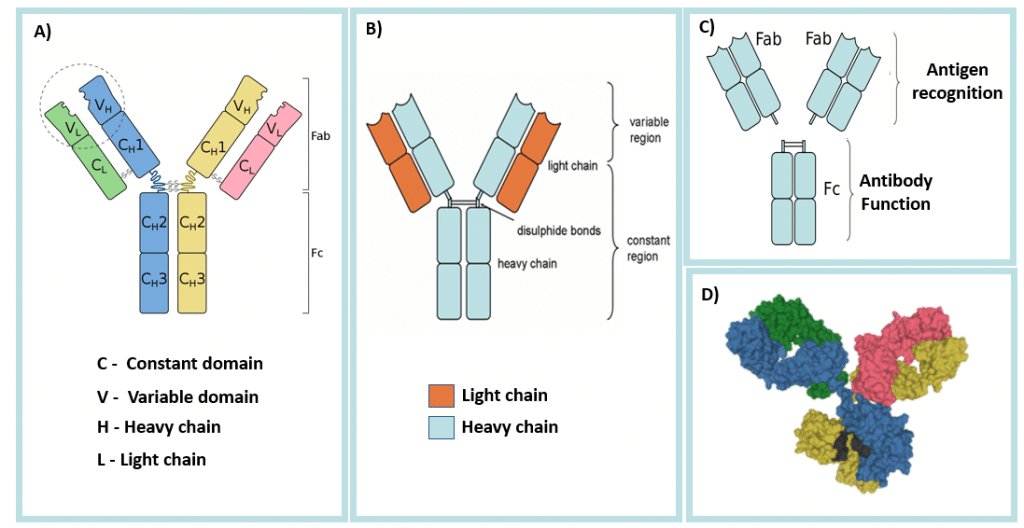
Biochemistry of Antibody-Antigen Interactions Schematic diagram of an antibody. The antibody is comprised of 2 heavy chains and two light chains. Both are comprised of a variable (V) and a constant domain (C). The amino-terminal domains in red correspond to the region of antigen binding, whilst the remained of the antibody domains exact effector functions. (Blamb/Shutterstock)
Antigen Antibody Reaction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics HIV antigen-antibody reactions have been used to develop relatively rapid, simple assays that do not require colorimetric readout. Such assays, called particle agglutination (PA), are based on the ability of sera containing HIV antibodies to crosslink small particles containing HIV antigens on the surface. PA has advantages of sensitivity and ...
Antigen-antibody reaction. Each antibody is able to bind its specific... | Download ... Download scientific diagram | Antigen-antibody reaction. Each antibody is able to bind its specific antigen, forming antigen-antibody complexes. Different laboratory testing techniques are based ...
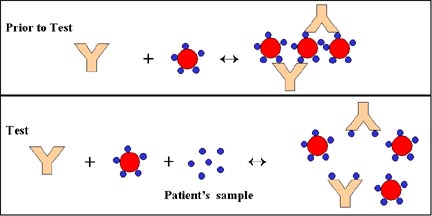
PDF Antigen- antibody reactions - St. Ann's College for Women to detect antigen antibody reaction. It provides flexible and useful method for semi quantitating of either antigen or antibody concentration. The reaction occurs between insoluble (particulate)antigen and appropriate antibody. The reaction will results in forming aggregate or agglutinate. Ag= agglutinogen, Ab= agglutinin
Antigen-Antibody Reactions - Bioscience Notes in antigen-antibody reactions. All these types of intermolecular forces depend on the close proximity of the antigen and antibody molecules. Multiple bonding between the antigen and the antibody ensures that the antigen will be bound tightly to the antibodies. Affinity. Affinity denotes the intensity of attraction between antigen and antibody.
Antigen-Antibody Reactions - an overview - ScienceDirect Antigen-antibody reactions cause inflammation and cell damage by a variety of mechanisms. If the reaction occurs in extravascular spaces the result is edema, inflammation, and infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, which may later be replaced by mononuclear cells. This is a common cause of mild inflammatory reactions.
Antigen and antibody reaction - SlideShare Binding Site of Antigen - Antibody Reaction: • In antigen - antibody reaction, the antibody attaches with the antigen. • The part of antigen which combines with antibody is called Epitope. • An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B ...
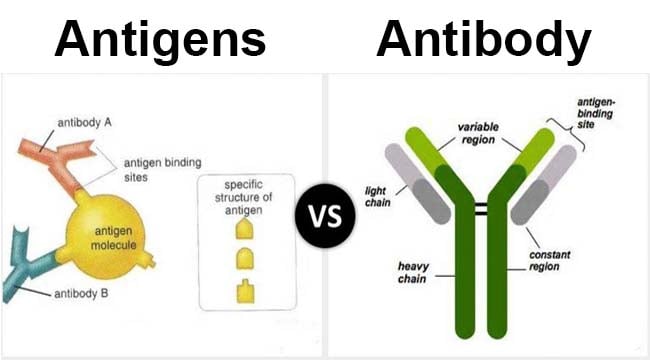
Structure of Antibody (With Diagram) | Organisms | Immunology | Biology Antigen-antibody reactions (Fig. 8) are highly specific and both fit into each other like a lock and key. Because an antibody fits precisely with an antigen, an antibody that binds to one antigen cannot bind to another antigen. Antibody can inactivate the invading agent in one of the following ways:
Antigen-Antibody Interaction The interactions between antigens and antibodies are known as antigen-antibody reactions. The reactions are highly specific, and an antigen reacts only with ...9 pages
Hypersensitivity Reactions - Types - T cell ... 17.01.2022 · Cross-linking of the antigen with T-cells, as well as co-stimulatory molecules, can lead to activation of that T-cell and subsequent differentiation into “primed” Th1, Th2, or Th17 cells, which are specific to that antigen and can stimulate further immune responses if they meet the antigen again. It is this second meeting that could result in a hypersensitivity reaction.
Antibody and Antigen stock vector. Illustration of heavy - 38744648 Illustration about Antibody molecule and Antigen. vector diagram. Illustration of heavy, detection, immunology - 38744648
Explore the Difference Between Antigen and Antibody - BYJUS Antigen and antibodies are two very different entities. In a nutshell, an antibody is a glycoprotein which is produced in response to and counteract a particular antigen. On the other hand, an antigen is a foreign substance (usually harmful) that induces an immune response, thereby stimulating the production of antibodies.
antigen-antibody reaction | biology | Britannica Antigen-antibody complexes form only after the nuclear contents of a cell are released into the bloodstream during the normal course of cell death or as a result of inflammation. The resultant immune complexes are deposited in tissues, causing injury. Certain organs are more commonly involved…. Read More. rheumatic fever.
| Antigen-antibody reaction Sample antigens are immobilised to a solid... | Download ... Download scientific diagram | | Antigen-antibody reaction Sample antigens are immobilised to a solid support, or present on a tissue sections, and are exposed to a specific primary antibody. A ...
Schematic representation of an Antigen-Antibody-Reaction: Schematic representation of an Antigen-Antibody-Reaction: fig. a fig. b fig. c fig. d Precipitation Aggregation Antigen - Antibody Complex Antigen Antibody So that a networking reaction can expire, the particles contained in the samplefluid must have a binding place for at least two antibodies and can function therefore as an antigen.
Factors affecting the antigen-antibody reaction - PMC The effects of antigen zygosity and red cell concentration are distinct: even when the concentration of the antigen in the reaction system is equal in both cases, and, for this reason, the concentration of the antigen-antibody complex too, the number of antibodies per cell changes and favours homozygous cells.
Chemiluminescent Western Blotting | Thermo Fisher ... Occasionally, an antibody to a specific antigen is unavailable or unsuitable for western blot analysis. Target protein–specific detection by blotting is possible if a corresponding binding partner is available for use as a probe. This type of application, referred to as a far-western blot, is routinely used for the discovery or confirmation of a protein–protein interaction. There are ...
Solved 4. The following diagram is an image of a dilution | Chegg.com The following diagram is an image of a dilution series of an antigen/antibody agglutination reaction. The small pellet indicates agglutination; the absence of the small pellet indicates no agglutination with the red cell hemagglutination reagents. The dilution is a 2-fold serial dilution beginning in column 1 or a 1/2.






















0 Response to "39 antigen antibody reaction diagram"
Post a Comment